Published in category: Oral diseases
Language
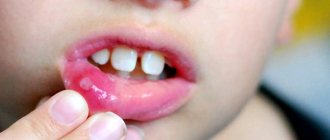
Many parents notice with alarm that the child’s tongue is undergoing changes - it suddenly changes its normal color, begins to peel and peel. Why do such changes occur, do they represent a serious pathology, and what treatment is required?
Geographic tongue, which is also known as desquamative glossitis, is a disease of an inflammatory-dystrophic nature, accompanied by external changes in the mucous surface of the tongue. This disease does not have any “age limits” - it can occur with equal frequency in adults and newborns. Most often, geographic tongue is diagnosed completely by accident, at a regular dentist appointment.
Peeling of the tongue: causes, treatment, photos | All about gums
Sometimes when brushing your teeth, a person notices that the surface of his tongue takes on a different shade and begins to actively peel off.
Even if there is no pain or discomfort, the condition is alarming and requires mandatory consultation. It is necessary to establish the reasons why the tongue peels: this problem accompanies not only household burns or injuries, but also serious diseases of the internal organs.
This will help identify pathologies and infections at an early stage and prevent their development.
Why does the skin peel off my tongue?
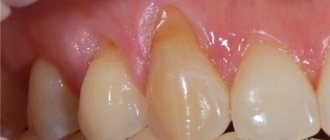
Healthy oral mucosa has a soft pink tint. Sometimes it changes to a reddish color due to a rush of blood or becomes white under a layer of plaque.
There is a special technique for diagnosing the health of the entire body based on the condition of the tongue. Therefore, during a visual examination, doctors always pay attention to its color and appearance.
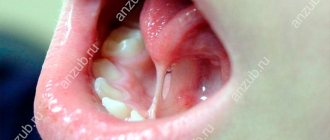
An unpleasant problem can arise at any age and under the influence of a wide variety of factors.
The entire surface is covered with a thin layer of skin with tiny papillae and cones. They are called taste buds and are responsible for the human perception of salty, sweet and sour shades.
They help determine the temperature of a dish, respond to spicy seasonings and transmit a signal to the brain. The tubercles are highly sensitive and instantly help to understand if food is spoiled.
Doctors have proven their relationship with the nose, so with a runny nose or rhinitis, patients may not be able to distinguish their favorite flavors for some period.
The most likely “everyday” reason why your tongue suddenly peels off could be an ordinary thermal burn. It can easily be caused by eating too hot food or drinks.
Sometimes the oral cavity reacts in a similar way to a person’s addiction to exotic spices, highly carbonated drinks and various chemical-based additives. In this case, the inner side of the cheek and lip receives damage, and the tender palate is injured.
These hypersensitive areas become covered with painful blisters of varying sizes and begin to burn and itch. The top layer is torn off after a few days and peeling occurs.
Medical problems also affect the external condition of the surface of the tongue. Flaky particles appear due to a lack of certain groups of vitamins and microelements. This happens in winter or after a long illness, chemotherapy or radiation. This is a symptom indicating an imbalance in the intestines and dysbiosis, disorders in the digestive system.
If the tongue is very peeling and peeling, the reasons must be sought in the following pathologies or diseases:
- ulcers of the stomach or rectum, which are accompanied by non-healing erosion;
- pancreatic dysfunction, gastroduodenitis;
- chronic pancreatitis;
- hepatitis C or B, pathologies in the hepatic ducts.
All these diseases have an equally strong effect on the functioning of the digestive system. During exacerbations, it ceases to properly absorb nutrients and minerals. In addition, the mucous membrane dries out, becomes covered with cracks and becomes vulnerable to any pathogenic bacteria. Inflammation affects not only the surface of the tongue, but also the nasopharynx and damages the larynx.
Often peeling and detachment of taste buds occurs against the background of some sexually transmitted infections in the acute stage: HIV, syphilis or gonorrhea.
Sometimes such an incomprehensible reaction becomes a side effect of complex medications: anti-inflammatory, decongestant diuretics, antibiotics and steroids.
The top layer almost always peels off after using compounds that are difficult for the intestines and the whole body, aimed at treating an oncological tumor.
In preschool children, the tongue peels off during exacerbation of diathesis. This congenital disease causes the child's body to reject certain types of foods or proteins.
Upon contact with irritants, inflammation begins. In addition to skin particles and deep cracks in the mouth, the baby is bothered by rashes on the cheeks, buttocks and abdomen.
The disease is difficult to treat and requires a long-term strict diet and rehabilitation under the supervision of a specialist.
Features of geographic language
This serious diagnosis in medical terminology is called “desquamative glossitis.” It occurs in patients of any age and complicates the life of newborn babies. Doctors have not yet established the cause of the disease, but it is associated with the following pathologies:
- hormonal imbalance during adolescence;
- severe dehydration after suffering enterocolitis;
- diabetes;
- systemic lupus;
- autoimmune processes in the body;
- overdose of hazardous substances and work with chemicals.
Geographic tongue is often observed in children with severe individual reactions to preventive vaccinations against measles, mumps or hepatitis. Vaccine components damage the immune system and make it vulnerable to bacteria. In most cases, the tongue does not hurt, practically does not bother the patient and goes away completely after treatment of the underlying disease.
The pathology received its original name for the similarity of the inflamed surface to a geographical map. After the infection develops, the mucosa becomes covered with deep, winding cracks, heavy furrows and whitish areas.
Externally, the picture strongly resembles a map. Sometimes the tongue peels off and hurts, the person feels excruciating discomfort and cannot eat normally.
For some time, the ability to distinguish between salty or spicy tastes completely disappears, all foods become bland and monotonous.
Peeling tongue: how to treat?
If detachments occur, it is necessary to undergo laboratory diagnostics. The doctor, using scrapings and tests, tries to identify the bacteria or pathogens that led to the disease.
A person may need the help of an infectious disease specialist, gastroenterologist or venereologist, consultation with an otolaryngologist or dentist.
In the vast majority of situations, the skin peels off the tongue as a secondary symptom, so it is necessary to first treat the underlying disease.
During exacerbation and cracking, it is important to prevent the development of infection. Therefore, doctors recommend thoroughly rinsing your mouth several times a day with special liquid solutions and antiseptics:
- Miramistin;
- Chlorhexidine;
- Fukortsin.
If severe burning and pain bother you, the surface of the tongue is treated with Orasept. The solution contains an anesthetic and effectively reduces the sensitivity of areas damaged by glossitis. In parallel, the patient should take a multivitamin complex with a high content of B vitamins. This will speed up the regeneration and healing process.
It is recommended to use simple folk recipes as auxiliary and effective methods of treatment. An oil compress softens and removes peeling well.
To prepare it, heat a few spoons of corn, olive or sea buckthorn oil in a water bath, soak a gauze swab in it and apply it to the tongue for half an hour.
The oral cavity can be rinsed with a decoction of calendula, St. John's wort, sage or chamomile, or combine these herbs in one infusion.
An important stage of treatment is a complete examination of the teeth, removal of plaque and prevention of caries. The dentist will give recommendations and select a care product that will help heal wounds and restore the damaged surface of the tongue to a healthy appearance.
Source: https://vdesnah.com/shelushenie-yazyika.html
Causes of the disease
Graphic language is most often provoked by some kind of disturbance in the functioning of the body. However, experts note that the definitive causes of the disease have not yet been identified.
The list of the most common factors that can cause pathology includes:
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract: gastroduodenitis, ulcers, gastritis, liver diseases, malfunctions of the pancreas;
- diabetes;
- problems with the endocrine system - with the pancreas, adrenal glands and thyroid gland;
- imbalance of B vitamins, which often provokes disruptions in the cardiovascular and digestive systems, and also contributes to the development of inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes;
- infections;
- autoimmune pathologies: arthritis, multiple sclerosis, lupus erythematosus;
- congenital diseases of the oral cavity;
- benign and malignant neoplasms.
The development of the disease can be triggered by vitamin deficiency or long-term use of certain medications. In some cases, spots on the tongue in children can be a reaction to vaccinations, and often a sign of the presence of parasites in the body. In girls, peeling of the tongue can accompany the onset of puberty, in other words, be a manifestation of hormonal imbalance.
In the middle of the tongue, as if the skin has peeled off - For doctors
- Peeling of the tongue: causes, treatment, photos | All about gums
- Spots on the tongue: photos, possible diseases, treatment options Causes of appearance
- Possible diseases
- Spots on tongue photo
- What it is?
Sometimes when brushing your teeth, a person notices that the surface of his tongue takes on a different shade and begins to actively peel off. Even if there is no pain or discomfort, the condition is alarming and requires mandatory consultation.
It is necessary to establish the reasons why the tongue peels: this problem accompanies not only household burns or injuries, but also serious diseases of the internal organs.
This will help identify pathologies and infections at an early stage and prevent their development.
Spots on the tongue: photos, possible diseases, treatment options
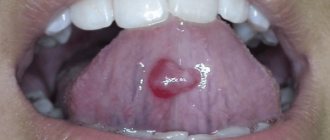
People often ignore spots that appear on the tongue. And they take a lot of risks. After all, unusual pigmentation in the oral cavity poses a hidden threat. Of course, it may simply be a reaction to an external stimulus, but sometimes in this way the body gives a sign that something is wrong.
Reasons for appearance
The main factors that provoke the appearance of pigmentation:
- allergies to oral hygiene products;
- irritating foods;
- smoking;
- alcohol;
- bite;
- wearing braces;
- dehydration.
Such spots on the tongue appear and disappear in the absence of negative effects on the mucous membrane. The situation with pigmentation that has arisen as a consequence of a developing pathological process is much more complicated. The color, shape and location of the rash helps in making a diagnosis.
Possible diseases
The most common pathologies are:
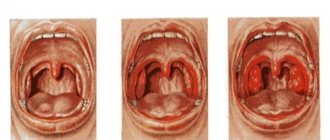
- Glossitis. Inflammation of the tongue caused by a bacterial or viral infection. It manifests itself in the form of swelling of the organ, the appearance of plaque and irregularly shaped spots on it. Salivation is impaired, a repulsive odor and ulcers appear. There are several types of glossitis, each of which has specific symptoms. To eliminate the disease, antiseptic rinses and applications are used. To heal ulcers, gels are applied to accelerate tissue regeneration. Depending on the pathogen, antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal agents are prescribed.
- Scarlet fever. An infectious disease caused by streptococcus. It begins with the appearance of fever, malaise, and headaches. A small rash appears on the mucous membranes of the mouth. It spreads to the groin, bends of the limbs, and sides of the torso. After a couple of days, granular growths appear on the tongue, and the organ acquires a crimson color. A constant companion of scarlet fever is tonsillitis. Treatment is usually carried out on an outpatient basis with antibiotics, infusion therapy, and vitamins. Patients are prescribed special nutrition and bed rest.
- Measles. An infectious viral disease that affects the respiratory system, mouth, and eyes. A highly contagious disease that often leads to death. Characterized by a sharp increase in temperature and other signs of a cold. Then conjunctivitis occurs, red and white spots appear on the tongue, palate, and inner surface of the cheeks. The rash then spreads to the entire body. A cure for measles has not yet been invented. Symptomatic treatment is used. Vitamin A supplementation is recommended to reduce the risk of death.
- STD. Sexually transmitted diseases can also affect the oral mucosa if infection occurs during oral sex. A rash and sores appear on the membranes, which can spread significantly. A purulent plaque forms there. Often such symptoms are combined with rashes on the genitals. Patients are prescribed antibiotics and antiseptics for local use.
- Lichen planus. Skin fungal disease. Sometimes it affects the oral mucosa. It is characterized by the appearance of numerous grayish nodules that merge together and resemble a cobweb in outline. Depending on the characteristics of the clinical picture and the type of disease, antifungal and anti-inflammatory drugs, immunity boosters, and corticosteroids are prescribed.
- Tongue cancer. Malignant neoplasm in epithelial and mucosal tissues. The main cause is smoking. Oncology can also be caused by injuries, herpes and the human papillomavirus. The tumor first appears as whitish plaques, lumps and red spots on the sides of the tongue. Then pain appears, salivation increases, and the submandibular lymph nodes enlarge. Part of the organ becomes numb, its surface bleeds. Ulcers, growths and cracks may appear. Combination cancer therapy. It includes chemotherapy, radiation and surgery up to complete removal of the organ.
- Leukoplakia. Thickening and keratinization of the epithelium. It occurs due to mechanical damage, chemical poisoning, and poor functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. White or gray areas appear in the oral cavity, the consistency of which resembles tissue paper. The formation of cracks, erosions, and warts is possible. For mild cases of the disease, epithelializing agents, anesthetics, and antiseptics are prescribed. In severe cases, surgery is indicated.
- Aphthous stomatitis. Inflammation of the oral cavity, characterized by the appearance of yellow or white spots surrounded by a red rim. Patients feel unwell, their body temperature rises and nearby lymph nodes become enlarged. For treatment, antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity is performed and symptomatic treatment is prescribed. During the recovery process, it is important to eat right and strengthen your immune system.
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and cardiovascular system also manifest themselves as spotting in the mouth. In the first case, the pigmentation is shaped like a map of the continents, and in the second, blue spots are formed.
The localization of the rash also says a lot about the source of the pathology. So, if a spot appears on the very tip of the tongue, there is some problem in the heart and blood vessels. Pigmentation located close to the edge is a sign of lung pathology.
The affected center of the organ indicates a malfunction of the spleen. A little further is the kidney zone. Signs of intestinal dysfunction appear at the root of the tongue. Rashes on the side parts indicate pathologies of the liver and gall bladder.
Spots on tongue photo
First of all, you should contact your dentist or therapist. The doctor will prescribe treatment or refer you to a specialized specialist. If it turns out that everything is fine with your health, you should follow preventive measures so that the problem does not return:
- choose high-quality toothpaste and rinses;
- do not eat rough foods too often, as well as sour, salty, spicy foods;
- give up cigarettes and alcohol;
- normalize water balance;
- when wearing braces, follow all the rules for their use and regularly visit the dentist;
- strengthen the immune system.
Spots on the tongue are not such a harmless phenomenon. Their appearance should definitely alert you. A lot of dangerous diseases lie behind pigmentation in the oral cavity.
Source: https://ovrachahl.ru/na-jazyke-poseredine-kak-budto-slezla-kozha.html
Causes of the disease
Graphic language is most often provoked by some kind of disturbance in the functioning of the body. However, experts note that the definitive causes of the disease have not yet been identified.
The list of the most common factors that can cause pathology includes:
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract: gastroduodenitis, ulcers, gastritis, liver diseases, malfunctions of the pancreas;
- diabetes;
- problems with the endocrine system - with the pancreas, adrenal glands and thyroid gland;
- imbalance of B vitamins, which often provokes disruptions in the cardiovascular and digestive systems, and also contributes to the development of inflammatory processes in the mucous membranes;
- infections;
- autoimmune pathologies: arthritis, multiple sclerosis, lupus erythematosus;
- congenital diseases of the oral cavity;
- benign and malignant neoplasms.
The development of the disease can be triggered by vitamin deficiency or long-term use of certain medications. In some cases, spots on the tongue in children can be a reaction to vaccinations, and often a sign of the presence of parasites in the body. In girls, peeling of the tongue can accompany the onset of puberty, in other words, be a manifestation of hormonal imbalance.
Why the skin peels off the tongue akwa21.ru
Many parents notice with alarm that the child’s tongue is undergoing changes - it suddenly changes its normal color, begins to peel and peel. Why do such changes occur, do they represent a serious pathology, and what treatment is required?
Geographic tongue, which is also known as desquamative glossitis, is a disease of an inflammatory-dystrophic nature, accompanied by external changes in the mucous surface of the tongue.
This disease does not have any “age limits” - it can occur with equal frequency in adults and newborns.
Most often, geographic tongue is diagnosed completely by accident, at a regular dentist appointment.
Reasons for the emergence of “geographical language”
The desquamative type of glossitis in adults has many reasons why it occurs, forming a geometric pattern on the surface of the tongue. The main ones include the following:
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in acute form: gastritis, ulcers, duodenitis, gastroduodenitis;
- diseases of the pancreas: pancreatitis in acute and chronic form;
- diseases of the endocrine system: diabetes mellitus;
- liver diseases, hepatitis;
- autoimmune pathologies: multiple sclerosis, lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis;
- severe or modified forms of viral infection: monoculosis, ARVI;
- hormonal changes: period of bearing a child, menopause, puberty;
- kidney diseases;
- long-term uncontrolled treatment with antibiotics;
- disturbance of the movement of food in the small intestine: malabsorption syndrome;
- metabolic disorder, which results in an acute lack of B vitamins;
- dental diseases;
- worms can also cause desquamative glossitis;
- pathologies of the skin and mucous membranes: exudative form of diathesis;
- genetic predisposition.
Cosmetology products
To keep your hands healthy, you need to use the right care cream. Since their range is quite wide, to make the right choice you should pay attention to the composition.
The caring cream should contain:
- Hyaluronic acid. It will help keep the skin hydrated.
- Collagen attracts and retains water in the cells of the epidermis.
- Glycerin stimulates the process of cell renewal.
- Linolenic acid. Helps improve the barrier properties of the skin and prevents its rapid drying.
- Hexahydric alcohol sorbitol. Gives the skin elasticity and softness. Capable of giving her deep hydration.
- Linoleic acid. Its main function is to create a protective barrier and ensure the resistance of the epidermis to external irritants.
Symptoms of desquamative glossitis with photos
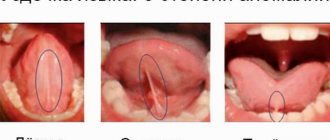
It will not be difficult for you to determine the presence or absence of desquamative glossitis. You just have to open your mouth and examine the surface of your tongue. Symptoms of the pathology will be the presence of whitish stripes, grooves and spots on its mucous membrane, which together resemble a geographical map, which is clearly visible in the photo.
The spots have different sizes: from one or two millimeters to several centimeters. They appear several at a time and only occasionally - one at a time. At the beginning of the desquamative disease, the spots are small in size, but then they quickly increase and merge with each other, forming a large-scale geographical pattern on the surface of the tongue.
Their outlines become less clear, and the middle of the desquamation focus returns to the normal process of keratinization of the filiform papillae. In areas where keratinization occurs, everything happens exactly the opposite - the peeling process begins there.
As a result of the fact that these processes constantly replace each other, the geometric pattern can change several times per day.
The desquamative form of the disease is predominantly localized on the sides and dorsum of the tongue. Then she moves to the lower part. Places of desquamation are painted bright red, have a smooth surface, and may be completely devoid of lingual papillae.
Forms of desquamative glossitis in adults
Desquamative glossitis occurs in three different forms:
- superficial;
- hyperplastic;
- lichenoid.
The superficial form is characterized by the formation of spots and stripes colored bright red. They have clear boundaries and are surrounded by a healthy mucous membrane. After the peeling has passed, the surface of the tongue becomes smooth and shiny. Symptoms of the process are a barely noticeable burning and itching.
The next form of glossitis is hyperplastic. It is characterized by the presence of compacted foci of desquamation associated with an increase in filiform lingual papillae. The following symptoms are added to the symptoms that are inherent in superficial glossitis: there is a feeling that there is a foreign object in the mouth, the places of peeling are covered with a white, gray or yellow coating.
The third form is lichenoid. It is characterized by the fact that the spots have different shapes and sizes. In addition, they do not have one place of localization and therefore constantly move across the entire surface of the tongue, forming a geographical pattern. In areas of desquamation, the fungiform papillae are enlarged.
Source: https://dens1995.ru/desny/pochemu-oblazit-yazyk.html
Treatment of desquamative glossitis
Treatment is carried out according to the diagnosis performed exclusively as prescribed by the doctor. In case of development of pathology against the background of any disease, complex medication will be required.
Additionally, it is recommended to make products based on natural products. In the presence of inflammatory infections, antibiotics may be prescribed.
Traditional ways
In the treatment of geographic tongue, the use of natural products is acceptable. These can be herbal decoctions, baths. The following recipes are recommended:
- Before and after eating, rinse your mouth with a decoction of sage, oak bark or chamomile. You will need to pour 1 tbsp. l. herbs with water in an amount of 200 ml and boil in a water bath. Instead of herbs, it is permissible to use green tea.
- Oil bath, for which you can use sunflower, olive, corn oil, heated in a water bath for 20-25 minutes. After which the oil is cooled and a cotton swab is moistened with it. Apply to the surface of the tongue for 15 minutes.
- Soda solution with iodine. The composition includes half a teaspoon of soda, 3 drops of iodine, diluted in a glass of water. The mixture is used to rinse the mouth.
INTERESTING: healthy tongue: photos and ways to maintain the organ in this condition
It is important to remember that treatment with folk remedies is permissible only after consulting a specialist. Most often, decoctions are prescribed in combination with other drugs.
Under the guidance of a dentist
There is no specific treatment for the disease. Of course, if we are not talking about serious disturbances in the functioning of the body.
Dentists most often give general recommendations:
- brush your teeth regularly,
- carry out the rehabilitation of all existing carious lesions of teeth and gum diseases,
- carry out antiseptic mouth rinses with specialized medications,
- limit or completely eliminate irritating foods from the child’s diet: spicy, salty, excessively hot or cold,
- take a course of vitamin complexes prescribed by a specialist,
- in some cases, regenerative and painkillers are prescribed.
Interestingly, some specialists do not consider it necessary to focus on the problem at all, especially if no painful sensations are observed. In particular, Dr. Komarovsky shares this opinion - a video with his participation can be viewed at the end of the article.
The skin peels off the tongue
Many parents notice with alarm that the child’s tongue is undergoing changes - it suddenly changes its normal color, begins to peel and peel. Why do such changes occur, do they represent a serious pathology, and what treatment is required?
Geographic tongue, which is also known as desquamative glossitis, is a disease of an inflammatory-dystrophic nature, accompanied by external changes in the mucous surface of the tongue.
This disease does not have any “age limits” - it can occur with equal frequency in adults and newborns.
Most often, geographic tongue is diagnosed completely by accident, at a regular dentist appointment.
What can a doctor do?
Since diseases of the oral mucosa are different, the doctor will, of course, first prescribe the necessary tests. In general, by looking at the mucous membrane, he will be able to approximately determine for what exact reason the disease occurred.
He will be guided by zones, since in a person’s mouth there are zones responsible for the internal organs.
If inflammation occurs in any of the zones, the doctor immediately makes the first diagnosis and, based on it, prescribes tests and, if necessary, an x-ray of the internal organs.
- Blisters
- Painful plaque
- Peeling skin with mucous membranes.
If one of these diseases suddenly appears and is located in a certain area, it means that there are problems with the internal organs and if they are not eliminated, then the disease itself will be difficult to cure.
White coating on the tongue
A white or yellowish coating on the tongue appears when bacteria or fungi actively multiply in the oral cavity, and their dead cells stick together and get stuck between the taste buds on the tongue. Coated or white tongue. The plaque usually collects at the root of the tongue and from there it seems to spread to the sides - this is its normal state.
Typically, plaque increases if you have an upper respiratory tract infection or thrush. And if you cure the underlying disease, then the plaque itself will disappear. Sometimes the cause of such plaque is constantly inflamed tonsils.
Smoking increases the likelihood that white tongue will accumulate on your tongue. By the way, smoking may cause the white bacterial coating to become colored and darken, but it will not change its essence.
Plaque itself is not harmful and does not pose any danger, but it can increase bad breath.
There is only one option - to look for the reason why the tongue is blocked and eliminate it. An otolaryngologist, that is, an ENT specialist, will help with this.
Geographic language
Geographic language
Geographic language is another likely reason. This is a condition in which smooth, bright red spots appear on the top or sides of the tongue, surrounded by a whitish rim of sloughing epithelial cells (superficial mucosal cells).
The main cause of the occurrence has not yet been precisely established by doctors, but most likely it is related to heredity. People who have this pathology also have a higher risk of encountering problems such as cracked tongue.
Initially, small whitish-gray areas appear on the surface of the tongue (up to 5 mm), after which swelling and protrusion occur in their central part with further desquamation of the epithelium and papillae.
As a result, an area of underlying mucosal tissue that is bright red or bright pink is exposed. Areas of peeling quickly increase, flaps of tissue are located along the rim of the spots.
Such lesions can appear on any side of the tongue, for example, on the sides, on top and even on the back, which gives the tongue the appearance of a geographical map.
Moreover, people with geographic tongue, if they like to take hot, spicy, spicy food and drinks, are likely to suffer more from effects such as mucous peeling. This is due to the fact that such foods increase the sensitivity of the tongue.
Home Remedies
Apart from the medications prescribed by your doctor, there are some home remedies that can be successfully used to solve the problems associated with tongue peeling.
Salt may be the best remedy for a white coated tongue. Its rough texture can act as a natural scraper to remove dirt and dead cells. Another important fact about salt is that it has antiseptic properties that will help kill the bacteria that causes bad breath.
Options for using salt to remove white plaque:
- First, you need to sprinkle some salt on your white coated tongue and gently rub (scrub) it with a toothbrush for a few minutes. After this, rinse thoroughly with warm water. To achieve good results, this process must be repeated three times a day.
- Another method that may be useful is to stir one teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water. Rinse your mouth thoroughly with salt water and then spit it out. This procedure must be repeated several times a day until the condition improves.
Other reasons
An allergic reaction can also cause the tongue to become patchy. This is often how citrus intolerance manifests itself. Although the products can be anything. This is especially true for children, whose sensitive body still does not cope well with irritants. You can try changing your diet to see what foods trigger this reaction.
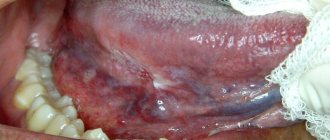
Injuries also often lead to changes in the mucous membranes. This could be a burn or wound due to eating hard or rough food. Even accidental biting can cause the tongue to temporarily change. No manipulation is needed - everything will be restored in a few days. Also, the tongue often peels off in adults due to vitamin deficiency.
One of the reasons for changes in the condition of the mucous membranes is problems with teeth and gums. This is especially true for people who neglect going to the dentist. However, just seeing your tongue peel off once is enough - the photos evoke such a feeling of disgust that it is better to overcome your fear, go to the doctor and reduce the likelihood of such problems.
In medicine, there is such a thing as “geographical language.” This is inflammation that occurs on its surface.
In addition to the fact that an adult or a child’s tongue peels off, spots with a pink outline appear, resembling patterns on a map. Determining the cause is sometimes difficult. Even helminths can lead to similar conditions.
Usually, an examination by a gastroenterologist is immediately prescribed, and then, based on the results, they decide whether it is worth referring the patient to other specialists.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with How to use iodinol for tonsillitis | The medic is here!
Yellow coating on the tongue
A light yellow tint, as a rule, indicates that these places will soon turn black. We have already written what will come of this: black furry tongue Yellow tongue.
But if the whites of the eyes or skin turn yellow along with the tongue, this may be a sign of liver damage. Here you need to quickly rush to the doctor and find out where your jaundice comes from. The yellowish tint of the plaque itself is normal and does not indicate any problems with the liver.
Infectious glossitis
Infectious diseases of the tongue can be recognized by photos and descriptions, but only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
Name of the disease Causative agent Symptoms Treatment
| Candidiasis (thrush) | Fungal infection – Candida albicans | A white coating with a cheesy consistency, as in the photograph. Removing the plaque is accompanied by pain and bleeding. Children often have fever. | Lubricating the inflamed areas with antifungal ointments, rinsing with soda solution, Furacilin or manganese. |
| Herpetic glossitis | Herpetic viral infection – Herpes simplex virus | Rashes in the form of small watery blisters, as in the photograph. If they open, erosions appear on the tongue. The rash is painful and accompanied by fever. | Taking antiviral drugs orally, lubricating the rash with antiviral ointments, rinsing the mouth with Chlorhexidine. |
| Streptococcal impetigo | Bacterial infection – streptococci | The tongue becomes inflamed, red spots appear, in place of which bubbles up to 1 cm in diameter develop, as in the photograph. When the bubbles open, ulcers form. | Taking antibiotics orally and in the form of ointments, rinsing the mouth with Furacilin, soda or manganese solution, Chlorhexidine, chamomile decoction. |
Additionally, symptoms accompanying the inflammatory process are treated: for fever, an antipyretic is used, for unbearable pain, analgesics are used, and more fluids should be drunk to prevent dehydration. Regular oral hygiene helps eliminate infections and ulcers on the surface of the tongue.
Catarrhal and ulcerative glossitis are also infectious diseases of the tongue, the symptoms and treatment methods of which are similar to the infectious diseases described above.
But the cause most often lies not in infection of the epithelium of the oral cavity itself, but in the complication of general infectious processes (ARVI, influenza) or inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract.
This diagnosis is often found in smokers and people who abuse alcohol.
With the catarrhal form of glossitis, taste perception changes, pain appears, and tingling occurs. Inflammation causes swelling, which leaves teeth marks on the sides of the tongue. A dense layer of white plaque accumulates on the root of the tongue.
If left untreated, catarrhal glossitis turns into an ulcerative form with the formation of bleeding ulcers covered with a layer of dead epithelium and the appearance of an unpleasant odor.
In case of catarrhal and ulcerative forms of glossitis, it is necessary to treat both the general disease, which entails pathological changes in the tongue, and external manifestations (erosions). May be assigned:
- Antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs by mouth.
- Rinsing the mouth with antiseptics and herbal decoctions to eliminate inflammation and heal ulcers that have affected the human tongue. You can use chamomile.
- If plaque accumulates, wipe it off with clean gauze.
How to treat plaque on the tongue
In most cases, plaque on the tongue does not need to be treated, because it is not a disease. If you don't like having it there, normal oral hygiene is sufficient. And if normal hygiene does not help, then you should consult your dentist and decide what you can add to the standard brushing of your teeth and tongue twice a day.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Herpes on the lips: TOP 8 remedies for quick treatment
What else will help cope with a coating on the tongue:
- The good old advice to drink more helps, because one of the reasons for the formation of thick plaque is dehydration What Causes a White Tongue and How to Treat It.
- Quit smoking, it helps with everything.
- During the day, try to eat something hard and juicy, such as apples or raw carrots.
- Try not to breathe through your mouth if you have such a bad habit. And if your nose is stuffy, use vasoconstrictor drops.
Problems with the gastrointestinal tract
Normally, the surface of the tongue is pink, moderately smooth, but with clear outlines of taste buds. Plaque is also present - if a person is healthy, he has a white color. Such deposits can be quickly removed with a regular toothbrush during oral hygiene. If the color of the plaque has changed, the tongue peels off, the reasons may be different.
One of the worst causes of a peeling tongue is esophageal cancer. Another alarming symptom is the appearance of a thick white coating. This occurs because the acid present in the stomach is refluxed into the esophagus and from there enters the oral cavity. Acid has a toxic effect on the mucous membranes, causing the tongue to peel and hurt.
When bile stagnates, the condition of the oral cavity also changes. First, a yellow coating forms on the mucous membranes. The thicker and darker it is, the more advanced the disease is.
When the skin peels off your tongue, you need help as soon as possible. Intoxication with damage to the liver and other vital organs is possible.
You need to contact a gastroenterologist, who will prescribe the necessary tests to make a diagnosis and develop an effective course of treatment.
The intestines are a rather complex system that has to remove decay products and harmful substances from the body that can affect the general condition of a person. Despite the fact that this is a very powerful organ, an unhealthy lifestyle, the presence of chronic diseases and other reasons lead to pathologies in its work.
Dream interpretation - skin
Leather dreams of a successful business and the favor of women.
If you dreamed that you were wearing leather clothes, then in reality, feel free to play on the stock exchange: you will be lucky.
Dreaming of leather jewelry means fidelity in love and a prosperous home.
Skin piled up in a pile portends good luck and happiness.
Leather trading means that all your activities contribute to the successful accumulation of wealth.
Dream Interpretation - leather (skin)
“to lose seven skins” to punish.
“shedding the skin” is a symbol of transformation. “Be in someone's shoes” - enter into the position of another person. "Thick-skinned" insensitive. “Rip off like a stick”; deprive of money and property.
“skin and bones”: thinness, poverty, illness. “Going out of your way (or skin)” excessive effort. “Sharing the skin of an unkilled bear” is an unreasonable plan and premature hopes.
"skin!" (this is how they speak about a vile person, a traitor). "A wolf in sheep's clothing" is a disguised enemy.
What tongue diseases occur and their diagnosis by color with description and photo
The tongue is a muscular, mobile organ of soft consistency, covered with a mucous membrane. On its entire surface there are receptors for sensing the taste of food. With the help of the tongue, a person speaks, swallows food and liquids, and the state of this organ shows changes in the internal organs.
Often the tongue is exposed to infectious influences, which is why its diseases develop. Anatomically, the tongue is divided into a root and an anterior part that is movable in different directions. In a healthy person, the organ has a pale pink color, the middle fold is smooth and pronounced, and the papillae are distributed evenly over the entire surface.
The condition of the tongue is temporarily affected by the color of food taken , treatment with certain medications, and consumption of hot foods and drinks.
In summer, the color of the taste buds - the papillae - has a reddish tint, and in other seasons their color remains light yellow.
To determine diseases of the internal organs, you need to look at the tongue in the morning, before eating, in natural light, after rinsing the mouth.
Tongue diseases
When the organ itself is in a painful state, its appearance, thickness, and size change:
- Glossitis is characterized by swelling of the tongue, the surface becomes smooth, severe redness is observed, pain is felt when moving, and the organ becomes inflamed.
- In geographic language, the symptoms are similar, but their manifestation is spotty, and the lesions can change location.
- Diagnostics establishes macroglossia disease with an abnormally enlarged tongue.
- Sometimes a small ulcer or white raised spot appears on the surface. This is an alarming sign, which in some cases indicates oncology (leukoplakia). A tissue biopsy of the spot is performed; if this is not done, cancer cells will develop in the surrounding gums, cervical lymph nodes and jaw. Timely detection of oncology cures cancer completely.
- Sometimes elongated tubercles appear on the surface, which are called hairiness; the tongue has an unsightly appearance, which indicates insufficient cleaning of the surface.
Causes of tongue diseases
Hairiness of the organ and its unnatural color can be caused by malicious use of tobacco , taking antibiotics or lack of oral hygiene. For these reasons, bad breath occurs. Sometimes the tongue becomes sick simultaneously with diseases of the body, for example, candidiasis, lupus erythematosus, syphilis or psoriasis.
Glossitis occurs as a result of a lack of B vitamins, which is caused by poor diet or impaired metabolism. Glossitis is manifested by superficial or deep tissue inflammation, the magnitude of which depends on the degree of the disease. It can be caused by disruption of the capillaries of the tongue and mucous membrane, which occurs due to organ injuries or burns.
Tongue ulcers , which do not have an oncological nature, appear with scarlet fever, other similar infections, or an overdose of toxic drugs. Herpes simplex entails ulcerative lesions on the surface of the organ.
An increase in size is caused by internal hypothyroidism (cretinism), Down's disease, a surge in growth hormones due to dysfunction of the pituitary gland, and amyloidosis.
Glossitis or even leukoplakia can occur when the edges of the organ are irritated from wearing incorrectly fitted dentures, a broken edge of a tooth, cigarette abuse, and sometimes this is a manifestation of HIV.
Cancers of the tongue appear most often in smokers, if this is supported by the joint intake of alcoholic beverages.
Symptoms
In addition to the above manifestations of tongue diseases, the following symptoms are observed:
- the abnormal shade may not be clearly expressed, but in some cases the organ has a bluish, brown or almost black color;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- copious uncontrolled secretion of saliva;
- difficulty swallowing due to large size or pain;
- immobility of the tongue.
Preventive and diagnostic measures
Prevention consists of careful treatment of the horizontal and lateral surfaces of the tongue when brushing your teeth. many types of brushes on sale , from which everyone can choose the product at their own discretion.
After eating, it is recommended to rinse your mouth. For a professional examination, you should visit your dentist once a year.
Excessive consumption of strong drinks and heavy smoking harms not only the tongue, but the entire body as a whole.
To diagnose a particular tongue disease, it is enough to examine the patient and pay attention to the history of his diseases. If it is necessary to exclude the oncological nature of organ changes, a biopsy is performed.
Treatment of tongue diseases
In most cases, the disease goes away if irritating factors that lead to changes are excluded. In other cases, symptoms are relieved when the underlying disease is treated.
For example, if there is a lack of vitamins, a comprehensive intake of them is prescribed, and changes in the diet are recommended.
After contacting the dentist, the patient adjusts the dentures or files off the rubbing edges of the tooth.
The resulting discomfort is relieved by rinsing with a concentrated salt solution, which helps heal wounds. There are appropriate antiseptic drugs that alleviate the course of the disease.
If the infection is infectious, the doctor prescribes antibiotics or antifungal agents; cancerous lesions require surgery and then radiation therapy is prescribed.
You should consult a specialist if the symptoms of the disease do not go away within several days or more.
Recognition of internal diseases by the condition of the tongue
Signs of damage to other organs are reflected in the color, size and condition of the tongue . Phenomena occur in diseases of the liver, heart, digestive tract and stomach.
Most often, it is changes in the tongue surface that indicate the onset of the disease. The appearance of a thin whitish coating indicates that the pathology of the internal organs has not yet manifested itself and is at the initial stage.
The grayish color of the plaque indicates the progression of the disease. During the examination, pay attention to:
- smell from the mouth;
- the shape of the tongue;
- condition and structure of the organ;
- shade and intensity of plaque;
- the appearance of neoplasms;
- ability to move;
- the ability to distinguish the taste of foods or a change in perception.
Individual parts of the tongue indicate a disease of the corresponding system in the body or a separate organ.
Heart ailments are reflected at the tip of the tongue , followed by the zone of the respiratory organs and lungs, and the condition of the spleen is manifested in the center.
On the deep posterior surface, kidney diseases are diagnosed, on the lateral sides, the condition of the liver and bile ducts is diagnosed. The worsening pathology of internal organs is indicated by an increase in symptoms on the surface of the tongue.
Varieties of configuration
During the study, the shape and thickness of the tongue plays a role. A thin tongue indicates a disease of the hematopoietic system and impaired metabolism; an organ that is too thick indicates a dysfunction of the liver and stomach.
An improperly functioning digestive system makes itself felt by swelling of the tongue, and an elongated tongue indicates heart disease.
If the central stripe on the tongue is curved, then the spine is sick, the appearance of bulges of various locations indicates pulmonary problems, changes on the surface indicate an insufficient supply of vitamins.
Changing the state of the language
Problems also manifest themselves in how the organ behaves:
- malfunctions of the thyroid gland are manifested by trembling of the tongue;
- gastritis will show bright colors and shades on the surface;
- a fungal infection in the body will cause neoplasms throughout the entire area;
- an increase in the acidity of the body will manifest itself as the appearance of ulcerative rashes;
- if the papillae in the front of the tongue become inflamed, this indicates diseases of the skeletal system in the pelvic area.
Visual inspection
A visual inspection will help identify diseases . For example, increased humidity and salivation indicate impaired digestion. Poisoning of the body, infection will manifest itself as dryness and the appearance of cracks.
The disappearance of papillae on the surface and the appearance of gloss suggests the presence of cancerous tumors in the body.
It is not recommended to independently determine such pathologies, nor to prescribe treatment; this requires examination by a specialist, and the language can only suspect the onset of diseases.
Changes in taste perception and the appearance of certain aromas
Such a serious violation of taste indicates disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine and nervous systems of the human body.
By the way the smell from the oral cavity manifests itself, a specialist can judge certain diseases. For example, a doctor will regard an ammonia smell as evidence of kidney and ureter disease.
A rotten smell occurs with diseases of the teeth or stomach. The acetone aroma suggests the occurrence of diabetes.
Diagnosis of internal diseases by tongue color
Characteristic colors , studied over many years, characterize the beginning pathologies of important organs of the human body:
- Red color signals improper functioning of the heart, lungs and other respiratory organs of the system, diseases of the hematopoietic system, and various infectious diseases.
- Raspberry speaks of severe infectious lesions, poisoning with symptoms of chills, complicated pneumonia.
- Dark red characterizes the same diseases as the red color, but they occur in a more severe form or are advanced. Toxic disorders and severe renal pathology occur.
- Alternating red and white areas on the surface of the tongue indicate scarlet fever, a red lacquered organ indicates the development of pellagra.
- A light bluish tint indicates impaired blood circulation and cardiac or pulmonary failure.
- The coloring of the lower area of the tongue in a bluish color indicates heart failure long before the onset of the disease. This indicator is especially typical for middle-aged people who do not expect such changes in the cardiac system, while older people have the opportunity to seriously take preventive measures.
- Purple color indicates severe disorders of the hematopoietic system and pulmonary diseases.
- Black color suggests cholera infection.
- A pale and bloodless tongue indicates anemia and severe general exhaustion of the body. In this case, tooth marks on the lateral surfaces indicate insufficient absorption through the intestinal walls. If discoloration appears only in certain areas of the tongue, then the disease threatens those organs that correspond to the anatomical distribution of surface zones.
Symptoms
Most often, neither the children themselves nor the parents notice either the onset of the disease or its course until a certain time. Identification occurs in most cases completely by accident - at a dentist’s appointment or an examination of the oral cavity by a general practitioner.
Sometimes older children can notice the problem on their own, for example, during daily oral hygiene procedures or by carefully looking at the tongue in the mirror.
Do you know when to start brushing your child’s teeth? The answer can be found in our article.
We will tell you in detail why a black coating occurs on the tongue in children.
At this address: https://www.vash-dentist.ru/detskaya-stomatologia/polost-rta/tantum-verde-dlya-detey-instruktsiya-po-primeneniyu.html - you will find instructions for using the drug Tantum Verde.
Main symptoms
- the appearance of areas of white-gray clouding of the surface of the tongue;
- swelling and then desquamation of the affected areas of the epithelium;
- the appearance of red or bright pink spots that have different sizes and shapes;
In those areas where desquamation occurs, the mushroom-shaped papillae of the tongue become very visible. They look like bright red dots. Quite rarely, areas of desquamation appear alone. Most often these are numerous lesions on different parts of the tongue.
Possible manifestations
- increased sensitivity of the surface of the tongue;
- burning sensation;
- itching;
- numbness;
- tingling;
- change in sensitivity;
- changes in the perception of taste;
- increase in size due to multiple foci of inflammation and desquamation;
- discomfort during a conversation;
- difficulty swallowing and chewing food;
- headache;
- enlargement of nearby lymph nodes;
- general deterioration of health.
Children often feel very anxious about the appearance of their tongue. This leads to stress, and stress can lead to a significant worsening of the disease. If the process worsens, the strength and speed of desquamation also increases
.
In almost half of the cases this leads to a manifestation such as a folded tongue
– the general shape changes, folds appear on the surface due to multiple foci of desquamation.
What to do if your tongue peels off?
If you notice signs of peeling of the tongue mucosa, please simply consult a doctor. Your doctor will give you the right treatment before your symptoms become serious. A list of essential medications that your physician or dentist may recommend includes:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Supplements containing zinc.
- Anesthetics for mouth rinsing.
- Corticosteroids that are applied directly to the tongue.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers.
In order to speed up healing and get rid of peeling of the tongue mucosa, you should avoid or limit:
- the use of tobacco and medications, which can cause the tongue to peel off;
- consumption of hot, spicy, sour foods, dried and salted nuts;
- using toothpaste with added whitening ingredients or strong flavors.
What does geographic tongue look like in a child?
When healthy, the dorsum of the tongue is covered with tuft-like projections (papillae) that give the tongue an irregular surface texture and a white-pink color. On the geographic tongue there are areas of atrophy (thinning of the mucosa) in which these papillae are absent .
The damaged surface of the tongue becomes erythematous (dark red) and smoother than unaffected areas. These areas are usually well demarcated and bordered by a slightly raised, white, yellow or gray, serpentine (wriggling) peripheral zone. In some cases there may be only one area affected, but this is rare.
The lesions typically occur in multiple locations on the tongue and coalesce over time to form a typical map-like appearance. The lesions usually change in shape and size and migrate to other areas, sometimes within a few hours. The condition may affect only part of the tongue, its tip and sides, or the entire upper surface at any one time. The condition goes through periods of remission and relapse. It is believed that the disappearance of the white peripheral zone indicates a period of healing of the mucous membrane.