March 3, 2020 Last revised: January 12, 2020 Dental diseases
It would seem that after tooth extraction all fears and pains were left behind. However, often relief after long suffering from toothache is replaced by anxiety from the emergence of new problems. The most common complication is swelling after tooth extraction. What to do in this case, and when such a sign signals the development of serious complications?
Not always a pathology
Most of us don't consider tooth extraction something out of the ordinary. Although we must not forget that this is still a surgical intervention. Naturally, the torn vessels and tissues will be swollen and painful, and this is absolutely normal. The more complex the intervention, the stronger these phenomena were. Even uncomplicated removal leads to normal tissue swelling. And since any swelling and pain are associated with stagnation and local deterioration of blood circulation, it is quite easy for inflammation to occur. The pain is especially severe after the effects of painkillers wear off. Normally, swelling and pain quickly disappear, and the hole heals.
Physiological local tissue swelling after tooth extraction is not a complication or threat to the patient’s health.
Drug treatment
Depending on the specifics of the operation, swelling after the operation is removed using different methods. When swelling is particularly severe, antihistamines are often prescribed.
A special anti-edema ointment can also be an excellent solution to the problem. Typically, such a remedy is prescribed by the specialist who performed the operation, and the ointment itself most often has an additional anti-inflammatory effect.
The most effective way to relieve swelling is by using hormonal drugs. Such medications are usually administered through regular and systematic injections. But you should understand that this method is applicable only with the permission of a doctor and under his close supervision, since the consequences for everyone can be different, and sometimes unpredictable.
Doctors also often prescribe diuretics and special decoctions of similar action in order to increase the outflow of fluid from the body and thus relieve swelling.
But remember, if swelling does not go away within two weeks, you should definitely consult a doctor, as this may be a direct signal of an ongoing inflammatory process after surgery and no ointment will help.
Causes
When a tooth is removed, there are a number of reasons that can easily lead to complications and the need for subsequent treatment.
The duration of swelling after tooth extraction directly depends on the qualifications of the doctor, the type of anesthesia, the complexity of the intervention, and the quality of the antiseptic used.
The main reasons that can make swelling the first stage of inflammation in the oral cavity may be:
- Dryness of the tooth socket, which is a consequence of the absence of a blood clot to protect against infection.
- Allergy to drugs used during removal (antiseptic, painkillers).
- Incompetent treatment by a doctor of the tooth socket after removal, followed by the entry of pathogenic microflora into it (remnants of soft tissue, exudate, dental plaque).
- Incomplete tooth extraction, when the interroot septum, tooth fragments or root part remains in the wound. Often, bone fragments remain in the gums after the removal of severely damaged teeth.
- The presence of a cyst that remains after removal. Typically, tooth extraction is combined with sanitation of the oral cavity and requires the prescription of antibiotics.
When swelling is predetermined
Everyone knows that you need to see a dentist as soon as your tooth starts to bother you. However, in reality, it often turns out according to the principle “until the thunder strikes...” Tooth extraction, of course, is a last resort in dentistry. This operation is most often performed when the disease is already advanced. Therefore, often a wound in the mouth after tooth extraction is adjacent to problems of an infectious-inflammatory nature or general diseases. In such cases, it is unlikely to avoid complications in the form of pain and swelling.
Cases where it is impossible to avoid soft tissue swelling after tooth extraction include:
- Alveolitis (inflammation of the tooth socket) from infection from the oral cavity. This is a particularly common cause of pain and swelling after tooth extraction surgery. Alveolitis often accompanies the removal of teeth (periodontitis) or the oral cavity (stomatitis) in chronic inflammatory processes. At the same time, the development of an existing infection in the mouth after removal takes a new turn. Alveolitis, in addition to swelling, is characterized by severe pain and bad breath.
- A combination of removal with a forced incision of the gum. This happens during purulent processes (abscess), which increases swelling. An incision in the mucous membrane is necessary to release pus from the tissues.
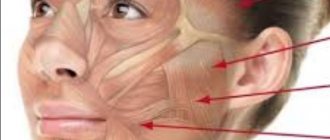
- Particularly traumatic removal procedure (for example, impacted or dystopic teeth). In this case, the tooth sits tightly in the jaw and has to be “pulled out” from there, which inevitably leads to swelling of the soft tissues.
- After the removal of third molars (they are also called “wisdom teeth” or “eights”). The specific location of these teeth suggests traumatic removal, with constant postoperative swelling and pain.
- General health problems. With many pathologies (vascular diseases, blood diseases, reduced immunity, hypertension, diabetes), tooth extraction is often more difficult to experience, accompanied by prolonged swelling and pain.
In such cases, it is unlikely to avoid swelling. However, often in such situations the swelling goes away on its own, without requiring additional medical intervention.
How to relieve swelling from the face after surgery: decongestants – Injuries
20.11.2019
Swelling after surgery is a common phenomenon that causes a lot of inconvenience, both aesthetic and physical. Neglect of edema can lead to unpleasant consequences, so you should know how to get rid of it correctly and safely.
Causes
When the integrity of body tissues is compromised, swelling may appear, this applies to even the most minor surgical interventions.
During operations of any complexity, tissues are damaged, so the body begins to react to this, which leads to the formation of swelling.
Edema is accumulated fluid in the tissues of a particular organ, and can sometimes collect in the space between the tissues. All edema can be divided into local and general.
Source: https://GidPain.ru/pomoshch/snyat-otek-litsa.html
When swelling is not dangerous
Swelling of the gums or cheeks is not always pathological. There is no need to panic or worry if:
- general condition is satisfactory;
- swelling is not accompanied by an increase in temperature (if it was not there before removal);
- swelling is in one place (usually in the gum or cheek area) and does not spread to the face;
- the pain is tolerable and lasts no longer than 2-5 days;
- the swelling of the cheek is hardly noticeable, goes away in 3-4 hours and is not accompanied by increased pain;
- no redness on the skin or mucous membranes;
- there is no suppuration, as evidenced by the absence of severe pain, bad smell and taste in the mouth.
If the temperature before removal was elevated, then on the first day after the intervention it may increase slightly (37-37.5 degrees).
Pain after removal is always present to some extent when the effect of anesthesia wears off. The so-called “background” aching pain can occur in the first days after removal. After complex removal, discomfort may persist for 2 weeks. The main thing is that the pain gradually decreases.
If there are no alarming symptoms, then at first it is enough to simply observe the swelling. The main thing is a gradual reduction in swelling and pain.
When there is cause for concern
There are situations when complications begin after tooth extraction. Then swelling becomes a sign of pathology. The combination of swelling of the cheek or gums with other dangerous symptoms is alarming:
- The swelling is accompanied by redness of the mucous membranes or skin, shortness of breath, and tachycardia. Rashes are possible in various places of the upper body. Sometimes these signs can be an indicator of an allergic reaction. Here, prompt medical assistance is necessary, since anaphylactic shock can lead to the death of the patient.
- There is no toothache with severe swelling of the gums or cheeks. This may be an indicator of poor-quality canal treatment and provoke pulpitis or the formation of cysts.
- The swelling has spread to the face.
- The body temperature is above 38 degrees and continues to rise, and the health condition is deteriorating. Possible difficulty swallowing or pain when moving the jaw. Here it is important to exclude an acute purulent process that spreads to the jaw (osteomyelitis, phlegmon, abscess).
- The pain lasts for several days and does not decrease. A visit to the doctor is necessary here.
- A sharp “bad” odor from the mouth often occurs when there is pus in the tooth socket.
- After the condition returned to normal, the swelling returned again.
Even one such symptom becomes a good reason to consult a doctor. And there is no point in delaying your visit to the dentist. A frivolous attitude towards such manifestations can have serious complications, even death.
Reasons for appearance
Any edema is the accumulation of excessive fluid in the tissues of the body. By creating increased pressure on the vessels and capillaries, the liquid penetrates through their walls into the tissues and muscles, saturating them, resulting in the formation of swelling.
There are two main causes of edema:
- accumulation of lymph in the area of tissue affected by the operation;
- postoperative inflammation.
In the first case, swelling is explained by natural causes: surgical intervention in the body’s functioning always leads to an increased load on the immune system, which strives to ensure the normalization of the body’s functioning and triggers increased formation of lymph. Lymph accumulates in the area of tissue damaged during surgery and causes swelling.
In the second case, the cause of edema is an infectious or inflammatory process. An exacerbation of a chronic disease caused by the operation, a cold, or non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations in the postoperative period can cause swelling of the face after surgery. This is often accompanied by hyperemia (redness) and increased body temperature.
Although postoperative swelling on the face almost always occurs, it can have different severity. The degree of swelling depends on the following factors:
- the general condition of the immune system (the stronger the immune system, the weaker the signs of swelling will be, and the faster it will subside);
- individual characteristics of the patient’s health (are there any chronic diseases, a tendency to edema, hypertension, etc.);
- proper adherence to doctor’s recommendations, compliance with restrictions and precautions;
- lifestyle (presence of bad habits, addiction to alcohol, etc.).
As a rule, swelling does not occur immediately after surgery, but on the second or third day; depending on the efforts made, it will subside after several days, or less often, a week. If postoperative swelling persists into the second week, or if fever, chills, or intoxication are added to it, a visit to the doctor should not be postponed. In this case, at a minimum, antibacterial therapy is necessary.
How and how to relieve swelling after tooth extraction
With the physiological form of swelling, it is usually treated without treatment. However, you can speed up the healing process using approved methods. To do this at home, they usually use:
- Applying cold (ice, a bottle of water, frozen food) to the cheek through the tissue layer at the site of swelling. You can use a wet towel. A wet cold compress is especially indicated when removing wisdom teeth. Cold is applied for 15 minutes throughout the day.
- Soda-salt compresses for 15 minutes every hour 2-3 times. To do this, pour half a teaspoon of soda and a teaspoon of salt into a glass of warm water. Soak a cotton swab in this solution and apply it to your cheek.
- Rinse your mouth with salt solutions (1 tsp per glass of water) or furatsilin, diluted propolis tincture (5 drops per glass of water), herbal decoctions (sage, oak bark, calendula or chamomile) 3-4 times a day. Do not overdo it with rinsing after removing wisdom teeth. In this case, it is better to take the solution and keep it in your mouth. If there was a dissection of the gums, then you can rinse your mouth no earlier than 2 days after the operation.
- “Aggressive” types of food are excluded: food should be soft, crushed and gentle (eat no earlier than 3 hours after removal).
- Sleep with the head of the bed raised. This eliminates swelling.
- Decongestants (homeopathic drugs "Traumel" or "Lymphomyosot", antiallergic drugs "Suprastin", "Loratadine", etc.)
Specialized assistance
Depending on the severity of the complications, pathological swelling after tooth extraction can be treated in an outpatient setting. In serious cases, the patient is also offered inpatient treatment.
What awaits such a patient in the hospital?
- The patient will definitely be examined. If there is suppuration in the wound (with a dry wound, alveolitis, periostitis), the wound must be sanitation with the removal of tooth fragments and purulent contents. Antiseptic rinses (chlorhexidine, furatsilin, dioxidine) and antibiotic administration (oxamp, cefazolin) are used.
- If there is an abscess, it is opened and a drain is placed to drain the discharge from the wound.
- In the postoperative period, antibiotics in tablets or injections (for example, ofloxacin), anti-inflammatory drugs (ibuprofen, ketorol), immunostimulants of natural or synthetic origin (welferon, immunal), vitamin complexes, proteolytic enzymes (trypsin, chymotrypsin) are usually additionally used.
- If anaphylactic shock is suspected (severe swelling, shortness of breath, panic), the patient is urgently hospitalized in the intensive care unit and given emergency care (first of all, hormones and antihistamines are administered). In difficult cases, a tracheotomy may be performed to restore breathing.
Postoperative swelling on the face and getting rid of it
You should try to follow some recommendations that will help eliminate post-operative swelling on the face faster.
- Limit hot water consumption. You should not wash your face with hot water, and it is also not recommended to take a hot shower or bath with hot water. The best option would be a contrast shower, which will help get rid of the accumulation of fluids in the tissues. Regarding hot water, it should also be mentioned that you should also avoid going to the bathhouse or sauna. You should not spend a lot of time outdoors in sultry and hot weather, as prolonged exposure to the sun can lead to increased swelling.
- For the first 2-3 days after the operation, it is necessary to provide cold compresses to the face or to a specific area. As an alternative, you can use cold cabbage leaves. Cold compresses should be applied every 3-4 hours.
- Rest and peace. After the operation, care should be taken to ensure complete rest and complete rest for the patient. An important point is the recommendation to keep your head slightly elevated while sleeping. You should also avoid straining your face of various kinds, for example, sitting at the computer or watching TV for a long time, reading a book late into the night, or using frequent and active facial expressions. You should also give up training in a gym or fitness club, morning jogging and other physical activities for a while.
- Properly formulated diet. First of all, the patient should exclude foods that may increase swelling. You should not drink too much liquid or consume salty foods, especially before bed. It is recommended to completely exclude salt from the diet for a certain time. Also, the foods you eat should contain a minimum of sodium. You should not drink alcoholic beverages, which affect blood circulation and lead to increased swelling.
- After surgery, stress on the body , both physical and mental, should be avoided. Any stressful situation or physical fatigue will contribute to the further development of swelling.
- Necessary specialist help. If you still cannot get rid of postoperative swelling on your face on your own, then you should consult a doctor. It is possible that additional massages or special exercises will be required to reduce swelling. Your doctor may also prescribe diuretics to help you quickly get rid of fluids in your body. In some cases, a specialist prescribes hormonal injections, but you should know that they are not suitable for all patients. Therefore, you should only contact professionals and experienced doctors.
How to remove swelling from the face after surgery quickly and effectively
There are some methods that will quickly get rid of post-operative swelling on the face at home:
- It is necessary to wipe the face or a certain area of the face with ice cubes. Moreover, ice can be made in advance from tea or chamomile infusion.
- You can make a mask, for which you need to brew a couple of tablespoons of green tea leaves, infuse, strain, cool and wipe your face with tampons or a towel.
- Raw potatoes or cucumbers will quickly help get rid of post-operative swelling on the face.
It should be remembered that the rapid disappearance of postoperative swelling on the face depends mainly on the responsibility of the patient, as well as the individual characteristics of his body.