What is gum coagulation
Gum coagulation is the surgical excision of mucous tissue using a hot instrument.
This is plastic surgery of gum tissue performed using electric current. Despite the frightening description, the procedure is as painless and comfortable as possible for the patient. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. Unlike classical surgery, the patient does not lose a drop of blood during the procedure.
The method is used to remove various types of tumors and to treat diseases such as:
- periodontitis;
- periodontal disease;
- inflammation of gum pockets;
- fibroma;
- hemangioma;
- tissue hyperplasia, etc.
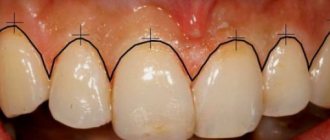
Periodontal diseases
Coagulation of the gingival papilla in dentistry - what is it?
In science, coagulation means the “coagulation” of particles under the influence of heat. An identical mechanism in medicine causes blood to clot in wounds and abrasions.
In surgery, such intervention is necessary for the most delicate operations and “sealing” bleeding in the vessels. To treat pathologies of the oral mucosa, doctors use an electrocoagulator or a laser beam as the most gentle method. Traditional surgery exposes the patient to infection, heavy bleeding and requires stitches.
It is important to be cured on time, since poor gum condition causes serious diseases and affects the immune system. How does the gum coagulation procedure take place?
The instrument is heated under the influence of an electric current, after which it is used to cut off the tissues with extreme precision and without pain, since the manipulation takes place under local anesthesia. High temperature conditions eliminate blood loss and accelerate healing.
The psychological comfort of the patient also affects the outcome of the operation. In this sense, the appearance of a “scalpel” helps - it does not resemble a traditional instrument for operations. These undeniable advantages of technology over classical surgery have made the method popular.
What is a diathermocoagulator
With the help of diathermocoagulators, bleeding from small vessels is stopped, and tissue dissection is also carried out. There are many options for devices of this type on the medical equipment market. For example, DKS-30 is more often used in dentistry, DKH-250 is intended for electrosurgeons, and DKU-60 is positioned by the manufacturer as a universal model.
The structure and functionality of models from different manufacturers may vary slightly, but they all have much in common. Any diathermocoagulator is actually the device itself with a power control function, electrodes and a set of different attachments (blades, loops, electric knives).
Diathermocoagulation devices can be stationary or portable. If surgery is to be performed on a large area of the body, then a special type of device is used - a spray coagulator. With its help, an electric arc is created above the working surface, under which, in fact, a cut is formed. Diathermocoagulators are electrosurgical and argon. The second equipment option, in addition to electricity, involves the use of argon. Thanks to the gas, a layer of plasma is created between the tip of the device and the tissue, which serves as a conductor and at the same time prevents the nozzle from sticking to the surface.
A diathermocoagulator can create both superficial and deep effects of high-frequency alternating current on tissue. This means that diathermocoagulation can be useful for the treatment of superficial wounds and skin lesions, as well as in the case of pathologies of internal tissues and organs. An example of the surface effect of a diathermocoagulator is the procedure for removing warts. When talking about the effect on internal organs, they most often mean cauterization of erosions on the cervix and genital warts, treatment of dysplasia and some other gynecological diseases.
Operating principle
The operating principle of the diathermocoagulator is based on the laws of physics. Or rather, the one that says that when exposed to high temperatures, organic proteins coagulate. The diathermocoagulator electrodes, thanks to electric current, heat up to a high temperature and upon contact with the body, cause coagulation - that is, the folding of proteins.
The electrosurgical effect of a diathermocoagulator is that the device produces a narrow stream of high-frequency current, which strongly heats biological tissue. When the current reaches certain levels, the tissue fluid at the point of contact is heated to such an extent that it turns into steam and ruptures the surface of the tissue. At such a high temperature, local protein folding begins - coagulation. This is the method used by surgeons to make that same bloodless incision in the tissue.
Under the influence of a diathermocoagulator, a kind of thrombus forms in the damaged vessel. After contact with high-frequency current, the inner and middle shells of the vessel fold and clog its lumen. Thus, you can quickly stop the flow of blood and relieve pain at the site of injury. It is this feature of the diathermocoagulator that makes it indispensable in surgery.
The use of the instrument requires high professionalism from the doctor performing the manipulation. The fact is that during the procedure it is extremely important to invest in a certain time frame and correctly determine the power of the electric current. If diathermocoagulation is carried out for too long or when the electric current is too high, there is a serious risk for the vascular system and internal organs. An incorrectly performed procedure can disrupt metabolic processes and cause many severe adverse reactions.
This is interesting: Tooth root fracture: is it possible to save a tooth, what methods of diagnosis and treatment are there?
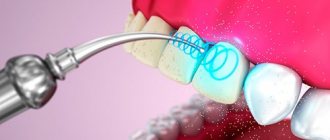
Features of laser gum treatment
The laser effect on the inflammatory process in the gums is highly effective and painless . Today, dentists use a variety of laser equipment, all of which have similar effects. But each type of light flux has its own purpose and performs specific functions.
The principle of operation is to emit a light flux. It comes in the form of electromagnetic waves with polarized and monochromatic qualities. Thanks to precise focusing of the beam, it is possible to act directly on the problem area.
Read also: How to eat after tooth extraction
Laser gum treatment
The therapeutic effect is achieved through tissue changes at the molecular level. When the laser beam exerts its influence, the liquid particles evaporate, as they actively absorb the waves from the device.
microexplosions occur on the treated surface . They contribute to the destruction of affected tissues and the destruction of pathogenic microflora. In this case, the therapeutic effect occurs directly on the changed tissues. Healthy ones remain untouched, because they are additionally processed by jet cooling of water.
Indications and contraindications
Gum coagulation is used to treat both benign and malignant gingival formations.
The operation is performed to eliminate the following pathological conditions:
- granulation neoplasms;
- overgrown mucosal tissue (gingival papillae);
- tumor formations (fibromas, hematomas, papillomas, etc.);
- corrosive cavities below the gum level;
- attachment of gums.
The operation is not performed if the patient currently has an unsatisfactory hygienic situation in the oral cavity. Once the dentist has provided effective treatment, the procedure can begin.
Absolute contraindications for performing the operation are:
- pathologies of the immune system, in which there is a high risk of infection during surgery;
- bleeding disorders;
- endocrine diseases to the degree of decompensation (in particular, diabetes mellitus);
- exacerbation of infectious diseases;
- decompensated cardiovascular pathologies.
If there are such contraindications, the operation is performed only under the supervision of a specialized physician and only if the expected harm from the progression of the disease exceeds the expected harm in the event of complications.
In addition, it is not advisable to perform gum coagulation if there is inflammation of the bone tissue.
Indications for gum resection
The indication for resection is insufficient effectiveness of drug therapy.
When medicine is placed into the canal of an unfilled tooth to resolve the cystic neoplasm, but to no avail.
Anti-inflammatory drugs for intramuscular administration are also prescribed in the complex.
- Patients who rarely visit the dentist and develop oral diseases;
- When the tooth is filled poorly or the filling has expired;
- People who are preparing for prosthetics;
- Cystic formations caused by poor-quality filling of dental canals and untreated pulpitis;
- In case of infectious infection of the tooth canal and the addition of a secondary infection;
- If there is a pin installed in the dental canal and the dental canal is not properly filled, gum resection is prescribed;
- The presence of a cystic formation under the crown;
- When the cyst is larger than one centimeter, resection is also performed.
Preparatory activities
No special preparation of the patient is required before the gum removal procedure.
It is recommended to eat before visiting the dentist, since immediately after the procedure you will not be able to eat for several hours. On the day of surgery, you should not drink alcohol, as it significantly impairs blood clotting.
Before carrying out the procedure, it is advisable for the dentist to show his medical record or extracts from specialized specialists - if the patient has any chronic diseases or characteristics of the body.
You should also inform the doctor whether the patient is allergic to local anesthetic drugs, since the operation is performed under local anesthesia.
If a dentist has questions about the nature of the neoplasm , he can refer the patient to various specialized specialists - oncologist, periodontist, infectious disease specialist or other specialist.
Immediately before coagulation, the oral cavity is sanitized, hygienic cleaning and (if necessary) removal of hard dental plaque.
If the condition of the patient’s oral cavity is unsatisfactory, there are inflammatory elements or signs of infection, then a course of treatment is carried out first.
How is the procedure performed?
The operation is performed only by an experienced dental surgeon. First, the doctor will sanitize the oral cavity and administer anesthesia (in the case of using a laser, it is often possible to confine oneself to local “freezing” in the form of gels and sprays, since the procedure causes virtually no pain to the patient). Next, the specialist works with an instrument designed for coagulation and performs the necessary manipulations.
Important! The patient should relax in the dentist's chair and not make sudden movements. Otherwise, the hand of even the most experienced specialist may tremble, and the instrument will damage healthy areas.
The duration of the operation directly depends on the degree of complexity of the actions performed, but on average coagulation takes no more than 20 minutes.
Methods
The advantage of the coagulation effect over the traditional mechanical effect (excision of the gums with a scalpel) is that under the influence of ultra-high temperatures, tissue cells are compressed, and bleeding does not occur in the area of exposure, which significantly reduces the healing time.
Coagulation of gums is carried out using various instruments:
- Electrocoagulator. Now there is a wide range of these devices on the market, and they are stationary, portable, having different modes, voltage and current.
The basic principle of operation of such devices is to expose tissue to high-frequency alternating current. - Laser. It affects the gums in a targeted and most gentle manner. The most effective and gentle method.
- Heated sharp instrument. Today it is practically not used, as it is a traumatic procedure and requires long recovery.
With the help of these devices, the pathologically changed area of tissue is cut off, and the cells at the site of damage are compressed, preventing the development of bleeding and eliminating infection. This way the tissue heals quickly.
Monopolar technology
A special return plate is placed on the patient’s body, which is responsible for closing the electrical circuit. A weak electrical impulse is passed through the patient's entire body and through the surgical instrument. With this procedure, you can get rid of even large neoplasms and tumors located in the deep layers of tissue. Due to its effectiveness, this method is used more often than others.
Bipolar technology
An electrical discharge is passed locally, only through the part of the body in which the tumor or inflammation is located. Therefore, the end plate is not used. This method is effective for the treatment of mild dental diseases.
The gum cauterization method is widely used in dental practice and shows good results in the treatment of periodontal diseases.
Before performing the operation, the doctor examines the patient’s oral cavity for injuries to the mucous tissues, since their presence can cause complications.
Bipolar gum coagulation technology
Upon completion of the operation, the patient is given a list of recommendations and a prescription for medications. For each patient, recommendations are made individually, depending on the disease and its severity.
General overview of the procedure
Gum coagulation in dentistry is a process during which diseased tissue is treated, cauterized, and also excised under ultra-high temperature. The procedure can be performed using different heating sources: heated instruments, electrocoagulators. Also, such an operation is often performed using a laser - it has the most gentle effect.
The description of the procedure sounds a little scary, but in fact this technique is completely safe for the patient’s health, as well as his psychological state. Do you agree that the absence of a scalpel (in the classical sense) and the need to carry out extensive intervention immediately puts you in a positive mood?
Manipulation techniques
For diathermocoagulation, special devices and devices are used. The manipulation itself can be carried out in the following ways.
Processing with a heated tool
This method is quite old and is practically not used in modern dentistry. A spatula, plugger or dental trowel was used as a cauterization tool.
This made it possible to cut off small damaged tissues localized on the gums. In addition, a heated instrument could stop bleeding from blood vessels or cauterize minor mechanical damage to the oral mucosa.
Cauterization using an electrocoagulator
These are special devices for carrying out these manipulations. Today they are widespread in all dental clinics. They are produced stationary, portable, which operate in various modes.
This is interesting: TRG image of teeth in orthodontics: what is it, how is it deciphered?
The operating principle of these devices is based on the use of alternating electric current, which provides heating to a special electrode. The doctor thus performs a gingivectomy or gingivotomy.
Using a laser
This technology is the most advanced and most gentle. The laser provides virtually painless removal of any tumors.
The big advantage of using this technique is that after treatment the wound does not bleed and becomes completely sterile. Thus, the laser beam provides significant prevention of the possibility of infection. You can learn how lasers are used in dentistry by watching the video in this article.
Application of laser in dentistry
After treatment with the coagulation method, the wound surface is quickly regenerated. To completely turn off sensitivity, local anesthesia is required. It can be carried out using injections or aerosol irrigation, as required by the instructions.
Basic methods of influence
Diathermocoagulation is indispensable in the treatment of cervical caries or when it affects the basal areas. Although the procedure is simple, the doctor must have certain professional skills to provide effective treatment.
Additional anesthesia allows the operation to be performed efficiently and without psychological trauma for patients. The price of diathermocoagulation is another indicator of the popularity of the technique. The cost is insignificant and additional costs are required for preparation and the postoperative period.
In addition, dentists actively use coagulation to remove tumors on the soft tissues of the oral cavity. After manipulation, as a rule, there are no complications or relapses that occur during surgical interventions by other methods.
Doctors mainly use 2 coagulation techniques:
- Monopolar technology . The peculiarity is that the electric current passes through the entire patient like a cutting instrument. This method is used most often, as it provides treatment even for deep-lying tumors or removal of large ones. To successfully carry out the procedure, a return plate is placed on the patient’s body, which allows the electrical circuit to be established.
- Bipolar technology. In this case, the electric current does not pass through the entire body, but only a certain area of the body. It closes over a short distance, providing treatment for only minor dental problems. An endplate is not required for the manipulation.
Gum cauterization is performed for various periodontal diseases. During surgery, a very important point is the absence of injury to adjacent tissues. This helps to avoid additional possible complications. After coagulation, the patient must follow the doctor's recommendations. They will be individual in each case.
Who should not undergo the procedure?
Indications for this procedure are:
- hypertrophic pulpitis;
- periodontitis (cauterization of the contents of the root canal is carried out, which ensures disinfection of the walls after removing the decay);
- removal of tumors on the oral mucosa (fibroma, papilloma, epulis, hemangioma);
- cauterization of the contents of periodontal pockets;
- removal of overgrown gum papillae with hypertrophic gingivitis;
- cauterization of some changed and enlarged vessels in the oral cavity.
Hypertrophy or neoplasm is the most common indication for coagulation.
However, this method of treatment is not always acceptable.
The main points regarding contraindications are the following conditions:
- in the case of treatment of baby teeth, especially at the stage of root resorption;
- damage to the cardiovascular system;
- obliteration of root canals;
- treatment of permanent teeth with unformed root tips;
- individual intolerance to the applied electric current.
Such a modern treatment method as coagulation is often used in dentistry for the following purposes:
- removal of formations on the mucous membrane: malignant and benign,
- removal of any granulation tissue,
- correction and plastic surgery of gums to give an aesthetic smile,
- treatment of periodontitis and periodontal disease (only in complex therapy): in particular, the procedure can be carried out to cauterize and treat inflamed gingival papillae that have grown during the course of the disease. And also for removing granulations and pathological tissues from periodontal pockets - at the end of the procedure, the periodontal pockets remain completely sterile, the tissues fit tightly to the tooth, which prevents plaque, bacteria and food particles from getting inside,
- cauterization of inflamed gingival papillae: pathology can occur not only against the background of periodontal tissue diseases, but also due to trauma to the mucous membrane, malocclusion, hormonal disorders in the body, incorrectly performed dental treatment, chipped fillings and the presence of uncomfortable prosthetic structures,
- removal of papillomas, fibroids: they may look harmless, but sometimes they grow greatly, causing inconvenience, and become dangerous to health.
Despite the fact that the described technique has a number of advantages (in comparison with traditional methods of surgical interventions), there are also some contraindications to the operation. Coagulation is not performed if the following problems have been diagnosed:
- intolerance to low-frequency electric currents: in this case, it is permissible to use only a laser,
- exacerbated infectious diseases,
- disorders of the cardiovascular system: there is a high probability of increased blood pressure,
- disruption of the hemostasis system: the risk of bleeding increases,
- chronic diseases: for example, diabetes.
Also, the use of “hot” instruments is unacceptable during the active change from primary to permanent occlusion in children, which occurs between the ages of 6-8 and 12 years.
The operation is performed only by an experienced dental surgeon. First, the doctor will sanitize the oral cavity and administer anesthesia (in the case of using a laser, it is often possible to confine oneself to local “freezing” in the form of gels and sprays, since the procedure causes virtually no pain to the patient). Next, the specialist works with an instrument designed for coagulation and performs the necessary manipulations.
The duration of the operation directly depends on the degree of complexity of the actions performed, but on average coagulation takes no more than 20 minutes.
Advantages and disadvantages
Of the two methods of electrical coagulation, biopolar is safer, but is not suitable for all cases. With its help, you can remove only small formations on the gums.
The monopolar method is more universal and is used most often; however, there is some risk of surgical complications, which is completely eliminated with biopolar treatment.
There is a danger if the device is of poor quality, or the surgeon makes mistakes in the surgical technique. Then heat treatment can cause burns, and in the most severe cases, electrical breakdowns.
Such operations should be carried out using good equipment and an experienced doctor, in which case they are completely safe. The laser coagulation method has appeared recently and is still under development. However, it is already recognized as the safest and most gentle. The disadvantages include the high price and low prevalence of laser coagulation.
Types of coagulation
The operation is performed using two devices: an electrocoagulator or a laser. Using a heated metal tool is an outdated but possible method. Laser therapy is more gentle compared to its predecessors.
Cauterization of gums in dental clinics is carried out using two methods:
- Monopolar. It is performed using an electrical device - a monopolar coagulator. Alternating current with high-frequency oscillations is supplied to the electrode, and through it into the tissue. It then passes through the body and returns to the end plate. In this case, coagulation occurs in a certain area. The procedure is safe and does not have a negative effect on the body.
- Bipolar. The tip of the electrocoagulator is bifurcated and does not have a closing plate. The current only affects the tissue sandwiched between the two ends that supply the electricity.
The bipolar technique is simpler and safer, but can only be used to remove small formations. Monopolar is suitable for all cases, but carries some risks. A burn may occur due to equipment malfunction or medical error. However, modern clinics are equipped with good equipment and experienced doctors, so you should not be afraid of the procedure.
Stages of the procedure
First of all, local anesthesia is done. It can be in the form of an injection or treatment of the gums with an anesthetic gel, depending on the complexity of the procedure.
Further, the doctor’s actions depend on the specifics of the disease:
- Tumor formations. The operation can be carried out using electrodes of three shapes - “loop”, spherical or “knife”.
If the disease affects only the gums, the growths are removed by coagulating them. In cases where part of the periosteum is inflamed, it is cut off in the usual surgical way, and coagulation is used to stop the bleeding.If the tumor is large, then a mucosal flap transplant is necessary.
- Pulpitis. A needle is inserted into the dried and prepared canal to necrotize the pulp. The current exposure time is several seconds. Then, the pulp is removed and further treatment of the tooth continues.
- Periodontitis. The root canal is coagulated with two needle insertions. The first is for 6-8 seconds, the second is for 3-4 seconds. Then, an eight-second warm-up is carried out, after which the canal is closed with a filling.
- Caries below the gum level. In this case, coagulation is used at the initial stage of treatment to open access to the affected area of the tooth.
- Granulation in periodontal pockets. The contents of the pocket are coagulated within 2-4 seconds. An electrode in the form of a needle with a blunt end is used.
How to perform gum cauterization
The operation is performed by a dental surgeon. The patient is anesthetized with local anesthetics. It is important to relax, as sudden movements will disturb the doctor.
Using an electrocoagulator or laser device, excess gingival tissue is excised and tumors are removed. The procedure time depends on the amount of work, but usually does not exceed a quarter of an hour.
To treat pulpitis or periodontitis, coagulation is carried out through the root canal. If the caries is located below the gum level, the tissue is coagulated to gain access to the affected area. In case of periodontal disease, coagulation of the contents of periodontal pockets is carried out.
Postoperative period
For some time, approximately 3-4 hours after the operation, you should not eat. In the future, it is recommended to use soft, non-hot foods. Each meal should end with rinsing the mouth.
This is interesting: Dental flux on the gum and cheek: treatment at home, effective remedies for gumboil, symptoms
It is better not to irritate the operated area with unnecessary manipulations or touches. On the first day, it is better to avoid brushing your teeth. Next, use a brush with soft bristles. Carry out care carefully. During the rehabilitation period you should stop smoking.
After the coagulation of the gums, a painful period of time follows. The patient will experience pain for two days, which will subside over time. Prescribed analgesics will help alleviate the condition.
The following will help relieve pain:
- rinsing with herbal decoctions: sage, chamomile, calendula;
- antiseptic mouth rinses;
- use of propolis.
Anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed to relieve the tumor. It is important to prevent infection from entering the oral tissues. In rare cases, antibiotics are prescribed.
Recovery takes from 2 to 10 weeks. It depends on the complexity of the pathology and the individuality of the human body. Tissues must regenerate. 5 days after the procedure, it is proposed to add the use of sea buckthorn oil to the hygienic care of the oral cavity. It will help speed up regeneration. To monitor the process of restoration and healing of soft tissues, you should visit a dental facility.
At the Cerekon , gum coagulation is performed using modern equipment by highly qualified specialists with sufficient clinical experience. The main thing is to follow the recommended medical rules in the postoperative period.
When is excision of part of the gum indicated?
When a gum pocket hangs over a third molar, a consultation with a dentist is always necessary. He will determine the condition of the hood and decide whether it requires excision. If appropriate measures are not taken in time, the entire molar will overlap, and inflammation will begin to spread to adjacent soft tissues. This, in turn, is fraught with the development of an abscess or phlegmon, the fight against which involves making special incisions on the affected gum.
Excision of the hood is done if:
- An unpleasant, persistent odor from the mouth that is difficult to overcome. It is caused by accumulated pus under the hood.
- Acute gingivitis. A person experiences severe pain, it prevents him from eating normally, and can also turn into a headache and shoot in the ears.
- Swelling of the gums and cheeks. As a result, it becomes difficult for the patient to open his mouth, since there is strong pressure on the masticatory muscle from the inflamed hood.
- Painful or difficult swallowing.
- General malaise, in which the patient may have a brief fever.
Inflammation of the gums above the wisdom tooth
It takes some time for the gums above the erupting wisdom tooth to become inflamed. At the beginning of the formation of a hood, there are no unpleasant sensations, and a person may not notice the presence of a problem. However, when food gets under the pocket, pathogenic bacteria begin to multiply quickly under suitable conditions.
Read also: Wound after tooth extraction
Unfortunately, saliva is not able to penetrate the gap between the wisdom tooth and the overhanging gum and perform its protective functions. This makes it impossible to wash away food residues and restore the acid-base balance, which contributes to the development of unfavorable flora.
Features of gum growth in a child
Other unpleasant symptoms may accompany the redness of the gums and the formation of a hood. At this point, it is important to consult a doctor promptly. If the child is small, he will constantly put his fingers in his mouth and can easily cause an infection or injure the gums, and this is fraught with inflammation and the formation of pus.
Care and possible complications
After the intervention, the dental surgeon will offer individual measures for recovery and write a prescription for the drugs necessary for this.
Food is consumed a few hours after the manipulation and only cold. Chew it with the undamaged side. Caring for your gums involves gently cleaning them with a soft toothbrush, or outside the home with dental floss or chewing gum.
Patients are concerned about how long the wound will take to heal and what to rinse the mouth with after gum coagulation. Soothing rinses with medicinal herbs, chewing propolis, and the use of medicinal pastes and gels will not interfere.
If inflammation or pain occurs in the first days, you should take anesthetics, as the discomfort can be very severe. Normally, unpleasant manifestations leave the patient two days after the operation.
Reference. It is extremely important not to smoke for the first time after the procedure.
The rate of periodontal healing after surgery depends on health conditions - usually this occurs within two to ten days. If the gums do not heal longer after coagulation, then you should seek advice from a doctor. Regular visits to the dentist will help avoid complications after gum coagulation.
Therapy for hypertrophic gingivitis
The disease is one of the most common in dentistry - it occurs with equal frequency in both adults and children. It is characterized by the proliferation of soft interdental tissues, which, if left untreated, can overlap the crowns of the teeth. The appearance of pathology is provoked not only by poor oral hygiene and hormonal imbalance in the body, but also by chewing hard pieces of food that injure the interdental spaces, and improper use of personal hygiene items (threads to remove plaque, brushes, etc.).
In complex therapy (taking anti-inflammatory drugs, physiotherapy, gingivectomy) to treat the disease, dentists recommend using a method such as coagulation.
Preparing for surgery
Before the procedure, professional oral hygiene is carried out: removing plaque, removing tartar. If there are concomitant diseases, the patient is referred for examination to specialized doctors. After eliminating contraindications, a treatment date is set.
Before visiting the doctor, you need to eat a hearty meal, since after dental procedures you cannot eat for several hours. It is recommended to quit smoking and alcoholic beverages the day before the procedure. Alcohol and nicotine have a bad effect on blood clotting.
Useful tips to help you recover after surgery
If you want the tissue healing process and rehabilitation period to go as quickly as possible, then be sure to follow these recommendations after surgery:
- refrain from eating in the first few hours,
- As soon as you can have a snack, follow the rules: exclude hot, cold, hard, spicy foods - dishes can be heated to a temperature no higher than 37 degrees. You need to adhere to the restrictions during the first few days,
- chew only on the side that was not coagulated,
- After each snack, rinse your mouth: for this you can use herbal decoctions with a mild bactericidal effect, antiseptic solutions, soda solution, special rinses, or at least regular drinking water.
Also, carefully perform oral hygiene, the main thing here is without fanaticism. Do not put strong pressure on the sensitive mucous membrane, so as not to injure it and cause the development of a repeated inflammatory process.
Sources:
- https://denta.guru/hirurgiya/chto-takoe-koagulyatsiya-desny.html
- https://FoodandHealth.ru/medodezhda-i-pribory/diatermokoagulyator/
- https://zubovv.ru/lechenie/desnyi/koagulyatsiya-byistroe-effektivnoe.html
- https://Denta.help/terapevticheskaya/desna/prizhiganie-desny-v-stomatologii-188
- https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/desnyi/kogda-opravdano-koagulyatsii.html
- https://cerecon.ru/uslugi/lechenie-desen/koaguljacija-desny/
- https://vashyzuby.ru/hirurgija/koagulyatsiya-desny.html
- https://mnogozubov.ru/chto-takoe-koagulyaciya-desny/
- https://www.familysmiledent.ru/uslugi/khirurgiya/prizhiganie-desny/