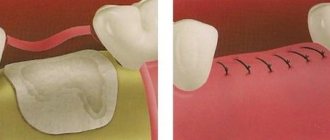
Gingivectomy is a surgical procedure to trim the gums to help restore a beautiful, healthy smile in a variety of conditions.
With age, periodontal tissue changes in structure. Gingivectomy surgery is used to correct congenital gum defects, as well as pathologies resulting from acquired oral diseases.
What is gingivectomy in dentistry?
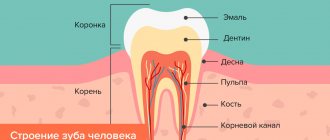
The complex of tissues surrounding the tooth is called periodontium. It performs protective functions, the violation of which leads to pathologies. Initially, the process is characterized by increased bleeding of the gums when brushing teeth, and the appearance of discomfort while eating. Next, periodontal pathological pockets are formed, food debris accumulates in them and the inflammatory process begins. Poor oral hygiene, tartar, and pathological periodontal pockets will eventually lead the patient to gingivectomy.
Gingivectomy is an operation in which excess gum is removed. A dental surgeon or periodontist excises overgrown tissue to achieve a beautiful smile line.
The gum can be trimmed locally or in the area of several teeth in the upper and lower jaws.
The mini-operation lasts about an hour, taking into account the effect of anesthesia.
The cost depends on the extent of the pathological process and the choice of gingivectomy: the use of a laser or the use of a surgical treatment method.
Operation stages:
- Anesthesia.
- Removing excess tissue.
- Formation of the correct gum contour.
- Treatment of the wound.
- Applying a sterile dental dressing.
Gingivotomy: contraindications
There are general contraindications that are typical for all types of surgical interventions, and specific ones that are relevant only for surgical interventions in the oral cavity.
General: pathologies of the cardiovascular system, cancer, endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus), weakened immunity, infectious lesions, cerebral and psycho-emotional disorders.
Private: bite pathologies, bone destruction (osteoporosis of the alveolar process), severe tooth mobility, oral infections and poor hygiene.
Indications and contraindications for gingivectomy and gum trimming
If therapeutic treatment of periodontal tissue does not help, gingivectomy is used. Trimming the gum above the upper front teeth to restore the smile line requires a large amount of tissue excision. Weakened gums hanging over the crowns of the teeth, as well as gum pockets, are removed. Periodontal pathologies interfere with normal oral hygiene and comfortable eating.
Main indications for gingivectomy:
- hypertrophic gingivitis;
- periodontitis;
- epulis;
- gum fibromatosis;
- ulcerative necrotizing gingivitis.
Gingivectomy can be used to provide access to the crown of a tooth when there is excessive gum growth, for example, to treat pulpitis and install a filling.
Contraindications:
- narrow zone of gum attachment - after surgery there should be at least 2 mm of free edge.
- cords, frenulums on the tissues in the operated area.
- bone tissue is damaged.
- the presence of acute inflammation (for example, acute periodontitis).
Gingivotomy or gingivectomy
During gingivotomy, the tissue incision is performed vertically in the area of projection of the tooth root in the direction from the free edge of the gum (with or without indentation) to the fold of transition to the moving tissues. The technique is relevant for the treatment of pathologically shaped periodontal pockets (deep and narrow), as well as for local periodontal and bone abscesses.
Gingivectomy is performed primarily through a horizontal incision; it is intended for the surgical treatment of moderate periodontitis (pocket depth from 4 mm) affecting a large gum area. This operation allows you to remove non-viable excess mucous membranes with tissue suturing. Contraindicated for bone abscesses.
Preparation period
Preparation for gingivectomy includes 2 stages:
- Professional teeth cleaning is carried out: soft and hard plaque is removed using ultrasonic or manual methods. Professional pastes, special brushes, and other dental instruments are used.
- Local anesthesia. An anesthetic that will not cause allergies is selected for each patient. If a patient who comes for help does not know which painkiller is suitable for him, allergy tests and an injection in the forearm are done. Patients prone to allergies are sent for tests at an allergy center.
After these stages, the surgical process of gingivectomy (excision of diseased tissue) is performed.
Types of surgery, stages of implementation
Gingivectomy surgery improves oral hygiene. There are 3 types of it. It is important to consult a doctor in time when the inflammation has just begun. The assistance provided will be more effective and less traumatic.
Types of gingivectomy:
- radical method;
- gentle;
- simple.
Gingivectomy technique:
- Anesthesia.
- Measuring pathological pockets.
- Cutting the gums with a laser or scalpel.
- Cleaning deposits.
- Tissue excision.
- Antiseptic treatment of the operated area.
- If necessary, stop bleeding.
- Gum bandage.
The choice of method depends on the body’s immunity, the condition of the affected tissues, the depth of periodontal pockets, and the width of the gums.
Simple gingivectomy
Stepping back from the gum edge to 1 mm, wavy, horizontal incisions are made. Excess tissue in the oral cavity or vestibule of the mouth is removed vertically. Curettage of the wound and bone pockets is carried out, the surfaces are smoothed, and deposits are removed. Antiseptic treatment with a bandage for 48 hours completes the operation.
Krekshina’s technique is also used: an incision is made parallel to the gingival margin at a distance of 1.5-2 mm, excess tissue is removed and curettage is performed in the area of 2-3 teeth. Stop the bleeding, carry out antiseptic treatment, and apply a bandage.
Radical gingivectomy
Surgical intervention with intensive excision of the gums and capture of bone tissue. Used in rare cases. An indent of 2 mm is made from the edge. The cuts in this case are deeper. Together with the marginal part, hard deposits, granulations, and part of the alveoli are cleaned. Then the edges are aligned, the surgical area is treated with an antiseptic, and hemostatic agents are used. A bandage is applied.
Radical gingivectomy is characterized by a long wound healing process.
Gentle gingivectomy
In this type of operation, 2–3 mm of gum is excised. The method is similar to simple gingivectomy. The difference is that a certain area of the pathological pocket is removed, and not the entire wall. Gentle pruning is considered the least traumatic of all. After the procedure, an aesthetic result is immediately visible.
Indications
Direct indications for surgical excision of necrotic tissues of the periodontal pocket are irreversible degrees of periodontitis (moderate and severe), with deep gum and bone pockets, persistent release of purulent masses, as well as the condition of periodontal abscess.
With periodontal disease, degenerative processes develop in the gum tissue and alveolar processes of the jaw bone. If the disease becomes advanced, it can cause loosening and subsequent tooth loss.
Gingivotomy for periodontal disease performs the following tasks:
- allows you to remove dead tissue and pathological granulations from the roots of teeth;
- keeps the alveolar process intact , which prevents smoothing of the jaw relief;
- prevents the deepening of gum pockets.
Gingivotomy is performed mainly in the presence of poorly visible periodontal pockets , when it is impossible to choose a less traumatic method of treatment and the disease has already become advanced.
The purpose of determining the periodontal index and the methods used.
Come here if you are interested in using the Vector device in the treatment of periodontitis.
At this address https://www.vash-dentist.ru/lechenie/zubyi/na-desne-poyavilas-belaya-shishka-foto.html read what danger the appearance of a white bump on a child’s gum poses.
Modern techniques of gingivectomy
Modern treatment of periodontal tissue using laser promotes rapid wound healing. During excision, a minimal amount of tissue is removed, and fewer complications arise after surgery. Gingivectomy occurs without contact, with minimal blood loss. The laser stays at a distance. The cut edges of the gums remain sterile throughout the entire procedure, thanks to the neutralization of oral microflora by the laser.
This operation is less painful. The laser allows you to carry out, if necessary, one of the methods: gentle, radical, simple. Laser gingivectomy is more favorable than surgery using surgical instruments.
Laser trimming of the upper gum frenulum also has advantages:
- no swelling;
- aesthetics;
- painlessness;
- does not require drug treatment with antibiotics.
Benefits of laser gingivectomy
The advent of lasers in dentistry has greatly facilitated the process of gingivectomy and rehabilitation. Wound healing occurs in a short time, minimal tissue areas are excised. Advantages of using a laser:
- less traumatic method;
- infection is excluded from the edges of the wound;
- precise cutting line;
- minimum blood;
- short rehabilitation period;
- does not cause complications.
The need for gingivectomy for periodontitis
Poor oral hygiene can lead to gum disease. If accumulations of food residues are not properly cleaned, they become colonized by pathogenic microflora. During their life, bacteria release harmful substances that negatively affect the condition of soft tissues, leading to inflammation and bleeding.
During the process of gingivectomy, the surface of the root and the inner wall of the periodontal pocket are cleansed from accumulated plaque and dental deposits. If in the early stages of periodontitis it is possible to eliminate the pathogenic contents of the pockets without the use of incisions, then in advanced situations it is impossible to do without radical treatment. Gingivectomy is also performed in cases where traditional therapy does not provide relief from chronic gum inflammation.
If the depth of the pathological pocket exceeds 5 mm in depth, then even after high-quality cleansing of stones and medicinal treatment, it will take a long time for recovery to occur. But in many situations, periodontal pockets cannot be eliminated on their own, which is why surgical intervention is required.
Features of rehabilitation
The speed of wound healing depends on the patient’s immune response and the method of gingivectomy. When using a laser, the recovery period takes less time. Rules to follow after surgery:
- timely brushing of teeth with special toothpaste;
- using rinses to clean plaque;
- soft bristles brush;
- light chewing loads;
- It is advisable to give up bad habits (smoking, alcohol);
- Avoid eating solid foods: nuts, crackers, apples, chips.
You should follow the dentist's recommendations, adhere to a gentle diet, and pay attention to hygiene. You should not eat spicy, salty or sour foods. Extremely hot or cold food can also be harmful.
By following these rules, you will be able to avoid complications. A few days after the gums are trimmed, the periodontal tissue begins to heal. You can return to your normal lifestyle and diet.
Complications and consequences
Most often, complications occur when medical recommendations are not followed. If a person suffered from chronic inflammatory processes, after surgery they may worsen, developing
, periodontal disease. When the wound rots, there is a risk of infection, which will slow down the rehabilitation process.
Periodontitis
Gingivectomy leads to a decrease in local immunity in the oral cavity. In the worst case, poor oral hygiene leads to the introduction of unfavorable microflora into the bloodstream, and serious inflammatory reactions (sepsis, etc.) can occur.
To avoid allergies to painkillers, when taking your medical history, you should tell your doctor about allergens, if any. And also report chronic diseases. If necessary, the doctor prescribes the necessary tests and additional examination.
Only 5% of patients experience complications after gum trimming. In general, the healing period is easy and quick if you conscientiously follow what the dentist recommends. Some patients take their health carelessly, which should not be done.
Contraindications
All contraindications can be divided into absolute, in which radical intervention is not permissible, and relative, when the operation can be performed after eliminating certain interfering factors. There are also local and general contraindications.
Gingivectomy is not performed in the following cases:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system in the acute period (less than three months after myocardial infarction, recent surgery to replace heart valves, congenital heart defects),
- weak immune system,
- diagnosed cirrhosis of the liver and other diseases that significantly weaken the body,
- bacterial endocarditis in the subacute stage,
- diseases of the blood clotting system.
Local contraindications for performing radical intervention on the soft tissues of the gums include:
- an inflammatory process that has already affected the bone structures surrounding the causative tooth (the operation is not performed due to the possible risk of tooth loss),
- if there is a frenulum or mucous cord at the site of the intended incision,
- the gum attachment area is too narrow, which will make it impossible to move the mucous flap and close the resulting tissue defect,
- the presence of deep intraosseous pockets.