Why don't we treat children's teeth with retention?
There is a solution.
What are the advantages of sleep treatment?
Is it safe?
Why you should trust us
Dental treatment with retention is gradually becoming a thing of the past. And we are very happy about this. Why?
- Treatment against the child’s will negatively affects his psyche, increases anxiety and fear of the next appointment.
- Treating a restless baby is much more difficult - there is a risk of injury with instruments.
- The main thing is that holding a child during treatment is equivalent to physical violence. In this case, the blame falls on both the doctor and the parent (Article 156 of the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation “Cruelty to children”).
What is included in the concept of “physical violence”? These are any physical acts of violence against a child under 18 years of age, including punishment options (forced retention in a dental chair, etc.).
For this reason, Stompraktika doctors do not recommend treatment with retention.
Teeth have been whitened before
Quite unusual is the fact that the ancient Egyptians monitored the whiteness of their teeth. This was especially important for those residents of Egypt who held a high position in society. The Canadian Academy of Dental Hygiene says these people used a special paste made from ground pumice and white vinegar. This paste was applied to the teeth using a special stick.
Around the same time, the inhabitants of Ancient Rome used human urine for bleaching. This product worked due to the fact that it contained a high amount of ammonia. Agree, what else could be worse?!
In the 17th century, people became more advanced in teeth whitening. A metal sheet was placed on the surface of the latter and treated with nitric acid. It was only in the 19th century that it was discovered that hydrogen peroxide could do the same with teeth, without pain or discomfort.
It’s a long time before the ceremony, but a new date has already been announced: the Oscars have been postponed to April
Decision or tradition: William and Kate are considering whether to send their son to boarding school
The new Suzuki Across is a plug-in hybrid of the Toyota RAV4 with a different front end
There is a solution!
You can have your teeth treated comfortably, without unnecessary anxiety and stress. And now this can be done “in your sleep.” What does it mean? Your baby takes a few breaths of the drug and falls asleep. And then our tooth fairies get down to business. A child falls asleep with bad teeth and wakes up with healthy ones.
Anesthesia (medicated sleep) in dentistry has long been used throughout the world, especially for dental treatment in children and even adults who previously suffered psychological trauma from forced dental treatment in childhood. Even the Russian Ministry of Health recommends it.
Order of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation No. 456n dated August 19. 2014, paragraph 19: “Treatment of multiple complications of caries in children under 3 years of age, as well as other dental diseases for medical reasons in children, regardless of age, is carried out under general anesthesia,” that is, under anesthesia.
Moreover, the Russian Ministry of Health has identified indications for treatment “in sleep”:
– large volume of treatment; – neurological diseases; – increased gag reflex; – psychological unpreparedness of the child for treatment; – an insurmountable fear of the dentist.
Dental implants
According to scientific research, the first dental implants appeared in Ancient Egypt in 2500 BC. They were made primarily to stabilize other teeth. Gold wire was used to make them. After another few thousand years, replaceable prostheses began to be created using gold wire and bovine bones.
The widow of Vladimir Etush was his most devoted fan. How does she look
What awaits us: doctors spoke about alarming symptoms during vaccination against COVID-19
I no longer use store-bought conditioner: my homemade product makes my clothes soft
The Phoenicians used ivory to make implants. And the Mayan tribe used shells for these purposes.
At the same time, excavations by scientists have proven that implants were used not only for their intended purpose, but also as a decorative element. Some archaeologists believe that in ancient times dentistry was used not only to treat teeth, but also to send the deceased to the afterlife with a full set of teeth, because in the next world he needed to chew grapes.
Is it safe?
Yes. Dental anesthesia is different from that performed in hospitals, which has negative associations. For treatment we use the certified drug “Sevoran”. Doctors from all over the world trust him because he:
- non-toxic;
- does not accumulate in the body;
- does not cause addiction or allergic reactions;
- allows the child to fall asleep quickly and wake up quickly;
- allowed for patients suffering from epilepsy, cerebral palsy, heart disease, etc.
The anesthesiologist selects an individual anesthesia regimen and monitors the child’s condition during the procedure. Awakening occurs almost immediately after the drug is stopped. There are some restrictions before and after the procedure. During the consultation, we issue special instructions that will help you prepare for treatment “in your sleep.”
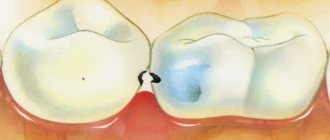
Care after removal of an impacted tooth
After surgery:
- in the first 15-20 minutes. after removal, you need to firmly press the gauze swab prescribed by the doctor, this will stop the bleeding;
- make sure that the blood from the wound does not flow too intensely, otherwise consult a doctor;
- You should abstain from food for a long time (at least 4 hours). After you start eating, and until the wound heals completely, you should not eat hot or soft food;
- if severe swelling of the mucous membrane appears, you can apply a cold compress to the cheek (for a short time);
- to avoid the occurrence of an inflammatory process, it is impossible to heat the hole from the extracted tooth;
- the protective blood clot formed in the hole cannot be removed, it prevents infection from entering it;
- on the second day after removal, you can apply a cotton swab soaked in retinol acetate (vitamin A) or rinse your mouth with a decoction of sage, chamomile, calendula, weak solutions of furatsilin, potassium permanganate or other antiseptic drugs;
- severe pain can be relieved with painkillers.
Complete healing of the socket tissue occurs in 3-5 weeks. It is important to monitor the healing process and notice any dental problems that arise. In case of suppuration of the surgical suture, you must consult your doctor.
Why you should trust us
- Conducted more than 10,000 successful operations.
- We have the best doctor of the year in the specialty “Anesthesiology and Reanimatology” in the Chelyabinsk region in 2020 - Nikolai Evgenievich Pankov.
- Modern operating and monitoring equipment. During the entire procedure, the anesthesiologist carefully monitors your baby's condition.
- We use the modern certified drug “Sevoran”, the safety of which is confirmed by international experience.
- We do not use narcotic drugs.
- The clinic has a temporary ward for recovery after the procedure.
To dispel all doubts, you can sign up for an anesthesia consultation and personally ask all your questions to our doctors.
Test with answers on the topic “Periodontitis of primary teeth”
An 8-year-old patient was treated with arsenic paste on a 5.5 tooth due to chronic simple pulpitis. The patient did not show up at the appointed time. Currently, there is aching pain, a feeling of an “overgrown” tooth. Formulate a diagnosis.
1. A mother and her 8-year-old child came to the clinic with complaints of pain in the lower jaw area on the right. According to the mother, the tooth was previously treated at the clinic. General condition is satisfactory, body temperature is 37 °C. Locally: a deep carious cavity is identified on the chewing surface of tooth 85, the bottom of the cavity is filled with softened dentin, the gum mucosa is hyperemic and swollen. Palpation along the transitional fold in the area of tooth 85 is slightly painful. On the orthopantomogram: rarefaction of bone tissue between the bifurcation area of the roots of tooth 85 and the follicle of tooth 45. Formulate a diagnosis.
1) Acute periodontitis of tooth 85; 2) Chronic fibrous periodontitis of tooth 85; 3) Chronic granulating periodontitis of tooth 85.+
2. The patient is 6 years old. Complaints of constant aching pain, intensifying when biting on tooth 7.5, “swelling” of the gums, increased body temperature to 37.6 °C. According to the mother, an “abscess” sometimes appeared on the gum, which disappeared without treatment. They didn't see a doctor. The tooth hurt 2 days ago, the pain is getting worse. Objectively: the face is symmetrical, the submandibular lymph nodes on the left are enlarged, painful on palpation, on the distal surface of tooth 7.5 there is a deep carious cavity filled with softened pigmented dentin. Suggest additional research methods.
1) Vital staining; 2) X-ray; + 3) Inspection, probing, percussion, palpation.
3. In a 10-year-old patient, during a routine examination, a fistulous tract with purulent discharge was found on the gum mucosa in the projection of root bifurcation 7.5. He makes no complaints. Tooth 7.5 was previously treated. Formulate a diagnosis.
1) Chronic fibrous periodontitis of 7.5 teeth; 2) Acute periodontitis of 7.5 teeth; 3) Chronic granulating periodontitis 7.5 teeth.+
4. In a 9-year-old patient, during a routine examination, a fistulous tract with purulent discharge was discovered on the gum mucosa in the projection of root bifurcation 6.5. He makes no complaints. Tooth 6.5 was previously treated. Suggest additional research methods.
1) Vital staining; 2) Inspection, probing, percussion, palpation; 3) X-ray.+
5. The patient is 4 years old. Two months ago, a fall caused a fracture of the crowns of two central incisors of the upper jaw. The teeth were restored in the clinic; within 3 weeks after the restoration of the teeth, the child complained of aching pain in teeth 5.1, 6.1, and a week ago the parents noted the appearance of a fistula on the gum near the central incisor. On the orthopantomogram: a focus of bone tissue destruction in the area of the apex of the roots of the 5.1 and 6.1 teeth with unclear contours. Formulate a diagnosis.
1) Chronic fibrous periodontitis of 5.1, 6.1 teeth; 2) Chronic granulating periodontitis of 5.1, 6.1 teeth; + 3) Acute periodontitis of 5.1, 6.1 teeth.
6. Parents with a 4-year-old child came to the clinic with complaints of destruction of the central incisors. Objectively: teeth 5.1, 6.1 are discolored, severely damaged, percussion is painless, probing of the carious cavity and tooth cavity is painless, there is mobility of the 2nd degree, the transitional fold is slightly hyperemic, there is a fistulous tract in the projection of the apexes of the roots of teeth 5.1, 6.1. A diagnosis of “periapical abscess with fistula of 5.1,6.1 teeth” was made. Record the diagnosis according to the International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision.
1) K04.4; 2) K04.5; 3) K04.6.+
7. The patient is 3 years old. According to the mother, the child complains of acute pain in tooth 5.5, which intensifies when touching the tooth, body temperature is 37.8 °C. From the medical history: 12 days ago, a devitalizing paste was applied to tooth 5.5 for chronic fibrous pulpitis. They did not show up for the appointment at the time prescribed by the doctor. In the evening pain appeared, the intensity of the pain increased, body temperature increased to 38 °C. Status lokalis: there is a temporary bandage on the occlusal surface of tooth 5.5, percussion of the tooth is painful. The gums in the area of tooth 5.5 are hyperemic. The submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged and painful on palpation. Formulate a diagnosis.
1) Acute apical periodontitis of 5.5 teeth; 2) Chronic fibrous pulpitis of 5.5 teeth; 3) Toxic periodontitis 5.5 teeth.+
8. The patient is 2 years old. Mom noticed a “sore” on the gum in the area of tooth 6.2. According to the mother, the child did not complain of pain. Status lokalis: on the gum in the area of the projection of the root of tooth 6.2 there is a fistula, on the medial surface of tooth 6.2 there is a carious cavity filled with pigmented soft dentin, the connection with the tooth cavity is not determined. Percussion of the tooth is painless. After removing infected dentin, probing the bottom of the carious cavity is sharply painful at one point. Electroodontodiagnosis 110 µA. On the orthopantomogram: a focus of bone tissue destruction in the area of the apex of the root of the 6.2 tooth with unclear contours. Formulate a diagnosis.
1) Chronic granulomatous periodontitis of 6.2 teeth; 2) Chronic granulating periodontitis 6.2 teeth; + 3) Acute apical periodontitis 6.2 teeth.
9. An 8-year-old patient was treated with arsenic paste on the 5.5th tooth due to chronic simple pulpitis. The patient did not show up at the appointed time. Currently, there is aching pain, a feeling of an “overgrown” tooth. Formulate a diagnosis.
1) Acute apical periodontitis of 5.5 teeth; 2) Chronic fibrous pulpitis of 5.5 teeth; + 3) Toxic periodontitis of 5.5 teeth.
10. A 4-year-old patient is seeing a dentist about pain in the 54th tooth and elevated body temperature (38 °C). On examination, the patient is lethargic and constantly cries. There is swelling of the cheek on the left, the mucous membrane in the area of the 54th tooth is swollen and hyperemic. The tooth is mobile, percussion is sharply painful. When examining the carious cavity located on the distal surface of the 54th tooth, the tooth cavity is not opened, probing the bottom of the carious cavity is painless. Suggest additional research methods.
1) Vital staining; 2) Inspection, probing, percussion, palpation; 3) X-ray.+
If you want to thank the author or say thank you, you can simply send a DONAT for the development of the project (for PC on the right, for mobile at the bottom of the site). This way we will see your support and feedback and will be motivated to do even more! Thank you.
Teeth of the dead
In the 19th century, sugar was introduced into the European diet. Since dentistry at that time was still considered an amateur activity, caries became widespread.
On June 18, 1815, the French army was completely killed. By then, about 51,000 people had died. Some enterprising people took to the battlefield to take back something from the fallen soldiers. According to the British Library, these were the teeth of the dead. These teeth were sold to dentists to be used to make dentures.
The same thing was observed during the American Civil War, as well as during the Crimean War. The teeth had to be of excellent quality.
Swedish scientists believe that the body develops immunity to Covid-19
The opening ceremony will make even the home Olympics official
An unknown portrait of Picasso will be put up for auction. His passion and love
However, this story has some negative sides. The fact is that not everyone wanted to install the teeth of the dead as prosthetics. Therefore, by the beginning of the 20th century, the use of such prostheses was no longer so widespread.
Medieval Methods
400 years ago, the most accessible and harmless way to eliminate toothache was proposed. The scientist Cardanus recommended his patients to be treated with moon rays. This required sitting for several hours, mouth open, waiting for the light falling from the Moon to heal.
In the first century, people, on the advice of the famous scientist Pliny, were treated with oil mixed with crow or sparrow droppings. The prepared ointment was placed in the ear. If this method did not bring relief, the person had to go to see a doctor.
Often, when providing assistance, doctors began their treatment not from the sore spot, but from a completely different part of the body. For example, doctors gave an already exhausted patient a laxative or performed an enema.
Thus, the Arab surgeon Abulkazi, who lived in the 11th century, taught other doctors unusual methods. To begin with, the patient was given a laxative and not allowed to eat.
The fasting person needed to take frequent baths and exercise. If the disease did not go away, they burned the tooth with a hot iron so that the fire reached the root.
To the forest oak
Not everyone had the opportunity to pay healers, so turning to the pagan traditions of their ancestors and the healing power of nature was considered an effective method. There were several ways to cure a bad tooth - and each time with the help of oak.
In the first case, it was necessary to find an old tree in the forest, but certainly near the source. Soak the bark in its water and wear it around your neck in an amulet.
The second method is more radical. For acute toothache, it was recommended... to gnaw and chew the bark. Despite the fact that the principles of treatment seem, to put it mildly, strange, there is a rational grain in them.
Oak bark contains substances that have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. It is not for nothing that healers recommended rinsing the mouth with oak decoction for bleeding gums, bad breath and colds.