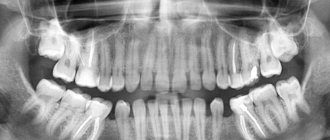
X-ray of baby teeth is a special study during which you can evaluate the condition of soft tissues, as well as diagnose inflammatory lesions of the oral cavity. This procedure is carried out quite often, as in children it allows you to quickly identify the exact location of caries. In addition, x-rays are prescribed for pulpitis and periodontitis and help determine the degree of tissue damage. With the help of this event it is also possible to diagnose the following diseases:
- Caries and carious interdental stains.
- Abscess and root changes.
- Loss of dental mass and anomalies in the structure of the dentition.
X-ray examination of primary teeth in children allows us to determine the location of the root primordia. Using this procedure, the treating specialist can easily assess the condition of the jaw and also determine the possible timing of tooth loss. X-rays have a number of features. It must be taken into account that during such a procedure the child is exposed to a small radioactive effect. To minimize it, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Children who have not received permanent teeth undergo bitewing and periopical x-rays once every 2 years.
- Adolescents undergo the same studies no more than once every 1.5 years.
- For adults over 18 years of age, x-rays can be taken once a year.
If there are recommendations from the orthodontist, photographs may be taken more often. In addition, children after restoration or with high blood sugar levels should have an x-ray at least once a year. The fact is that their teeth are prone to faster destruction.
In children, x-rays of the oral cavity (dental) are performed much more often than in adults.
The difference between baby teeth and molars
A child’s milk teeth differ from permanent teeth in their structure, shape and color. We strongly recommend that you look at numerous photos in which you can easily tell the difference. In addition, children's teeth have a thin layer of enamel, a small crown and dentin. In the photographs you can easily notice that such teeth have widely spaced roots that are located at an angle. This feature is explained by the need for the formation of permanent teeth.
An X-ray of a child's jaw with baby teeth will help determine how much the new molars have formed. If you pull out children's teeth before the molars are formed, you are likely to encounter serious deficiencies. This usually causes a cosmetic defect in the form of a diastema, or a large gap between the teeth. In addition, it is very important to monitor the condition of baby teeth. If they are not treated promptly for caries and other diseases, there is a high risk of developing serious problems in the future.
How safe is x-ray?
If all examination standards are followed and radiation safety parameters are observed, x-rays of children's teeth are an absolutely safe procedure. If X-rays are carried out too often or if the standards are not followed, the risk of a decrease in immune abilities increases. It should be noted that the influence of an X-ray machine alone cannot lead to radiation sickness. It has also not yet been proven that such procedures can affect the development of cancerous tumors.
To increase the safety of such exposure, they resort to a targeted study of the oral cavity. In this case, the radiation used becomes minimal. The study of children is carried out on devices equipped with a radiovisiograph. This device is equipped with a beam tube and a sensor that is placed in the patient's mouth. In this case, the duration of exposure becomes minimal, any changes in the body are instantly recorded on the monitor screen. In addition, the child is put on a special apron that protects the body from consuming excessive amounts of radiation.
Treatment of caries and its complications is extremely rarely carried out without x-raying the child’s teeth.
Types of X-rays for children
A targeted radiograph evaluates a specific area of the gum or other part of the oral cavity. With a panoramic view, the entire dentition becomes visible. Typically, during a targeted examination, the beam tube is installed near the soft tissues, and 2-3 nearby teeth are clearly visible in the image. Only your dentist will determine which study will be most optimal in a particular case.
In addition, 3D modeling will help assess the condition of the oral cavity. With the help of such an examination, you can easily determine the location of damaged fillings, roots or canals. Typically, babies are sent for this procedure before implantation surgery.
How is computed tomography useful in dentistry?
In dentistry, a computed tomography procedure is often performed, which allows one to evaluate the rudiment and perihilar cyst in the smallest detail. Modern experts strongly recommend conducting such a study using a radiovisiograph. It helps to study the following structures of the oral cavity:
- Separate groups of teeth.
- Lower and upper jaw.
- Paranasal sinuses.
- Soft tissues of the mouth.
Using computed tomography, it is possible to assess the condition of teeth in several projections at once. Thanks to three-dimensional models, a specialist can easily build the required sections. If necessary, the results of such a study can be recorded on disks or flash cards. This is especially convenient in cases where it is necessary to consult several specialists at once to determine treatment tactics. Without this type of X-ray examination, it is impossible to imagine the procedure of prosthetics, dental orthodontics or implantology.
X-rays can be used to photograph one tooth or a specific part of the jaw.
A little about the need for research
How necessary is it to take an x-ray and is it possible to do without it? Most dental pathologies cannot be seen during a simple examination, since only the crowns of the teeth and mucous membranes are visible in the oral cavity. Assessing the condition of the roots, periodontium, periodontium, alveolar process and body of the jaw without the help of x-rays can only be done surgically, which is extremely impractical - few people will consent to such an intervention.
If there is a need to frequently take x-rays, then it is advisable to use a radiovisiograph - in this case, the load level is minimal with a high level of information content.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Making a stamped crown video
Much greater harm will be caused by ignoring unpleasant symptoms or treating “blindly”. For example, cysts located at the roots of teeth grow for a very long time without any signs. Root canal treatment of a tooth whose roots are involved in the pathological process will not bring success - in the future it will be necessary to re-treat the tooth or remove it altogether.
Indications and contraindications
To have an x-ray of baby teeth, the child must have strong indications, since this study has a number of contraindications. Typically, such an examination is prescribed in the following cases:
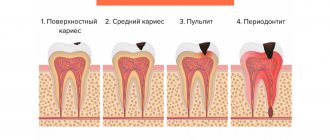
- To determine the extent of caries damage.
- To identify periodontitis and pulpitis.
- To assess the condition of the primordia of permanent teeth.
- When planning endodontic treatment.
- To diagnose and determine a treatment plan for pathologies of occlusion or teething.
- To determine the reasons for the delay in the appearance of permanent teeth.
It is strictly forbidden to perform x-rays on children in the following cases:
- If there is bleeding.
- If you feel unwell.
- In the presence of serious pathologies of the thyroid gland.
X-ray during pregnancy
Dentists should not prescribe diagnostic tests to women in the first trimester of pregnancy. After this period is over, dental x-rays are taken only in urgent cases, when it is impossible to carry out treatment without it.
To reduce radiation exposure, specialists need to use a special film (E-class). It is recommended to use a digital method that will not cause any harm to the woman and her fetus.
It is also possible to take dental x-rays during breastfeeding. Since the radiation dose is small, breast milk does not accumulate any radiation, and accordingly the baby’s body will not be harmed.
Dental X-ray is a procedure that is not dangerous to the human body, since the radiation used has a low dose. Only women during pregnancy and young children should undergo such examination with caution.
In the first trimester, such diagnostics are contraindicated.
How is research conducted?
Usually, an X-ray of the tooth can be obtained immediately after the examination. However, the methodology for carrying them out may differ significantly from each other. During intraoral radiography, a special metal apron is put on the child and seated on a chair. After this, the specialist asks him to open his mouth wide, after which he fixes a protective film inside the cavity. It is usually installed in the area of the outer tooth. After this, a tube is installed near the mouth. The procedure takes no more than a minute, there is no recovery period.
When taking a panoramic photograph, the technique is slightly different. To get the correct image, the child is placed in front of the machine and a special tube is placed in the mouth. He must squeeze it as tightly as possible, after which the scanning starts. At this moment, the plates that rotate around the head begin to work. Thanks to this, it is possible to obtain an extended model. It allows you to assess the condition of the entire dental system. Only a qualified specialist will be able to decipher the results of such a study; a person without education is unlikely to be able to do this.
X-ray for babies
Dental X-rays are usually not performed on babies under one year old. However, such a study can only be carried out to clarify the diagnosis. X-rays are also performed in cases where other diagnostic methods are uninformative. Most often, the indications for such a study are birth injuries or a fall from a height. Remember that the first baby teeth appear at the age of 4-6 months, in some cases they may appear later. If the child does not have them after a year, it is advisable to consult with your doctor. Most likely, he will send the baby for an x-ray to determine the stage of emergence of temporary teeth. In addition, the study allows us to determine the features of the skull.
Types of X-ray diagnostics of a child's teeth
X-rays of children's primary teeth are one of the basic diagnostic procedures in pediatric dentistry. This method helps to assess the condition of dental roots, soft tissues near the element of the dentition, and identify the rudiments of molars. Using X-rays, the specialist assesses the condition of the jaw and announces the likely timing of the loss of primary teeth.
Baby teeth and molars - what's the difference?
The differences between temporary and permanent are the following characteristics:
- The roots of baby teeth are shorter, widely spaced and angled. This is explained by the need for the formation of molars;
- the enamel of temporary teeth is bluish, it is much thinner, and therefore more susceptible to the development of caries;
- The child’s milk teeth are smaller than the molars;
- The number of some teeth is not equal to the number of others. There are fewer temporary ones, because some elements of the series immediately grow as radicals;
- the tissue of baby teeth is poorly mineralized;
- temporary teeth grow vertically, and the crowns of permanent teeth are directed outward (towards the lips and cheeks).
Find out the dose received during dental x-rays using a modern digital device, and compare the indicators with the natural background. Go to “Dosimeter”.
When is an x-ray indicated in childhood?
An x-ray of the child’s baby teeth is scheduled the day before treatment. The doctor resorts to this measure to make sure that the upcoming therapy will not harm the process of formation of permanent teeth.
Specific indications for radiography include:
- the presence of carious lesions and other destructive processes;
- the appearance of jaw anomalies;
- diagnosing abscesses;
- the need to control impacted teeth and the natural change of temporary elements to molars;
- Carrying out bite diagnostics;
- inappropriate condition of the root system of temporary teeth.
More often, the procedure is resorted to in case of delayed growth of permanent elements of the series.
X-ray of babies jaw
Often the patients examined include children aged 6 years and older. For infants under one year of age, x-rays are prescribed only to clarify the diagnosis.
Doctors resort to this measure in cases where alternative methods (for example, ultrasound) are ineffective.
Typically, infant patients include children with birth injuries and babies who have fallen from a height.
Types of x-rays when examining children
Depending on the goals of the study, there is a need to obtain one or another type of x-ray. Among them:
- targeted radiographs - show one or a pair of teeth and nearby soft tissues;
- panoramic image of the jaw - displays a picture of the dentition along with the rudiments of the radical elements;
- 3D images are three-dimensional images of the entire jaw (upper, lower row) or a section of it.
The difference between panoramic and targeted radiographs
The difference between a panoramic X-ray and a targeted X-ray is the area of study. In the first case, the object of study is the jaw row, in the second - a specific area of the child’s gums, jaw or oral cavity.
Spot shot Panorama shot
In the process of targeted radiography, the beam tube is brought closer to the soft tissues. A successful shot shows one or two elements adjacent to each other.
3D modeling in negative
We are talking about a procedure carried out using innovative equipment that allows one to obtain a 3D image of the jaw row or its area. Such an image helps to determine the location of pathological canals, areas of the root system, and fillings. A study is scheduled on the eve of endodontic therapy and implantation.
3D
In dental practice, certain dates for performing oral x-rays are followed:
- for children with temporary teeth - once every 2 years;
- for adolescent patients - once every 1.5-3 years;
- for patients aged 18 years and older - once every 1.5 years.
Frequent x-rays are permissible for special medical indications.
Features of the procedure
To x-ray the jaw of a child with baby teeth, a film or digital device is used. The equipment is placed in a specially designated room, where the photo laboratory is also located.
The algorithm of action for the specialist and the patient is as follows:
- Before the procedure, the child needs to remove metal items (watches, jewelry, glasses, etc.).
- A special protective apron is put on the patient’s body, into which lead plates are sewn. Thus, the child’s internal organs are protected from the adverse effects of x-rays.
- The subject is asked to press a plastic plate with his teeth. The patient's lower jaw should be pressed tightly against the septum of the device. During the examination, the patient is required to remain motionless.
- The plates of the X-ray equipment begin to move around the child's head. This process takes no more than 20 seconds.
At the end of the examination, the panoramic image is printed on paper or transmitted electronically.
The principle of intraoral radiography (sighting) is somewhat different. The patient is seated on a chair and a protective apron is used. After the child opens his mouth, the specialist installs a film or matrix inside the examinee’s oral cavity. The doctor then places the machine's tube near your mouth. The duration of the procedure is no more than 60 seconds.
The result of the x-ray examination is saved on the computer. This makes it possible to further monitor the dynamics of the clinical picture.
Is it possible to refuse x-rays for a child?
Parents can easily refuse to have their child undergo an X-ray examination. This procedure is completely voluntary. However, they must understand that in this case any therapeutic measures will be carried out on the basis of an instrumental examination. A referral for an x-ray is a recommendation, but not a requirement. However, such images will help the doctor form a complete picture of the condition of the child’s oral cavity. Without an X-ray examination, it is impossible to carry out full prosthetics, therefore, in case of refusal, the doctor will refuse to carry out such procedures.
X-ray examination of teeth is a completely safe procedure that cannot cause harm to the body. You should not refuse to carry it out because of the radiation, because it is minimal and cannot harm the child’s body. With the help of such a study, it is possible to identify numerous deviations in the early stages.
Are x-rays harmful?
Many patients in dental clinics ask the question: is it harmful to their health to take dental x-rays? According to SanPiN standards, the permissible level of gamma ray radiation is 1000 microsieverts (µSv) per year. A feature of modern X-ray examinations is the fact that the exposure time of the device is reduced to a minimum, so the radiation dose is insignificant.
As for specific numbers, one procedure using a digital radiovisiograph is equivalent to 2 microsieverts. As for research using film, the dose is 10 microsieverts.
We suggest you read: When you tap, a tooth hurts after nerve removal - Dentistry
When answering the question of how harmful dental x-rays are, it should be noted that the frequency of examination is determined by the attending physician. On average, you can take about 100 photos over the course of a calendar year. It is obvious that even in a complex clinical case, such a number of x-ray examinations will not be needed.