Drugs that relieve pain due to pulpitis
If you feel a sharp toothache that takes the form of unexpected attacks, in particular when all kinds of irritants come into contact with a damaged tooth, this most likely indicates the onset of an inflammatory process in the dental pulp.
Pulpitis is characterized by pain, which immediately makes it clear that you need to urgently consult a dentist and under no circumstances hesitate. Naturally, it is not always possible to immediately get an appointment with a doctor; usually, you can make an appointment with a dentist only after a couple of days, but in this case, you cannot delay the treatment of pulpitis.
The pain is felt more and more and pulpitis begins to develop quite quickly. In the near future, the attacks will become stronger and longer, and the sensations will not be pleasant.
Is anesthesia necessary to treat pulpitis?
Pulpitis is a very common dental disease, which is accompanied by a throbbing toothache that is constant. This is primarily due to the fact that a fifth of the pulp consists of nerve endings and nerves, which is why it is very sensitive to destruction.
Read about the treatment of pulpitis in detail here.
Important! If during a dental operation there is an accidental contact between a dental instrument and the exposed pulp, the patient may simply lose consciousness from severe pain, which is why anesthesia in the treatment of this disease is considered mandatory.
Even knowing how serious the treatment of pulpitis is, many patients, having felt pain in the tooth, nevertheless do not rush to the doctor, which only worsens their situation. Remember that delaying a visit to the dentist can cause significant dental problems, causing longer and more painful treatment. In addition, pulpitis can cause a number of complications, which should also be taken into account.
Anesthesia for the treatment of pulpitis
Modern dentistry involves the use of a number of anesthetics. Both public and private clinics actively offer the use of various anesthesia in the treatment of even mild forms of caries, let alone such a complex and painful phenomenon as pulpitis. In addition, pain relief can significantly reduce people's fear of dentists.
Today, treatment of pulpitis is carried out only under anesthesia, because not every person has a low pain threshold. Thus, the most painful stage of treatment is the feeling of a prick in the gum. After this, all painful sensations disappear.
Home first aid kit
Dental specialists “Valentina” state that only a doctor can cure pulpitis without negative consequences and complications, and you should not self-medicate. However, you can temporarily relieve pain and relieve symptoms on your own. Among the mild analgesics that are usually present in every home medicine cabinet, you can use analgin, aspirin, and citramon. They help a little, but not enough. The main thing is not to give in to impulses to drink all the medicines in your medicine cabinet because of severe pain, as this is dangerous to your health.
Tips for suppressing painful symptoms of pulpitis
- Use warm water to rinse your mouth if you do not have any purulent discharge. If there is such discharge, rinse with cool water, this will help relieve the pain.
- Try not to allow any irritants in the form of hot or cold water, something sour or sweet, to touch the aching tooth. Such irritants will only increase the pain.
- Do not chew food on the side of your jaw where the sore tooth is located.
- If you sleep on the painful side, this will lead to blood flow to the tooth and pulp, which will immediately increase the pain.
- It is possible to relieve pain from pulpitis during pregnancy or breastfeeding only by using paracetamol and folk remedies that are not contraindicated in such a situation.
- If your body reacts absolutely normally to painkillers, then to instantly eliminate pain you can use drugs such as ketanov, ketonal, baralgin, pentalgin-N or nurofen. But, before visiting a doctor, do not use them, otherwise this will prevent the dentist from clearly and clearly determining your disease situation.
Frequent use of painkillers is strictly prohibited. This can lead to the transition of the disease to the chronic stage and severe complications. In addition, such drugs do not have a beneficial effect on the overall health of your body.
- Contrary to some popular advice, do not apply analgin to the inflamed pulp. It destroys gum tissue and tooth enamel, but does not bring much help. You can apply a cotton swab with a couple of dental drops, which will help relieve some of the inflammation.
- Use the anti-inflammatory drug dimexide. True, it has an unpleasant odor and can cause allergies if used for a long time, but the product can really help for the first time.
Dentists at the Valentina clinic remind you of the possible contraindications of the above-mentioned drugs and urge you to promptly contact the appropriate specialists for advice and treatment.
We invite you to a free reception! Call us now and make an appointment:
- by phone in St. Petersburg and 983-09-03;
- or use a special registration form;
We accept daily*, from 10 to 20 hours, at the address: St. Petersburg, st. Budapestskaya, house 17, bldg. 3
*On Saturday and Sunday we open by appointment.
How a mosquito bites - types of pain relief in the treatment of pulpitis
A dental disease such as pulpitis, in the greatest number of cases, is characterized by severe pain.
Throbbing pain is a consequence of the fact that the pulp itself is much more sensitive than other tooth tissues.
The pulp consists of approximately 20% nerve endings and, when it is inflamed, sensitivity increases significantly.
In cases where a dental instrument touches the pulp, a pain impulse passes through the human body. In connection with this phenomenon, patients question whether it is painful to treat pulpitis and how much it hurts.
How to reduce your fear of visiting the dentist?
Tooth pain often brings not only physical discomfort, but for many it also causes a strong fear of visiting the dental office. In order to reduce anxiety, you can take any natural tincture that has a sedative effect. These tinctures include:
- Motherwort tincture.
- Peony tincture.
- Novo-passit.
- Corvalol.
- Valerian tincture.
It is recommended to start taking such medications a few days before your scheduled visit to the dentist. The usual dose is ten to twenty drops at bedtime.
As you can see, today the patient does not have to worry about whether it is painful to treat pulpitis, because there are many painkillers that can remove all the unpleasant sensations that arise during the treatment process.
Is it painful to treat tooth pulpitis?
For many people, pulpitis symptoms and its treatment are necessarily associated with fairly sensitive dentist manipulations that cause discomfort. Accordingly, for most, going to the dentist is a very scary event.
As recently as the beginning of the 2000s, dental treatment of pulpitis was considered a rather painful procedure.
This happened for the reason that arsenic was used for treatment to devitalize the pulp, that is, to destroy the nervous tissue in it. A temporary filling was placed over the arsenic, and the patient was sent home for two days.
After the death of the nerve, the dentist cleaned the cavity of arsenic and removed dead nerve tissue.
The painfulness of the procedure was also due to the fact that by the time the nerve was removed, it was not yet completely dead.
Upon completion of the treatment of removing the nerves of the tooth, filling of the roots and the tooth itself was performed.
At a particular point in time, arsenic is practically not used in dental treatment, and modern devitalizing drugs have a milder effect.
During the treatment process, the paste is applied to the pulp, and after a week, the dentist cleans and fills the root canals of the tooth and, two days later, a permanent filling is installed.
Depending on the degree of tooth destruction by disease, options for placing fillings on pins are possible.
Duration of treatment
Typically, treatment of pulpitis is carried out in 2-3 visits, depending on the stage and form of the disease. The pulp can be removed during the first visit, or the doctor will put a paste into the tooth canals, which will kill the nerve within 1-10 days (depending on the paste). If the pulp is removed immediately, then a therapeutic pad is applied and the canals are temporarily filled, and the tooth is finally treated during a second visit to the doctor.
When paste is placed in a tooth, three visits are required - the first to use a special preparation, the second to clean the canals and apply a medicinal gasket, and the third for final filling and restoration of the tooth crown. In some cases (for example, a severe inflammatory, purulent process), the doctor may use several different pastes - and the treatment may be even longer.
Modern dentists do everything possible to preserve the functions and aesthetics of the tooth - removal is carried out only for appropriate indications.
Anesthesia for the treatment of pulpitis
Is it painful to treat pulpitis with an injection? Modern dentistry, when treating a specific disease, uses many variations of painkillers. But, regardless of this, there remains a strong opinion that treatment of pulpitis in dentistry is necessarily accompanied by severe pain.
Read also: Wisdom tooth rots, what to do
At the same time, virtually every dental clinic is able to offer a variety of high-quality anesthetic drugs that can not only reduce the pain of manipulation, but also eliminate it altogether.
In cases where the disease is in an advanced form, specialized anesthesia can be used.
It is injected directly into the pulp of the tooth before any treatment is performed. In dentistry, only two techniques are used that help reduce pain to the minimum or avoid it altogether.
Determining the specific type (general or local) of anesthesia, that is, the choice between local and general anesthesia, depends only on:
- patient's health status;
- the complexity of the dental procedures required;
- the volume of dental procedures required;
- psychological state of the patient - if panic is present, then in the absence of other contraindications, general anesthesia is used.
Types of pain relief
If we consider the most common techniques for anesthetizing dental procedures, we can find that local anesthesia is the most common in the treatment of pulpitis.
This type of local anesthesia is widespread due to the fact that local anesthetic medications can eliminate pain in the very part of the mouth, gums and tongue where the necessary dental procedures will be performed.
The human body, when using local anesthetics, experiences much less stress because it remains conscious.
Local anesthetics are divided into two variations:
- Application anesthetics. A specific category of medications is applied to the surface of the mucous membranes using the spray method.
- Injectable anesthetics. A medicinal anesthetic is injected directly into the gum cavity using a carpule syringe, although ordinary ones are sometimes used.
To remove the pulp, only the injection version is used, for the reason that application preparations do not have the same degree of effectiveness - they are not able to cope with such a serious pain syndrome.
The drug is often injected into the area of the periosteum or into the area of the ternary nerve.
In some clinical cases, before the injection is performed, sprayed anesthetics can be used to numb the moment of injection.
Previously, only lidocaine and novocaine were used as the main anesthetics in dentistry. At the moment, even in public clinics, specific drugs are almost never used.
In their place, anesthetics were introduced for dental anesthesia, which in their formula contain articaine or mepivacaine. For specific types of anesthetic active ingredients, the effectiveness is several times higher than the effectiveness of novocaine and lidocaine.
Enlightened means armed. What are the stages of caries and their clinical manifestations - information that will help reduce visits to the dentist to a minimum.
By the way, caries at the initial stage can be defeated at home. No, really. Find out which techniques are most effective by clicking here.
If they didn’t save you, toothache doesn’t give you life. Which tablets are best to take for toothache - a review of the most optimal drugs.
Epinephrine (adrenaline) can be added to the painkiller as an auxiliary component.
Due to the fact that these drugs have high performance and effectiveness, general anesthesia for pulpitis has found practically no use.
The use of general anesthesia is often approved only in cases where:
- the patient suffers from an advanced form of dental phobia;
- a highly complex operation is being performed;
- there is an allergy to all drugs that could be used for local anesthesia.
When considering the situation as a whole, you may get the impression that general anesthesia is ideal in all respects - you fall asleep at the beginning of a dental operation to treat pulpitis, and wake up with healthy teeth.
The true state of affairs is that general anesthesia can have a whole range of negative effects on the health of the human body as a whole.
In medicine, two techniques are used that refer to variants of general anesthesia:
- Inhalation . It is the most gentle option. It is even used to treat dental problems in children.
- Intravenous. Involves the intravenous administration of an anesthetic drug based on narcotic substances.
Conducting general anesthesia
This is interesting to know! Dentophobia is a disease of dentists, a panicky fear of dental treatment.
The use of general anesthesia is advisable for patients suffering from dental phobia, as well as during operations of high complexity or in case of allergies to all local anesthetics.
Today, general anesthesia is most often used in the treatment of pulpitis in children under 6 years of age.
Important! It may seem ideal to many that you fall asleep at the beginning of the procedure and wake up when everything has already passed, but you should remember that general anesthesia has a negative effect on the body, and in particular on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
Today there are two types of general anesthesia used for dental purposes:
- The safest method is considered to be inhalation anesthesia. It is simply irreplaceable in the treatment of pulpitis under a microscope. During this procedure, the patient wears a special mask, through which gases are supplied into his respiratory tract. As soon as the patient falls asleep, the doctor removes the mask from him and begins treatment.
Photo: inhalation anesthesia
- Intravenous anesthesia, which involves injecting a solution into a vein into the patient. This method of anesthesia is also very common, and its main advantage is that it is characterized by an almost instantaneous effect after administration.
Photo: intravenous anesthesia
Important! Before administering intravenous anesthesia, it is necessary to make sure that the patient does not have allergic reactions to the components contained in this composition. The doctor also needs to remember that any type of anesthesia should last no more than an hour and a half.
In order to treat pulpitis under general anesthesia, the patient should undergo a series of tests and consult with the treating dentist. Let's consider the main contraindications to the treatment of pulpitis under general anesthesia:
- Heart disease.
- Diabetes.
- Arterial hypertension.
- Kidney failure.
- Asthma.
- Ischemic disease, heart attack, stroke.
- All kinds of hormonal diseases.
This is interesting to know! Endotracheal anesthesia for dental treatment is inapplicable, since in this case the doctor simply will not be able to carry out effective work due to artificial respiration devices.
Painkillers for pulpitis
General anesthesia in the treatment of pulp diseases
is currently used to a limited extent due to technical difficulties associated with instrumentation and filling of tooth root canals, insufficient equipment for direct x-ray monitoring of the quality of their filling, as well as the lack of a rubber dam in some medical institutions.
Therefore, the main method of pain relief
is local anesthesia. When using it, it must be borne in mind that anesthesia of the pulp is much more difficult than that of the periodontal tissues. Acute forms of pulpitis are most difficult to anaesthetize, aggravated chronic forms are easier to anaesthetize, and chronic forms are most effective.
The same drugs
, which are used for tooth extraction. The most effective at present should be recognized as “Ultracain-DS” and “Ultracain-DS forte” (Hoechst, Germany), which differ in the concentration of adrenaline (1: 200,000 and 1: 100,000, respectively). (France) produces a similar drug called Septonest. The active principle of these anesthetics is articaine at a concentration of 4%.
It is also successfully used to anesthetize dental pulp.
2% solution of scandicaine with adrenaline, norepinephrine (Scandonest, France), 2% solution of lidocaine with adrenaline and other modern anesthetics. The effectiveness of 2% solutions of novocaine and trimecaine with adrenaline is significantly lower. With their single injection in the case of acute pulpitis, pain relief is achieved in 33.3% and 50% of cases, respectively (AM Salikhov et al., 1993), which limits the use of these drugs only to chronic forms of pulpitis.
Read also: Ulcerative pulpitis
For reliable pain relief
, especially in acute forms of pulpitis, it is necessary to carry out two-stage anesthesia (V.I. Lukyanenko, 1968). The first injection of an anesthetic eliminates the parabiotic inhibition of the nerve endings of the pulp, and the second injection causes true anesthesia.
In the vast majority of cases, with inflammation of the dental pulp
It is recommended to use anesthetic solutions with the addition of adrenaline, the use of which can enhance and prolong anesthesia of the pulp. For patients with hypertension, coronary heart disease, elderly patients, etc., the administration of adrenaline is not indicated. In these cases, it is advisable to use a 3% solution of scandicaine (Scandonest, France). It should be borne in mind that the anesthetic scandicaine itself has a slight local vasoconstrictor effect.
Application of anesthetic solutions
without adrenaline, it is indicated in the treatment of pulpitis using a biological method and in the treatment of functional pulp deficiency with a course of blockades.
In addition to traditional infiltration and conduction methods of anesthesia
Currently, intrapulpal and intraligamentary anesthesia are widely used, based on the injection directly into the pulp and into the periodontal gap of a small amount (about 0.1 - 0.2 ml) of an anesthetic solution. To perform intraligamentous anesthesia, it is necessary to use a special syringe. The limited amount of the administered drug and the high reliability of these methods of pain relief make it possible to use these methods in children, elderly and debilitated patients, as well as to supplement infiltration and conduction anesthesia to increase their effectiveness.
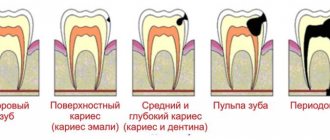
The cause of toothache with pulpitis, what is its character
The cause of pulpitis is an infection that has penetrated through the tooth enamel and affects dentin . Dentin is the last barrier to infection on the way to the pulp. Passing through it, pathogenic microorganisms affect the nerve endings and blood vessels located in the pulp chamber and root canals. And this is precisely what causes the severe pain that occurs with pulpitis.
Attention should be paid to the fact that pain tends to intensify at night . This is due to the physiological position of the body during sleep.
In a horizontal position, blood flows more to the head, and, in particular, to the jaw, which increases blood flow to the inflamed area and creates excess pressure on it. This leads to the fact that the central nervous system signals sent by the nerve bundle are amplified.
Among other things, under the influence of human biorhythm in the evening, blood pressure can increase even in healthy people. This can also cause toothache if a person has not yet gone to bed.
In acute
As mentioned earlier, pain with pulpitis varies depending on the type of inflammation.
The clinical picture of acute pulpitis is as follows:
- The nature of the pain is cutting, tearing, shooting.
- The pain is very strong, paroxysmal . It intensifies at night, but can also appear during the day.
- Painful sensations can intensify with mechanical pressure on the tooth, exposure to heat, cold, spicy or sour foods.
- The pain persists for 2-3 weeks , gradually subsiding.
- In acute inflammation, the tooth cavity is most often covered with softened dentin tissue.
Reference. Unlike caries, when there is also a reaction of the teeth to food or temperature, with pulpitis the pain does not go away immediately after removing the irritant.
Acute pulpitis has 2 stages:
The initial stage of inflammation lasts up to two days . During this period, the causative tooth is easy to detect, since irradiation is not yet observed and only part of the neurovascular bundle is involved in the inflammatory process.
At this time, pain occurs in spontaneous attacks, which can be provoked by various types of irritants. The duration of the pain is about half an hour , and with further development of the disease it can increase to two hours and intensify at night.
The next stage of the disease, in which inflammation covers the entire pulp. During this period, the pain is diffuse, radiating to different parts of the jaw , temporal and occipital parts of the head, and cheekbones. If there is inflammation in the teeth of the lower jaw, the pain radiates to the ear and back of the head, in the upper jaw - to the superciliary area and temple.
During this period, it is impossible to indicate the causative tooth, as with focal pulpitis. Attacks of pain become longer and can last for hours.
The pauses between them are only 30-40 minutes .
Acute diffuse pulpitis lasts no more than two weeks , after which it can become chronic.
How long can it last for chronic?
Chronic pulpitis also has several stages. During the development of each of them, the pain is not as severe as in the acute form of the disease. In some cases, when a cavity has formed inside the tooth and it continues to secretly deteriorate from the inside, painful symptoms may be completely absent.
The danger is precisely the lack of severity of the pain syndrome. It can last, without disturbing the patient too much, for up to several years . Toothache is significantly dulled, you can get used to it, although chewing is difficult, and with external influences the pain intensifies. Bleeding may occur at times.
Causes of pulpitis
The inflammatory process that occurs in the pulp is a kind of response to irritants that penetrate the neurovascular bundle of the tooth from the carious cavity. These can be pathogenic bacteria and their metabolic products, which enter the pulp tissue through various routes:
- Cariesogenic pathway. Microorganisms penetrate into the pulp from a carious cavity, which affects the deep layers of dentin. The protective layer of hard tooth tissue becomes thin, and foreign agents are able to penetrate the pulp chamber and cause inflammation. If, during the treatment of a carious cavity, microgaps remain between the walls of the carious cavity and the filling, pathogens can enter the dental nerve through it.
- Periodontal path. The sudden appearance of acute pulpitis may be a consequence of deep curettage, gingivectomy (gum excision), gingivotomy (gum incision) or periodontal plastic surgery for generalized periodontitis.
- Another route - hematogenous - opens through lymphatic and blood vessels (arterioles and venules). With the blood flow, the infection “floats” to the tooth and penetrates into the pulp. In such cases, the tooth may remain externally intact (undamaged), but pulpitis occurs due to a descending infection.
There are several other reasons that contribute to the occurrence of pulpitis:
- Tooth trauma (fracture of the crown or part thereof, fracture of the crown or root, accidental opening of the pulp chamber when grinding a tooth under a crown, improper orthodontic treatment).
- Therapeutic and surgical manipulations on the periodontium (hard and soft tissues surrounding the tooth).
- Exposure to low frequency but high intensity ultrasound.
- Denticles and petrification begin to form when there is a metabolic disorder in the pulp. Deposited in pulp tissues, they can compress nerve endings and blood vessels, contributing to irritation and inflammation of the pulp.
- In addition to bacteria, the inflammatory process can be caused by chemical (components of filling materials, negative effects of inorganic cements and acids) and temperature irritants (pulp burn when grinding a tooth). In this case, the effect occurs through the dentinal tubules (dentinal tubes communicating with the dental nerve).
Why does a tooth hurt after removal of pulpitis?
Soreness after treatment of pulpitis can be either insignificant or have a more pronounced form. The appearance of such a reaction in some cases may be associated with tissue trauma at the apex of the tooth root. Treatment of pulpitis is inextricably linked with the removal of the inflamed neurovascular bundle and filling of the canals, which can cause pain. In this case, the pain continues for 2-3 days , after which it will subside.
Read also: Tooth root rotting symptoms
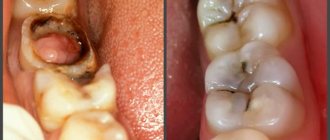
Photo 1. A tooth with pulpitis with a removed nerve. After such a procedure, pain may be felt.
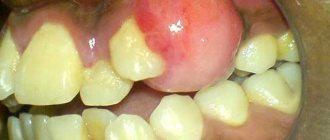
Also, the cause of pain can be improperly filled root canals . In this case, the pain is accompanied by swelling of the gums in the area of the affected tooth, and lasts until the pulpitis is properly cured completely, or until it becomes chronic.
Important! an x-ray must be taken to rule out errors in treatment tactics and the onset of new inflammation.
Local anesthesia for pulpitis
Local anesthesia is the most common type of anesthesia used in the treatment of pulpitis. This popularity is due to the fact that this technique allows you to anesthetize only a certain part of the oral cavity, to which treatment procedures are supposed to be carried out.
Important! With local anesthesia, the human body experiences less stress on all systems and organs, since the patient remains conscious during the procedure.
For local anesthesia, there are two types of agents:
- Applications that are sprayed onto the oral mucosa. This may be a spray or gel containing icecaine.
Photo: injection of anesthetic into the mucous membrane
How to relieve pain: first aid at home
The first thing that worries you when pulpitis occurs is pain, and accordingly, initial help is aimed specifically at its elimination. For these purposes, you can use medicinal drugs both for oral administration and for local use. Let's look at each point in more detail.
How to relieve pain: oral medications, the best painkillers
This group of drugs is represented mainly by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
These include:
Ketorol/Ketanov - eliminates inflammation and pain, often used in dentistry. You should use no more than 2 tablets per dose 3 times a day .
The main contraindications for use are gastric and duodenal ulcers in the acute stage, age under 16 years , and the risk of bleeding .
- Ketonal , a drug based on ketoprofen, has a more pronounced analgesic effect. Take 100 mg 2 times a day , or 150 mg once , depending on the dosage form. It should not be taken if you have the aspirin triad, are under 15 years , or have gastrointestinal diseases in the acute stage.
- Nurofen is an over-the-counter ibuprofen-based drug. It has less pronounced effectiveness in dentistry, but in the form of capsules it has a faster effect. Take 200 mg up to 4 times a day, or 400 mg up to 3 times . Prescribed to persons over 12 years of age. Not used for the same diseases as the first two drugs.
- Aspirin can also be easily purchased at any pharmacy. Use 1 tablet up to 6 times a day. It should not be taken by children under 15 years of age , persons with gastrointestinal diseases in the acute phase, or hypersensitivity to the drug.
- Analgin - relieves pain, should be used in a dosage of 250-500 mg 2-3 times a day. The maximum daily dosage is 3 grams. Contraindicated for use in cases of severe impairment of liver and kidney function.
Important! Pregnant and breastfeeding women should not take painkillers without a doctor's prescription!
Slightly less popular for toothache are drugs from the group of analgesics and combination drugs:
Photo 2. Packaging of Analgin in tablet form. There are 20 pieces in a pack.
- Baralgin is an imported analogue of analgin. It is distinguished by the quality of the medical substance and fewer side effects.
- Citramon is a combined remedy that relieves inflammation and pain. You should take 1 tablet every 4 hours , but no more than 8 times a day . Contraindicated for persons under 15 years of age and for aspirin-induced asthma.
- Pentalgin is a combination drug with a pronounced analgesic effect. Single dosage - 1 tablet, no more than 4 tablets per day . Do not use by persons under 18 years of age or at risk of developing stomach bleeding.
As local remedies, it is allowed to use rinsing with Oka anti-inflammatory solution , as well as applying Kamistad and Cholisal ointments for the purpose of temporary pain relief and relief of inflammation. Dental drops are also suitable, which are first applied to cotton wool and applied under the sore tooth.
Important! Pain relief for pulpitis is only a temporary measure . Lack of proper treatment can cause serious consequences.
General recommendations for pain relief
- Rinse with warm water if there is no purulent discharge or slightly cool water if there is any.
- If any kind of irritants come into contact with a tooth, they should be removed as quickly as possible .
- It is necessary to avoid chewing food on the same side of the jaw where the diseased tooth is located.
- It is best to sleep on the side opposite the diseased tooth to avoid blood flow to it and the development of pain.
How to relieve pain with folk remedies
The condition can also be alleviated using traditional medicine.
Let's look at the most effective of them:
- Rinsing with a concentrated solution of salt or soda , to which you can also add one drop of tea tree essential oil, will help relieve pain
- Rinsing with sage decoction has an astringent effect, reducing tissue sensitivity and thereby reducing pain.
- Alcoholic drinks are an excellent gargle for short-term pain relief. You should not use pure alcohol or sugar-containing drinks for these purposes.
- Two drops of clove oil , applied to a cotton swab and applied to the gum, after some time also remarkably dulls the pain.