Principles of dental prosthetics
The difficulty of planning lies in the close relationship of the three elements of the dental system, which must always be taken into account when drawing up a treatment plan:
- Shape, location and number of teeth;
- Function of masticatory muscles;
- Function of the temporomandibular joint
These three points determine the trajectory of the lower jaw, and therefore our ability to effectively communicate and chew food. A slight change in one of them can lead to a violation of the other two. This means that even in seemingly simple cases of prosthetics, it is important to conduct a thorough diagnosis and only then begin treatment. There are principles that are always important to consider when drawing up a prosthetic plan. Here are some of them:
Dental treatment planning
As noted earlier, drawing up a plan for examination and treatment in dentistry is especially necessary when the dentist is planning dental implantation and prosthetics. These manipulations are considered the most complex and expensive. What will help a specialist create the best dental examination and treatment plan for each specific case?
Of course, this is the most complete dental examination and consideration of the patient’s financial capabilities. Without a combination of these factors, your dentist will not have a good treatment plan.
What examination methods in dentistry are used to make the correct diagnosis and draw up a dental treatment plan?
- The main methods of examination are a visual examination of the oral cavity by a doctor, percussion (tapping) and palpation (feeling) of teeth, gums and chewing muscles, probing of the dental surface, temperature tests, checking occlusion (closing teeth), carrying out chewing loads and determining hygiene tests and indices.
- Additional methods of dental examination include targeted and panoramic radiography, computed tomography of the hard tissues of the teeth and jaws, MRI of the soft tissues of the oral cavity and mandibular joint, tests of blood, gingival fluid and saliva, electroodontodiagnosis, photographs of the oral cavity, diagnostic models of plaster jaws, accurate 3- D lithographic models of jaws and teeth, ultrasound examinations of the oral cavity, dental microscope, data from histological examination of oral tissues.
The use of these methods helps with differential (comparative) diagnosis and allows for comprehensive dental treatment according to the optimal plan. Only a dentist can prescribe and carry out oral cavity examination methods.
You can't think locally (limitedly)
Is it possible to make beautiful crowns for the teeth of the upper jaw (for example, from metal-free ceramics) if the teeth on the lower jaw are almost completely destroyed. However, this is not visible, so the patient does not want to deal with them? The unequivocal answer is no! Because this will lead to the rapid destruction of such restorations. The only correct solution is to treat both the upper and lower teeth at the same time.
These and many other principles are extremely important to consider before planning dental prosthetics. They are the basis of CORRECT DENTAL PROSTHETICS - the production of functional, aesthetic work that will serve a person for a long time.
Mutual understanding is the first component of successful dental prosthetics
For most clinical situations, the prosthodontist can formulate several treatment options. Each of them will take into account the specifics of your particular case, but treatment plans may differ quite significantly in a number of points:
- Type of prosthetics . You can achieve the same result using different designs and technologies.
- The material from which the orthopedic restoration will be made.
- The cost of treatment directly depends on the above points and can also vary greatly.
- Time costs for treatment . Dental prosthetics can take anywhere from several hours to 2-3 years. Therefore, try to choose time that you can truly devote to your health.
Among the proposed options, the patient must independently choose the type of care that suits him best. To consciously make such a choice, you must understand their essence, and also tell the doctor all your expectations . In turn, the doctor will try to take them into account in future work. The success of treatment depends on mutual understanding at all stages of dental prosthetics.
Why do you need a smile design?
In addition to collecting the necessary information about the patient’s orthodontic health, it is necessary to correctly interpret it and apply it in treatment. The next step is to perform a calculation using computer technology (for example, teleroentgenogram, tomogram, etc.). The use of modern, improved examination methods allows us to make the most accurate prognosis and draw up a treatment plan. Typically, it takes an experienced specialist up to 1.5 weeks to analyze the information received and draw up a detailed therapeutic plan.
It is worth understanding that the choice of one or another diagnostic method is determined individually by the attending physician, in accordance, among other things, with the wishes of the patient. There is no need to be alarmed if your doctor additionally recommends that you be examined by specialists in other fields of medicine and undergo laboratory tests. The main task of the specialist is to tell the patient about his problems and options for getting rid of them, to mention possible risks in case of refusal of treatment or certain types of diagnostics. But the decision always remains with the patient.
Discussion of treatment plan
Discussion and selection of a treatment plan may take some time. That is why the first visit is a consultation and getting to know your dentist. To simplify communication and understand the essence of the treatment offered by the doctor, the following tools can be used:
- Diagnostic models of the patient's upper and lower jaw, on which the final treatment result is modeled using wax. This is a convenient and visual tool that allows you to discuss all the details of the appearance of the future structure.
- Temporary structures that are installed in the oral cavity on top of the patient’s own teeth.
- Computer programs for three-dimensional planning make it possible to visually represent all stages of treatment. This is especially true when prosthetics are performed on implants.
The following pages talk in more detail about the diagnosis before dental prosthetics.
Orthopedic dentist Dmitry Viktorovich Martynov
Favorites
…
Orthopedic treatment of pathological tooth abrasion
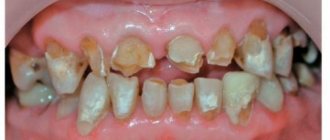
Prosthetics for pathological tooth wear has both therapeutic and preventive purposes. The first means improving the chewing function and appearance of the patient, the second means preventing further abrasion of hard dental tissues and preventing diseases of the temporomandibular joint. What specific problems are solved when using prosthetics for a particular patient depends on the characteristics of the clinical picture.
In case of localized and diffuse forms of abrasion without a decrease in the height of the lower third of the face, prosthetics are of a preventive nature, preventing further abrasion of the teeth.
Back in 1904, Preisswerk used for these purposes metal inlays in antagonizing teeth, located at three points: in the front teeth and in the lateral teeth of the left and right sides. You can also use counter crowns made of stainless steel. Gold crowns are not suitable for this due to their softness.
With pathological abrasion, accompanied by a decrease in the height of the lower third of the face, the tasks of prosthetics are complicated. Here it is necessary not only to improve chewing function and prevent further tooth wear. At the same time, it is necessary to increase the height of the bite. This will change the patient’s appearance and normalize the position of the articular head in the articular cavity.
Increasing the height of the bite is achieved by restoring the shape and height of worn-out crowns of natural teeth, for which they are covered with porcelain, plastic, metal or combined crowns. When choosing a material for crowns, you should take into account both the aesthetic side of the issue and the possibility of abrasion of the material of the artificial crown. Full metal crowns are not aesthetically convenient. Plastic ones are the most profitable, but they also wear out quickly. Preference should be given to porcelain or combined crowns, the chewing surface of which is cast.
Prosthetics are carried out in the following order. First, natural teeth are prepared taking into account the type of future artificial crowns (porcelain, plastic or metal). After this, the height of the bite is determined, for which the height of the lower third of the face at rest of the lower jaw is first measured. Then a roller of wax or other thermoplastic mass is placed between the teeth and the desired bite height is fixed. The occlusal height of the lower third of the face should be less than the resting height, but not more than 2-3 mm. The correctness of determining the height of the bite can be checked by radiography of the temporomandibular joint. With a correctly determined bite height, the joint space is the same width in both the anterior and posterior sections. If these relationships are violated, the bite height should be changed by reducing or increasing the bite ridge.
Then impressions of the dentition are taken and models are cast based on them. Using a bite roller, the models are prepared in the position of central occlusion, they are plastered into the articulator and the modeling of the crowns begins.
If there is a large difference in the height of the lower third of the face when the teeth are closed and in the resting position (6-8 mm), increasing the height of the bite can be done in two steps. First, the bite is raised with a temporary removable aligner to normal height. If in this case no disorders occur in the activity of the temporomandibular joint, then after 2-3 weeks the final prosthetics are performed in the manner described above. If joint pain appears, the bite should be lowered, and after a while raised again, bringing it to the desired value.
When applying prefabricated hollow metal crowns, keep the following in mind. Since artificial crowns are longer than the tooth, when applied, it is easy to push them deeper into the gum pocket than necessary, and thereby damage the mucous membrane of the gum pocket. The height of the bite will be reduced. Hollow crowns are also inconvenient because when they are rubbed, saliva gets into the holes formed. It dissolves the cement, and the cavity in the crown is filled with food debris, which subsequently decomposes.
In order to prevent these complications, crowns should be applied in two steps. First, the crowns are fixed, for example, on the right, and in order not to push their edge deep under the gum, a stens bite roller should be placed on the left side, with the help of which the desired bite height was fixed. After strengthening the crowns on the right, do the same on the left side. Only in this case the role of a limiter is played by the crowns of the right side.
A more convenient method of prosthetics is metal combined crowns. In this case, first only caps are made for the teeth. They are fixed to the teeth with artificial dentin and the height of the bite is determined. Impressions are taken, models are cast, they are composed in the position of central occlusion and plastered in an occluder. The missing part of the crown (chewing surface, cutting edge) is modeled on wax caps. The wax is then replaced with metal in the usual manner and the crown parts are soldered to the copings. Crowns with a cast occlusal surface are more advantageous than stamped full crowns because they can help prevent a decrease in bite height when they are applied; In addition, they are less abraded when chewed.
You can restore the shape of worn-out crowns and increase the height of your bite using removable plastic aligners. To do this, impressions are taken from both jaws and combined models are cast: the teeth are made of low-melting metal, and the rest is made of plaster. Before taking an impression, determine the height of the bite. The models are plastered in the position of central occlusion in the occluder. After this, the mouthguard is modeled from wax and the latter is replaced with plastic. The finished mouthguard is placed in the oral cavity. Any inaccuracies in its fit to the teeth are eliminated with quick-hardening plastic.
Removable plastic mouthguards, which are very aesthetically advantageous, have a big drawback. Under them, despite careful hygienic care, systemic enamel necrosis develops. To avoid this, worn teeth should first be covered with metal caps, and then replaced with a removable mouthguard. In this case, it is possible to achieve a satisfactory aesthetic effect, facilitate the fitting and insertion of the mouthguard, and also prevent its harmful effect on dental tissue.
Partial tooth loss can occur against the background of already developed pathological abrasion of teeth. On the other hand, the loss of, for example, molars can lead to pathological wear of the front teeth due to their mixed function. The clinical picture is very complex, since the pathological abrasion is layered with the symptoms of partial tooth loss. In this regard, the tasks of prosthetics are expanding. The tasks pursued during prosthetics for pathological abrasion include the replacement of defects formed as a result of tooth loss.
The designs of prostheses used to solve the latter problem are determined by the specific clinical picture. If defects are included without reducing the bite height of the lower third of the face, fixed dentures can be used. When the height of the lower third of the face decreases, prosthetics provide, in addition to replacing defects, and increasing the height of the bite.
For terminal defects (unilateral or bilateral), the use of various designs of removable dentures (arch and plate) is indicated. Increasing the height of the bite is carried out on fixed dentures or on removable arch ones, equipped with special metal overlays for worn-out teeth.