How does enlarged lymph nodes manifest?
If the submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged, it will be difficult for the child to swallow and chew food
As the name suggests, the submandibular lymph nodes are located under the lower jaw. They are the first to respond to diseases of the oral cavity (teeth, gums, tongue, palate).
If the submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged, the child will experience the following symptoms:
- swelling of the area under the lower jaw,
- discomfort when chewing,
- general malaise,
- difficulty swallowing,
- redness of the skin.
It is quite simple to discover that a child has an enlarged lymph node under the jaw, since this group of lymph nodes swells significantly. Upon palpation, a tubercle under the skin is noticeable, pressure on which causes discomfort.
It is necessary to distinguish between lymphadenopathy (enlarged lymph nodes) and lymphadenitis (inflammation of the node). In the first case, the pain syndrome manifests itself as moderate discomfort when swallowing. With lymphadenitis, the nodes swell and swell more, pain appears with any movement of the jaw. If lymphadenopathy is an accompanying symptom and in itself is practically harmless, submandibular lymphadenitis in children, the treatment of which was not started in a timely manner, threatens the development of complications.
Causes of inflammation of the lymph nodes of the face
Facial lymph nodes play the role of “guards” of the body as a whole. And they are sensitive to the invasion of any infection or the onset of an inflammatory process in the human body.
inflammation of the lymph nodes on the face can result from the following troubles:
- Infectious disease (cold, flu, rhinitis, sinusitis, sore throat)
- Tuberculosis
- Dental problems (periodontal disease, caries)
- Decreased immunity
- Skin diseases on the face
- Allergy
- Otitis
- Periodontitis
Inflammation of the lymph nodes on the face most often occurs as a result of a person's hypothermia. Your feet may freeze, and after 2-3 days you will see the results in the literal and figurative sense. The lymph node becomes denser and begins to cause pain not only upon palpation
Why do lymph nodes enlarge?
In all cases of unusual local enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes, a thorough examination of the child is necessary.
The reasons for enlarged submandibular lymph nodes in children are varied – from systemic infections to pathologies of the oral cavity.
Common causes of lymphadenopathy include:
- immunodeficiency,
- tuberculosis,
- Infectious mononucleosis,
- post-vaccination reaction of the body,
- rheumatoid arthritis.
The listed diseases and conditions can provoke enlargement of lymph nodes in different parts of the body. Often, with these pathologies, there is an increase in lymph nodes in several regional groups at once.
In cases where there is an increase in only the submandibular lymph nodes, the causes should be sought in pathologies of the oral cavity or ENT organs. Knowing the typical symptoms of diseases that are potentially dangerous due to enlarged lymph nodes will help you recognize the disease in a timely manner and consult a doctor.
ARVI
Most often, the submandibular lymph nodes in a child enlarge due to ARVI of viral or bacterial etiology. ARVI is considered to be a harmless disease, despite its rather severe symptoms. The peak incidence of acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections occurs in the autumn-winter period; infections develop against the background of weakened immunity.
Symptoms appear differently depending on the type of virus. General signs are severe weakness, fever, runny nose. Symptoms may include cough, inflammation of the tonsils, laryngitis or pharyngitis.
If the above symptoms appear and the temperature rises above 37.5 degrees, you should call a doctor to see your child.
The doctor you need to see is a pediatrician. Necessary examinations for diagnosis: physical examination, complete blood count, urinalysis, palpation of lymph nodes.
Acute otitis media
Acute otitis media occurs due to infection entering the middle ear cavity; most often the causative agents are bacteria - pneumococci and Haemophilus influenzae.
Enlarged submandibular lymph nodes may be a consequence of otitis media. This is a fairly common disease among children of primary school age, which is associated with age-related narrowness of the Eustachian tubes in children.
The disease manifests itself as an inflammatory process, often an infection penetrates into the ear canal and purulent inflammation develops. Symptoms of the disease:
- acute pain in the ear,
- discharge from the ear canal (with purulent inflammation),
- increase in body temperature,
- stuffy ears,
- headache.
With this disease, the behind-the-ear and cervical lymph nodes can also become inflamed. The pain syndrome depends on the type of inflammatory process. With aseptic inflammation, the pain is acute and paroxysmal, but can subside on its own. With a purulent inflammatory process, the pain is excruciating (“shoots” in the ear), often spreads along the trigeminal nerve, and therefore can radiate to the jaw, eye, or throat.
The symptoms that you need to pay attention to at the beginning of the development of otitis media are stuffy ears and a dull aching pain. The doctor you need to visit is an otolaryngologist. Diagnostics: analysis of complaints, otoscopy, x-ray of the temporal bone.
Inflammation of the sinuses
Sinusitis, sinusitis and sinusitis are all inflammations of the sinuses. The disease develops against a background of decreased immunity and is caused by the addition of an infection. Most often, inflammation is caused by various bacteria. Inflammation of the nasal sinuses in a child can be an independent disease or a complication of ARVI, influenza, or scarlet fever.
Symptoms:
- nasal congestion,
- headache,
- pain when tilting the head,
- increased body temperature,
- throat irritation.
As a rule, during inflammation the temperature rises to 37.5 degrees, but in advanced cases higher values may be observed. The headache spreads to the forehead and is not relieved by analgesics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
With chronic sinusitis, the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes may become enlarged, but symptoms other than difficulty breathing may be absent.
The first alarming symptom: nasal congestion, which is accompanied by a headache and does not go away for more than five days.
The doctor you need to visit is an otolaryngologist.
Necessary examinations: examination by a doctor, x-ray of the nasal sinuses.
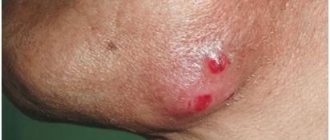
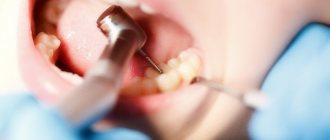
Tooth root abscess
A tooth abscess in a child is dangerous and requires urgent medical attention.
Inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes in children may be associated with a root abscess of the tooth. This complication develops against the background of advanced caries or a jaw cyst. An abscess is a large cavity filled with pus. Typical symptoms:
- noticeable swelling of the tissues around the tooth,
- acute excruciating pain,
- symptoms of general intoxication,
- increase in body temperature,
- lymphadenitis of the submandibular nodes.
The pathology is dangerous and requires urgent medical attention. A tooth abscess is the case when surgical intervention is performed immediately, since the abscess should not burst on its own, otherwise the purulent contents may enter the blood. Inflammation of the lymph nodes is caused by pathogenic microbes entering them.
The first alarming symptoms: compaction near the tooth, accompanied by severe pain. You should contact your dentist. The diagnosis is made based on an examination by a doctor and an x-ray of the diseased tooth.
Acute pulpitis
Another dangerous complication of advanced caries is acute pulpitis. The disease is manifested by inflammation of the neurovascular bundle (“nerve”) of a tooth affected by caries. The main symptom is acute excruciating pain.
Pulpitis affects a child’s baby teeth in cases of advanced caries and requires urgent treatment.
Pulpitis is potentially dangerous due to tooth loss. Baby teeth are rarely removed, but advanced pulpitis can complicate the growth of permanent teeth.
Gingivitis in children
With gingivitis, the submandibular lymph nodes in a child may become enlarged, as inflammation of the gums leads to a decrease in immunity
Another reason to visit a dentist in a children's medical facility is gingivitis. This pathology is manifested by inflammation of the gums. The cause of inflammation is a lack of oral hygiene and the presence of plaque and tartar.
Symptoms of inflammation:
- redness of the gums,
- swelling of the gums,
- painful sensations,
- increased pain during thermal exposure.
With gingivitis, the submandibular lymph nodes in a child often become enlarged, since the inflammatory process in the oral cavity negatively affects general immunity.
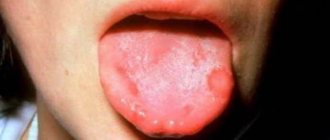
Oral fungus
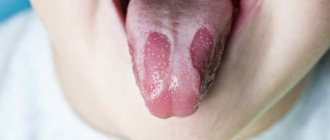
Another reason for enlarged lymph nodes under the jaw is fungal infection of the oral cavity. It is most often caused by a fungus of the genus Candida. This condition is also known as oral thrush.
Typical symptoms: whitish coating on the mucous membranes of the cheeks and tongue, the formation of ulcers (stomatitis), discomfort when eating. The mucous membrane affected by the fungus reacts negatively to sour foods. Eating spicy food causes pain in the mouth.
Oral fungus is most often encountered by young children, from the first days of life to 5 years. The proliferation of pathogenic microflora is associated with the imperfection of the child’s own immune system.
Alarming symptoms: redness of the oral mucosa and the appearance of a cheesy coating. The doctor you should contact is a pediatrician or pediatric dentist. To make a diagnosis, an examination and a throat smear are performed.
Drug treatment
Inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes in a child should not be treated independently, but should be immediately contacted by a qualified specialist.
Treatment of lymph nodes in children is aimed at eliminating the cause of their enlargement. For this purpose, antiviral drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs or antibiotics are prescribed, depending on the nature of the underlying disease and its causative agent.
A tooth abscess is treated surgically. The doctor opens the cavity and cleans out its contents, then stitches are applied. Pulpitis is treated either by removing the nerve (for permanent teeth) or using antibiotics (for children with baby teeth). For fungal infections of the oral cavity, the use of antimycotics and antiseptic rinsing solutions is indicated.
Symptoms of lymphadenitis behind the ears in children
If a child has a temperature of 37 - what to do?
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Dental Implantation for Oncological Diseases
The inflamed lymph node, located behind the child’s ear, is easy to feel. It resembles a pea placed under the skin. Along with an increase in the filter organ, other symptoms can be noted:
- runny nose;
- dry cough;
- red throat;
- high temperature;
- ear pain (otitis media);
- weakness;
- pallor.
Interesting! The enlargement of the postauricular lymph node can be affected by the eruption of teeth in the upper jaw. Inflammation of the gums causes an increase in lymphocytes, which, in turn, affect the size of the body’s filters.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine is powerless against pathologies of the lymph nodes, since they cannot be cured without knowing the cause of the development of lymphadenopathy.
As a rule, traditional medicine suggests using various decoctions and infusions for rinsing the mouth if swollen lymph nodes are associated with infectious processes in the mouth. For this purpose, decoctions of calendula, sage, oak bark, and chamomile are used. You cannot rely on such remedies; you must show the child to a doctor and consult with him about the advisability of using traditional medicine recipes.
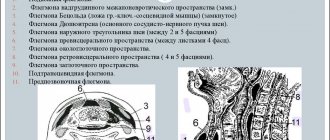
Lymph node locations
Lymph nodes are also called collectors. Because they collect lymph from the entire body. Lymph nodes can be superficial or splanchnic. It is impossible to detect the inflammatory processes of the latter without ultrasound.
The same cannot be said about external ones. Lymph nodes are classified depending on their location on the body:
- Occipital. They are located in the area where the neck meets the skull.
- The popliteal lymph nodes are located at the back, on the surface of the knee joint.
- The inguinals are located in the inguinal folds.
- The lymph nodes of the mediastinum are located in the chest cavity. This location is considered one of the most dangerous, since vital organs are nearby: heart, lungs, trachea.
- Axillary lymph nodes are located in the armpits. Their number constitutes a fairly powerful group of lymphatic tissue, which filters about 70% of lymph.
- The parotid can be located in front or behind the auricle.
- Facial lymph nodes are usually located on the lower jaw, cheek and chin.
We suggest you read: When to start brushing your baby’s teeth: at what age
They are also found in the area of the nasolabial folds, eyes and facial muscles.