October 5, 2020 Last revised: December 17, 2020 Oral diseases
Tonsillitis plugs are purulent accumulations ranging in size from 1 mm to several centimeters that form in the recesses (or lacunae) of the palatine tonsils. Often this pathology occurs with neglected or untreated tonsillitis. Suppurations cause a person pain and discomfort when eating, but at first they may go completely unnoticed.
The main reason for their appearance is pathogenic microorganisms that have entered the oral cavity, which, in the case of weakened immunity, begin to multiply intensively. In the absence of timely treatment, serious complications are possible, so at the first signs of the disease it is recommended to consult a doctor.
Main symptoms
The severity of symptoms depends on the size of the purulent formations and the stage of the underlying disease. Thus, with chronic tonsillitis, the signs of pathology are not as pronounced as in the case of its acute stage. The same applies to size: small tonsillitis plugs (from 1-2 mm) do not cause pain, while large ones cause discomfort and inconvenience.
In general, the symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- Unpleasant putrid odor from the mouth.
- White coating on the tongue.
- Redness of the mucous membrane of the larynx (visual examination).
- Severe swelling of the palatine tonsils with the formation of a yellowish-white coating on their surface.
- Painful sensations when swallowing.
- Unreasonable sore or burning sensation in the throat.
- Enlargement of the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes.
- Sensation of a foreign object in the throat (with large plugs).
Note! In the acute form of tonsillitis, intoxication of the body is possible, characterized by such symptoms as increased body temperature, headache, general weakness and malaise.
Main signs of manifestation
Often, plugs in the tonsils, especially if their size is small, may not appear for a long time.
If the pathology is in the acute stage, which is characterized by numerous large tonsillitis plugs, then the patient experiences the following symptoms:
- Large plugs enlarge the tonsils, which prevents free swallowing
Discomfort when swallowing. Nerve endings located at the site of inflammation become more sensitive. Large plugs enlarge the tonsils, which prevents free swallowing.
- Enlarged lymph nodes. It is the result of the outflow of infected lymph from the tonsils to the lymph nodes in the neck. As a result, they increase in size, become painful, and redness and swelling of the skin appear.
- Temperature change. According to the stage of progression and etiology of the disease, body temperature may be low-grade for several days, or it may rise sharply.
- General malaise. Dysfunction of the immune system and metabolic processes, characteristic of the formation of plugs of any etiology in the tonsils, is manifested by a general deterioration in health. Unreasonable weakness, rapid fatigue appears, and tone decreases.
- Spots on the tonsils. On visual examination, a change in the structure and color of the tonsils is observed. They become loose and can be white, yellow or dark in color. Their sizes also change upward.
Important! If you experience the slightest signs indicating the presence of plugs in the tonsils, you should immediately seek qualified help from an otolaryngologist.
Causes of tonsillitis plugs
The culprits for the appearance of purulent plugs are various microorganisms (streptococci, chlamydia, adenoviruses, staphylococci, etc.). They penetrate into the pharynx through the air and, in case of existing damage to the tonsils (small scratches, abrasions, etc.), cause an inflammatory process.
Other common causes of the disease include the following:
- Advanced form of caries.
- Untreated tonsillitis, sinusitis or tonsillitis.
- Weakened immunity (for example, after a serious illness or in case of a lack of vitamins).
- Severe hypothermia of the body.
- Inflammatory processes in the oral cavity and nasal sinuses.
- Communication with a sick person.
- Using other people's personal hygiene items (toothbrush, towel, etc.).
- Injuries to the tonsils that can be unknowingly caused by a fork, toothpick or fish bone.
- Deviation of the nasal septum.
- Wide lacunae (depressions) on the surface of the tonsils, in which food particles and dead cells accumulate.
Reasons for the formation of tonsillitis plugs
What causes accumulations of pus? There are quite a few different reasons. The most important of them:
Chronic tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils with periods of exacerbation and remission over a long period of time. Despite episodes of relative well-being, the “dormant” focus of infection causes local structural changes. This leads to disruption of the self-cleaning of the canals, accumulation and calcification of purulent masses.
Acute infections - purulent tonsillitis (lacunar, follicular, phlegmonous). In 8 out of 10 cases, plugs form during tonsillitis due to beta-hemolytic streptococci of group A. Less commonly, we are talking about staphylococci, viruses, and yeast-like fungi. There is information about the detection of Helicobacter pylori in the tonsils, but this infection does not play a decisive role in the formation of sore throats.
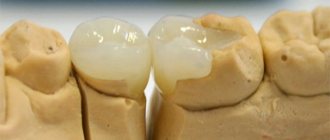
Tonsillitis plugs: what the photo looks like
Injury. Most often it occurs when eating rough food or getting a fish bone in the throat. Pus accumulates directly in the area of the resulting wound.
Anatomical features (wide lacunae in initially healthy people). Such tonsils are less self-cleaning; small fragments of food can get into them. This type of structure is for the most part a predictor of chronic inflammation.
In some sources, the causes include bad habits, unfavorable environmental conditions, anatomical defects of the respiratory tract (deviated nasal septum), and caries. In any case, they all lead to a decrease in local defenses and the formation of chronic foci of infection.
Diagnostics
If multiple purulent accumulations of several millimeters in size are detected (including painful sensations), you must consult an otolaryngologist (ENT) and undergo an examination. Otherwise, the situation may worsen, which will subsequently lead to complications.
In addition to a general examination and analysis of the patient’s complaints, patients undergo the following diagnostic procedures:
- Palpation - feeling the neck, larynx and lymph nodes for pain.
- Pharyngoscopy - examination of the pharynx and pharynx using a special mirror for the presence of plugs, redness and swelling.
- General blood test - allows you to identify pathogens in the body (or their absence).
- A smear from the inflamed area - to determine the microflora of the tonsils.
- X-ray of the paranasal sinuses - prescribed for prolonged runny nose and nasal congestion.
Differential diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis
Tonsillitis plugs have pronounced general symptoms, and with physical and laboratory tests, upon confirmation, a diagnosis of “chronic tonsillitis” is made. An instrumental examination is usually connected to a physical examination and consists of determining the purulent contents by pressing a spatula on the tonsils. Pus can be abundant or scanty in volume, in a liquid, mushy form, cloudy, yellowish. The detection of purulent contents indicates a chronic course of the inflammatory process in the tonsils.
Differential diagnosis implies that the symptomatic picture characteristic of chronic tonsillitis may appear under the influence of other foci of infection: pharyngitis, gum disease, dental caries. Therefore, it is important to distinguish chronic tonsillitis, for example, from vulgar tonsillitis (acute primary tonsillitis), hyperkeratosis of the pharynx and palatine tonsils (in which the desquamated epithelium is like plugs), malignant lymphogranulomatosis (in which the tonsils, cervical lymph nodes are enlarged, the spleen and other lymphoid formations are affected) and other diseases.
| The classic picture of tonsillitis plugs in chronic tonsillitis |
It is necessary to consult with different specialists (therapist, cardiologist, nephrologist, ophthalmologist, dentist, neurologist) if diagnosed with chronic tonsillitis. In some cases, additional examinations (ECG, radiography of the paranasal sinuses) will be required to determine all the causes and signs of the disease.
Treatment methods
To eliminate tonsillitis plugs, the following types of therapy are used:
- Drug treatment (taking antibiotics).
- Gargling.
- Irrigation.
- Inhalations.
- Folk remedies.
- Surgical methods of removal.
If the patient feels well (except for traffic jams), then treatment can be done at home under the supervision of a specialist. If purulent collections are accompanied by severe pain and fever, hospitalization will likely be required.
Why do plugs form in the throat?
The main cause of traffic jams is considered to be chronic tonsillitis. Some patients, having fallen ill with a sore throat (or acute tonsillitis), neglect qualified medical care, take medications uncontrollably, complete a course of antibiotics ahead of time, or do nothing at all in the hope that everything will go away on its own. As a result, a chronic disease develops, the consequence of which is the formation and deposition of caseous detritus in the tonsils.
Chronic tonsillitis is a disease in which periods of exacerbation are followed by a resting stage, when the sore throat does not bother the patient for some time.
But in moments of exacerbation, the symptoms, and with them the traffic jams, return.
The formation of purulent accumulations can also be provoked by:
- injuries and mechanical damage to the tonsils (for example, due to hard or tough food, bones accidentally falling into the throat, etc.);
- acute infectious diseases, such as purulent types of tonsillitis, also occur with the formation of tonsillitis plugs;
- anatomical features of the structure of the palatine tonsils - there are cases when the lacunae of a person’s tonsils are enlarged, and this is the norm for him. In such tonsils, the self-cleaning process is difficult, which leads to the accumulation of purulent masses in their thickness.
Indirect causes of traffic jams also include bad habits, poor environment, deviated nasal septum, dental problems - all these factors weaken the body’s defenses and lead to the formation of foci of infection.
Signs of a blockage in the throat.
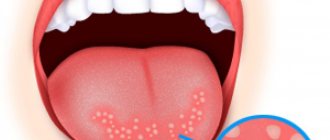
To diagnose tonsillitis plugs in yourself, you do not need a medical education: they are visible if you look in the mirror and open your mouth wide. Their appearance (if we are talking about chronic tonsillitis) coincides with the beginning of an exacerbation of the disease. But other signs also indicate the presence of caseous detritus in the lacunae of the tonsils.
- Bad breath.
- A sore throat
- Discomfort while swallowing.
- Thickening of the palatine arches.
- The surface of the tonsils becomes loose, adhesions and scars appear.
- Increase in body temperature to 37.5℃.
- Sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the throat (if the plugs are large).
- Malaise, weakness.
Caseous masses are pus, and pus tends to smell extremely unpleasant. Moreover, this smell is felt not only by the patient, but also by those around him. It is this symptom that brings many patients to the otolaryngologist’s office to remove blockages from their throat.
All these symptoms are a good reason to contact an ENT doctor to carry out comprehensive treatment of tonsillitis, including drug therapy, removal of tonsillitis plugs and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Taking antibiotics
The following antibiotics are prescribed to patients:
- Azithromycin is an antibiotic that has a bactericidal effect. Available in the form of tablets and capsules. It is recommended to take the drug 1 tablet orally 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals (but not more than once a day). Approximate course of treatment: 3 days. Approximate cost: 80 rubles (for 3 tablets).
- Amoxicillin is an antibiotic from the penicillin group. The drug is available in the form of tablets, capsules and granules for the preparation of suspensions. Approximate daily dosage: 1 tablet 3 times a day (children under 10 years old should take half a tablet). Take within 1-2 weeks. Average price: 140 rubles (12 tablets).
- Cephalexin is a drug with antibacterial and bactericidal action, which is produced in the form of capsules for internal use. Daily dosage: adults - one tablet (or half a tablet) 4 times a day, children - 1/4 several times a day. Course of treatment: 1-2 weeks. Price: 90 rubles (16 pcs.).
- Sumamed is an antibiotic of the macrolide group with a wide spectrum of therapeutic action. The product should be taken 1 capsule per day 1 hour before or a couple of hours after meals. Course of treatment: 3 days. Approximate cost: 450 rubles (for 3 tablets).
- Erythromycin is a bacteriostatic antibiotic in tablet form. Take half a tablet every 4-6 hours (either 1 hour before or 2-3 hours after meals). Course of treatment: 1-2 weeks. Average price: 107 rubles (for 20 pieces).
Self-medication with antibiotics is strictly contraindicated. Your doctor will help you choose the right dosage (depending on the severity of the symptoms) and course of treatment.
Rinse
Local antiseptics used for rinsing have not only antibacterial, but also anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. So, for the treatment of tonsillitis plugs, doctors recommend the following remedies:
Miramistin
For rinsing, use a 0.01% solution of Miramistin. A single dosage is 10-15 ml of the product (or 1 tablespoon), it does not need to be diluted with water. Directions for use: 30-40 minutes after eating, pour Miramistin solution into the mouth and gargle for 1-2 minutes, then spit out the product. Perform at least 4-5 times a day. The course of treatment is 10 days.
Furacilin
To prepare 200 ml of solution you need:
- Grind two Furacilin tablets to a powder (with a mortar or spoon).
- Pour the resulting powder into a glass and add 200 ml of warm water.
- After waiting for complete dissolution, mix and strain through cheesecloth.
Gargle up to 6-7 times a day, using the entire single portion of the product (200 ml). Course of treatment: 7-10 days.
Chlorhexidine
A 0.05% solution is suitable for rinsing. Before the procedure, it is recommended to first rinse your throat with warm water. Then gargle with Chlorhexidine for 30 seconds (single dosage: 1 tbsp). Do not eat or drink anything for the next hour. Perform the procedure 3-4 times a day for 5-7 days.
Soda-salt solution
To prepare the product you will need:
- Dissolve 1 tsp in a glass of warm water (approximate temperature 38-40 degrees). salt and baking soda.
- To increase efficiency, you can add a couple of drops of iodine.
Rinse up to 5-6 times a day. During and after the procedure, a slight burning sensation in the throat is possible. Approximate course of treatment: 7-10 days.
Note! In addition to rinsing, to increase the effectiveness of therapy, you can lubricate the inflamed tonsils with Lugol's solution 2-3 times a day (for example, using a cotton swab). The drug stops the spread of infection and facilitates easier separation of purulent plugs.
Irrigation
Irrigations are perfect for people who, for some reason, cannot rinse (for example, the elderly, small children). Such drugs are available in the form of aerosols (just spray the product onto the affected area). Here are some of them:
- Inhalipt - shake the bottle and spray the product into the mouth for 1-2 seconds. Carry out the irrigation procedure 3-4 times a day. Course of application: 5-7 days.
- Chlorophyllipt - spray into the mouth for 2 seconds, use 2-3 times a day. Course of application: 1 week.
- Cameton - spray the product into the mouth for 1-2 seconds, repeat the procedure 3-4 times a day. To improve performance, use the drug for a week (without skipping).
What are plugs in the tonsils of the throat?
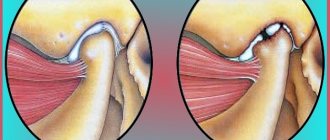
These are pathological accumulations in the tissues of the throat that fill the depressions in the tonsils. They consist of calcified substance. The plugs contain atrophied cells of the oral cavity, food particles and bacteria that decompose organic compounds.
Most often, these neoplasms are white with a yellowish tint. In some cases, there are gray, brown or red plugs. The color of the plugs depends on the main component.
Etiology of neoplasms:
- Unbalanced diet , in which monotonous protein-containing foods predominate. Poor content of foods with B vitamins and ascorbic acid, which leads to the development of vitamin deficiency.
- Improper hygiene creates favorable microflora for the proliferation of bacteria on the teeth and soft tissues of the oral cavity, and their migration into the lacunae of the tonsils.
- A decrease in the level of immune defense contributes to the activation of pathological microorganisms contained in the oral cavity.
- Chronic inflammation of the ENT organs of infectious etiology contributes to the constant release of bacteria into the nasopharynx area.
- Injury to the tonsils can cause infection. In addition, the wound can be an ideal place to localize purulent plugs.
Tonsil plugs - normal and pathological
Inhalations
For inhalation, it is recommended to purchase a nebulizer device into which the medication is poured. But you can get by with improvised means (for example, breathe over a pan of hot steam, covering your head with a towel). The duration of one procedure is 5-10 minutes. Frequency of use: 3-4 times a day. You need to inhale the steam very slowly.
So, for inhalation, decoctions of medicinal herbs are used (1-2 tsp per glass of boiling water):
- Chamomile flowers.
- Sage.
- Eucalyptus, etc.
Inhalations should not be carried out after walking in the fresh air. Upon completion of the procedure, you must dress as warmly as possible and avoid drafts in the room.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are effective in cases where tonsillitis plugs are small (no more than 1-4 mm) and the disease is mild, without intoxication of the body (fever, weakness, severe sore throat, etc.). In other cases, traditional methods can be practiced only as additional therapy and in no case should they replace the main treatment.
Here are some effective recipes using medicinal herbs and other traditional medicine:
- Oak bark decoction - 2 tsp. Pour a glass of boiling water over the dry product, cool slightly and strain through cheesecloth. Rinse every 3-4 hours. Course of application: 1 week.
- Decoction of sage and chamomile - pour chamomile flowers and sage (1 teaspoon each) with a glass of boiling water and let it brew for half an hour. It is recommended to gargle up to 5-6 times a day (until symptoms are eliminated or weakened). You can use grass in filter bags.
- St. John's wort decoction - 1 tbsp. l. dry raw materials, pour 2 cups of boiling water, cool and strain. Gargle a sore throat several times a day. Practice treatment for 5-7 days.
- Mint tea - 1-2 tsp. Pour a glass of boiling water over dry mint leaves, cool to an acceptable temperature (about 38-40 degrees) and drink as tea or use as a rinse. Repeat the procedure 2 times a day. Course of application: 1 week.
- Garlic broth - pour a few medium-sized cloves of garlic into a glass of boiling water, cool for half an hour and use for procedures (up to 4-5 times a day for a week).
- Fir oil - dip a cotton swab or gauze swab in fir oil and gently apply to the inflamed tonsils. After the procedure, it is not recommended to eat or drink for half an hour. Lubricate the tonsils with oil 2-3 times a day. Course of treatment: 1 week.
If, after using one or another product, an allergic reaction occurs (redness of the skin, rash on the face and body, itching, etc.), the procedure must be temporarily stopped and consult a doctor. Otherwise, an exacerbation of the disease is possible.
Pus on the tonsils: treatment
Treatment of purulent plaque is a set of measures aimed at removing the pathogen from the body, alleviating unpleasant symptoms and cleansing the tonsils.
Pharmaceutical drugs are the most effective part of drug therapy.
Drug treatment
All medications for treating the throat can be divided into two groups: general and local action. They complement each other, and also allow you to quickly get rid of the painful manifestations of diseases.
Systemic drugs:
Antibiotics.
They occupy first place in the treatment of tonsillitis. The drugs of choice with a wide spectrum of action are penicillins (Amoxiclav, Augmentin), cephalosporins (Zinnat, Cefuroxime), macrolides (Erythromycin).
Antihistamines
(Suprastin, Zodak, Tavegil). Slightly reduce irritation and pain in the throat, reduce tissue swelling.
Antipyretic drugs.
Used when body temperature rises.
It is preferable to take medications based on paracetamol, ibuprofen (Panadol, Nurofen), as they have fewer side effects. Local treatment includes gargling and throat sprays.
Rinsing is carried out with antiseptic solutions, decoctions, and infusions of medicinal herbs. The method allows you to partially wash out the purulent plugs in the lacunae.
Most often used:
- Saline solution. Prepare by adding a tablespoon of table salt to one glass of warm water.
- Sea water. The prepared solution is sold at the pharmacy.
- Soda solution. A teaspoon of baking soda is added to a glass of warm water.
- Furacillin. The ready-made solution is commercially available, or the tablet form of Furacilin is dissolved in warm boiled water and used according to the instructions.
- Sage infusion has an antimicrobial and calming effect. Prepared by infusing a teaspoon of sage in a glass of hot water for an hour.
How to gargle effectively:
- Take the solution into your mouth, tilt your head back and pronounce the sound “Y”. This facilitates irrigation of a larger area of the affected surface with the medicine.
- During the first days of the disease, you should alternately use different solutions for rinsing every 1-2 hours. After inflammation subsides, the interval can be reduced to 3-4 hours.
- After rinsing, do not drink or eat for half an hour.
- Children should gargle under adult supervision.
On topic: How to gargle correctly? Solutions. For children and adults
Irrigation of the throat with sprays that have an antibacterial (Bioparox, Faringosept, Gramicidin) or antiseptic (Cameton, Ingalipt, Tantum Verde, Lugol's solution) effect.
Depending on the constituent components, drugs can additionally have anti-inflammatory, analgesic, enveloping, wound-healing, softening, and moisturizing effects.
Folk remedies at home
The disease can be effectively managed. But it is necessary to understand that these methods should not be used independently, but only in conjunction with traditional medicine.
Before treating your throat with folk remedies, you should consult your doctor.
1
Gargling with chamomile decoction, which has a weak antiseptic, healing, anti-inflammatory effect. To prepare such a decoction, you need to pour two tablespoons of chamomile flowers into a glass of hot water.
2
Calendula tincture has an antimicrobial effect and reduces inflammation. The finished infusion is sold at the pharmacy. Mix a teaspoon of this solution with a glass of warm water and gargle several times a day.
3
Rosehip infusion has a strengthening and stimulating effect on the immune system. To prepare it, 40 grams of rose hips are poured with boiling water in a thermos and left to steep for 10 hours. Used instead of tea for oral administration.
4
Tea with lemon normalizes metabolic processes and increases the body's protective properties. Thanks to the vitamin C content in lemon, this tea helps relieve inflammation.
5
Chewing propolis has a softening, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and analgesic effect on the throat. It should be remembered that propolis, like any beekeeping product, is highly allergenic.
Therefore, it is used with caution, especially in persons predisposed to allergies. It is recommended to chew propolis up to 3 times a day for 15 minutes. [ads-pc-1][ads-mob-1]
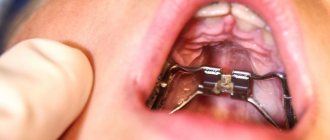
Is it possible to squeeze out tonsillitis plugs yourself?
Some patients believe that removing tonsillitis plugs is possible at home, especially if they are small in size (for example, squeeze out tonsillitis plugs with a cotton swab or tongue). However, experts categorically do not recommend doing this, since in this way you can introduce an infection through damaged tonsils and thereby cause complications. To do this, you should contact an otorhinolaryngologist and a specialist will carry out this procedure in a safe environment, without unpleasant consequences.
Causes
Tonsillitis plugs
Blockages in the throat often form as a result of complications of chronic tonsillitis. Tonsillitis plugs are more likely to form in the cold season; in summer, the development of the disease is observed less frequently. Chronic tonsillitis develops due to uncontrolled use of medications or poorly treated disease. Many patients stop taking antibiotics without completing the course of treatment, and this can lead to the development of purulent plugs.
There are also other reasons that can provoke another relapse:
- deviated septum;
- damage to the palatine tonsils;
- weak immunity;
- existing chronic areas of infection (rhinitis, carious teeth);
- bad habits (smoking, alcohol);
- allergic manifestations;
- bacterial, viral infections;
- hereditary tendency;
- hypothermia of the body;
- sinus infections;
- inflammation of soft tissues;
- adenoids.
The main irritants of tonsillitis are streptococci, staphylococci, and adenoviruses. With chronic foci of inflammation, the infection expands to the tonsils. Infection can occur through household contact and airborne droplets.
During pregnancy, the appearance of tonsillitis plugs is a common occurrence. Reasons: decreased immunity, hypothermia, chronic diseases.
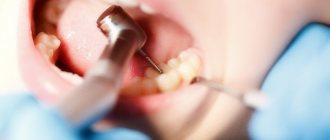
Surgical methods of treatment
Surgical intervention is usually resorted to in the most extreme cases: when purulent plugs have reached large sizes and are capable of blocking the airways. The operation involves partial or complete removal of the tonsils and is called tonsillectomy.
Palatine tonsils are removed using one of the following methods:
- The classic method - the operation is performed using a scalpel under local or general anesthesia.
- Removal using a microdebrider - a device with a rotating cutter (during its rotation, inflamed tissue is cut). Before surgery, the patient is given a strong painkiller.
- Laser removal - the diseased tonsil is grabbed with forceps and cut off using a laser beam (under local anesthesia). The procedure is contraindicated for small children.
- Electrocoagulation - inflamed tissue is cauterized with high-frequency electric current.
- Cryodestruction is the effect of cold on affected tissues (liquid nitrogen is used).
Possible consequences
In the absence of timely treatment, the following consequences are possible:
- Peritonsillar abscess (infection penetrates into the tissues adjacent to the tonsils and causes purulent abscesses).
- Cellulitis of the neck (purulent inflammation of the tissue).
- Sepsis (pathogenic microorganisms spread through the bloodstream throughout the body, causing damage to certain organs).
- Kidney failure (an extreme form of complication).
- Inflammation of the joints (streptococci penetrate the bloodstream and cause swelling of the lower extremities).