Causes of poisoning
Today, arsenic is widely used in some areas of human activity, it is also found in soils and minerals, and is suspended in water and air. Its use is widespread in the agricultural, electronics, metallurgical, woodworking industries, and medicine.
Poisoning with this dangerous substance is possible in the following cases:
- when living in areas where there is arsenic contamination of the environment,
- when inhaling polluted air,
- when consuming food or tap water that has a high concentration of arsenic,
- in direct contact with the substance during operation.
Effect on the body
This element of the periodic table very easily and quickly penetrates the human body in several ways: through the digestive tract, lungs or skin. Some arsenic compounds, such as inorganic ones, are absorbed much faster than organic ones.
The greatest danger to the population is arsenous hydrogen or arsine gas. Pure arsene has a neutral odor, so before use a special admixture is added to it, as a result of which it acquires a specific garlic “aroma”.
If arsenic enters the body, it will affect all human organs and systems within 24 hours. It spreads throughout the circulatory system, and after a couple of weeks it can be detected even in the epidermis, bone tissue, nails and hair.
There are two possible ways for it to be eliminated from the body through urine or feces. In the first case, removal is about 93%. And only 7% of arsenic compounds come out with feces. Even if the dose of a toxic element taken was a one-time dose, traces of it remain in tissues and organs even after two weeks.
From a medical point of view, arsenic affects the human body as follows:
- Forms a bond with blood hemoglobin when it enters the bloodstream,
- It spreads through the smallest vessels to all organs, affecting the nervous system,
- Disturbs the processes of oxygen metabolism of cells.
How can you get poisoned by arsenic?
Due to the widespread occurrence of this metal in nature, the environment, and in various industries, there are many ways of poisoning with this poison:
- Inhalation of toxic vapors;
- Eating foods treated with herbicides;
- Drinking untreated water;
- Excessive consumption of seafood (shrimp, oysters, mussels);
- Violation of safety precautions when working with alloys, paints and other toxic substances;
- Exceeding the dose of medications containing arsenic (novarsenol, aminarsone, miarsenol and others);
- Intentional poisoning in an attempt to kill or for suicidal purposes.
Arsenic can enter the body in 3 ways : through the lungs by inhaling vapors, through the digestive tract, through the skin and mucous membranes.
The most dangerous thing is inhalation of arsine (arsenic hydrogen) contained in the air; even small concentrations in the air - up to 0.05 mg/l - cause poisoning, and if it is about 5 mg/l - instant death occurs.
Questions are often asked: is it possible to get poisoned by a temporary filling that the dentist puts in to “kill” the nerve? Poisoning is unlikely, because a tiny dose of a toxic substance is applied, and after 2 days the seal is removed. If it remains in the tooth for a longer time, then not only the nerve, but also the tooth itself is destroyed, and stomatitis may develop.
Modern dental offices are abandoning the use of arsenic, replacing it with new, safer agents.
Symptoms of arsenic poisoning
The nature and degree of manifestation of acute damage by this toxin depends on the scale of the dose that entered the body. If it is very high, then poisoning can be fatal. Arsenic exposure also increases the likelihood of cancer in important organs such as the kidneys, lungs, liver, bladder and prostate.
The main symptoms of poisoning with arsenic compounds and the element in its pure form include the following:
- pain of varying degrees in the stomach,
- nausea turning into vomiting,
- diarrhea,
- slow regeneration of leukocytes and erythrocytes,
- cardiac dysfunction,
- changes in the elasticity of blood vessels and their damage,
- numbness in the extremities (lower and upper),
- paralysis of some parts of the body,
- convulsions,
- the appearance of a “garlic” odor from the mouth,
- partial blindness.
Men who work in industries associated with the harmful effects of arsenic may diagnose themselves with the following changes:
- abnormally rapid growth of the outer layers of the epidermis (hyperkeratosis),
- peeling and peeling of the skin even in those areas of the body that are protected by clothing during work,
- pigment formations in the area of the eyelids, temples, necks, chests in the form of red spots,
- white stripes on fingernails and toenails.
Arsenic antidote
Arsenic (Arsenicum) is a chemical element belonging to the group of semimetals. Designation in the periodic table is As. In its pure form, the substance has a gray color with a greenish tint and a fragile structure.
Arsenic and its compounds are highly toxic to all mammals, including humans.
This element received its Russian name for its field of application: with its help, rodents have been fought since ancient times, so the term is made up of two words - “mouse” and “poison”.
Arsenic compounds occur naturally:
- The element is part of many rocks (arsenic pyrite, silver, lead, gold, copper ores, etc.).
- Found in ponds and groundwater.
- Found in small quantities in seafood.
Near mineral processing plants, arsenic may be present in the air in the form of arsine - H3As. This gas is very toxic and is classified as hazard class II.
Arsenic is found in many pesticides and dyes. It is used in electrical engineering to create semiconductors.
Previously, arsenic was widely used in dentistry, placing it under a temporary filling to kill the nerve.
Most dentists now use less toxic treatments, but some doctors still use unsafe arsenic paste.
Causes of arsenic poisoning
Toxic compounds enter the body in several ways:
- by mouth – when swallowing drugs containing poison;
- when inhaling air containing arsine;
- through the skin.
Arsenic poisoning in humans can be caused by a number of factors:
- Unfavorable environmental situation: living near mining plants, ore processing plants, pesticide production plants, etc.
- Industrial accidents.
- Violations of technological processes in production.
- Picking mushrooms, fruits and berries in the technical area.
- Failure to comply with safe work practices when working with arsene-containing substances.
- Improper storage of rodent poison.
- Low quality of dental services.
- Consumption of water and seafood with high concentrations of arsenic.
- Attempted suicide.
- Attempted murder.
Most often, household arsenic poisoning is unintentional and occurs due to the consumption of poisoned products (mushrooms, water, seafood, etc.). Children are more susceptible to poison than adults.
Rodent pesticides left around the house often cause poisoning in children.
Signs of arsenic poisoning
Intoxication can be chronic or acute. In the first case, a person is exposed to small doses of poison for a long time.
They may meet the maximum permissible concentrations, but over time they accumulate in the body and cause serious disorders.
In the second case, a person is poisoned with arsenic after receiving a single high dose of the substance.
Symptoms of chronic intoxication
Poison ingested in small quantities can accumulate in the body for years. But already in the first month, chronic arsenic poisoning can be recognized by the following signs:
- whitish stripes on the nails;
- hyperpigmentation of the skin in the area of the armpits, scrotum and neck;
- severe peeling of the skin and its thickening.
Chronic intoxication leads to the development of encephalopathy and other pathologies of the nervous system. Often with arsenic poisoning, diseases of the respiratory system (bronchitis, tracheitis, etc.), heart, and liver occur. Since arsenic compounds are carcinogens, their long-term exposure can provoke the appearance of tumors.
Symptoms of acute intoxication
With a significant dose, symptoms of arsenic poisoning appear half an hour after ingestion or inhalation.
External signs of poisoning:
- general weakness;
- smell of garlic from the mouth;
- the occurrence of pain in the head and stomach;
- nausea followed by vomiting and frequent diarrhea;
- dehydration: extreme thirst, dry mouth.
The victim's heart rate accelerates and blood pressure drops. Failure to provide assistance at this stage of intoxication leads to the following consequences:
- Cardiac conductivity decreases and the pulse becomes irregular.
- Convulsive muscle contractions occur.
- Gastric bleeding begins.
- Laryngospasm leads to pulmonary failure.
- The victim falls into a coma.
- The skin turns yellow (due to the destruction of red blood cells).
- The urine becomes dark and kidney failure develops.
When 0.2 g of poison enters the body of an adult, symptoms develop very quickly. If you do not provide medical assistance to a person, he will die. For children, the lethal dose is 0.05 g.
The poison is absorbed into the blood especially quickly if taken on an empty stomach.
First aid for arsenic poisoning
If the intake of harmful substances occurs at work through the skin or respiratory tract, the victim should be immediately isolated from exposure to the harmful factor. He must be taken out from the scene of the accident into fresh air, having first called an ambulance.
If you suspect oral poisoning, you must first call an ambulance, then immediately begin gastric lavage (if the person has not lost consciousness). The following liquids can be used at home:
- Water;
- Saline solution (2 tsp/1 l of water);
- Suspension of magnesium sulfate (20 g/1 l of water);
- Ipeaquana syrup (1 tsp).
Lavage is carried out several times to remove as much poison as possible from the stomach. If the victim loses consciousness, the procedure should be stopped, turn the person on his side and wait for the ambulance team to arrive. Health workers should rinse the stomach of children and unconscious people using special equipment (probe).
Source: https://infomm.ru/protivojadie-ot-myshjaka/
Treatment of poisoning
Elimination of the consequences of arsenium exposure on the body must be comprehensive and begin with medical diagnosis. Doctors recommend taking urine, blood and hair (nails) tests.
Treatment of poisoning with arsenic-containing drugs consists of several stages. The first is stabilization of the victim’s condition: elimination of pulmonary edema, shock, arrhythmia, stopping bleeding, normalizing the electrolyte balance in cells and tissues. At the next stage, you need to remove the poison that has not yet been absorbed into the body. Chelation therapy is carried out after all previous operations.
First aid for poisoning
This measure is considered very important, since first aid will make it possible to stabilize the victim’s condition. Not only medical workers can provide it, if there is a first aid kit with the appropriate medications at the workplace. You should pour in a glass of water through your mouth (or using a probe), in which you have previously dissolved 3-4 g of tartaric or citric acid (can be replaced with one spoon of ordinary table vinegar).
Then the antidote in an amount of 100 ml should enter the human stomach. This is an antidote against metals - a stable solution of hydrogen sulfide water. It will neutralize the poison that gets inside, converting it into a completely harmless compound - arsenic sulphide. To enhance the effect, a standard gastric lavage is done and any sorbent that is available is given. It is also necessary to ensure a constant flow of fresh air into the room where the patient is located.
Antidote
An antidote in medicine is a substance that has the ability to bind and neutralize those toxic compounds that enter the human body during poisoning. Several substances can neutralize arsenic.
The main antidote to arsenic is unithiol. It forms non-toxic complexes with the poison in tissues and blood, which are gradually excreted in the urine. To ensure a neutralizing effect, 5-10 ml of unithiol is administered intravenously, drip or intramuscularly up to 4 times a day. Then the dose is reduced to 1-2 times a day.
Dimercaprol 5% solution is used for intoxication in the amount of 1 ml per 10 kg of adult weight. Immediately after poisoning, it is recommended to give up to 8 intramuscular injections (depending on the dose of the toxic substance). Then the number of drug administrations is reduced to 2-3.
If intoxication is chronic, then D-penicillamine is considered the best antidote for arsenic. The patient should take it orally about 4 times a day, 1 g.
Medicines
The outflow of fluid from human tissues and organs can be prevented by intravenous administration of calcium chloride, sodium thiosulfate or droppers from a mixture of saline solution with the drug adrenaline and glucose. If abdominal pain intensifies even after gastric lavage, then an injection of a certain amount of atropine with morphine should be given. In a situation where pronounced symptoms of renal failure appear, the doctor performs hemodialysis or a blood transfusion procedure.
Medical therapy of the patient
Treatment of the consequences of arsenic intoxication is quite long and can last up to 1-2 years. Therapy includes the use of known pathogenic agents, proper drinking regimen, alkaline baths and a balanced diet. The patient is advised to take sugar water, milk, and egg whites. But drinking a lot of water or using ammonia is prohibited. They are replaced with a solution of magnesia or egg white (1 egg white per ½ glass of water). As soon as the poison, which has not been absorbed into the tissues and organs, leaves the body, the patient should take as much fat as possible in the form of liquid (vegetable fats are ineffective).
Arsenic poisoning during dental treatment – OnlineTherapist
page Poisoning
Arsenic is one of the toxic chemical elements that can cause serious intoxication of the human body.
The substance has a wide range of applications, including in dentistry, which increases the risk of taking it in high dosages and ingestion.
To save a person and minimize dangerous and serious health complications, it is necessary to know the signs of arsenic poisoning and a set of measures to provide emergency care.
Causes and symptoms
The toxic substance and its compounds are used in agriculture and industry. It can be found in:
- ground and surface waters;
- in dyes, pesticides, antifungals, preservatives, herbicides and other chemical products;
- in seafood caught in areas with unfavorable environmental conditions;
- when burning various wastes, smelting ores and burning coal.
- inside electronic devices.
Poisoning can occur:
- in the respiratory system;
- on the skin;
- in the oral cavity.
After penetration, the poison enters the bloodstream and spreads throughout the body.
Acute intoxication poses a great danger to health. Entering the blood, arsenic reacts with hemoglobin and provokes the development of severe anemia. Jaundice may develop.
The first sign appears 30 minutes after the substance enters the body. When inhaled, the symptomatic picture develops instantly.
Pathogenesis:
- The person experiences increased thirst.
- General weakness, malaise.
- Headache.
- Decreased urine output.
- The mouth smells like garlic.
- Vomiting begins.
- The mucous membranes and skin are dry, the skin turgor decreases.
- Cramping pain in the abdominal area.
- Decreased blood pressure.
- Copious and frequent diarrhea, stool looks like rice water.
- Tachycardia.
If urgent medical care is not provided, the patient’s condition worsens, the degree of intoxication becomes more severe, which leads to damage to internal organs and systems.
Symptoms of severe arsenic intoxication:
- laryngospasm;
- convulsions;
- yellow coloring of the skin;
- the appearance of ulcers on the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract, which provokes bleeding and pain;
- arrhythmia;
- discharge of dark-colored urine;
- disturbance of consciousness and coma, replacing each other;
- destruction of red blood cells and release of hemoglobin into the environment;
- pulmonary edema and, as a result, respiratory failure.
There is a high risk of developing acute renal failure.
With regular intake of small doses of poison, the first symptom of poisoning appears after 2-8 weeks. During this period of time, chronic arsenic poisoning and significant changes in the body occurred.
First of all, the nervous tissue suffers, which leads to neuropathy and encephalopathy. These diseases cause impaired sensitivity of the skin and severe pain in the limbs.
Constant contact with a dangerous substance threatens damage to the heart muscle, which provokes diseases: myocarditis and pericarditis.
With chronic intoxication, there may be other problems with the health of internal organs:
- Bronchitis.
- Toxic hepatitis.
- Severe anemia.
- Laryngitis.
- Tracheitis.
Externally, intoxication is manifested by the following signs:
- thickening of the stratum corneum of the epidermis;
- increased formation of pigment spots and redness in the temples, neck, under the arms and in the scrotum area;
- increased peeling of the skin with its thickening;
- White transverse lines appear on the nail plates.
Arsenic has a highly toxic effect. The chronic version of poisoning often ends in the growth of malignant tumors on the skin and in the lungs.
First aid for intoxication
In case of acute intoxication with poison, first aid is called immediately!
Until the doctor arrives at the scene of the incident, proceed as follows:
- If poisoning occurs through the respiratory tract, remove the patient from the room where it occurred and provide a flow of fresh air.
- Place the unconscious patient on his side so that he does not choke when he vomits.
- If there are no signs of life or consciousness, perform resuscitation yourself. To do this, clean the oral cavity, removing vomit and foreign objects from it. First perform chest compressions, and then take two large breaths into the victim’s mouth. Immediately perform 30 compressions on the chest area. These rescue operations are best carried out together.
- If the substance enters the mouth, it is necessary to rinse the stomach. For these manipulations, warm, clean water is used. It is important that the patient is conscious at this time! Give him plenty of water until he vomits. Quantity is not limited. If there is no vomiting, press on the root of the tongue.
- You can remove arsenic from the skin with water and detergent.
- To prevent dehydration, the victim must constantly drink water in small portions.
- It is allowed to take the sorbent, but with small doses of poisoning.
Do not treat yourself! Do not take laxatives!
In all cases, specialized medical care is required. For mild intoxication, outpatient treatment is possible. Moderate and severe degrees require regular monitoring with the patient staying in a hospital.
Therapy in a medical institution involves a set of measures. First, laboratory diagnostics are carried out. Only a blood and urine test can determine the severity of the disorders.
Using an antidote
A specific antidote for arsenic is available in all medical institutions. It is dimercaprol, the main potent component of the drug Unithiol. Once the substance enters the body, it attracts poison, binds its molecules and is excreted naturally along with urine.
The antidote for dangerous arsenic is calculated strictly according to the patient’s weight according to the following scheme: 2-3 mg/1 kg. It is administered intravenously. On the first day of injection every 6 hours, in the next 2 weeks it is necessary to place droppers twice a day.
The dose of the drug depends on many factors: the adult or childhood age of the victim, the dose of poison in the body, the severity of intoxication, etc. A timely professional approach allows you to quickly eliminate the serious consequences of contact with a dangerous substance.
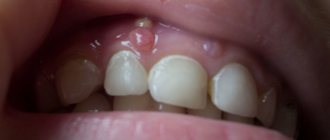
Is it possible to get arsenic poisoning during dental treatment?
When a tooth hurts, many people are deprived of the ability to think rationally and completely surrender to the hands of a specialist. To reduce pain, the doctor adds arsenic. The substance kills nerve cells, causing them to stop responding and hurt. For several decades it was used everywhere, like iodine.
A paste containing arsenic anhydride is applied under the temporary filling. The maximum period of stay in the oral cavity is 3-7 days, depending on the concentration of the paste. Extending the period threatens poisoning. Toxins affect the tooth and the tissues surrounding it. As a result of prolonged exposure, inflammation of the gums develops, which threatens bone necrosis.
Signs of poisoning begin with an unpleasant metallic taste in the mouth. Tell your doctor about this to prevent complications.
If even small doses of arsenic enter the body of a pregnant woman, it can cause health complications for the expectant mother and disturbances in the development of the fetus. The most common consequence is a miscarriage or the birth of a child with psychological and physical defects.
The body of a pregnant woman is under serious stress, it is weakened, and the risk of intoxication exists even during dental treatment. Bone tissue is weak and the risk of accidental ingestion of arsenic is high. The use of poisonous paste in this category of patients is prohibited.
In other cases (if you follow safety precautions and correctly calculate the concentration of a toxic drug), poisoning during dental treatment is an unlikely occurrence. The pharmaceutical market offers a wide range of medicines that do not contain toxic components.
Arsenic pastes are used today in rare cases.
Possible complications and prevention
Arsenic poisoning is dangerous to life and health. The consequences are severe and are associated with massive damage to vital organs and systems of the body. Chronic poisoning provokes the development of kidney and liver failure and failure of the lungs. With serious damage to the nervous tissue, patients become disabled. In severe cases, death is possible.
Prevention:
- if production involves chemicals, follow safety precautions;
- do not drink water from unfamiliar sources;
- refuse to work at an enterprise where arsenic is used if your health worsens;
- Keep these products out of the reach of pets, the elderly and children.
Always read package labels! Arsenic causes serious poisoning in humans!
Poisons can turn a healthy person into a disabled person or take his life. They are especially dangerous for young children and people with weakened bodies.
If arsenic accidentally enters the body through inhalation or ingestion, immediately call an ambulance and begin to eliminate the dangerous consequences yourself. Your task is to reduce the concentration of the substance in the body so that it causes less harm to internal organs and systems.
If you follow all the recommendations quickly and correctly, you can save a person and keep him healthy. Remember! Do not use unknown powders or products of unknown origin! Is it dangerous!
Link to main publication
articles:
Source: https://onlineterapev.ru/otravlenie-myshyakom-pri-lechenii-zubov.html
Possible consequences
The consequences of exposure to a dangerous toxin on the body can result in any of the symptoms. With prolonged exposure to arsenic on human health (for example, at work), pathological changes are observed in the structure of the skin and lungs. Such poisoning is especially dangerous for children. They experience long-term consequences in the form of decreased hearing acuity, impaired speech activity and coordination of movements.
Most often, even after time, people suffer from polyneuritis with pain. Exposure to arsene causes a significant decrease in immunity, which can aggravate chronic diseases. The effect of the toxin on the central nervous system is accompanied by dizziness and pain in the temples, forehead, and back of the head.
Causes of death from arsenic poisoning
Arsenic poisoning can occur purely by accident, for example, in children or in people exposed to occupational hazards at work.
The source of arsenic poisoning can be poisons and chemicals that enter the human body through the gastrointestinal tract, skin, or inhalation. With constant long-term work in hazardous industries, a person experiences chronic arsenic poisoning.
There are two types of arsenic poisoning, which can cause death. The first type of arsenic poisoning is called paralytic, and occurs with large doses of arsenic. With such arsenic poisoning, the following symptoms of intoxication occur - damage to the central nervous system, expressed in fainting and spasms, coma and paralysis of the systems responsible for breathing and blood supply. From the gastrointestinal tract, symptoms of paralytic poisoning such as diarrhea and vomiting are noted. Death from paralytic arsenic poisoning can occur almost immediately after the poison enters the body or on the first day.
The second type of arsenic poisoning is gastrointestinal. With this poisoning, such manifestations of intoxication as a taste of metal in the mouth, a burning sensation in the throat and profuse vomiting occur. Later, as the disease develops, abdominal pain and diarrhea, as well as convulsions, are added to these symptoms.
As arsenic poisoning progresses, diarrhea begins to take on the appearance of mucus. The body suffers from dehydration. Due to blood thickening, serious disorders of the cardiovascular system and nervous system begin to develop. The cause of death is usually heart failure. Depending on the intensity of arsenic poisoning, the victim can live from one day to a week.
Acute arsenic poisoning is expressed in nausea and profuse vomiting, abdominal pain and cramps. In addition, after poisoning, stomatitis begins to develop and blood pressure rises. In severe cases of acute arsenic poisoning, intravascular coagulation is observed, which leads to kidney failure. Quite often this condition leads to the death of the victim.
In case of chronic arsenic poisoning, the manifestations are less intense. There is sudden weight loss, nausea, diarrhea or, on the contrary, constipation. Disorders of the nervous system in the periphery can lead to sensory disorders and muscle weakness. If arsenic poisoning lasts a long time and is severe, then disturbances in worldview, epileptic seizures and death are noted.
Treatment of arsenic poisoning
In case of acute arsenic poisoning, it is necessary to take all measures to improve the condition of the victim as soon as possible. It is necessary to prevent further penetration of the poison into the body, to remove the amount of the toxic substance that has not had time to be absorbed into the walls of the gastrointestinal tract. To do this, thoroughly cleanse the stomach using enemas.
In case of a decrease in blood pressure, injections of corticosteroid drugs are required. Normalization of the water-electrolyte ratio is of great importance. If the victim experiences excruciating pain, then, as a rule, therapy for arsenic poisoning is based on the use of unithiol, which is administered intramuscularly. In case of severe poisoning, a blood transfusion may be necessary. With timely treatment, all disorders that occurred due to arsenic poisoning can be restored.
source
Prevention
Treatment of arsenic intoxication is quite complex and lengthy. Therefore, doctors strongly recommend using all possible preventive measures to help avoid it. In potentially hazardous workplaces, you should use personal protective equipment, follow all safety rules, and undergo regular examination at a medical facility. Never buy products from little-known manufacturers, use in everyday life only water that has gone through all stages of purification. Never store substances at home that contain even a minimal percentage of arsene.
Is it possible to get poisoned during dental treatment?
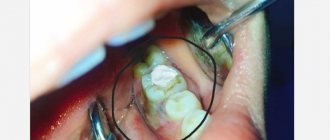
Previously, almost every dental clinic used arsenic paste for dental treatment. In modern offices it is no longer used so often. But if a filling is placed on the affected tooth from this particular material, then it can remain inside for no more than two days, otherwise complications and intoxication cannot be avoided.
There are the following features of dental treatment with arsenic paste:
- the material is used if it is necessary to anesthetize the soft tissue inside the tooth, and modern means cause allergic reactions,
- after arsenic gets on the nerve, it dies,
- poisoning from such a small dose of a substance is impossible even when the patient is a child,
- It is allowed to keep arsenic paste on single-rooted teeth for up to 24 hours, and on the rest - no more than two days.
If during the treatment you accidentally ate part of the paste, then poisoning will not occur. But dentists recommend taking the following measures:
- Prepare a warm infusion of chamomile or a weak solution of baking soda, rinse your throat, mouth and hole in the tooth thoroughly,
- Blot the space in the tooth with a clean cotton swab,
- Take any sorbent that is in your home medicine cabinet, drink a glass of warm milk,
- Visit a specialist who will eliminate the possibility of poisoning.
Clinical picture
Signs of arsenic poisoning in humans are quite varied. Poisoning develops quite quickly and within 30 minutes if a large dose is ingested by any route, the symptoms will be pronounced. In such a short period of time, symptoms increase quite quickly, provided that the person has an empty stomach. In most such cases, everything ends in death, since in the absence of food the mucous membrane quickly absorbs toxins into the blood. Symptoms of arsenic poisoning will vary from person to person.
If arsenic was consumed in food, symptoms appear after a few hours. The following symptoms are observed in case of arsenic poisoning:
- Headache.
- Signs of intoxication (weakness, malaise).
- Stomach ache.
- Rice-water-like stool.
- When breathing, you can smell garlic.
- Intense thirst.
Since such poisoning affects most important organs and systems, the corresponding signs can be detected:
- From the cardiovascular system, palpitations, decreased blood pressure, and poor pulse filling are observed.
- From the nervous system, mental disorders, hallucinations, even coma can be observed.
- From the respiratory system, there is difficulty breathing, swelling of the larynx and lungs.
- From the gastrointestinal tract there is a burn of the larynx, ulcers of the stomach and intestines, as well as possible bleeding.
- When urinating, the urine becomes dark in color. Accompanied by the development of jaundice.
- The kidney tubules become blocked, which provokes the development of acute renal failure.
When urinating, blood appears in the urine. Basically, such poisoning is characterized by gross hematuria and therefore the presence of blood is easy to determine. Depending on the symptoms that appear, gastrointestinal and paralytic forms are distinguished. In the gastrointestinal form, symptoms associated with disruption of the gastrointestinal tract predominantly appear. In the paralytic form, neurological symptoms appear that can develop to coma.
If chronic poisoning occurs, then symptoms appear from 2 to 8 weeks after the toxin enters the body. Due to the poison, the cerebral cortex suffers and encephalopathy develops. When nervous activity is disrupted, problems with the lower extremities appear. This mainly manifests itself as weakness in the legs.
Due to damage to the heart muscle, the development of myocarditis and pericarditis is provoked. If the liver is damaged, hepatitis may appear. The level of hemoglobin in the blood decreases, which provokes anemia. This is why nails become brittle and severe hair loss occurs.
When exposed to arsenic, not only the functioning of organs and systems changes, but also the structure of hair and nails is disrupted. This is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Redness on the eyelids, armpits, pubis, scrotum;
- Skin growth;
- Peeling and detachment of skin;
- White stripes appear on the nails.