When to panic and run to the doctor if you find a green coating
In the morning, almost all people develop a small white-yellow coating on the tongue, which disappears after hygienic cleaning of the oral cavity. If this does not happen and the plaque is difficult to remove, dense, and of an uncharacteristic color, you should consult a doctor. This symptom can appear in an adult, a child, and even an infant. The tongue can have absolutely any color - from white to black, and sometimes even green. Such plaque on the tongue in adults and children most often occurs due to fungal infections, as well as as a consequence of natural aging of the body, HIV infection, diabetes mellitus or cancer. Read more about what this symptom means, why it occurs and how to treat it in today’s material.
Reasons for rejection
Factors that can cause the formation of green deposits on the tongue are:
- A dark green coating on the tongue indicates hormonal imbalances and dehydration.
“Emphasis” on fatty, spicy, heavy foods, which impair liver function. This causes not only the formation of green plaque, but also constant dry mouth;
- Long-term use of antibiotics. Such medications affect the composition of the microflora in the digestive tract and oral cavity, reducing the number of beneficial bacteria. Under such conditions, pathogenic microorganisms actively develop, the waste products of which contribute to the appearance of plaque;
- Failure to comply with hygiene standards for oral care;
- Fungal diseases of the oral cavity, usually oral candidiasis. The green color of plaque is caused by chromogenic fungi, which usually develop in people with reduced immunity;
- Intoxication of the body with carcinogens, salts, heavy metals;
- Diseases of the digestive tract. In this case, in addition to the appearance of a green coating, cracks form on the tongue;
- Diseases of the oropharynx of a viral and bacterial nature (chronic tosillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis);
- Changes in hormonal levels (often a green coating on the tongue appears during puberty);
- Alcohol abuse, smoking, drug use;
- HIV infection;
- Injuries to the tongue and subsequent infection (for example, during piercing);
- Decreased immunity.
Important! Another reason for the appearance of a green coating on the tongue is a lack of nutrients and vitamins in the body.
What does pathological plaque on the tongue look like?
Before deciding what a coated tongue means and what it is talking about, that is, before making a final diagnosis, the specialist needs to carefully examine the patient’s oral cavity, and also take into account all the accompanying symptoms and complaints. A slight yellowish coating is not a reason to worry. Its formation may be associated with natural physiological processes occurring in the body. If the surface of the tongue has acquired a greenish tint, you should consult a doctor. Perhaps it is a matter of some hidden pathology. Thus, plaque may differ in the following characteristics:
- color, its intensity (we repeat that the norm is a white or slightly yellowish, easily detachable coating),
- consistency (oily, dry, curdled),
- thickness,
- localization.
Why might there be a green coating on the tongue?
What can this mean if a patient has a greenish film on his tongue and a fever? Most often, such symptoms indicate the development of an infectious process in the body. In any case, it is better to immediately consult a doctor so that he can detect the problem at an early stage and offer timely treatment.
Symptoms
Since plaque on the back of the tongue is itself a symptom of various pathologies, doctors need to somehow distinguish between all possible ailments. Therefore, the indicator manifests itself in the following signs:
- plaque thickness - indicates the degree of development of the disease;
- localization – full or partial coverage of the language;
- ease of cleaning - quick and gentle removal is the norm, but compaction of the layer and difficult removal indicate obvious problems;
- consistency – wet, dry, curd or fatty.
The symptoms of the disease are quite extensive. Plaque on the tongue may be accompanied by a number of other signs that indicate a particular disease:
- a sore throat;
- bad breath from the mouth;
- dyspnea;
- belching;
- broken stool;
- heat;
- change in skin tone;
- heaviness in the stomach;
- weakness;
- anxiety.
The appearance of a green tint on the surface of the tongue is a signal of many diseases and abnormalities. The presence of any specific pathology can be determined by the main parameters of plaque.
These include:
- If deposits are present in the form of a thick layer, it can be concluded that the disease progresses over a long period of time
. Consistency. Plaque can be dry, wet, or greasy; - Deposit thickness. If the layer of green plaque is thin, then this indicates the initial stage of development of the pathological process. If deposits are present in the form of a thick layer, it can be concluded that the disease progresses over a long period of time;
- Hue. The darker the plaque covering the surface of the tongue, the more dangerous the disease that caused the appearance of such a symptom;
- Extensive plaque. Deposits can be observed both over the entire surface area of the tongue and in its individual areas (for example, at the tip or root);
- Easy to remove. The harder the deposits are removed, the more serious the pathology progresses in the body.
Only a specialist can identify the true cause of the appearance of a green coating on the tongue after carrying out diagnostic measures.
Why does the symptom occur?
So, now let’s figure out why a suspicious green coating forms on the surface of the tongue of a child or adult. The cause of this symptom is most often associated with certain disturbances in the functioning of individual organs or internal systems:
- decreased immunity and, as a consequence, the body’s vulnerability to attack by pathogenic bacteria, or more precisely, fungi,
- improper functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, increased stomach acidity,
- irritating toothpastes and rinses,
- food products containing dyes,
- smoking,
- tongue injuries, including piercings,
- pregnancy,
- taking certain medications: hormone replacement therapy, oral contraceptives, certain antibiotics and corticosteroids.
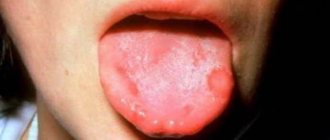
This is what a fungal infection on the tongue looks like
“This morning I discovered green spots on my one-year-old son’s tongue. We made an appointment with the pediatrician. The doctor examined him. It turned out that antibiotics weakened the baby’s immunity. A month ago we suffered from pneumonia. The pediatrician told me to treat my mouth with a special solution.”
Yulia Egorova, 28 years old. Tobolsk
Diagnostics
First you need to make an appointment with a therapist. Based on the results of the initial examination, the specialist will prescribe the necessary diagnostic measures.
In order to identify the reasons why the tongue may have turned green and what this symptom means, the following is carried out:
- blood sampling for tests - general, biochemical, to determine hormone levels;
- collecting plaque fragments to study the composition;
- bacteriological culture from the mucous membrane of the tongue;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs;
- fibrogastroduodenoscopy.
Consultation with specialized specialists (for example, an immunologist) may also be required.
In order to identify the reasons why the tongue may have turned green and what this symptom means, an examination is carried out
Types and associated manifestations
As part of the diagnosis, the specialist must take into account the main characteristics - first of all, the color and intensity of manifestations. Conventionally, several varieties of green plaque can be distinguished, depending on the shade, location and accompanying symptoms. Let's look at these types in more detail.
White with light green spots
A small thickness of plaque is normal. This color may appear during hot weather due to loss of moisture and dehydration. If the tongue is covered with a dense white film, the patient most likely has hyperthermia (high temperature), which indicates an inflammatory process. A sore throat combined with a symptom can trigger an upper respiratory tract infection.
Streptococcal and staphylococcal infections give rise to a white-green coating on the tongue and the presence of viscous, purulent contents on the surface of the tonsils and in the maxillary sinuses. Oral candidiasis is caused by yeast fungi of the genus Candida and also leads to the formation of a white-green plaque1.
White coating with light green spots
Yellow-green or gray-green
This symptom may be a consequence of a recent inflammatory disease of the ENT organs. Yellow-green or gray-green plaque appears in the following cases:
- pathologies of the liver and gall bladder (hepatitis, cholecystitis),
- diseases of the stomach and intestines (gastritis, gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, colitis),
- pathology of the duodenum (pancreatitis),
- diseases of the adrenal glands and kidneys,
- pulmonary pathologies.
Yellow-green coating on the tongue
If the color of the surface of the tongue changes and a light green coating appears, it is better to see a doctor immediately. Timely diagnosis will allow you to identify pathology at an early stage, and therefore quickly cure it.
Dark green coating
This is one of the signs of severe functional disorders of the digestive system (GIT). If nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or general intoxication occurs, urgent assistance from an infectious disease specialist is required.
If the dark green coating is accompanied by a burning sensation, as well as growth and enlargement of the taste buds, a so-called “hairy” tongue can be diagnosed, which most often becomes a consequence of poor hygiene, dehydration, radiation therapy, long-term use of antibiotics, and too frequent consumption of coffee , tea and smoking.
Dark green coating on the tongue
Green-brown and black-green
Green-brown plaque indicates dangerous and severe pathologies of the hematopoietic system. With complicated infectious lesions of the intestines, in particular with cholera, dehydration occurs catastrophically quickly: the blood thickens, the intensity of saliva production decreases, and the black-green coating on the tongue thickens. In the absence of the necessary treatment, everything can end in death.
Green-brown coating on the tongue
Symptoms
Normally, in a healthy person, the surface of the tongue may be covered with a thin layer of translucent white coating.
There is no: unpleasant odor, formations on the oral mucosa, elevated body temperature, or enlarged lymph nodes.
If green plaque is detected, you should consult a doctor, since the symptom indicates the presence of some kind of disease, unless, of course, you have previously consumed products with green natural pigment or food coloring.
A greenish coating indicates the following health problems:
- fungal infection (most often thrush, chlamydia);
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the gallbladder and pancreas;
- infectious diseases (sore throat, HIV, colds);
- the presence of helminths in the body;
- oncology.
When diagnosing, the totality of symptoms is taken into account, so in addition to the green plaque, specialists also take into account other manifestations that are uncharacteristic of a healthy person.
Thickness
A rich color and a dense layer of plaque indicate a complex pathology, the presence of chronic diseases.
During examination, the thickness of the layer is studied. The thinner it is and the lighter the color, the milder the form of the disease.
A rich color and a dense layer of plaque indicate a complex pathology and the presence of chronic diseases.
If problems with diet, insufficient hygiene or bad habits are identified, it is easier to get rid of the symptoms; just quit smoking/alcohol, review the menu, making it balanced, and follow all the rules of hygiene procedures.
In just a week nothing will remind you of the problem. If after 5 days the thickness of the plaque and its dislocation have not changed, then you cannot do without the help of a specialist.
Easy to remove
If the layers are easily removed, then the disturbances in the body are minor, close to normal.
Dense plaque is difficult to remove; even with mechanical force, it is impossible to get rid of it with a spatula. This sign indicates a pathological condition of the body.
Consistency
During visual inspection, attention is paid to the consistency of the green layer. The plaque itself can be dry, greasy, cheesy, or moist. Each symptom, in combination with other signs, indicates a specific problem in the body.
Localization
Eastern healers identify diseases in particular by language. When detecting an unnatural coating, they took into account the location of the green spot.
Each section of the lingual surface reflects the functioning of an internal organ:
- the tip of the tongue is responsible for the heart;
- behind the spleen – the center and zone closer to the base;
- the functioning of the liver and gall bladder can be assessed by the lateral parts of the tongue;
- the core and the area closer to the tip are responsible for the lungs;
- the intestines are diagnosed by the root.
When visually examining the tongue by a specialist, these data are also taken into account.
Since green plaque is an independent symptom of a number of diseases, it may differ in some associated symptoms.
Among them are:
- Tongue overlay thickness. This symptom can tell you about the extent of the disease that caused the plaque. If the layer is thin, then the pathology is just beginning, for example, it could be ARVI or influenza. When the layer of overlay is thick, the disease progresses for a long time and, most likely, it is associated with more serious problems than a mild infection.
- An important symptom is the location of the plaque: whether the tongue is completely covered with it, or the deposits are located in separate areas.
- Ease of removing plaque from the organ. If it is soft and easy to remove, then in some cases this may be normal. If the deposits are caused by organ pathology, then the plaque thickens and removing it becomes problematic.
- Depending on the reason that caused the formation of plaque, its consistency changes. It can be wet or dry, curdled or oily.
How is diagnosis carried out: we establish the exact cause of the pathology
Self-diagnosis is ineffective - only a specialist can make the correct diagnosis. The therapist or dentist will conduct a visual examination and pay attention to the shade, density and volume of pathological deposits. For in-depth diagnostics, the doctor will prescribe tests and refer you to specialized specialists. You may need to take a clinical blood and urine test, an immunogram, an HIV test, as well as kidney tests to detect kidney inflammation and adrenal dysfunction.
After examination, the otolaryngologist prescribes bacterial culture of the oral mucosa for microflora and sensitivity to antibiotics. If inflammation is confirmed, the specialist will prescribe a course of antibiotic therapy for at least 7-10 days. An x-ray diagnosis of the paranasal sinuses may also be required to rule out sinusitis and sinusitis.
The gastroenterologist prescribes a biochemical blood test, fibrogastroscopy (FGS) with sampling of gastric juice, duodenal intubation and bile sampling, sigmoidoscopy to exclude ulcerative colitis. The results of these tests will help to exclude the presence of gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, and diagnose hepatitis and bile duct dyskinesia. An abdominal ultrasound may also be prescribed. In severe cases, it is necessary to diagnose vascular pathologies, infectious diseases with similar symptoms and exclude cancerous tumors.
Color palette of deposits on the tongue
With different diseases, the plaque differs in shades.
| Plaque shade | Meaning |
| Yellow-green | Liver diseases, congestive processes in the gallbladder, acute infectious intestinal processes, adrenal dysfunction |
| White-green | Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract |
| Gray-green | Ulcerative lesions of the stomach or duodenum |
| Dark green, black-green | Hormonal imbalances, dehydration |
| Brown-green | Alcoholism, smoking, dysfunction of the respiratory system |
| Light green | Lack of vitamins, anemia |
| Analysis of health status by the shade of plaque on the tongue | |
| Name | What disease does the shade indicate? |
| Yellow-green | This symptom indicates the following problems: diseases of the biliary tract, congestion in the gallbladder, excess bilirubin in the body. Yellowness may appear against the background of ARVI, after taking certain medications. |
| White-green | Such plaque does not cause concern if it is easily cleaned off and disappears spontaneously. If there is an intensive build-up of green deposits, you should sound the alarm, because the symptom may indicate an infectious disease. Localization of plaque at the root indicates problems with the gastrointestinal tract (enterocolitis, stomach ulcer, gastritis, duodenal ulcer). |
| Dark green | A dark green or black-green tint is rarely observed and indicates a serious pathology in the body: pancreatic dysfunction, disorders in the bile ducts or gall bladder, dehydration, Crohn's disease, cholera, etc. |
| Gray-green | The color of the plaque indicates problems with the digestive system. After conducting research, the gastroenterologist will determine for sure whether the problem is in the intestines, stomach, or an ulcerative lesion. |
| Brown-green | A brownish color on a green coating indicates fungal or bacterial flora, hepatitis, and acute intestinal poisoning. The shade is also considered characteristic of people who abuse alcohol, as well as heavy smokers. |
Green coating on the tongue - how to treat it
The treatment process can be short-term in the presence of easily correctable conditions. It will take more time to identify the pathology. Treatment methods in this case include the following:
- regular and high-quality oral hygiene (brush your teeth and tongue, rinse your mouth after every meal),
- rinsing with “Chlorhexidine”, “Chlorophyllipt”, “Furacilin”, “Miramistin”. The drugs are used according to the instructions,
- using a special scraper to clean the tongue,
- normalization of diet and drinking regime - you need to reduce the amount of salt consumed, give up fatty and spicy foods.
Chlorhexidine is often prescribed for the treatment of pathology.
As we have already found out, the phenomenon under consideration is not an independent pathology, but a symptom of disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems. Therefore, in order to get rid of the greenish coating once and for all, you need to eliminate the root of the problem.
If you have a fungal infection
As we have already noted, it is a fungal infection that is the main reason for the appearance of green deposits on the tongue. As a rule, it is localized in the oral cavity. Therefore, in such a situation, antibiotics will definitely be prescribed - but, preferably, after passing the appropriate tests. However, you shouldn’t hesitate either - the situation can be dangerous.
The specialist will also prescribe general strengthening and immunostimulating drugs, multivitamin complexes and sorbents, as well as agents that normalize intestinal microflora.
For other pathologies
Here, of course, you need to contact a specialized specialist to prescribe specific treatment - these are various drugs to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, compliance with the drinking regime and diet.
Diseases accompanied by this symptom
Normally, in a healthy person, the surface of the tongue may be covered with a thin layer of translucent white coating.
There is no: unpleasant odor, formations on the oral mucosa, elevated body temperature, or enlarged lymph nodes.
If green plaque is detected, you should consult a doctor, since the symptom indicates the presence of some kind of disease, unless, of course, you have previously consumed products with green natural pigment or food coloring.
A greenish coating indicates the following health problems:
- fungal infection (most often thrush, chlamydia);
- dysfunction of the gastrointestinal tract;
- diseases of the gallbladder and pancreas;
- infectious diseases (sore throat, HIV, colds);
- the presence of helminths in the body;
- oncology.
Is it possible to use traditional medicine?
To eliminate the symptom (namely, the manifestations, but not the treatment of the underlying disease!) You can use vegetable oil. A small amount should be kept in the mouth for 15 minutes. Then spit it out and clean the surface of the tongue using a brush or a special scraper.
Gargling with medicinal herbs will help in treatment
It is also recommended to rinse your mouth with a decoction of herbs: mint, calendula, St. John's wort. To do this you need to take 15 grams. each of the herbs, brew the mixture in 250 ml of boiling water and let the product brew. You can wipe the surface of the tongue with a soda solution: 2 tbsp. You need to dilute it in 150 ml of water, then moisten a cotton pad or gauze pad in the resulting solution and cleanse it. The procedure should be repeated twice a day.
It is important to immediately note that traditional medicine can only act as a supportive therapy, but not the main one! Do not try to self-medicate, because you can not only aggravate the situation, but also trigger the pathology, bring it to the stage of development when complex and lengthy treatment, possibly even surgery, is required. You can use “grandmother’s” recipes only after agreement with your doctor.
Treatment
The choice of treatment method depends on what disease, manifested as a green coating on the tongue, was identified during diagnostic procedures.
Conservative treatment
The choice of treatment tactics directly depends on the presence of a particular pathology in the patient.
Table 2. Treatment of diseases that cause the appearance of a green coating on the tongue:
| Cause | Treatment method |
| Fungal diseases of the oral cavity | Antifungal drugs (Clotrimazole, Amphoglucamine, Miconazole). Such drugs act on the lesions and reduce the amount of plaque. Antimicrobial and antiparasitic drugs are also prescribed that stop the proliferation of fungi (Fluconazole, Diflucan). |
| Hormonal disorders | Hormone replacement therapy (drugs are selected individually, depending on which hormone levels need to be brought back to normal). Women are prescribed various hormonal contraceptive drugs (Logest, Yarina), men are prescribed drugs containing androgens (Andriol, Proviron). For diseases of the endocrine system, vitamin and mineral complexes containing iodine are prescribed. |
| Long-term use of antibiotics, which provoked dysbacteriosis | Antibiotics and antifungal drugs. Additionally, probiotics (Linex, Bifiform) are prescribed, which “seed” the intestines with the correct microflora. In order to create conditions for the growth of beneficial microorganisms, Lactofiltrum and Duphalac are prescribed. |
| Diseases of the throat and larynx | For diseases of a viral nature, it is recommended to take antiviral (Kagocel, Cycloferon, Amiksin) and immunomodulatory (Interferon, Anaferon) drugs. |
| Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract | The prescription of a specific drug also depends on the disease found in the patient. For example, for gastritis and peptic ulcers, medications are prescribed that promote the proliferation of epithelial cells and have an antibacterial effect. These are Afobazol, Gastal, Perfectil, Iberogast, Arpenal. For diseases of the pancreas, it is necessary to take medications that protect it from the action of aggressive factors (Ketorol, Pilobact, Omez). For increased acidity, drugs such as Pentagastrin and Afobazol are indicated. |
| Liver diseases | To restore the liver, drugs of various origins are recommended - plant (Gepabene, Karsil, Hofitol), animal (Hepatosan, Essliver, Phosphogliv, Essentiale Forte). |
Traditional methods of therapy
Also, if a green coating appears on the surface of the tongue, you can use folk recipes to remove it. It should be borne in mind that such products only eliminate plaque, but not the cause of its appearance.
In this case, the following tools will help:
- It should be borne in mind that folk remedies only eliminate plaque, but not the cause of its appearance.
Mouth rinse composition with essential oil. To prepare the solution, take 15 drops of mint or eucalyptus essential oil and add them to 250 ml of warm water. Rinse your mouth every 3 hours;
- Soda-salt solution. Add half a teaspoon each of soda and fine salt to 200 ml of warm water and mix. Rinse your mouth every 2-3 hours;
- Essential oil with antibacterial effect. When plaque forms, it is best to take pine, eucalyptus, lavender or tea tree oil. You need to put a teaspoon of oil into the oral cavity and hold it, without swallowing, for 15 minutes. After this, spit out the oil and rinse your mouth with water;
- Herbal infusion for internal use. You need to take 30 g of raw material from a mixture consisting of oregano, plantain leaves, linden and yarrow, pour 300 ml of boiling water. Divide the broth into equal parts and drink them throughout the day, in three doses;
- Baking soda solution for wiping mucous membranes. Add 2.5 teaspoons of soda to 200 ml of warm water, stir, dip a gauze swab into the resulting mixture. You need to clean the surface of your tongue in this way up to four times a day.
Important! If a green coating appears, you must consult a doctor promptly and not self-medicate, as this sign can signal dangerous pathologies.
Prevention measures
To minimize any risk of an unpleasant symptom, competent and systematic prevention of diseases of the oral cavity and digestive system should be ensured. In this regard, experts suggest being guided by the following principles:
- double daily brushing of teeth and oral cavity,
- rejection of bad habits,
- normalization of diet and drinking regime,
- use of multivitamin preparations,
- undergoing preventive examinations for early diagnosis of pathologies,
- timely treatment of chronic diseases.
The tongue serves as a kind of indicator of the state of the whole organism. If spots, dense plaque of an unhealthy color, or suspicious growths appear on its surface, you should immediately run to the doctor. The sooner you seek help from a professional, the easier and faster the problem can be resolved.
- Banchenko G.V. Language is the “mirror” of the body: a clinical guide for doctors, 2000.
Disease prevention
The best option for any disease is not treatment, but prevention. Disease prevention includes a number of actions:
- keep the house and children's room clean - wet cleaning and disinfection must be carried out daily;
- Do not self-medicate your child under any circumstances - antibiotics and other medications must be agreed with the doctor;
- a child’s tongue, like an adult’s, is normally pink in color without ulcers or plaques (with the exception of white plaque on the infant’s tongue) - take this into account and regularly monitor the child’s oral cavity;
- sweets containing synthetic dyes should be excluded from the diet as much as possible - this will prevent color changes, the appearance of plaque, and protect delicate children’s teeth from irritants;
- support the child’s immune system with natural vitamins - fresh berries and vegetables, dairy products;
- If any symptoms of the disease appear, immediately seek qualified medical help.
The tongue is an indicator of the health of the body. Regular monitoring of the appearance, color, and shape of the tongue will increase the chances of recognizing organ problems in the early stages, and the shade of possible plaque will indicate the location of the disease.
Take care of your children's health!