Leukoplakia of the tongue is a serious disease of the oral cavity, which is accompanied by the appearance of white hair on the mucous membrane. Hairy leukoplakia is more often associated with weakened immunity, and is almost always diagnosed in HIV-infected people.
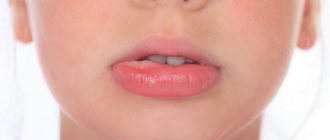
Visually, in such patients you can see a whitish coating on the tongue, but it can also be in the form of a gray spot. The onset of the pathology is asymptomatic, but in the future it brings a lot of discomfort and health problems.
In addition to the tongue, hairy leukoplakia affects the mucous membrane of the cheeks, the floor of the mouth, and in advanced cases it is observed on the genitals. Treatment of this disease is aimed at increasing immunity, that is, eliminating the root cause of the pathology.
Causes of the disease
The direct etiological factor in the occurrence of a pathological focus of hyperkeratosis is the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). 90% of the planet's inhabitants are infected with this virus. Its activity is inhibited by T lymphocytes. With a significant decrease in the level of immunity, EBV activation occurs.
Estain-Barr virus
Experts identify the following risk factors:
- infection with human immunodeficiency virus;
- acute leukemia;
- regular use of drugs that inhibit the body’s protective properties;
- smoking and alcohol abuse;
- irradiation of the mucous membrane with ultraviolet rays;
- galvanosis of the oral cavity, which develops when installing multi-component metal prostheses;
- chronic trauma to the tongue, cheeks and gums due to orthodontic and orthopedic structures.
What are the symptoms of leukoplakia?
Leukoplakia is dangerous because of its hidden onset. And there are no characteristic symptoms at the initial stage. And, nevertheless, certain signs of the development of pathology are present.
Symptoms of the disease may be as follows:
- formation of white or grayish spots on the mucous surface of the oral cavity (tongue, gums, cheeks, palate);
- gradually its surface coarsens and becomes rougher to the touch;
- eventually the stain will harden.
The process of transformation of the mucous membrane is most often not accompanied by painful sensations. But sometimes the inflamed surface can react to touch, and also become irritated when eating spicy or hot food.
Clinical picture of the disease
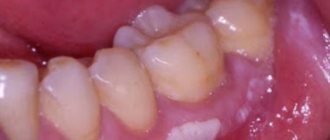
In most cases, only a dentist can detect symptoms of oral leukoplakia, since the disease, as a rule, is asymptomatic. The most striking sign of this pathology is a grayish or whitish coating on the mucous membrane of the tongue. Sometimes such lesions are concentrated on the gums, cheeks or soft palate.
Appearance of a tongue affected by hairy leukoplakia
Pathological lesions can be unilateral or bilateral. Sometimes they spontaneously disappear and form again. Subjective complaints in patients appear when a fungal infection occurs.
In such cases, patients complain of:
- mild discomfort in the mouth;
- progressive change in taste properties;
- feeling of constant dryness in the mouth.
Pathogenesis of hairy leukoplakia
In the initial stage of the disease, whitish folds become noticeable on the surface of the tongue against the background of the rough mucous membrane. These pathological lesions rise above the surrounding soft tissues.
Some authors note the similarity of the hyperkeratosis area to a “washboard”. Further progression of the disease is accompanied by fusion of plaques.
In this case, a spot ranging in size from 1 mm to 3 cm is formed. The disease gets its name from the fact that leukoplakia on the tongue, due to damage to the filiform papillae, resembles a lump of hairs.
Hairy leukoplakia of the tongue
Stages of development of leukoplakia of the tongue
The disease develops quite slowly and goes through several stages. The danger of the disease is that in the initial stages a person does not experience any unpleasant sensations. In addition, quite often the inflammation is located at the base of the tongue, which makes it completely invisible. The stages of pathology are formed in the following order:
- The first stage is characterized by the appearance of small foci of inflammation.
- The next stage is the beginning of keratinization of the epithelial layer, accompanied by the formation of white spots typical for this pathology. Quite often visually they resemble a white coating, but it is impossible to remove it yourself. And in this case we can already talk about the presence of simple (flat) leukoplakia.
- Then the condition worsens and a verrucous form of pathology develops. Here the surface of the spot becomes covered with warts. In this case, the spots become denser to the touch and begin to rise above the surface of the oral mucosa.
- In the absence of adequate treatment, the surface of the inflamed area cracks and the disease develops into an ulcerative form.
Advice! The ulcerative form of the pathology is an already advanced stage of the disease, dangerous because if left untreated it can turn into cancer.
Diagnosis of the disease
Instructions for diagnosing dental diseases include the following activities:
- Anamnesis collection . During a preliminary interview with the patient, the specialist pays special attention to detecting signs of immunodeficiency in the form of sudden loss of body weight, night sweats, periodic rise in body temperature, bouts of diarrhea and increased susceptibility to infectious diseases. At the same time, the doctor checks with the patient whether he has HIV infection.
- Visual and instrumental examination of the oral cavity. At this stage, the dentist examines the location, size and consistency of the pathological focus.
- Biopsy. The collection of biological material allows for a histological examination, the result of which is the final diagnosis.
Laboratory analysis of biopsy
Diagnosis of leukoplakia
In addition to a visual examination of the patient by a doctor, to make an accurate diagnosis, the patient should undergo a number of procedures and tests:
- general urine examination;
- bacterial culture of urinary fluid;
- Nechiporenko test;
- analysis to search for atypical cells in the mucous membranes of the bladder and ureters;
- general and biochemical blood tests to identify possible changes in blood parameters;
- immunogram - a blood test aimed at identifying any traces of changes in the immune system;
- tests that determine the presence (their absence) of trichomonas, chlamydia, mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas, infection of which can only be through sexual contact;
- Ultrasound of the bladder, uterus and appendages, which will determine the usually associated diseases, such as endometritis, inflammation of the ovaries, cervical erosions, which are foci of infection and provocateurs of inflammatory processes in the ovaries, uterus, vagina, bladder;
- a biopsy to clarify the actual diagnosis, if fibrourethrocystoscopy indicates the presence of transformations in the mucous membrane;
- histological examination of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity in case of doubts about clinical data, allowing to differentiate leukoplakia from other diseases, such as lichen planus, lupus erythematosus, as well as some forms of candidiasis and syphilis, in order to identify tissue transformation;
- cytological examination to determine possible cellular modifications towards oncology.
Leukoplakia is often mistakenly considered to be mild leukoplakia, which most often affects very young members of the population and women. Elderly men suffer from a typical type of disease, which is caused by excessive drinking and smoking. Partial keratinization of tissue is present in both forms of leukoplakia.
It has been determined that almost 90% of patients bite on particles of the oral mucosa, and then white spots can be seen on the bite marks. A typical form of leukoplakia affects young people and middle-aged patients, and in older people, accumulations of keratinized lesions in areas of the lower lip are visible as pre-oncological hyperkeratosis of the red lip edge.
Treatment methods
Treatment of the disease is predominantly conservative, but in some cases specialists may resort to a surgical solution to the problem.
Drug treatment of hairy leukoplakia
If this pathology develops against the background of HIV infection, the patient is prescribed antiretroviral therapy in the form of taking the following drugs:
- reverse transcriptase inhibitors (ddidanosine, lamivudine and zidovudine);
- HIV protease inhibitors (nelfinavir, saquinavir and indinavir).
Drug therapy
In each clinical case, treatment of oral leukoplakia requires drug activation of the body's protective properties. To do this, doctors include immunomodulators and immunostimulants in the course of therapy.
If the patient has a concomitant fungal infection of the oral mucosa, the patient should additionally take antimycotics (amphotericin B, fluconazole and ketoconazole). At the local level, the pathological focus of hyperkeratosis should be treated with keratolytic agents and medications based on retinoic acid.
Surgery
Radical intervention for leukoplakia is usually a last resort. In such cases, the dental surgeon removes the atypical lesion using a laser beam. The price of such treatment is determined by the qualifications of the surgeon and the level of the medical institution.
Laser therapy in dentistry
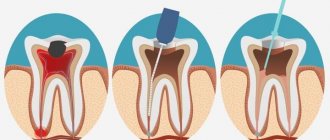
Procedure for radical treatment:
| Surgical manipulation | Clinical picture |
| Anesthesia |
|
| Excision of the pathological focus |
|
| Postoperative treatment |
|
Treatment of leukoplakia of the tongue
The disease, no matter what stage of its development it is in, requires treatment adequate to its current condition. And, first of all, the doctor is engaged in establishing the causes that caused the development of inflammation in order to eliminate them, if possible.
At the initial stage, treatment consists of adjusting incorrectly installed or inappropriately sized dentures. It is necessary to carry out professional sanitation of the oral cavity and eliminate dental problems with teeth. It is also important to start taking vitamin complexes and quit smoking.
Treatment also includes drug therapy necessary to relieve the consequences of the inflammatory process. One of its stages is local treatment of the oral cavity.
Treatment of flat leukoplakia
The disease, which has not yet reached the verrucous stage and is diagnosed at the level of a small whitish plaque, can be treated without any problems. To remove plaque you can use:
- laser;
- radio waves.
Treatment of advanced forms of leukoplakia of the tongue
If the pathology was detected at later stages and became malignant, then therapy is carried out in two stages. Treatment is performed according to the following scheme:
- surgical intervention is performed;
- a course of radiotherapy (as a rule, this stage of treatment is quite long in time).
Upon completion of the course of therapy and the onset of recovery, a person with a predisposition to inflammation of the oral mucosa needs long-term outpatient observation.
The risk of re-inflammation, even with successful treatment, still exists. Do not forget that the symptoms of the disease increase gradually and can develop over several years.
Alternative treatment for leukoplakia of the tongue
Drug treatment can be combined with traditional medicine recipes.
Purified (odorless) olive oil or regular sunflower oil helps eliminate inflammation and get rid of irritation in the mouth. You need to soak the tampon in oil and treat the areas of leukoplakia formation several times a day.
Disease prognosis
Hairy leukoplakia, in the absence of symptoms of severe immunosuppression, has a favorable course. Thus, timely elimination of the irritating factor and conservative therapy lead to a complete recovery of the person.
But all antiviral treatments can only slow down the activity of the Epstein-Barr virus. As a result, another decrease in immunity may be accompanied by a recurrence of leukoplakia.
The most severe consequences are observed in HIV patients. Their pathological lesions can degenerate into malignant tumors.
Definition of leukoplakia
The most severe form of pathology is considered to be its development in conjunction with HIV infection. To prevent the appearance of Burkitt's lymphoma, specialists send the patient for chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Hairy leukoplakia is a disease of the oral mucosa that occurs due to the fourth type of herpes virus (Epstein-Barr) and most often affects patients with HIV infection and people who have recently undergone surgery or undergone an internal organ transplant.
This disease received its name because of its pronounced symptoms: the affected area of the mucous membrane as a result begins to become covered with white villi. In this case, the inner surface of the tongue is more like a fleecy carpet.
The disease includes three forms:
- Simple. In this case, there are white spots that cannot be easily eliminated.
- Verrucous. Flat spots in the form of plaques and warts spread across the surface of the mucosa.
- Erosive. There are ulcers on the surface of the pathological area, which eventually develop into malignant formations.
Leukoplakia - modern diagnostic methods, treatment methods and disease prevention (145 photos)
Leukoplakia is a disease characterized by damage to the mucous surface, resulting in a pathological change in the epithelium.
When the disease occurs, the lesions acquire a white or grayish tint. The danger of leukoplakia is that it can acquire a malignant form.
Etymology of the disease
If leukoplakia occurs with characteristic symptomatic manifestations, the patient is sent for an examination, as a result of which areas of dead cells of white or gray color are identified.
The edges of the affected area are clearly defined, the shape and size may vary.
Most often, the disease does not cause discomfort, so patients do not rush to medical specialists for advice.
Doctors classify the disease as precancerous, since under the influence of a number of negative factors it can provoke a transition to a malignant form.
The main signs of pathological complications include compaction of the lesion, the formation of erosion, the occurrence of proliferation and an increase in size.
The patient may be diagnosed with leukoplakia of the oral cavity, respiratory tract, anus and genitals.
Types of leukoplakia
Depending on the form and characteristics of appearance, the disease is divided into several types:
- simple (flat) - is a film of cloudy texture, has clear boundaries and a rough surface;
- warty - characterized by the formation of small plaques;
- erosive - can cause pain to the patient, has clear edges and a grayish-white color, often cracks appear in the central part of the affected area;
- hairy - the area has a hairy covering, occurs as a result of insufficient activity of the immune system or as a result of HIV diagnosis.
Most often, the disease forms in the cervix and is discovered during an examination by a gynecologist.
In this case, the patient may notice pain, discomfort during sexual intercourse, and discharge with an unpleasant odor.
Causes
Currently, several possible factors that can influence the occurrence of the disease are known.
The most common ones include:
- the presence of a virus in the human body;
- injury to internal organs;
- thermal or chemical effects;
- presence of bad habits;
- use of stimulators made of latex or silicone;
- avitaminosis;
- decreased activity of the immune system;
- predisposition at the genetic level.
The appearance of the disease on the genitals can be caused by a cauterization procedure using electric current.
Gastric leukoplakia is diagnosed as a result of the activity of existing pathological processes in the gastrointestinal tract.
Symptomatic signs
The signs of the disease that appear are largely related to the factor that provoked the development and the area of localization.
The initial form of the disease is characterized by the occurrence of an inflammatory process in a separate area of the mucous membrane. Gradually keratinization occurs.
The most common signs of the disease include:
Cervix. It is characterized by the appearance of bloody discharge and unpleasant sensations during sexual intercourse.
Oral cavity. There may be a burning sensation and tightness. Often there is a violation of taste functions.
Larynx. Accompanied by a constant dry cough, a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the larynx, and hoarseness.
Leukoplakia of the bladder and urethra. It is characterized by the presence of pain in the lower abdomen, reminiscent of cystitis, and disruption of the process of emptying the bladder.
Genital organs. Accompanied by gradually increasing pain, swelling and burning.
Most often, at the initial stage of development, the disease is not accompanied by visible symptomatic signs. The appearance of symptoms of leukoplakia indicates the development of a pathological process.
Diagnostic measures
Typically, diagnosis is made by examining the affected area. Doctors take into account the possible presence of symptoms.
A histological examination is mandatory to confirm the diagnosis and exclude pathologies with similar symptoms.
Therapeutic measures
When the diagnosis is confirmed, patients have a question about how to treat leukoplakia. There are several ways to treat leukoplakia. The technique is selected depending on the location of the pathology.
The main ones include:
Diathermocoagulation. It is a cauterization process using high temperatures. The method is not good enough due to the possibility of endometriosis.
Exposure to liquid nitrogen. The procedure is carried out using low temperatures to provoke the necrosis of pathological cells. Subsequently, restorative therapy is required.
Laser therapy. The method is considered the most popular and modern. Carbon dioxide laser is used for treatment.
Use of radio waves. The procedure is painless and quick.
Most often, surgery is required after childbirth or the shape of the cervix has changed. In such a situation, therapy involves removing the affected tissue areas.
Disease prevention
To prevent the occurrence of the disease, certain recommendations must be followed.
Special attention should be paid to hygiene standards: regular sanitation of the oral cavity, optimal prosthetics. Rejection of bad habits.
Identification and elimination of pathological processes must be timely. Patients should monitor metabolic processes in the body and the state of the immune system.
Possible complications
The most dangerous complication is the transition of pathology to cancer. Most often this is possible when diagnosing oral leukoplakia.
If the patient has been diagnosed with cervical leukoplakia, then in the absence of timely diagnosis and treatment, infertility may occur.
Forecast
In the absence of any complications, the further prognosis is favorable. In the absence of timely treatment, the transition of the disease to a malignant form cannot be ruled out.
After eliminating leukoplakia in women, in the future, when planning pregnancy and during the period of bearing a child, regular medical supervision is required. In some cases, relapse cannot be ruled out.
Photo of leukoplakia
Please repost
Source: https://doktorvilechit.ru/lejkoplakiya/
Leukoplakia - treatment and symptoms of the disease; Features of treatment on various organs
Leukoplakia affects the mucous membranes. It causes keratinization of varying degrees of severity. The disease itself is highly treatable if detected early. It can appear in both men and women. There are also manifestations in children.
Leukoplakia is a focal chronic inflammation of the mucous membrane, accompanied by varying degrees of keratinization of the epithelium
Types of leukoplakia
Leukoplakia comes in several types. With flat leukoplakia, the mucous membrane becomes cloudy. The cloudiness looks like a pale film, but it is not removed with a cotton swab or by scraping. The mucosal surface becomes dry.
With verrucous leukoplakia, white plaques or grayish growths several millimeters high appear. Erosive leukoplakia is characterized by the appearance of cracks and erosions in the affected areas. Painful sensations may appear.
There is also a type of disease known as Tappeiner's leukoplakia (or smoker's leukoplakia). At the same time, the entire soft palate turns white and becomes completely horny. The disease goes away quickly if you undergo therapy in time and quit smoking. Oral leukoplakia most often appears before the development of a cancerous tumor, so action must be taken as soon as possible.
The disease may also appear on the tongue. Leukoplakia of the tongue manifests itself in the same way as in any part of the mouth. White film and plaques can appear on any side of the tongue, although they usually appear on the back of the tongue.
If the disease resolves without complications and does not cause tumors after removal of the lesions, then it is called simple leukoplakia.
But it is still recommended that patients continue to be observed by a doctor for some time in order to detect abnormal cell growth in time.
Leukoplakia most often appears on the oral mucosa, although there are other cases. Thus, with leukoplakia of the cervix, the multilayered epithelium is affected. This may be accompanied by leucorrhoea, but in general the disease is initially asymptomatic. Leukoplakia of the vulva is much more pronounced.
The stratified epithelium becomes keratinized, whitish plaques appear, and the woman complains of itching and burning on the external genitalia. Leukoplakia of the labia can occur together with kraurosis of the vulva. With kraurosis, the skin becomes thinner, gradually loses pigmentation and becomes easily wounded.
Itching is also observed, almost constant, intensifying at night. When leukoplakia affects the bladder, its walls are covered with keratinized squamous epithelium, which does not protect against the effects of urine. Chronic inflammation occurs.
This disease occurs much more often in women than among men.
Leukoplakia can also affect the cervix
In men, leukoplakia can also occur on the external genitalia. Leukoplakia of the penis is a rather rare disease. People with diabetes are more susceptible to it.
This disease is also considered precancerous and should absolutely not be neglected. The disease manifests itself in the form of whitish spots with raised edges on the mucous membrane.
Leukoplakia of the esophagus usually occurs as a consequence of heartburn, burns of the mucous membrane. It leads to half of the cases of esophageal cancer.
Doctors also distinguish hairy leukoplakia. This type of disease is a sign of HIV infection. Hairy (or hairy) leukoplakia is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus, which develops against the background of immunodeficiency.
The difference between hairy leukoplakia is the possible presence of whitish growths on the lesions that resemble hair. This disease usually appears on the tongue (hairy leukoplakia of the tongue), on one or both sides.
Sometimes hairy leukoplakia can be localized on the cheek. Lesions of this kind are usually not painful.
If leukoplakia appears during pregnancy, then there is no need to panic. Stress and nervous strain can have a negative impact on the development of the fetus. But leukoplakia itself does not harm the gestation and development of the unborn child.
The problem lies elsewhere. During pregnancy, a woman’s body may be susceptible to the growth of various formations, and leukoplakia can often be detected only during a routine examination by a gynecologist.
So visits should be regular.
Leukoplakia can appear in both adults and children. Among children it occurs between the ages of 5 and 15 years. And it is almost always a consequence of chronic mechanical injury, and is called soft leukoplakia. Such damage can be caused by the habit of biting lips and cheeks, for example, when a child is nervous. Manifests itself in the form of keratinized scales in the oral cavity.
Symptoms, causes and diagnosis of leukoplakia
As previously written, the main symptom of leukoplakia is whitish spots and plaques. These affected areas become horny and dry. But such symptoms can be found independently only if they appear in the oral cavity or on the external genitalia.
If leukoplakia of the bladder develops, it can only be detected through examination. But most patients complained of frequent urination and pain. Cervical leukoplakia is also almost impossible to detect without examination.
But if it appears along with other diseases, then usually there is itching, pain during and after sexual intercourse, as well as discharge that has an unpleasant odor.
If leukoplakia begins to develop on the penis, then whitish spots first appear in the area of the external opening of the urethra. Usually the affected surface is smooth, but cracks may appear. Patients quite often complain of difficulty urinating. This occurs due to narrowing of the urethra in the warty form of the disease.
Leukoplakia usually appears in men over the age of 30. The consequence of advanced leukoplakia can be penile cancer. If alarming symptoms appear, you should consult a urologist or andrologist for advice.
In children, soft leukoplakia can be of two types: typical and atypical. In the typical form, the affected areas are painless and are usually located along the line of the teeth on the cheeks or lips. But with an atypical form of soft leukoplakia, lesions can spread throughout the entire oral cavity.
There are many reasons for the development of oral leukoplakia. For example, alcohol, especially strong and in uncontrolled quantities. It irritates the mucous membrane, just like smoking.
The tars contained in cigarettes not only contribute to irritation of the mucous membrane, but also support the inflammatory process.
Excessively hot, salty, spicy foods also contribute to the disruption of the integrity of the mucous membrane not only in the oral cavity, but also lower in the esophagus.
An equally likely cause of the disease can be a side effect from medications, as well as poor-quality dental crowns and sharp edges of the teeth, which damage the integrity of the oral mucosa. Patients with HIV, anemia, diabetes and problems in the gastrointestinal tract (gastrointestinal tract) are at risk.
The causes of the development of leukoplakia of the bladder can be: diseases of neighboring organs, promiscuity, diseases of the endocrine system, hypothermia.
Leukoplakia of the bladder is the process of formation of pathological epithelial plaques on its mucosa
Many reasons can also lead to the development of vulvar leukoplakia. It is usually a sign of chronic inflammation. The disease is also promoted by impaired metabolism (including due to obesity), constant trauma to the vulvar mucosa, and vitamin A deficiency.
In addition, it is not recommended to neglect the rules of personal hygiene; this is fraught not only with leukoplakia, but also with a number of other unpleasant diseases. Women over 40 are also at risk due to a disruption in the body’s hormonal balance, which is associated with age-related changes.
Leukoplakia of the uterus usually develops after suffering from infectious and inflammatory processes. Physical and chemical damage to the cervix (such as during surgery during abortion, etc.) can also be the cause.
To correctly diagnose leukoplakia, a visual examination is first performed. The doctor takes a history and then does a biopsy (takes a sample from the affected area of the mucous membrane). The biopsy is performed under local anesthesia, so the patient does not feel any pain at all. Next, the material is examined in the laboratory using cytological methods and then an accurate diagnosis can be made.
Such methods are good for leukoplakia of the oral cavity and external genitalia. When diagnosing vulvar leukoplakia, the Schiller test with Lugol's solution is also performed. Leukoplakia affected areas are not stained and become clearly visible. The smear is also examined for microflora and oncocytology.
To diagnose leukoplakia of the cervix, an examination is performed using mirrors. Then a scraping and biopsy is taken from the cervix and a cytological examination is performed. To exclude cervical cancer, doctors perform curettage of the cervical canal. And the Schiller test reveals iodine-negative areas.
Children's soft leukoplakia must be distinguished from lichen planus and candidal stomatitis. Diagnosis requires a very detailed history in order to understand when exacerbations of the disease occur and what may cause it.
Treatment of the disease
In order to cure leukoplakia, you first need to get rid of the source of irritation of the mucous membrane. For example, to treat oral leukoplakia, it may be necessary to smooth a tooth or replace (repair) a crown, denture, etc.
If the disease is caused by smoking, then it must be minimized or switch to other tobacco products. Of course, the best option in this case would be to completely quit smoking. If the disease is not advanced, after eliminating the source of irritation, the foci of the disease should go away on their own.
If this does not happen, then the affected areas are removed surgically. But hairy leukoplakia needs to be treated with antiviral drugs.
Treatment of bladder leukoplakia depends entirely on the stage of development of the disease. At first, the disease can be completely eliminated with medication. The doctor prescribes several groups of medications for a complex effect on the affected areas. These are antibiotics, immunocorrectors and general strengthening medications (both tablets and injections can be prescribed).
To avoid damage to the walls of the bladder from urine, it is irrigated with drugs that restore damaged epithelium. If therapeutic treatment does not help, then surgical intervention has to be used.
A cytoscope equipped with a camera is inserted into the bladder through the urethra, and the affected areas are cut off using a special loop.
It is not always possible to avoid surgery when treating leukoplakia.
To treat cervical leukoplakia, as a rule, both therapeutic and surgical treatment (or radio wave destruction) are used. The drugs strengthen the immune system and treat associated diseases.
Foci of the disease are also removed using one of the appropriate methods. If leukoplakia occurs with another disease of the internal genital organs (hypertrophy, kraurosis, etc.), it can lead to amputation of the cervix.
When treating vulvar leukoplakia, it is necessary to take into account concomitant diseases and the age of the patient. In addition to drug therapy, physiotherapy is carried out and a diet is prescribed. The diet is mainly dairy-vegetable.
Special hygiene procedures are carried out (for example, douching), and the source of irritation of the mucous membrane is necessarily eliminated. If all this does not help, or the disease has developed too much, then surgical intervention is required.
In extreme cases of vulvar leukoplakia, vulvar extirpation (excision of the female external genitalia) is performed.
The main method of treating leukoplakia in men is surgical. After a biopsy and tests are performed, the affected areas are excised to prevent cancer. Often this is accompanied by circumcision of the foreskin. But in general, methods and methods of treatment are selected individually for each case, taking into account the area of distribution, the severity of the disease and the biological characteristics of the body.
To cure mild leukoplakia, you need to get rid of the habit of biting your lips, cheeks or tongue. To prevent infection of the affected areas, rinse your mouth with antiseptics. Your doctor may prescribe vitamin A by mouth.
Prevention of leukoplakia
To prevent leukoplakia, it is necessary to avoid bad habits and unhealthy foods. It is necessary to visit doctors regularly to detect the disease in time. To avoid leukoplakia of the vulva and cervix, it is necessary to promptly treat hormonal imbalances and inflammation in the body. Of course, it is very important to adhere to the rules of personal hygiene.
Treatment of the disease with traditional methods
Folk remedies will come to the aid of medications in the treatment of leukoplakia. To begin with, you can lubricate the affected areas with unrefined sunflower oil. You can soak tampons with it. Unrefined oil does not give a burning sensation.
The disease will be alleviated by washing with the herbs St. John's wort and calendula. The herbs need to be brewed separately and replaced one with the other every day.
Another good folk remedy is potato flowers. Red or lilac flowers are brewed with a glass of boiling water and cooled. Then the broth is filtered and squeezed. It should be divided into three parts and drunk three times before meals (about half an hour).
Potato flowers are often used as a folk remedy to treat leukoplakia.
To treat leukoplakia, you can undergo a course of treatment with birch tar. Take it like this: the first day - one drop, then add a drop daily until the 18th day. And from 19 - they reduce it by one per day until they reach zero.
It is recommended to drop the tar with a pipette. It is poured with warm milk (half a glass) and taken once a day in the morning on an empty stomach. After taking it, you need to lie down for a couple of hours without moving. Then you need to have a good breakfast.
This treatment is carried out once a year.
And to replenish vitamin A in the body, it is recommended to drink half a glass of carrot juice before meals.
Do not forget that self-medication may not only not improve your condition, but also worsen the disease, so it is best to see a doctor. This will make it possible to accurately and timely identify and treat the disease. You need to remember about regular visits to specialists to avoid complications and dangerous consequences.
Source: https://simptom.org/lejjkoplakiya-lechenie-i-simptomy-zabolevaniya/
Causes of leukoplakia
An important role in the development of oral leukoplakia is played by external stimuli:
- Alcohol;
- Smoking;
- Constant friction from sharp edges of teeth or dentures.
When exposure to these irritants stops, it may go away, but it can also progress. Oral leukoplakia can be caused by human papillomavirus types 11 and 16. In the etiology of leukoplakia, certain importance is attached to hereditary predisposition.
The following endogenous factors are identified that provoke the development of leukoplakia in the oral cavity:
- Systemic lesions of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Disease, endocrine system;
- Diabetes;
- Anemia;
- Hypovitaminosis.
The disease develops as a result of chronic irritation and inflammation of the mucous membrane.
Prognosis for leukoplakia
The danger of leukoplakia is the progression of the process with the likelihood of malignant transformation. Regardless of the form of the disease, the development of a malignant process is observed in a third of all cases. Moreover, malignancy of a simple form, although probable, occurs in a delayed period - after several years and, as a rule, when therapy is ignored. If treatment for verrucous and erosive types of disease is refused, malignant degeneration is noted in every 4-5 cases.
Primary erythroplakia, as a variant of inhomogeneous leukoplakia according to the WHO classification, is already 90% suspicious for cancer in situ at the stage of primary diagnosis. The likelihood of malignancy increases especially significantly in women who smoke - almost 70%. Taken together, all inhomogeneous forms are four times more likely to develop into cancer than homogeneous leukoplakia.