Indications and contraindications
Pulp removal is recommended if the following factors preclude the possibility of tissue preservation:
- Developed pulpitis, which causes irreversible changes in the structure of the organ;
- Mechanical damage to the crown, including fractures;
- Periodontal diseases that cannot be treated with conservative methods.
In addition, surgical intervention is also performed in cases where the connective tissue is not susceptible to pathology, but prosthetics are planned.
The list of restrictions that exclude the possibility of carrying out the procedure temporarily or completely includes:
- Obstruction of root canals;
- Pathological deviations in root formation;
- Late stage somatic diseases;
- Presence of HIV or other severe diseases of the immune system;
- Intolerance to anesthetics used in surgery.
The decision to perform extirpation is made based on the results obtained during a comprehensive examination of the patient.
Depulpation of teeth during prosthetics
But there is also the exact opposite process. If the patient wishes to install a permanent denture, the specialist must examine the teeth that will be involved in the procedure. In some cases, the dentist prescribes pulpotomy of all or some elements of the dentition:
- with increased tooth sensitivity;
- in case of deformation and incorrect positioning of the tooth in the row;
- with initial signs of pulpitis;
- for chronic caries.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Upper palate as if it were burned.
Reasons why the palate in the mouth may hurt Depulpation before prosthetics is carried out, since after installing a permanent prosthesis, it will be more difficult to treat the tooth; it will be necessary to remove the bridge or crown, which is a traumatic factor. In addition, under the bridge, pathological processes can develop much faster and be more widespread.
Techniques used
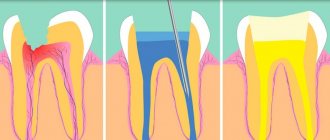
In modern dentistry, two methods are used to eliminate the affected pulp.
Vital method
The procedure is carried out in one session, during which devitilizing drugs are used that can have a negative effect on the condition of the periodontium. The operation algorithm includes the following manipulations:
- Diagnosis of pathology and development of a treatment plan;
- Cleaning the mouth and affected area;
- Injection of an anesthetic that does not cause an allergic reaction in the patient;
- Installation of a rubber dam to drain secreted saliva;
- Excision of the dental arch and pulp extirpation;
- Correction of the position of the root canal followed by disinfection;
- Formation and fixation of a permanent filling.
To remove decayed tissue within the framework of this technique, evacuation can also be used to avoid the entry of destroyed fragments into the canal cavity.
Devital method
The method involves complete amputation of previously killed connective tissue filling the cavity. At the preliminary stage, the affected area is treated with a paste containing arsenic or a paraformaldehyde composition. In particularly difficult cases, characterized by obstruction of the canals, the technique of electrochemical necrosis is used, which makes it possible to kill tissue in hard-to-reach areas.
The operation will require two visits to the dental clinic. During the first session, the following manipulations are carried out:
- Diagnostics, cleaning and disinfection of the work area;
- Opening the crown cavity and applying a tissue killing composition;
- Installation of a temporary filling tab.
The second visit is scheduled depending on what material was used to process the pulp. If the fabric was treated with a paste with arsenic, two days is enough, if with paraformaldehyde, a week is enough. During the repeat session, the doctor:
- Removes the temporary filling tab;
- Provides access to the dental canal;
- Removes affected tissue and cleans the canal;
- Installs a permanent filling.
The devital method belongs to the category of cardinal methods, and is recommended only in cases where vital extirpation is impossible.
An important factor in avoiding complications is strict adherence to medical recommendations - both in preparation for the procedure and after the operation.
Devital and vital pulp extirpation: what are the differences between the methods?
Dentists extremely rarely use words such as vital and devital pulp extirpation when communicating with patients. Why frighten an already frightened patient?! Meanwhile, if you have filled teeth in your mouth, there is a high probability that you have undergone vital extirpation. What kind of procedure this is, when and how it is carried out, you will learn from the article.
2 style=”text-align: center;”>Pulp and its meaning
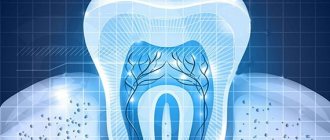
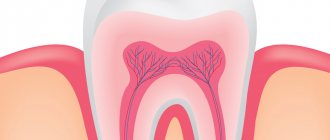
Before talking about extirpation methods, it is worth talking about the pulp. Known to most of us as the dental nerve, the pulp is the “flesh” of the tooth, that is, the inside of the tooth. If you look at a tooth in cross-section, you can see that there is a cavity inside it. Its shape resembles the outline of the tooth itself. This is the pulp chamber. It is filled with loose connective tissue, rich in nerve fibers and blood vessels - pulp.
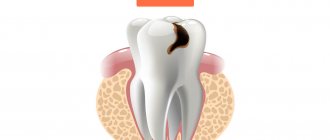
The photo shows a pulp affected by the carious process.
The pulp is divided into coronal and root parts. Often in the incisors the boundary between these parts is imperceptible, but in premolars and molars it is noticeably expressed.
The pulp in a child's newly erupted tooth will be larger than that of an adult. Over time, due to the deposition of secondary dentin, its size will decrease. Dentin formation is one of the important functions of the pulp. Pulp cells - odontoblasts - are responsible for its implementation.
In addition, it performs a trophic function and provides nutrients to the rest of the tooth tissue. The pulp has a high pain temperature sensitivity, which ensures its receptor function.
It is believed that as long as there is pulp in the tooth, it is alive. After its removal, the tooth becomes fragile, and during the procedure to remove the nerve, a significant amount of hard dental tissue also has to be lost. Therefore, doctors try to leave the nerve alive or amputate only part of it. But such an opportunity is extremely rare. Patients are often afraid to go to the dentist and put off visiting the clinic until the toothache becomes unbearable. In such cases, the pathological process affects the pulp so much that treatment without its removal becomes impossible. Removing the pulp is called extirpation.
If you contact your dentist in time, pulp removal can be avoided!
2 style=”text-align: center;”>Methods of pulp extirpation
The term “extirpation” comes from the Latin word “exstirpatio”, which translates as “removal from the root”. In medicine, this term is used not only in relation to the dental pulp. Extirpation can be performed on internal organs and glands. In dentistry, vital and devital pulp extirpation is practiced. They refer to surgical methods for treating pulpitis – inflammation of the pulp.
When implanting teeth, it is often necessary to perform a sinus lift. Find out what features an open sinus lift has.
Read: how to rinse your mouth with hydrogen peroxide to eliminate unpleasant odor and how effective this method is.
3 style=»text-align: center;»>Vital extirpation
Vital pulp extirpation is one of the methods most used by dentists. Its essence is the simultaneous removal of the dental nerve (both the coronal and root parts) under anesthesia. Subsequently, after cleaning and antiseptic treatment of the root canals, the cavity in the tooth is filled with filling material. The method has a second name – pulpectomy.
Vital extirpation is performed under local anesthesia.
Extirpation using the vital method is possible for any form of pulpitis, both acute and chronic, which is irreversible. In addition, the pulpectomy method is used if, after amputation of the coronal part of the dental nerve, the pathological process continues in its root part. Indications for vital extirpation may also include:
- retrograde pulpitis - in this case, the infection enters the pulp chamber not from the carious cavity, but through the openings of the root canals, for example, with advanced periodontitis;
- location of the carious cavity in the area of root cement and cervical caries;
- pulpitis complicated by periodontitis;
- preparation of supporting teeth for installation of a bridge;
- the presence of root cysts and their treatment.
Important: a contraindication to pulpectomy is if the patient is allergic to anesthetics.
4 style=»text-align: center;»>Stages of the operation
The method of vital extirpation is considered quite complex and requires high professionalism of the doctor. The success of the procedure as a whole depends on compliance with the rules at each stage. Vital extirpation is carried out as follows:
- First, teeth in the affected area are cleaned and treated with antiseptic;
- the next stage is pain relief; before administering anesthesia, the doctor must make sure that the patient is not allergic to anesthetics; for this, a provocative test can be performed - a small amount of the drug is dripped under the tongue and the body’s reaction is observed;
- fissure burs are used to expand the carious cavity;
- then the pulp cavity is opened and access to the pulp is gained;
- Using a special tool - an excavator, the coronal part of the pulp is first removed;
- the cavity is treated with antiseptics;
- further, the mouths of the root canals are expanded with a bur, they are given the shape of a cone, this will allow endodontic instruments to easily penetrate them in the future;
- Using a pulp extractor, the dentist removes nerves from the root canals;
- to stop bleeding, special preparations are introduced into the pulp chamber;
- To prevent the development of complications, the canals are treated with drugs that dissolve the remaining pulp.
Important: since the pulpectomy procedure can take 1-2 hours, depending on the complexity of the case and the number of roots in the tooth, when using the injection method of anesthesia, combinations of amide anesthetics (Lidocaine, Trimecaine, Bupivacaine, Articaine) with vasoconstrictors are used - substances that reduce blood flow in blood vessels due to their narrowing (adrenaline).
After treatment of the root canals, they are filled with filling material, a gasket and a permanent filling are installed on the tooth. In order to ensure the quality of endodontic treatment, an x-ray examination is performed. In multi-rooted teeth, especially with branched canals, electrophoresis and depophoresis can be performed to remove remaining pulp.
The entire procedure for treating pulpitis using the vital pulp extirpation method is carried out in one visit to the dentist.
Read: can pregnant women use dental drops?
Find out which disease may cause unpleasant odor from your gums.
We recommend that you find out how seizures are treated.
3 style=»text-align: center;»>Devital extirpation
The method of devital pulpectomy involves the complete removal of the dental nerve after killing it with devitalizing pastes.
Important: the devital technique is used in patients intolerant to local anesthetics.
To carry out the procedure, the patient will have to visit the dentist at least twice:
- During the first appointment, the tooth cavity is opened, a drug that kills the pulp is placed in it, and the tooth is closed with a temporary filling;
- At the second appointment, the pulp is directly extirpated, the tooth cavity is prepared, the root canals are cleaned, processed and filled (similar to the vital technique).
Important: before applying the paste, the doctor must open the pulp horn. This procedure is painful for the patient.
Before proceeding with the second stage of extirpation, the doctor must make sure that pulp necrosis has occurred. Between the first and second visits, it can take from 24 hours to 15 days, depending on the drug chosen and the location of the tooth. Thus, the minimum time for applying the paste to single-rooted teeth is 24 hours, and when treating multi-rooted teeth, the drug is placed in the cavity for at least 48 hours.
The absence of pain in the tooth will be a sign of pulp necrosis.
4 style=»text-align: center;»>Devitalizing pastes
To devitalize the pulp, the dentist can use formaldehyde or arsenic paste. Formaldehyde pastes are left to act in the tooth cavity for 5-7 days, arsenic pastes act faster. Most often, dentists use arsenic pastes Devit-Ars, Kaustinerf Rapid, Septodont. Formaldehyde-based pastes are considered less toxic, although their shelf life is longer. Among such preparations is Devit-S paste, containing paraformaldehyde, creosote and lidocaine.
Treatment of pulpitis using both vital and non-vital methods is a complex procedure that requires the doctor to be careful and have certain skills. If the pulp is not completely removed, this will lead to the development of serious complications.
Consequences and possible complications
What complications can develop from a pulpless tooth? If the procedure is performed correctly, the risk of problems occurring is minimal. The patient only needs to carefully monitor oral hygiene. This is especially important if the reason for removing the nerve is tooth decay. If it recurs, a pulpless tooth will not signal the presence of problems with pain, which means there is a risk of “triggering” the disease.
This is where the list of preventive measures ends, but when talking about the possible negative consequences of the procedure, one cannot fail to mention the complications that arise as a result of the dentist’s mistakes. Among them:
- root fracture or perforation of the dental floor due to insufficient attention of the dentist to the specific structural features of a particular molar;
- flux, fistulas, granuloma and other inflammatory problems associated with infection due to improper sanitation or dirty instruments;
- burns and mechanical (to the point of bleeding) damage to the gums and mucous membranes of the oral cavity due to the dentist’s careless handling of the drill;
- violation by an insufficiently experienced doctor of the integrity of previously undamaged tooth tissues, due to which the latter becomes fragile and loose.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Lidocaine price in Ramenskoye from 30.99 rubles, buy Lidocaine in Ramenskoye in an online pharmacy, order