Lincomycin or Amoxicillin: which is better?
Lincomycin has an antimicrobial effect and belongs to the group of lincosamides.
It is capable of destroying a wide range of microorganisms. If you increase the dosage, it will have a bactericidal effect. Photo 1. Lincomycin capsules, 20 pcs., 250 mg, manufacturer - PROMED.
The medicine works on the principle of inhibiting protein synthesis in bacterial cells. The antibiotic destroys gram-positive aerobic and anaerobic organisms:
- Bacillus anthracis.
- Actinonomics spp.
- Bacteroides spp.
Lincomycin itself acts as the main active ingredient, since it is a good antibiotic that is part of others. Lincomycin should be taken for pneumonia, which is often a harbinger of a more serious illness. In the later stages, this drug, unfortunately, is powerless.
The difference between Amoxicillin and Lincomycin is that these two drugs belong to different antibiotic communities. Lincomycin is classified as a lincosamide, and Amoxicillin is one of the drugs that make up the penicillin group. Moreover, the latter is better resistant to acidic environments.
Which drug is better: Lincomycin or Amoxiclav?
Quite often, people develop diseases caused by various bacteria . First of all, people try to eliminate the symptoms of the disease. However, it is necessary to eliminate not only the symptoms, but also the cause itself.
Antibacterial drugs are used for this . Popular ones are Lincomycin and Amoxiclav .
Patients often have questions about which drug is more effective? To give an answer, you need to conduct a comparative assessment of these medications and determine what is more effective in a particular case.
Lincomycin
The active ingredient is lincomycin . Available in the form of capsules, solution and ointment. It is an antibiotic of the lincosamide group.
Has an antimicrobial effect. It is a broad-spectrum antibiotic. When using an excess dosage, a bactericidal effect may be observed.
After oral administration, it is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. About 50% of the substance is observed in the systemic circulation. The maximum amount of the product is observed 2-4 hours after use.
It is well distributed throughout the body and penetrates all tissues and organs. Also passes into breast milk. The half-life is 5-6 hours. It is excreted primarily by the kidneys.
In people with kidney pathologies, the half-life may increase.
The medication in the form of tablets and injections is prescribed for:
- Diseases of bones and joints caused by pathogenic microflora.
- Infections of ENT organs.
- Skin infections.
- Inflammatory and purulent diseases of soft tissues.
It is also widely used in dentistry for the development of infectious processes in the oral cavity.
Contraindications for use are:
- Allergic reaction to the components included in the composition.
- Children under 6 years old.
- Severe liver and kidney diseases.
The dosage and treatment regimen are determined by the attending physician , depending on the patient’s disease and his age.
Amoxiclav
The active ingredients are amoxicillin and clavulanic acid . Available in the form of tablets, suspensions, and also in the form of powder for the preparation of a solution for injection. Belongs to the group of penicillins. Affects various pathogenic microflora.
Well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract even with food. The highest concentration is observed after an hour. The active components cross the placenta and enter breast milk. The half-life is 90 minutes . It is excreted primarily by the intestines and lungs.
Indicated for infections:
- ENT organs and respiratory system.
- Urinary system.
- Gynecological organs.
- Soft tissues.
- Telchny ways.
Amoxiclav is contraindicated for:
- Infectious mononucleosis.
- Previous liver diseases.
- Allergic reactions to components.
- Lymphocytic leukemia.
Children can be prescribed from birth.
What to choose?
Both drugs are antibiotics , but belong to different subgroups . Accordingly, their composition is also different. Medicines have different dosage forms. Lincomycin is available in the form of capsules, solution and ointment. Amoxiclav comes in the form of tablets, suspension and injection solution.
Their indications for use are almost the same. However, Amoxiclav has a little more of them. Unlike Lincomycin, it can be used for gynecological infections.
But Lincomycin can be used for dental infections. However, Amoxiclav has a few more contraindications.
The main difference is that Lincomycin can be used by children from 6 years of age, while Amoxiclav is allowed for children from birth.
Both medications should not be used during pregnancy . They also cannot be combined with alcohol. When drinking alcohol, the absorption of the active components is impaired, and the half-life is reduced. That is, a smaller amount of active substances enters the body.
Both medications have side effects. Lincomycin has the following side effects:
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Stomach ache.
- Allergic reaction.
- Headache.
- Increased blood pressure.
Amoxiclav has many more side effects. Common ones are:
- Decreased appetite.
- Nausea, vomiting.
- Allergic reactions.
- Dizziness.
- Headache.
- Cramps.
- Nephritis.
Both drugs are available by prescription only.
Reviews about Lincomycin are mostly positive . Patients note that, regardless of the form of the drug, it has a good antibacterial effect and eliminates the symptoms of infectious diseases in a short time. Also in dental practice, the drug effectively eliminates purulent diseases of the oral cavity.
Reviews about Amoxiclav are also positive . Many note that the drug copes well with respiratory tract infections. Parents also note the convenience and pleasant taste of the suspension, so it is well accepted by children. After using this antibiotic, it is recommended to take drugs that restore the microflora.
Lincomycin is produced in Russia. The price for 10 ampoules is about 50 rubles . The price of capsules is 60-90 rubles . The ointment costs around 30 rubles . The cost of Amoxiclav tablets ranges from 200 to 500 rubles , depending on the concentration. The suspension costs around 300 rubles .
Conclusion
Thus, both drugs are quite effective in infectious diseases . If you choose a drug for small children, then you should prefer Amoxiclav, since it is prescribed even to newborn children.
This medication is also convenient in that it comes in the form of a suspension. Lincomycin is convenient because it comes in an ointment form. That is why it makes it possible to treat infectious diseases of the skin.
Based on the price category, Lincomycin is much cheaper than Amoxiclav.
In any case, the drugs must be prescribed by a doctor. Only he will be able to determine the causative agent of the disease and determine which medication will be most effective, as well as select the optimal treatment regimen.
Source: https://vchemraznica.ru/kakoj-preparat-luchshe-linkomicin-ili-amoksiklav/
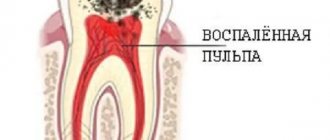
Characteristics of lincomycin
The spectrum of action of lincomycin is quite specific - it acts predominantly on gram-positive flora (staphylococci, pneumococci, some protozoa, streptococci, peptococci, fusobacteria and bacteroides).
There are both oral and enteral forms of the drug. After administration, high concentrations of the drug are created in the biliary tract, bone tissue and inflamed tissues. The antibiotic practically does not pass through the blood-brain barrier. The therapeutic concentration of the drug is maintained for 6 hours after taking a dose of lincomycin. The drug is not metabolized in the body and is excreted primarily by the kidneys, and partly through bile.
Today, the range of sensitivity to the drug allows it to be used in dentistry. This is also helped by the ability of lincomycin to accumulate in inflamed tissues of the oral cavity.
Lincomycin is also used to treat bacterial pathologies of the lower respiratory tract (pneumonia with pleurisy, abscess, lung destruction), soft tissues (cellulitis, erysipelas), as well as some forms of sepsis.
Among the contraindications for prescribing lincomycin, it is necessary to highlight impaired liver and kidney function, individual hypersensitivity to the drug, as well as pregnancy and lactation. The antibiotic is also not recommended for use in children under one year of age.
Side effects when prescribing lincomycin include allergic reactions, dyspeptic disorders, the addition of secondary bacterial or fungal infections, toxic effects on the liver, inhibition of hematopoiesis, headache, dizziness, local phlebitis with intravenous administration and the development of a sterile abscess.
But there are situations when taking this antibiotic is impossible. Then it is not lincomycin that is used: analogues.
Antibiotics for toothache and inflammation - lincomycin, tsifran, amoxiclav
Many people have experienced toothache, and probably everyone knows how much discomfort it causes. The presence of this symptom may indicate the development of a pathological process - caries, infection, inflammatory process.
The inflammatory process is especially dangerous, which can lead to serious health problems. To eliminate it, it is recommended to use antibiotics, which must be used in accordance with the instructions.
Types and classifications
Antibiotics should be prescribed by a doctor after a complete examination. They should be used during the development of an inflammatory and infectious process; the active substances suppress the activity of pathogenic organisms, which leads to rapid restoration of the structure of the affected tissue.
All antibiotics are divided into types, which are listed in the table below.
| View | Description |
| Beta-lactams | They are of the bactericidal type. They have a weak ability to penetrate microbial cells and also do not affect intracellular microorganisms. But at the same time they cause destruction of the synthesis of the outer membrane of bacteria. They are also divided into 4 groups - penicillins, cephalosporins, mono-bactams, carbalenems. |
| Imidazole and nitroimidazole derivatives | Antibiotics of this type can penetrate into all environments of the body. They affect the focus of the inflammatory process from the inside and have an inhibitory effect on the synthesis of microbial DNA. |
| Macrolides | Causes blocking of protein synthesis. Prevents the proliferation of pathogenic organisms. Compared to antibiotics, beta-lactams have a lower degree of toxicity and practically do not cause allergic reactions. |
| Fluoroquinolones | They have an effective effect on bacterial infections that develop in the structure of soft and bone tissues. |
| Lincosamides | They have pronounced osteotropic properties. Currently, antibiotics of this type are used in rare cases, mainly to eliminate inflammation in bone tissue. |
Methods of application
You definitely need to know how to properly use any antibiotic for dental inflammation. It is better to first consult with a doctor, because a specialist will be able to prescribe the optimal regimen for using drugs of this type.
In the field of dentistry, antibiotics have long been used in the treatment of dental flux. Their use makes it possible to stop the development of the purulent process, and they also prevent its spread throughout the body.
It is advisable to use medications at the initial stage, they will help prevent the development of pustules, and this means that they will provide treatment for gumboil at the earliest stage of its development. But in the later stages, the use of antibacterial agents is possible only after opening the purulent formation.
To understand how to use antibiotics, it is worth considering important recommendations:
- antibiotics, which are produced in the form of capsules, tablets, powders, must be taken orally. Medicines available in the form of tablets and capsules must be taken with a sufficient amount of water when taken. The powder should be dissolved in water. The solution can be used as a rinse or for oral administration;
- in the form of ointments. The drugs are recommended for external use; they are applied to the area with inflammation. They should be used at least 2-3 times a day;
- injections. Medicines in this form are considered the most effective for flux. Injections are recommended to be administered intravenously or intramuscularly.
Adverse reactions
Before taking any antibiotic, you should carefully study its instructions. The fact is that many antibacterial drugs cause side symptoms that can negatively affect your health.
The most common side effects that occur when taking these medications are:
- manifestation of arterial hypertension;
- feeling of weakness in the muscles;
- disruption of the digestive system - manifestations of dysbacteriosis, nausea, vomiting, flatulence, pain in the epigastric region, esophagitis;
- dizziness;
- headache;
- symptoms of swelling;
- skin dermatitis;
- allergic reactions;
- sometimes there is pancytopenia, thrombocytopenia;
- bleeding may occur.
If at least one of the above side symptoms appears while taking antibiotics, then you should stop using them. You should definitely consult your doctor.
What antibiotic to take for dental inflammation
For inflammation of teeth and gums, dentists often prescribe antibiotics that will help eliminate all pathological manifestations.
You should not self-medicate, because it can cause harm to your health. Dentists usually select appropriate medications that are suitable for treating dental problems.
Tsifran
Tsifran has long been successfully used in dentistry in the treatment of many pathological processes. Many pharmacies have an improved formula of this drug - Cifran ST.
It contains ciprofoxlacin hydrochloride and tinizadol, components that help eliminate anaerobic and aerobic bacteria.
Indications for antibacterial medications include:
- if there is a risk of a diffuse infectious process;
- if there is a likelihood of inflammation of the purulent process;
- exacerbation of chronic periodontitis and other maxillofacial diseases;
- abscesses;
- phlegmon;
- development of osteomyelitis;
- complications during tooth extraction;
- after prosthetics;
- when cleaning teeth or implants with open bleeding.
The popularity of Cifran in the dental field is ensured by the fact that no side symptoms or overdose occur when taking it. It also quickly prevents the development of purulent processes.
Amoxiclav is an effective bacterial agent that suppresses the activity of pathogenic organisms. It destroys those bacteria that exhibit increased sensitivity to its active elements.
The product is available in the form of tablets, water-soluble powder, and suspension. For this reason, both adults and children can take it, but in strictly prescribed dosages. Only a doctor should prescribe it, and he will also determine the appropriate dosage regimen.
Important features of the antibiotic:
- It is recommended to take the drug orally;
- taken before each meal;
- The tablet cannot be chewed and must be taken with plenty of water;
- the drug prevents the inflammatory process around and inside the tooth, eliminates pain;
- the medicine is excreted primarily through the kidneys, partly with air. Complete elimination occurs within 6-7 hours.
Clarithromycin and its features
This remedy is an antibiotic belonging to the macrolide group. It is a derivative of erythromycin. Clarithromycin is a semi-synthetic drug that has the property of disrupting the protein synthesis of bacteria that enter the body. In this it is similar to the antibiotic described earlier.
It is capable of destroying the following types of bacteria:
- Legionella pneumophila.
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
- Helicobacter pylori.
As in the antibiotic described earlier, in Clarithromycin itself acts as the main active ingredient.
When to use
If we are talking about the treatment of tuberculosis, then the medicine should be used during chemotherapy (in the later stages of the disease). It is worth noting that one of the most noticeable differences between Clarithromycin and Amoxicillin is that the former does not have strong side effects. For this reason, it can be used to treat patients over 12 years of age.
DETAILS: Mouth is constantly dry and thirsty
The product has some contraindications. Clarithromycin should not be used in case of individual intolerance to its components, liver failure and glucose malabsorption syndrome.
During pregnancy (during the first and second trimester), you should also stop taking Clarithromycin.
The product should not be given to children under 6 months of age.
Sumamed is a broad-spectrum antibacterial drug. Its main active ingredient is azithromycin. This is a new generation drug that is prescribed to both children and adults. It is used to treat infections caused by bacteria.
Photo 2. Sumamed, 6 capsules, 250 mg, manufacturer - PLIVA.
Sumamed suppresses the proliferation of anaerobic microorganisms.
- Chlamydia trachomatis. Causes inflammation in the pelvic organs.
- Peptostreptococcus spp. Promotes the appearance of mixed infections when interacting with other bacteria.
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Provokes diseases of the respiratory system - lungs and throat.
Important! The antibiotic in question helps in the treatment of tuberculosis in the early stages. With its help, you can cure pneumonia, which often precedes this terrible disease.
The difference between Sumamed and Amoxicillin is that they belong to different groups of antibiotics, that is, the first is a representative of macrolides, and the second belongs to the penicillin group. They act on different bacteria: Sumamed can cope with pneumococci, streptococci of groups G and GF, and Amoxicillin destroys only aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms.
As a result, both drugs have a wide spectrum of action, but it is worth noting that the macrolide is a more universal remedy than its penicillin counterpart. An additional difference is that the drugs are manufactured in different countries.
Azithromycin or Tsiprolet: which is better and is it possible to do it at the same time?
Nowadays, infections haunt us at every step, and some have a fatal effect on our body, so do not underestimate them. Diseases are caused by bacteria, but you need to remember that not all bacteria are harmful, some, on the contrary, contribute to the functioning of the body.
For many years, scientists tried to find a cure for infections to protect health, and finally, in the 20th century, a cure was discovered - an antibiotic.
As the years go by, new viruses appear and the variety of antibiotics increases. There are more and more of them on the drug market. Let's consider and compare the antibiotics Amoxicillin and Tsiprolet.
How to choose an antibiotic
Any medicinal product is chosen not based on its price category or ease of administration, but on the indications for use according to the instructions.
Usually the following are taken into account:
- suspected type and type of pathogen;
- metabolic characteristics of the drug, its absorption, distribution and routes of elimination from the body;
- presence of concomitant diseases;
- possible side effects;
- interaction of the drug with other drugs.
That is why comparing drugs is not always correct. A drug has a better or worse effect on the pathogen, since it may be chosen incorrectly.
Summarize
There are many infections, and your life may depend on the correct selection of antibiotics. Amoxicillin and Ciprolet do an excellent job against bacteria, only each fights against certain microorganisms.
The main thing to remember is that the choice of a particular medicine should be primarily before the attending physician, and not the patient. So do not self-medicate, but rather trust the advice of specialists.
And follow the dosage and period of use of medications, because this is very important. If you drink the drug insufficiently, the disease may develop into a more complex form.
And if antibiotic consumption is prolonged, this can lead to a worsening of the condition and side effects.
You also need to remember that when taking antibiotics, you need a course of vitamins that will restore the body's microflora and ensure the coordinated functioning of all systems.
Medicine and healthComment
Azithromycin
Today, azithromycin-based drugs are widely used in the treatment of various infectious diseases. This is due to both the ease of taking such medications and their low toxicity.
These drugs are available in the form of capsules, tablets and powders for the preparation of suspensions and solutions for intravenous administration. They are usually prescribed in short-term regimens (treatment is carried out over several days) and are taken once a day.
The list of Azithromycin analog drugs is quite wide, however, Sumamed and Amoxicillin are considered one of the most popular antibacterial agents in this group. These are quite strong drugs that help well in the fight against infectious diseases of the respiratory system, digestive system, genitourinary area and other generalized conditions.
In some cases, for acute or complicated infections, to enhance the therapeutic effect, doctors may prescribe a combination of antibiotics from different groups, for example, sometimes Tsiprolet and Azithromycin are prescribed together .
However, Ciprolet (ciprofloxacin) belongs to the fluoroquinolone group of antibiotics and can provoke the development of unwanted side effects. Unless absolutely necessary, compatibility between Tsiprolet and Azithromycin is not recommended.
Drug differences
By release form: amoxicillin is produced in the form of capsules, tablets, granules for suspension. And tsiprolet is in tablets and drops. Due to this, we can conclude that the use of amoxicillin, due to the variety of release forms, is easier. For example, it is easier for children to take medicine in the form of a suspension.
Pharmacological action: Tsiprolet is much higher, since it affects the DNA of bacteria. Also, unlike the other representative, it acts on microorganisms that produce beta-lactamases.
Contraindications: Ciprolet has a much longer list than amoxicillin, which is only sensitive to penicillins. The list for the ciprolet also includes:
- Pregnancy.
- Lactation.
- Representatives under 18 years of age.
- Elderly contingent.
- Patients with epilepsy.
- Vascular diseases.
- CNS disorders.
Dosage: Amoxicillin 500 mg 3 times a day, Tsiprolet 200 mg 2 times a day.
Side effects: Amoxicillin causes urticaria, angioedema, rhinitis, joint pain, nausea and loose stools. And Tsiprolet also has migraines, tachycardia, lack of appetite, anorexia, lack of sleep, depression, tinnitus or temporary hearing loss, sweating, fungus, colitis, anemia, headache, kidney problems and muscle weakness.
Tsiprolet
Medicines from the fluoroquinolone group are broad-spectrum antibiotics. Treatment regimens using these drugs are chosen for the treatment of pneumonia, severe infectious gynecological and urological diseases, as well as in surgery.
Today, one of the most widely used drugs in this group is Tsiprolet. It affects a large number of pathogenic microorganisms, including bacteria sensitive to penicillins and macrolides.
However, due to possible adverse reactions, Tsiprolet is rarely prescribed in the treatment of ENT and respiratory diseases. The compatibility of Tsiprolet and Azithromycin becomes especially relevant in the treatment of pneumonia , when the combination of “azithromycin + amoxiclav” does not help for three days.
Penicillin group
Antibiotics of this group are prescribed more often than any other. This is due to their knowledge and effective action.
The therapeutic effect of these antibiotics is based on the ability to suppress bacterial cell synthesis. Penicillins are made from natural substances such as fungi, mold, etc.
, but can sometimes be slightly modified in the laboratory to increase efficiency. Such penicillins are called semisynthetic.
The action of penicillins is aimed only at pathogenic microorganisms, so the natural flora of a person is practically not affected during treatment.
The disadvantage of this group is the frequent development of side effects in the form of allergic reactions:
- Amoxil (tablets) is a broad-spectrum drug that is active against all bacteria that provoke inflammation in the bronchi. Amoxil does not affect the flora that produces penicillinase. For children under 2 years old, a single dose of 30 mg per 1 kg of weight is prescribed, from 2 to 5 years old - 125 mg, from 5 to 10 years old - 250 mg. The daily dose for an adult is 500 mg, but can be increased to 1 g;
- Ampicillin (tablets, granules, capsules, powder) is a semi-synthetic drug. It has a wide spectrum of action, making it effective against: staphylococci (except those that synthesize penicillinase), streptococci, enterococci, listeria, neisseria. Ineffective against bacteria that produce beta-lactamase. The dosage of ampicillin is determined individually, but a single dose for adults should not exceed 500 mg, and for children weighing up to 20 kg - 25 mg;
- Amoxicillin (tablets, granules, capsules) is a semi-synthetic drug that is acid-resistant. A wide spectrum of action makes it effective against most microorganisms, except those that produce penicillinase. For the treatment of children under 10 years of age, it should be used with extreme caution and in the form of a suspension. Dosage: less than 2 years – 20 mg per 1 kg of weight, 2-5 years – 2.5 ml at a time, 5-10 years – 5 ml at a time. The recommended dose for adults is 500 mg 3 times a day;
- Augmentin (tablets, powder) contains clavulanic acid, which makes it effective against bacteria that produce beta-lactamase. Therefore, Augmentin is prescribed more often for bronchitis than other penicillins. The dosage of the drug is prescribed based on the individual characteristics of the body and the course of the disease. To achieve the maximum therapeutic effect, Augmentin must be taken for at least 5 days, but the total course of therapy should not exceed 2 weeks;
When is the combination of Ciprofloxacin and Azithromycin possible?
The question of whether it is possible to take Azithromycin and Tsiprolet together is asked by many patients. In fact, drugs from the fluoroquinolone group (Ciprofloxacin, Tsiprolet, Tsifran and other analogues) combine well with Azithromycin.
Such regimens are successfully used in the treatment of a number of acute infectious pathologies. This primarily includes pulmonary diseases and ENT pathologies. Prescribing the drugs Tsiprolet and Azithromycin together gives an optimal therapeutic result. They are usually well tolerated, however, there remains a risk of side effects and individual intolerance.
Sources:
Vidal : https://www.vidal.ru/drugs/azithromycin__24064 GRLS : https://grls.rosminzdrav.ru/Grls_View_v2.aspx?routingGu >
Found a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl + Enter
Azithromycin and Ciprofloxacin enjoy an extremely good reputation among doctors. Patients also respond positively to treatment with these drugs.
A large role in the popularity of these products is played by the convenient form of packaging, especially Azithromycin. It is packaged in blisters of three tablets each, capsules, powders and suspensions. The dosages are also very convenient to use: 500 mg, 250 mg, 125 mg.
Ciprofloxacin is available in tablets of 250 mg or 500 mg, drops and solutions.
Cephalosporin group
Cephalosporin antibacterial drugs have a wide spectrum of action and minimal toxicity.
The destruction of pathogenic flora is achieved by destroying the cells of their membrane, which provides a quick effect after taking the drugs. Cephalosporin antibiotics are divided into three groups, where the latest, third generation, has the highest productivity rates. Antibiotics in this group have low rates of side effects.
Source: https://cosmeton.ru/preparaty/ciprolet-ili-amoksicillin.html
Lincomycin analogues
Ceftriaxone
Ceftriaxone is the most common cephalosporin. It is an antibiotic with a wide spectrum of bactericidal effect against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The mechanism of action of the drug is its ability to disrupt the integrity of the cell membrane of microbes, which leads to their lysis.
Unlike lincomycin, ceftriaxone is considered safe for pregnant women and newborns. It is used exclusively in the form for intramuscular or intravenous administration. Among the main indications for prescribing the drug are bacterial pathologies of soft tissues, abdominal cavity, lungs (pneumonia), respiratory tract and digestive system. Ceftriaxone also passes well through the blood-brain barrier, which allows it to be used for meningitis.
The main contraindication for prescribing ceftriaxone is the presence of hypersensitivity to beta-lactam drugs (penicillins, cephalosporins, monobactams, carbapenems).
Among the side effects of ceftriaxone, it is necessary to highlight allergic reactions of various forms and severity - rash, redness in the injection area, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock. Functional disorders of the digestive tract, the addition of a secondary bacterial infection, a transient increase in liver enzymes and headaches with dizziness are also possible.
Doxycycline
Doxycycline is a drug from the tetracyclic series. It is characterized by a bacteriostatic effect - antibiotic molecules pass inside the microbial cell, where they inhibit the ribosomal subunit and stop protein synthesis in it. Doxycycline acts against streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococci, meningococci, gonococci, Shigella, salmonella, enterobacteria and other pathogens.
DETAILS: Which antibiotics are best to take for periodontal disease?
A feature of doxycycline, like other tetracyclines, is the ability to bind to calcium salts, which significantly increases the specificity of the drug to bone and dental tissue. Its bioavailability for oral administration is about 100%, so this drug is widely used in tablet form.
Doxycycline is prescribed for bacterial inflammation of soft tissues, bones, as well as for a number of specific infectious pathologies (such as typhoid, brucellosis, tularemia, cholera). This antibiotic has also found its use in dentistry.
The following side effects are found with doxycycline:
- hypersensitivity reactions;
- digestive system disorders;
- blurred vision, headache, dizziness, increased intracranial pressure;
- inhibition of hematopoiesis;
- violation of the formation of the skeleton and tooth enamel;
- increased sensitivity to sunlight;
- pain in joints and muscles;
- increased liver enzymes.
Contraindications also include porphyria and uncompensated liver diseases.
Clarithromycin
Clarithromycin belongs to the macrolide group of antibacterial agents. The drug is capable, like most bacteriostatic drugs, of blocking the 50S ribosomal subunit, which makes it impossible for the microorganism to further reproduce. Clarithromycin molecules are able to accumulate in foci of the inflammatory process, where they can remain for up to 72 hours. This is due to the long potentiating effect of the drug.
Clarithromycin acts against staphylococci, streptococci, Haemophilus influenzae, Listeria, Neisseria, mycobacteria, mycoplasma, chlamydia and toxoplasma. The antibiotic is produced exclusively in tablet form.
Among the indications for prescribing clarithromycin tablets are inflammatory processes of soft tissues, respiratory tracts, ENT organs and the genitourinary system. The antibiotic is produced exclusively in the form of tablets or syrup for children.
Among the side effects, it is necessary to note the addition of a secondary infection, the development of allergic reactions, cases of cardiac tachyarrhythmias, disorders of the digestive system, renal failure, increased liver enzymes in the blood and dizziness.
Ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a bactericidal antibacterial drug from the group of fluoroquinolones. Its molecules are capable of inhibiting DNA replication of bacterial cells, which leads to gradual lysis and death of microbes. Ciprofloxacin is an antibiotic with a broad spectrum of action. It is effective against Escherichia coli, Neisseria, staphylococci, streptococci, listeria, chlamydia, clostridia and Haemophilus influenzae.
Ciprofloxacin is prescribed for the following pathologies:
- community-acquired pneumonia (as a second-line treatment);
- generalization of infection (sepsis);
- inflammatory bacterial processes of the genitourinary system;
- phlegmon, erysipelas, abscesses of various locations;
- prevention of infectious complications after surgical interventions;
- chronic osteomyelitis;
- bacterial pathologies of the biliary tract.
When using ciprofloxacin, the most common side effects are associated with dysfunction of the digestive tract, toxic effects on the central nervous system (dizziness, headache, patient anxiety), kidneys (interstitial nephritis), liver (lysis of hepatocytes).
Ciprofloxacin is prescribed with caution to children under 12 years of age, as well as to patients who suffer from epilepsy and congenital pathologies of the central nervous system. If the glomerular filtration rate decreases, it is necessary to calculate the individual dose of the drug.
Azithromycin and Ciprofloxacin: compatibility or rejection?
Ciprofloxacin is a well-known fluoroquinolone antibiotic that is actively used in diagnosing a number of acute and chronic pathologies.
Diseases cannot always be cured with just one antibiotic.
Doctors often prescribe a combination of antibacterial drugs or add other drugs to treatment to enhance the bactericidal and bacteriostatic effect, and also to avoid bacterial resistance or side effects.
Ciprofloxacin can be easily combined with other drugs, but patients are most often interested in the specifics of such a combination, because enhanced antibacterial therapy does not benefit the body.
ontakte
Odnoklassniki
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic produced with the aim of extended action against pathogenic bacteria. The drug is suitable for the treatment of many diseases, and its effects are varied. Antibiotics are most often not prescribed alone, because the treatment of many pathologies requires an individual and combined approach.
Photo 1. Ciprofloxacin, 20 tablets, 500 mg, manufacturer – Aliud Pharma.
In the aggressive course of the disease, bacteria become resistant to the active components of the drug, which leads to incomplete recovery and increased frequency of relapses. Ciprofloxacin, like a fluoroquinolone, is not a highly effective antibiotic, which justifies the prescription of additional medications.
Most often it is combined with the following antibiotics and antimicrobials:
- Doxycycline;
- Levofloxacin;
- Metronidazole;
- Azithromycin;
- Ciftriaxone;
- Cephalosporin;
- Fluconabosis;
- Ibuprofen.
It has been proven that the effectiveness of Ciprofloxacin increases and is enhanced when combined with other antibacterial medications, but in some cases additional treatment is prescribed to relieve pain symptoms, as well as eliminate side effects.
Compatibility of Ciprofloxacin and Doxycycline
Both drugs are antibiotics, but Doxycycline belongs to the group of tetracyclines , that is, it has a completely different chemical composition. These groups of antibacterial drugs do not have any contraindications for combination.
Thanks to the combination of Doxycycline and Ciprofloxacin, an enhanced antibacterial effect occurs and resistance to other antibiotics is reduced.
Ciprofloxacin is a drug with a unique chemical formula, which means there is no cross-resistance with drugs of other antibacterial series. It goes well with Doxycycline.
The components of both drugs do not block or reduce the pharmacological actions of each other, but only complement (synergy).
Doxycycline itself is a very strong and toxic drug, so its simultaneous administration with Ciprofloxacin is a case of exception , not the rule. This combination is prescribed for the following pathologies:
- acute inflammatory diseases of the pelvis in women;
- specific urethritis caused by STIs;
- infectious complications after operations, abortions;
- pneumonia;
- tuberculosis;
- sepsis;
- sinusitis, sinusitis, acute frontal sinusitis.
Most often, Ciprofloxacin + Doxycycline is used in obstetrics and gynecology , but cases vary. Doxycycline has many dangerous side effects, and additional use of other antibiotics will only increase their manifestation. The doctor must monitor the patient's condition.
Important! Ciprofloxacin + Doxycycline can be taken together only for acute or complicated infections.
Sluggish and chronic pathologies do not imply the combined use of drugs, but this option is possible if other treatment is ineffective.
The dosage, as well as the combination of drugs, depends on the doctor’s recommendations and clinical diagnosis.
For acute, severe infections or severe foci of inflammation, Ciprofloxacin and Doxycycline are taken together or combined every other week in order to block resistance.
In cases of ineffectiveness of Ciprofloxacin, Doxycycline is prescribed, which is taken strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
Ciprofloxacin and Levofloxacin: can they be taken at the same time?
Levofloxacin is a 3rd generation fluoroquinolone antibiotic that belongs to the same drug group as Cifprofloxacin.
In clinical practice, such combinations of drugs can cause cross- resistance, that is, the usual resistance of bacteria to the active components of all fluoroquinolones.
Prescribing them together does not make sense and carries certain risks, but at the same time they are compatible and do not cause any negative manifestations on the part of the body.
The side effects of each antibiotic are dangerous in any case. Levofloxacin is often prescribed after ineffectiveness or intolerance of Ciprofloxacin. They should not be taken together, but Cifprofloxacin can be combined with another fluoroquinolone after 7-10 days to reduce resistance.
Photo 2. Levofloxacin, 10 tablets, 250 and 500 mg, manufacturer – Vertex.
Ciprofloxacin + Levofloxacin are theoretically used for any infectious diseases, since they have a wide spectrum of action, but taking the drugs together leads to the risk of resistance .
Ciprofloxacin and Metronidazole: their interaction
Metronidazole is not an antibiotic; according to its pharmacological group, it is an antimicrobial drug that is intended for auxiliary treatment during antibacterial therapy.
Ciprofloxacin and Metronidazole can be taken both together or separately, but in the latter case, Metronidazole is prescribed after the end of Ciprofloxacin to maintain the therapeutic effect.
Ciprofloxacin + Metronidazole are effective against the following pathologies:
- protozoal diseases: amoebiasis, giardiasis, trichomonas urethritis/colpitis/vaginitis;
- cystitis caused by STIs;
- bacterial endocarditis
- meningitis;
- pneumonia;
- sepsis;
- infections caused by Bacteroides spp, Peptostreptococcus spp, Clostridium spp, Peptococcus spp;
- diseases of the pelvic organs;
- skin diseases;
- postoperative complications in gynecology/urology.
Reference! Metronidazole is also available under another trade name Trichopolum , which contains a similar pharmacological composition.
Metronidazole is ineffective when taken alone, so it is always prescribed with other medications or antibiotics.
Concomitant use of drugs is not dangerous, but Metronidazole has many side effects , which usually occur when interacting with other antibiotics.
Doctors either reduce the dose of Metronidazole or prescribe it after antibiotic therapy.
What is Flemoklav and how does it differ from Amoxicillin
Flemoklav is an antibiotic with a wide range of action. It belongs to the group of penicillin drugs of the semi-synthetic variety. The role of the active substance in it is played by amoxicillin and clavulanic acid.
Auxiliary components:
- apricot flavor;
- crospovidone;
- microcrystalline cellulose;
- saccharin;
- vanillin;
- Magnesium stearate.
The product has an antibacterial effect and can destroy the following bacteria:
- enterococci, which cause intestinal infections;
- streptococci, including beta-hemolytic strains;
- staphylococci, including aureus.
DETAILS: Lincomycin capsules dosage
Important! The principle of action of this drug is to block the synthesis of the cell membrane of microorganisms. At the same time, it is capable of destroying the walls of both gram-positive and gram-negative microbes.
Femoclav can be used to treat tuberculosis in the early stages; if pneumonia occurs, taking this drug is necessary. Moreover, it can be used to treat a similar disease not only in the lungs, but also in other organs, in the intestines, skin or bones.
Flemoklav differs from Amoxicillin in composition. The first drug includes the second and is supplemented with clavulinic acid, which expands the spectrum of its action. Amoxicillin has no additional components.
Can Tsiprolet and azithromycin be taken together?
Amoxiclav is a broad-spectrum antibiotic of the penicillin group, containing amoxicillin and clavulanic acid.
The purpose of the latter substance is to prevent bacteria from neutralizing the effect of amoxicillin. In its pure form, the drug is useless in the fight against many microorganisms, while clavulanic acid completely changes the situation.
The following pathogenic bacteria are sensitive to the combination drug Amoxiclav:
- Streptococci
- Staphylococcus
- The causative agent of salmonellosis
- The causative agent of brucellosis
- Echinococcus
- Listeria
- Moraxella
- Proteus
- Klebsiella
- Shigella and others.
Amoxicillin is widely used for:
- Bronchitis, pneumonia
- Inflammations of the urinary system
- Tonsillitis, sinusitis, otitis
- Chronic cholecystitis
- Gonorrhea
- Gynecological diseases
- Skin infections
- Inflammation of musculoskeletal tissues.
Amoxiclav is contraindicated in children diagnosed with atopic dermatitis and bronchial asthma. Also, the ban on amoxicillin applies if the child does not tolerate the components of the antibiotic, or if previously taking such medications revealed a negative reaction of the body. The ban on amoxicillin also applies to:
- Lymphocytic leukemia
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Kidney/liver diseases.
If jaundice appears due to the effects of the medication, use is suspended. It is unacceptable to take amoxicillin simultaneously with:
- Sulfonamides
- Macrolides
- Tetracyclines.
The side effects of this medication are mild and intermittent. They can be divided into 5 groups:
Digestive system: loss of appetite, diarrhea, nausea/vomiting, abdominal pain, deterioration of liver function, hepatitis, cholestatic jaundice, pseudomembranous colitis.
Nervous system: dizziness, headaches, hyperactivity, insomnia, anxiety, convulsions.
Urinary system: crystalluria, interstitial nephritis.
Hematopoietic lymphatic system: reversible leukopenia/neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia, eosinophilia, pancytopenia.
Allergic reactions: itching, erythematous rash, urticaria, allergic vasculitis, anaphyalctic shock, exudative erythema multiforme, angioedema, exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis
Tsiprolet is an antimicrobial drug from the fluoroquinolone group, endowed with one highly active substance - ciprofloxacin hydrochloride. Ciprofloxacin – perfectly resists an abundance of pathogenic microorganisms. It has an inhibitory effect on the bacterial enzyme responsible for DNA synthesis. Copes well with the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria.
Detailed instructions are available at the link: https://lekhar.ru/lekarstva/protivomikrobnye-preparaty/ciprolet-instrukciya-po-primeneniyu/
Currently, doctors are actively using Tsiprolet in the treatment of various diseases, since the number of drug-resistant bacteria remains minimal
Sensitive pathogenic microbes to ciprofloxacin can be divided into 3 groups:
- Gram-positive
- Gram-negative
- Intracellular
An antibiotic is prescribed for:
- Pneumonia, bronchitis
- Sinusitis, otitis, sinusitis, mastoiditis, sore throat
- Inflammation of the bladder and kidneys
- Infectious inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract
- Inflammation of the gallbladder
- Skin lesions
- Purulent processes in connective tissues
- Peritonitis, sepsis
- Immunodeficiency.
In some conditions, ciprofloxacin should not be taken. Among them:
- Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency (heredity)
- Pseudomembranous colitis
- Pregnancy
- Lactation.
It is prescribed with extreme caution to people suffering from atherosclerosis, insufficient cerebral circulation, seizures and mental disorders. Occasionally, doctors prescribe the use of ciprofloxacin to patients suffering from kidney/liver inflammation. Also, the antibiotic is not suitable for minor children. An exception is children over 15 years old under the supervision of a doctor.
The side effects of the drug are similar to Amoxiclav, but there are additions in 9 groups:
- Digestive system: anorexia, flatulence, hepatitis
- Nervous system: insomnia, nightmares, sweating, depression, confusion, fainting, migraine
- Sense organs: impaired sense of smell, change in taste, hearing loss, visual impairment
- Cardiovascular system: decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, facial flushing, irregular heart rhythm
- Hematopoietic system: anemia, leukocytosis, hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia
- Laboratory indicators: hyperglycemia, hypoprothrombinemia
- Urinary system: urinary retention, urethral bleeding,
- Allergic reactions: blistering, drug fever, swelling of the face/larynx, increased sensitivity to light
- Musculoskeletal system: arthritis, tendon ruptures, arthralgia and others.
Amoxiclav and Tsiprolet are completely different drugs, both in their composition and in their effectiveness. Therefore, replacing one with another without consulting a specialist is unacceptable; it certainly won’t make things better.
Amoxiclav is available in three forms - powder for preparing a suspension, suspension and tablets. Tsiprolet can be found in pharmacies in the form of eye drops, tablets and solution for infusion.
Of course, Amoxiclav is 2 or even 3 times more expensive than Tsiprolet, while the latter, despite its low cost, is more effective.
It is important to note that ciprofloxacin is prescribed in isolated cases to children over 15 years of age; it is intended for the treatment of serious infectious diseases in people over 18 years of age, while amoxicillin is also perfect for treating children over 3 months of age, and the drug is available in the form of a suspension better suits the baby.
In most cases, Amoxiclav is prescribed to children with tonsillitis. Amoxicillin does its job perfectly. Treatment with Tsiprolet is prescribed by a doctor in more serious cases of infection - it helps even when other drugs are powerless.
It is difficult to say which drug is better, Amoxiclav or Tsiprolet.
The latter is a very strong antibiotic; its use should be approached with great caution; it is not for nothing that it has a wide range of contraindications, and can also lead to many serious side effects.
For the most part, the contraindications for the drugs are similar, with the exception of age restrictions for taking ciprofloxacin.
If we talk about side effects, amoxicillin is much milder, more gentle on the body than ciprofloxacin, which can lead not only to gastrointestinal disorders or headaches, but also create extremely unpleasant sensations in the heart area. That is why it is strictly forbidden to use Tsiprolet in self-medication or simultaneously with other medications, only after consulting a doctor.
Ciprofloxacin is rarely used for purulent tonsillitis due to the large number of side effects it has. This is a very effective antibiotic, but its use is about as dangerous as a sore throat itself, and therefore it can only be prescribed if it is impossible to take safer remedies.
For outpatient treatment for home use, ciprofloxacin is prescribed 0.5 tablets 2-3 times a day for 7-10 days, if the disease is severe - 1-1.5 tablets 2-3 times a day.
At the discretion of the doctor, the duration of treatment of purulent sore throat with ciprofloxacin can be increased to 3-4 weeks for reliable protection against complications of the disease. In any case, this antibiotic should continue to be used for at least 3 days after the temperature has subsided and the patient’s condition has normalized.
Specific dosages and timing of antibiotic use are prescribed only by a doctor after examining the patient, studying his medical history and taking a swab from the throat.
Ciprofloxacin is prescribed only to adult patients over 18 years of age! It is forbidden to give it to children and adolescents until the formation of the skeleton is complete. It is also prohibited to use it during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Ciprofloxacin in tablet form is most effective when taken on an empty stomach. In this case, it is absorbed as quickly as possible. During the day, tablets are taken after meals and washed down with water.
Ciprofloxacin is one of the most effective antibiotics of the fluoroquinolone class. It has a bactericidal effect and, when taken correctly, destroys bacteria in the tonsils within 1-2 days.
As a rule, within a day after starting to take the drug, the patient’s temperature begins to subside and his health improves. On the 2-3rd day of taking the drug, the ulcers spontaneously open.
Some strains of staphylococci are resistant to ciprofloxacin (in particular, strains resistant to methicillin). Therefore, in rare cases of purulent tonsillitis, taking this antibiotic may not produce results.
Staphylococcus aureus. By itself, it becomes the cause of purulent sore throat relatively rarely - in less than 5% of cases.
However, in the vast majority of cases, ciprofloxacin works effectively for purulent tonsillitis and allows you to quickly get rid of the disease.
The main disadvantage of ciprofloxacin is the large number of severe side effects that occur with its use.
It is because of them that this antibiotic is still not used in any significant quantities for sore throat.
The fact is that a sore throat can be successfully treated with much safer means, and some of the consequences of taking ciprofloxacin turn out to be more severe and dangerous than the symptoms of a sore throat itself.
Structural formula of ciprofloxacin
Thus, when taking ciprofloxacin, patients regularly experience:
- Hepatitis;
- Cholestatic jaundice;
- Insomnia;
- Nightmares in sleep;
- Depression;
- Hallucinations;
- Various psychopathic reactions up to life-threatening for the patient himself;
- Thrombosis of cerebral arteries;
- Visual impairment (including diplopia, changes in color vision);
- Taste disturbances;
- Heart rhythm disturbances;
- Urinary retention;
- Hematuria (presence of blood in the urine);
- Allergic reactions;
- Arthritis;
- Tenosynovitis…
Obviously, taking into account the possible development of such side effects, only a doctor can prescribe ciprofloxacin and only in situations where safer antibiotics - penicillins, macrolides, cephalosporins - cannot be taken for one reason or another. This rarely happens, and therefore ciprofloxacin is used extremely rarely for purulent tonsillitis.
For the treatment of sore throat, there are a large number of significantly safer drugs than ciprofloxacin
In most cases, instead of ciprofloxacin for purulent tonsillitis, it is much more reasonable and safer (with the same effectiveness) to use inhibitor-protected penicillins and macrolides, and sometimes cephalosporins. For example:
- Amoxicillin with clavulanic acid (Amoxiclav, Flemokrav Solutab);
- Cefadroxil;
- For inpatient treatment - Ceftriaxone;
- Azithromycin (mainly the drug Sumamed and its analogues)…
It is strictly prohibited to prescribe ciprofloxacin yourself for a purulent sore throat. Moreover, you cannot do this for a child. Without consulting your doctor, using this antibiotic can be very dangerous!
Sinusitis is an inflammatory process in the maxillary paranasal sinus. Depending on the nature of the infectious agent that caused the disease, the patient is prescribed systemic pharmacological therapy.
For example, catarrhal (viral) sinusitis can be cured without the use of local and systemic antibiotics. Viral infection of the maxillary sinuses is treated with antihistamines, immunomodulatory and vasoconstrictor drugs.
If a bacterial infection occurs, sinusitis requires treatment with antibiotics.
Currently, there are countless antibiotic drugs successfully used to treat maxillary sinusitis. However, most otolaryngologists prefer to treat sinusitis not with β-lactams and macrolides, but with fluoroquinolones.
At the same time, despite the wide variety of medications produced in this group, the drug of choice is Tsiprolet.
But, before treating sinusitis with systemic antibiotics, it is important to accurately determine and confirm the bacteriological nature of the infectious agent.
Source: https://rustland.ru/raznoe/tsiprolet-i-azitromitsin-mozhno-li-pit-vmeste/
Tsiprolet and Amoxicillin: the difference
Like any antibiotic, the drug has an antimicrobial effect. It belongs to the pharmacological group of fluoroquinols. Tsiprolet acts by destroying the reproductive abilities of microbes that have entered the human body.
This remedy can destroy both dormant and active pathogens. The following microorganisms are sensitive to it:
- enterobacteria;
- coli;
- pathogens of tropical diseases in the digestive system;
- germs that can cause plague;
- staphylococci of many varieties.
The main substance included in Tsiprolet is Ciprofloxacin, thanks to which the drug is able to have a bactericidal effect.
Important! The medicine can be used at any stage of tuberculosis, as long as it has not progressed too far and can be treated. However, Tsiprolet alone is not enough.
As a rule, such an illness must be treated over a long period of time using several types of compatible antibiotics.
Tsiprolet and Amoxicillin belong to different pharmacological groups. The first is a fluoroquinolone, the second is a drug of the penicillin group.
The main active ingredients in both antibiotics are different substances. It is worth noting that Tsiprolet has a wide spectrum of action, since it is able to cope with a huge number of varieties of microorganisms that cause bacterial infections.
What is Ciproflaxin
Ciproflaxin is one of the most effective drugs. It has found wide application in clinical practice. Belongs to the group of fluoroquinolones.
Active against the following microorganisms:
- Chlamydia trachomatis.
- Listeria monocytogenes.
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
The functions of the main active substance are performed by the drug itself, and it is presented in the form of hydrochloride monohydrate.
Like many antibiotics, Ciproflaxin is used to treat pulmonary tuberculosis in the early stages. It must be used together with other drugs.
Ciproflaxin and Amoxicillin differ from each other in that they are part of different pharmacological groups: Amoxicillin is part of the penicillin drugs, and Ciproflaxin is part of the fluoroquinolone group.
Let's sum it up
Amoxicillin is used to treat bacterial infections due to its broad spectrum of action and a small number of side effects. However, there are reasons why it is impossible to use such a drug.
These include individual intolerance and age restrictions. In such situations, it can be replaced by Tsiprolet, Sumamed, Ciproflaxin, Flemoklav or Lincomycin. Of the listed drugs, the most effective in treating tuberculosis are those that belong to the group of macrolides. As a result, the best of the listed remedies is Clarithromycin.