Price list Treatment of pulpitis
| Name | Price |
| Beginning of treatment (applying devital paste, anesthesia, temporary filling) | 1,400 rub. |
| Root canal treatment (medical and mechanical treatment) | 1,400 rub. |
| 1 channel | 3,000 rub. |
| 2 channel | 3,500 rub. |
| 3 channel | 4,100 rub. |
| 4 channel | 4,300 rub. |
| 1-channel machine processing | 3,600 rub. |
| 2-channel machine processing | 4,100 rub. |
| 3-channel machine processing | 4,600 rub. |
| 4-channel machine processing | 5,100 rub. |
| Intermediate tooth treatment (calasept, antiseptic) | 1,400 rub. |
| 1 channel gutt. pins | 1,900 rub. |
| 2ch gutt. pins | 2,300 rub. |
| 3ch gutt. pins | RUB 2,650 |
| 4ch gutt. pins | 3,000 rub. |
| Tooth restoration with glass ionomer material | 3,100 rub. |
| Tooth restoration with composite material (incisors) | 3,400 rub. |
| Tooth restoration with composite material (molars and premolars) | RUB 3,950 |
| Restoration of tooth stump (incisors) | 2,900 rub. |
| Restoration of tooth core (molars and premolars) | 4,100 rub. |
| Restoring the tooth wall | 1,650 rub. |
| Restoring the tooth wall | 1,650 rub. |
| Temporary filling | 450 rub. |
| Long-term temporary filling | 1,000 rub. |
| Difficult access | 550 rub. |
| Installing the fiberglass pin | 3,000 rub. |
| Insulating or healing pads | 350 rub. |
| Using a rubber dam | 550 rub. |
Make an appointment
Body protection
If there is too much filling material, the excess may be squeezed out through the apical foramen into the periodontal tissue. The body will begin to reject foreign particles and protect itself by forming a granuloma around them.
Granuloma formation
The above situations are also possible when a dental instrument breaks in the root canal. If the dentist does not remove the fragment in time, it will not be possible to completely fill the dental canal. A piece of instrument can also penetrate the periodontal tissue and form a granuloma or abscess around it.
Classification of pulpitis
Acute pulpitis
Acute pulpitis is an inflammatory process that penetrates into the tooth (pulp chamber, root canals). It is a frequent complication of medium and deep caries, the causative agents of which are streptococci, staphylococci, and fusobacteria.
Chronic pulpitis
Chronic pulpitis is a form of dental disease that occurs as a result of untimely consultation with a doctor or as a complication as a result of concomitant diseases. With chronic pulpitis, the pain is not so pronounced, sometimes it goes away on its own and patients, unfortunately, do not always pay due attention to this condition. Cold and hot, solid foods can increase pain, so patients try not to put stress on the diseased tooth (do not eat food on this side). Sometimes such teeth begin to hurt when patients fall ill with colds, acute respiratory viral infections, and sinusitis.
Complications of pulpitis
You can, of course, endure pulpal pain by using folk remedies and modern painkillers toothache But such self-medication usually leads to the development of serious complications. Treatment of pulpitis at home is possible only in emergency cases by calling a dentist at home, who will arrive with all the equipment necessary for treatment. In other cases, treatment of pulpitis with folk remedies will not lead to anything other than complications. One of the most common complications of pulpitis is periodontitis . The infection located in the inflamed pulp slowly but surely penetrates beyond the tooth and causes inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth root - periodontitis develops. Periodontitis is dangerous because with this disease there is a gradual destruction of bone tissue near the roots of the tooth. In chronic periodontitis, the formation of granulomas, cystogranulomas and perihilar cysts often occurs . Such chronic foci of inflammation respond very poorly to therapeutic treatment and often lead to the removal of the diseased tooth. In addition, these chronic inflammatory foci cause the spread of infection through the bloodstream throughout the body, which can provoke chronic diseases of the internal organs of a person.
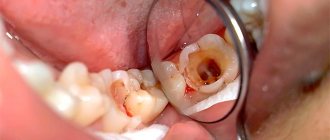
Treatment of pulpitis
The scope of work in the treatment of pulpitis includes several stages, each of them is controlled by special equipment (apex locators) and is accompanied by x-rays. The goal of treating a diseased tooth is to maximize the release of the tooth canals from the pathologically inflamed dental pulp (nerve). In dental treatment, along with instrumental processing, various chemical solutions of different directions are used. The final stage is filling the canals and restoring the anatomical shape of the tooth (fillings, crowns). In order for such teeth, as dentists call them “dead”, to last longer, it is necessary to undergo a preventive examination once every 6 months.
Treatment methods for pulpitis
Commonly accepted methods of treating pulpitis are:
- biological method,
- amputation method (more often used in childhood and adolescence),
- extirpation method.
Biological method
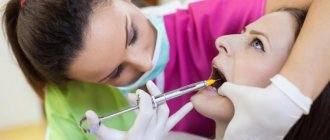
This method is used in case of accidental exposure of the dental pulp, during the treatment of deep caries, in case of tooth trauma, positive results with this method of treatment are usually achieved in patients under the age of 27 years and the results are quite high. The treatment takes place in two stages: at the first visit, a special medicine is given, the tooth is closed with temporary cement, if there is no pain, then at the second visit a permanent filling is placed. If the patient’s tooth is bothering him, then treatment begins with the extraction method.
Amputation
This method is used mainly in the treatment of pulpitis in children and adolescents. The pulp is removed only from the crown part of the tooth, and it remains in the canals. The treatment is the same as with the biological method, but before the medication and temporary cement are applied, the pulp is removed from the crown of the tooth.
Extirpation
Today, the extirpation method is the main one in the treatment of pulpitis. With this method, the pulp is completely removed from the root canals of the tooth, then the canals are treated using mechanical and medicinal methods, with these manipulations the doctor strives to achieve sterility of the root canals and the possibility of saving the tooth.
Stages of pulpitis treatment
- On the first visit, the tooth is treated for carious lesions; a special paste is applied to the inflamed nerve to remove (“kill”) the nerve. Or the nerve is removed at the same time and the root canals are treated.
- On the second visit, as a rule, the root canals are treated and filled.
- At the third visit, the anatomical part of the tooth is restored in various ways (filling, orthopedic construction).
It is important to know that each stage of pulpitis treatment is accompanied by diagnostic images! The number of visits depends on the anatomical structure of the tooth and the general condition of the body as a whole.
Features of the treatment of pulpitis in children
Treatment of pulpitis in children is difficult and painstaking work for a doctor, since our children require a special approach, attention, and patience. Peculiarities of childhood suggest a certain method of treating pulpitis.
Post-filling pain
It is difficult to avoid some pain when treating pulpitis even after all procedures are completed. Residual effects are due to the fact that the internal tissues have just experienced a strong intervention in their structure and integrity. It will take time to recover, usually after two weeks the pain goes away.
Sometimes the nature of the unpleasant sensations is defined by the patient as diffuse and implicit. Sometimes the patient feels pain in the canal when pressing on the tooth or biting into food. Such accompaniment also occurs with high-quality, solid fillings.
In some cases, the doctor uses physical therapy and treatment with painkillers, making a person’s life easier. If prolonged pain persists with an intensification or change in the nature of the experience, it cannot be tolerated. It is possible that the therapy was carried out incorrectly or periapical inflammation develops due to the release of material to the outside. Consultation with a dentist is required.
Treatment of tooth enamel erosion, causes, photos, price
Treatment of pericoronitis of the wisdom tooth in the lower jaw
Dental treatment without a drill, placing a filling without drilling in Moscow
Mistakes and complications in the treatment of dental pulpitis
Restoration of tooth enamel, price, drugs
Treatment of dental caries using the Icon method without preparation
Root canal treatment for chronic periodontitis
Reasons for such situations
- Inclined teeth - the doctor does not take into account the position of the pulp chamber when changing the position of the tooth.
- The doctor’s ignorance of the anatomy of the location of the root canal orifices.
- Curved, narrow and obliterated canals – applying more force to pass through them can perforate the root wall.
- Feeling of the instrument “sinking”.
- Pain on probing (if the patient is treated without local anesthesia).
- Bleeding from the perforation site.
Prevention consists of analyzing an x-ray before endodontic treatment of a tooth in order to identify features of the location and direction of the canals.
Removal of material beyond the root apex
It is a frequent complication, but the danger can only be the presence of a large amount of filling material, as well as its removal into the maxillary sinus (in the treatment of upper premolars and molars). Such situations can lead to inflammation of the sinus lining (sinusitis), which may require tooth extraction to clear the sinus of infection.
If the patient has no complaints, in most cases such teeth are dynamically observed.
Post-filling pain
A frequent complication that can be caused by either the removal of material beyond the apical foramen, poor-quality filling, or the reaction of periodontal tissue to intervention.
The last option is the most common. If the tooth canal is adequately sealed, the patient may experience pain when biting on it. Within two weeks after endodontic treatment (canal filling), pain of varying intensity may be present, mainly when pressing on the tooth.
Typically, such sensations go away on their own within a few days, but in some cases painkillers (for example, nimesulide) and physiotherapeutic treatment are prescribed.
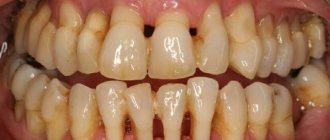
Complications in the treatment of periodontitis
The main complications that arise as a result of incorrectly administered or untimely therapy are considered:
- Transition of the pathological process from serous to purulent form with the formation of an extensive abscess.
- Phlegmon of the gums.
- General blood infection – sepsis. It is a deadly condition.
For a successful outcome, it matters not only when, but also how periodontitis is treated: an experienced dentist can cope even with an advanced disease, while a doctor who is not very competent or does not have the proper experience in endodontic therapy is quite capable of making a mistake. If during treatment the patient notices that his condition is worsening, the pain is intensifying and his general well-being is suffering, it is highly advisable to urgently consult with another specialist.