Causes of cysts
The main predisposing factor for the occurrence of a problem in the upper or lower jaw is the penetration of microbes into the thickness of the soft tissue. But this is not always the only reason. The oral cavity is never sterile; microbes are always present in it, and the mucous membranes are often damaged by microtraumas. And this state of affairs does not lead to the formation of cysts. For an organism with a correct immune system response, the mere fact of infection is not enough.
In the case of tooth extraction, additional points that contribute to the establishment of infection are:
- extensive insemination from the inflamed root and high damaging ability of microbes - occurs when a blood clot in the socket is destroyed after tooth extraction;
- incomplete root extraction – presence of debris in the jaw;
- violation of sanitary and epidemiological standards during tooth extraction surgery;
- reorientation of the body's defenses to heal the hole after tooth extraction.
Important! The infection can enter the jaw not only exogenously - from the outside, but also enter the bloodstream from foci of inflammation already existing in the body - exogenously.
Indications and contraindications
Removing a tooth with a cyst on the root is a last resort. They resort to it when:
- formation in diameter exceeds 1 cm;
- the capsule has grown into the nasal cavity;
- it is impossible to preserve the root system;
- there are significant lesions of bone tissue;
- fusion of the root with the cyst occurred.
For a number of reasons, the operation is postponed until a more prosperous period. These include:
- first and last trimester of pregnancy;
- menstruation;
- acute respiratory diseases;
- blood clotting abnormalities;
- severe cardiovascular pathologies;
- oncology.
The tooth is removed if conservative therapy does not produce results.
These are relative contraindications. If there is a risk of infection spreading to other structures and organs, the procedure is carried out under the supervision of a specialized specialist.
Symptoms and signs
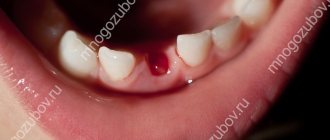
The cyst does not always develop quickly. With a small initial amount of pathogenic bacteria, they are encapsulated into a small cavity, and this event does not in any way affect the well-being of the host. In most cases, this limits the infectious effect on the body. Without a sufficient nutrient medium, not very strong microbes stop multiplying, the formation gradually decreases in size, and over time it completely resolves.
With a simultaneously significant amount of pathogenic flora and its increased aggressiveness, the spherical body containing the infection gradually increases in size. At the same time, melting of the walls of the cyst occurs, their perforation, and penetration of pyogenic elements into the periosteum of the jaw and bone.
These processes manifest themselves as symptoms of acute odontogenic osteomyelitis:
- pain in the area of the extracted tooth;
- local increase in temperature;
- swelling and pulsation of tissue in the area of inflammation.
Important! If signs of inflammation appear, you should urgently consult a doctor: lack of treatment and attempts to cope with the problem on your own aggravate the situation and cause serious complications.
Why does a cyst appear at the site of an extracted tooth?
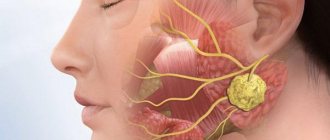
The neoplasm is a hollow capsule of dense tissue filled with serous or purulent contents. It occurs as a response of the body to an infection to limit its spread. Thus, the main reason for its appearance is pathogenic microflora.
Provoking factors:
- Tissue infection during nerve extraction or removal. This may be insufficient antiseptic treatment of the surgical field, unsterile instruments, or other doctor’s shortcomings during the procedure.
- The tooth was removed, but the cyst remained. This option is possible if the necessary diagnostics were not carried out and the doctor simply did not notice the pathological formation.
- Dry hole. After extraction, a blood clot is formed, which protects deep tissues from the penetration of bacteria and food debris. If the blood plug comes off or falls out, the opened cavity becomes the center of an accumulation of pathogenic organisms, which become provocateurs of pathology.
- Medical errors during implantation. If the implant is installed soon after removal, infection and capsule formation may also occur during the procedure.
- Failure to follow the doctor’s recommendations during the rehabilitation period. If the patient is negligent about his health, the risk of developing inflammatory processes increases.
Neglecting antibiotic therapy can ultimately cause a purulent infection. A dry socket is formed due to intensive rinsing of the mouth and licking of a blood clot. If the patient smokes or abuses alcoholic beverages, the wound in the mouth does not heal well, which means the risk of complications increases.
First aid
If for some reason an urgent visit to the hospital is not possible, you can take measures to alleviate the condition of inflammation:
- rinsing the mouth with a warm solution of furatsilin (or soda) several times a day;
- taking painkillers - no more than 4 times a day;
- cold on the painful area.
The pre-medical period should be shortened as much as possible. Without medical help, dangerous complications of the cyst develop very quickly:
- phlegmon - after melting of the walls and penetration of the contents of the cyst into the tissue;
- abscess - local suppuration;
- destruction of the integrity of the jaw, especially the lower one;
- spread of infection through the maxillary sinuses into the nasopharynx, bronchi, lungs and inflammation in these organs;
- generalization of infection - sepsis.
Treatment of a cyst under an extracted tooth
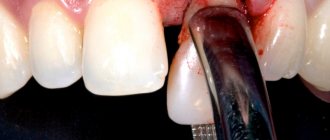
The neoplasm is treated surgically. An x-ray is taken first. The image shows the area where the capsule is localized, its size, complications, for example, bone melting after rupture of the bladder with advanced pathology.
The doctor removes the cystic sac, cleans the cavity of pus, if there is any, and carries out an antiseptic treatment. When using a laser, the operation is performed practically without blood, and wound healing is faster. In any case, you need to take antibiotics to prevent relapse.
Elimination of pathology
Medical care consists of identifying the source of infection, which is carried out using x-rays, medication and surgical treatment.
If the cyst does not show signs of inflammation and its size is small, antibiotics and physiotherapy are prescribed. Often these actions are enough to deactivate microbes and dry out the cyst.
With the development of inflammation, and even more so complications, the cyst capsule must be opened, drained or completely removed. These are serious dental interventions that stop the destruction process. The soft tissue is sutured, and the jaw sometimes has to be restored by applying a splint.
Thus, the prognosis for the occurrence of a cyst after tooth extraction can be quite favorable if you consult a doctor in time.
Features of rehabilitation
After extraction of a tooth with a cyst, swelling, a rise in temperature to subfebrile levels (37.5°), toothache and headache may occur. To alleviate the condition and avoid complications, it is recommended:
- avoid physical activity;
- do not take a bath or go to the sauna;
- make sure that the blood clot is not washed out of the hole: it is forbidden to rinse your mouth for 2 - 3 days, smoke, drink alcohol for at least a day;
- Take medications prescribed by your dentist: painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs are most often prescribed.
To avoid complications, antibiotics are prescribed.
Important! Education often recurs. Therefore, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed: Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav, Lincomycin.
Baths after tooth extraction
Since rinsing after the removal procedure is prohibited, it is necessary to make baths.
Doctors usually recommend making baths using soda and salt, medications or decoctions of various medicinal herbs. For these purposes, drugs such as Miramistin and an aqueous solution of Chlorhexidine are suitable.
The procedure is easy to carry out. You just need to put a small amount of bath liquid in your mouth, tilt your head so that the liquid moves to the area of the pulled out tooth, and freeze in this position for 30-60 seconds. There is no need to take any active action; the medicinal solution should simply gently wash the damaged gum tissue. After this, the liquid must be spat out.
Antiseptic or therapeutic baths are recommended to be done every 3 hours during the day, preferably after eating and cleansing the mouth.
After the patient has taken a bath, it is advisable not to eat any food or even drink for 1 hour.
Alternative Treatments
Teeth with cysts should be removed when it is impossible to get rid of the formation by other methods. Modern dentistry can cure the disease using therapeutic or surgical methods.
Read also: How to quickly cure gumboil at home
Conservative treatment
It is performed in the early stages of the disease, when the capsule size does not exceed 0.8 mm. To provide access to education, the canals are unsealed. Pus is pumped out of the cavity, antiseptically treated and filled with osteoinductive materials.
Afterwards a temporary filling is installed. After a few weeks, the procedure is repeated. Medicines are changed until the formation poses no threat.
This method is the most gentle. But treatment takes several months. Relapses are also common.
The recovery period after laser treatment is easy.
Important! An alternative physiotherapeutic method is the administration of a copper-calcium suspension and subsequent exposure to electrical impulses.
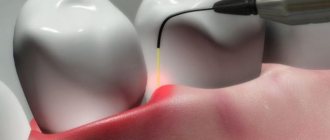
Laser therapy
The most progressive method. A laser is inserted into the opened root canal and the capsule is exposed to radiation. It removes the formation and disinfects the cavity.
The recovery period after laser treatment is easy. Complications and relapses appear very rarely.
Laser therapy is also used when the capsule does not exceed 0.8 mm. However, not every clinic is equipped with the necessary equipment.
Cystectomy
Type of surgical intervention. Access to the formation is provided through an incision in the gum. The capsule is completely removed along with the affected root tip. Afterwards, the wound is sutured, and antibacterial and antiseptic therapy is prescribed.
Cystotomy
Removing a tooth with a cyst is a last resort.
It also represents a surgical procedure. The anterior wall of the formation is removed and communicated with the oral cavity. The procedure is carried out when a large cyst has formed on the lower jaw or on the upper row with penetration into the nasal cavity.
Hemisection
It is considered the most reliable tooth-preserving method. It is performed only on molars. The capsule is removed along with one of the roots and part of the crown. Subsequently, dental prosthetics is performed.
Extraction of a tooth with a cyst is carried out when it is impossible to preserve the root system or in case of serious damage to bone tissue. The operation resembles a regular removal. But after extraction, it is necessary to carry out enucleation, treatment of the hole with antiseptics, antibacterial therapy, and suturing.
What is a dental cyst, and how can it be cured?
A cyst is a formation in soft tissue with hard walls. It is formed for a number of reasons. The first of these is infections that could get into the gums due to damage or errors during root canal treatment. This problem can also arise due to exacerbation of sinusitis and a number of other infectious diseases.
The appearance of a cyst has no symptoms. A person may not notice this problem for a long time. Externally, the tooth and gums do not change in any way. The first noticeable sign of cyst formation is pain when chewing food. Further, the cyst can develop into a fistula, a formation on the front side of the gum, and this is a more serious problem. If a cyst is detected in time, it can be treated in three different ways. The first is the most famous, removal of the tooth along with the cyst. Lately it has been used extremely rarely. It is increasingly possible to save a tooth. Therapeutic treatment is more common. It is much easier for both the dentist and the patient. With this procedure, the cyst is reached through the root canal, completely cleaning it out. Next, pus is pumped out of the cavity and it is filled with an antiseptic. The canal is closed with a temporary filling, which the patient wears until the dentist is sure that all bacteria have been destroyed. At the end of the treatment, the root canal is closed with a permanent filling, and the tooth remains in the same form as it was originally. The latter treatment method was developed quite recently, and not every dental clinic has the necessary equipment for it. We are talking about removing a dental cyst with a laser. At the beginning, as in the previous type of treatment, the root canal is completely cleared. The pus is pumped out and the damaged area is illuminated with a laser, which has an antiseptic and healing effect. After such treatment, after just a few days of wearing a temporary filling, a permanent one can be installed.
Other possible complications
Sometimes, even if all the rules for caring for and treating the hole are followed, complications develop. It is not recommended to delay treatment in such cases. Possible complications:
- Alveolitis
Alveolitis. The disease, the symptoms of which are pain, swelling, general weakness, inflammation, develops due to the absence of a blood clot. A hole left unprotected becomes accessible to infections. The danger of the disease lies in the transition of inflammation to the alveolar process and the development of osteomyelitis. The success of treatment depends on the degree of neglect of the process. As a mandatory measure, specialists scrape out the hole again, drain it, and prescribe analgesics and antibiotics from medications. - Cyst
Cyst. A neoplasm in soft tissues located at the root zone appears as a result of infection of the hole or an inflammatory process. Liquid from dead cells and bacteria accumulates in the sac. If the cyst is not removed in a timely manner, sepsis (blood poisoning) may occur. The formation of a cyst is provoked by the following factors: prolonged retention of the tampon in the socket, dry socket, non-compliance with the doctor’s recommendations for care. Treatment involves surgery to cleanse the tissues of the tumor and drug therapy using anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents. - Flux
Flux. The disease develops against the background of an inflammatory process occurring on the periosteum of the alveolar process. Causes: damage to the blood clot or lack of treatment for alveolitis. Treatment involves opening the purulent focal area and carrying out antibacterial therapy. - Purulent inflammation of the periodontium
Inflammation of the periodontium. The disease usually appears against the background of a dry socket or after the loss of a blood clot. The wound fills with granulation and fibrous tissue and pus. The gums swell, bleed, and a strong pulsation is felt. The outbreak is localized at the edge of the gum surface. To solve the problem, an integrated approach is being taken: - curettage;
- treatment of the hole with antiseptics;
- taking antibiotics.
antibacterial therapy;
Hematoma. This complication most often occurs as a result of labor-intensive tooth extraction, when long roots must be extracted. It is not possible to perform the operation in the usual way, so you have to press on the gums, as a result of which blood enters the soft tissues. Hematoma can be eliminated using special ointments and gels.
Bleeding. It can occur either immediately after surgery or 12-24 hours later. The complication can be caused by several factors: the use of adrenaline, vascular damage, non-compliance with rules of behavior in the postoperative period. Loss of blood is dangerous for the body, as the functioning of all vital systems is disrupted. The problem is eliminated by applying cold, squeezing the vessel, using a hemostatic agent, or applying sutures to the gum.
Dry socket. This effect occurs due to an unformed blood clot or as a result of its damage. Signs of the disease: pain, sometimes radiating to the ear, redness of the tissue around the hole, a specific smell in the mouth. Dry sockets can also be triggered by: smoking, poor hygiene, frequent mouth rinsing, and mechanical stress on the wound. If a mild or moderate degree of complexity of the disease is detected, doctors prescribe antiseptic, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy. Severe cases require hospitalization and complex treatment.
Paresthesia. Occurs as a result of nerve damage during surgery. The following signs indicate a problem: numbness of the tongue, lips, chin, cheeks. This phenomenon is considered temporary and disappears after 2-10 days. As treatment, the patient is recommended to take vitamins B, C, as well as injections of Galantamine or Dibazol.
We have already said above that one of the most unpleasant and dangerous complications is alveolitis. In a short period of time, this phenomenon can lead to the development of a very dangerous disease - osteomyelitis. Here we are talking about inflammation of bone tissue. The disease is serious and requires complex and lengthy treatment. Experts include the following complications as other potential problems:
- inflammation of the soft tissues of the gums - occurs after a traumatic procedure or loss of a blood clot. In the wound, pus begins to secrete, fibrous and granulation tissue begins to form. The mucous membrane swells noticeably, the wound begins to bleed, and the patient experiences throbbing pain. The cause of the problem is often an incompletely removed cystic formation,
- flux - if a tooth had to be removed due to severe damage as a result of suppuration of the periosteum or the formation of a purulent cavity in the thickness of the gums, then there is a certain risk of re-inflammation. This can happen if insufficient quality antiseptic treatment was carried out,
- dry socket - loss of protective barter in the form of a blood clot leads to drying out of the wound. Pain appears, the surrounding tissues turn red, and bad breath occurs. Poor hygiene, smoking, too frequent and intense mouth rinsing, as well as accidental mechanical damage to the clot can be a provoking factor.
- paresthesia - appears due to irritation of nerve endings during the procedure. The patient may experience numbness in the tongue, lips, chin and cheeks. This phenomenon is usually temporary and goes away on its own after 5-10 minutes.
The patient may experience numbness in the tongue, lips, chin and cheeks.
To avoid such problems, sometimes doctors perform gum curettage after tooth extraction. A similar procedure is often prescribed as part of the treatment of the complications described above. Essentially, this is the cleansing of gum pockets from plaque and deposits. But in this case, the doctor removes abscess lesions, fragments of crowns and fillings, as well as other foreign particles that can cause inflammation.
Read more about potential complications after tooth extraction in our special material {amp}gt;{amp}gt;{amp}gt;
What to do after wisdom tooth removal
The third molar is usually pulled out due to inflammation that appears around it. At the same time, pus and infectious agents are likely to get into the wound. Therefore, in the postoperative period, the patient must follow general recommendations, as well as be as attentive as possible to his feelings, and note the slightest changes in his condition.
As soon as the hole stops bleeding, you should immediately remove the compression tampon. Its presence in the wound provokes the proliferation of bacteria and increases the likelihood of the onset of an inflammatory process.
The patient should be prepared for the fact that his gums will hurt for 3-5 days after the procedure. You need to purchase recommended anesthetics and take them on schedule. If the pain syndrome has become stronger, swelling of the face and gums increases over the course of several days, the elevated temperature does not subside, and an unpleasant odor begins to come from the socket, you need to call the dentist.
What pain relief methods are used when removing a dental cyst?
Whether it hurts to remove a dental cyst depends on what type of treatment you use. Oddly enough, the most difficult method is the easiest for the patient, if we talk only about the operation itself. During this procedure, general anesthesia is often used. For therapeutic and laser treatment, local anesthesia is used. It only numbs the area where the operation will be performed. People with a low pain threshold may experience minor discomfort during the procedure, but such sensations can only be called pain with a stretch.
Local anesthesia for dental cyst removal
Local anesthesia is used for a number of simple and complex dental procedures. It is carried out through an injection into the gum area near the source of infection. The drug acts only on the injection site and the area around it. Usually about half of the face is numbed. The undoubted advantage of this technique is complete safety. All local anesthetic preparations are carefully monitored and have been repeatedly studied for harmful effects after use. Local anesthesia is allowed even for dental treatment in the youngest patients and pregnant women.
After the procedure, the patient can immediately go home. The problem is that most anesthesia lasts long after the operation is completed; half of the face will still be immobilized. In some ways, this feature of the use of local anesthetics can even be called an advantage. The nerve endings do not return to normal for a long time; the tooth often hurts after treatment of the cyst. A few extra hours after pain-free surgery will only be beneficial. Further, it is allowed to use painkillers, which can be purchased at any pharmacy without a doctor’s prescription.
General anesthesia for dental cyst removal
Despite the fact that local anesthesia can provide all the conditions for painless cyst removal, some still prefer to perform even such simple operations under anesthesia. There may be several reasons for this: 1) The pain threshold is too low. 2) Panic fear of any dental intervention. 3) Strong gag reflex. 4) Carrying out several types of dental operations simultaneously. Only for these reasons will a specialist agree to perform such a simple operation under anesthesia. In all other cases it is not required.
The patient is put into a state of general anesthesia using a special mask, through which he inhales the vapors of the drug, or through an injection. Anesthesia affects the entire nervous system as a whole, turning off pain, all reflexes and feelings. Surgeries are often performed on young children under general anesthesia. The operation may be significantly delayed, and the child will simply be bored sitting in the dental chair. In order to prevent him from causing harm to himself, he is put into a state of sleep. Such pain relief measures are not used for dental treatment in pregnant women. The effect of general anesthesia on the fetus has not been fully studied. It is impossible to fully say whether it harms or does not harm the child. Considering all the developments in the field of anesthesiology and their widespread availability, it cannot be said that removal of a dental cyst is painful. Having chosen the right anesthetic, you won’t even notice how the procedure went.