Concept of paresthesia
Paresthesia is a decrease in sensation in various parts of the human body. The normal state of the body allows you to feel heat and cold, respond to compression, stretching and other mechanical or chemical influences. With paresthesia, the signal from nerve endings to the brain is disrupted and sensations are dulled. You may experience tingling, burning, or numbness in some areas of the body. This is not a disease. This is a change caused by damage to nerve fibers. Due to malfunctions of the central nervous system, some part of the body sends different signals, and the body “gets lost.”
Numbness after dental anesthesia: symptoms, causes
The problem with diagnosing complications of anesthesia is that numbness of the jaw is a natural condition after anesthesia. If accompanying symptoms are added to it, you should consult a doctor. Associated symptoms:
- numbness of the tongue, burning and tingling;
- numbness of the cheek;
- sagging part of the face;
- tooth pain;
- pulsation in the gums;
- profuse salivation.
There are only three factors influencing the symptom:
- a needle entering a blood vessel when injecting an anesthetic;
- nerve damage;
- exposure to the anesthetic due to its increased toxicity.
The needle gets into the vessel and may break off. The nerve is damaged when instruments are applied. The toxicity of the anesthetic increases with minimal errors by anesthesiologists.
What is the reason for the decrease in sensitivity after visiting the dentist?
The human body has 24 nerves that control the skull, face, and are responsible for salivation and jaw movement. Among them are the maxillary and mandibular. Their damage can cause paresthesia. Most often, numbness occurs after wisdom tooth removal. During this operation, the dentist may accidentally touch the nerve ending of the lower or upper jaw. This can cause facial numbness, cheek numbness, and tongue numbness. The nervous apparatus branches near the tips of the “eight” roots. That is why it is often touched when surgical instruments are inserted. The timing of the loss of sensitivity and in which areas the patient will experience discomfort will depend on how extensive the affected area is.
In addition, as a result of surgical intervention, swelling of the gums around the socket may appear, and the surrounding dental tissue may become inflamed. The problem may also be due to incorrect administration of the painkiller. The inflamed tissue compresses the nerves, and then symptoms of paresthesia appear. Also at risk are older people, especially women, and those whose teeth are positioned at an incorrect angle.
Application method
The severity of pain during tooth extraction is determined by the quantity and quality of the anesthetic drug that was used to numb the prepared area. Today, three types of anesthesia are common for dental procedures: application, infiltration and conduction, also called regional.
The severity of pain during tooth extraction is determined by the quantity and quality of the anesthetic drug.
The application type is produced in the form of gels or sprays, which are applied externally to the gums surrounding the diseased tooth. The active substance penetrates only into the surface layers of the periodontium, and its effect lasts no more than 15-20 minutes, so these drugs are not suitable for removing permanent teeth (with the exception of weakened milk teeth).
For this reason, topical anesthesia is used only as an anesthetic before using the main anesthetic to reduce the discomfort of a needle stick.
Important! Such sprays and gels are produced with flavoring additives and aromas, due to which they are positively perceived by children and patients with high sensitivity.
Symptoms
- Decreased sensitivity, similar to the effect of painkillers;
- Light burning sensation;
- Loss of taste;
- Goosebumps syndrome;
- Sensation of a small, thin foreign object entering the oral cavity.
Different people experience different sensations. Someone's entire tongue or a small part of it becomes numb. Some people note stiffness of the lips, others complain of numbness of the entire jaw. But, even if it seems that you can endure it, you still need to get rid of these feelings.
Numbness occurs quite often. When 1-2 weeks pass after tooth extraction, paresthesia disappears. But, if the process continues longer than this period, you must definitely visit the doctor who removed the tooth.
How to treat numb gums
If the patient's gums are numb, it is necessary to begin treatment early. The problem requires an integrated approach, since it is important to establish the cause of its occurrence.
The medications that are most often used if the gums are numb include:
- ► Antibacterial drugs. To eliminate pathogenic microflora in dentistry, Amoxiclav or Clindamycin are used. Preference is given to tablet or injection forms of release. The average duration of treatment is 7-14 days.
- ► Local antiseptics. They are used in the form of an ointment, gel or rinse solution.
- ► Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The drugs reduce pain and tissue swelling. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are often taken for two weeks. The doctor selects medications individually.
- ► Traditional methods. A decoction of chamomile or calendula has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, which restores tissue sensitivity if the gums are numb. However, traditional methods can only be used on the recommendation of a dentist.
If there is no effect from the drug therapy, surgical intervention is prescribed, which is aimed at removing purulent masses or the implant. This will improve the patient's condition and prevent the spread of infection to other organs and tissues.
At the recovery stage, when the gums become numb, physiotherapeutic procedures are used:
- ► laser therapy
- ► dynamic current treatment
- ► UHF therapy
- ► electrophoresis
Treatment of paresthesia
Numbness after wisdom tooth removal can be treated with medication. It is recommended to take vitamins B and C, which promote rapid wound healing, as well as medications that restore blood circulation. For example, Piracetam or Trental. You should be aware that such drugs have contraindications: high blood sugar, heart disease, taking the drug during pregnancy and breastfeeding, stomach and duodenal ulcers, impaired renal function, strokes. The doctor may also prescribe injections of dibazole and aloe extract.
Physiotherapeutic procedures help a lot. These include:
- Exposure of the diseased area to electric current of ultra-high frequencies, relieving muscle tension, improving blood flow and relieving the inflammatory process;
- Therapy using the beneficial properties of a magnetic field, which promotes the restoration of nerve fibers and fights swelling;
- Injection of drugs into the diseased area using a low-intensity electrical discharge. This helps to achieve rapid restoration of damaged tissues, relieve swelling, and get rid of pain;
- Acupuncture. Thanks to the impact on special points on the body, it will improve blood flow and increase the body's resistance;
- Mud treatment, which has a general strengthening effect for the whole body.
In rare cases, paresthesia persists for several months. Then the only treatment option is surgery. It is usually done if numbness symptoms persist for a year or two. But such operations are carried out in extremely rare cases.
The return of sensitivity is preceded by a slight tingling sensation. Mild itching and burning may be felt. This suggests that the doctor chose the treatment correctly and that the body will soon recover.
How long does it take for a painkiller injection to wear off?
Dentists use several types of anesthesia:
- Applique. An anesthetic in the form of a gel or ointment is applied to the desired area of the gum.
- Conductor. Administered by injection.
- Infiltration. Three-stage anesthesia is usually performed before complex manipulations.
After treatment or tooth extraction, depending on the type of anesthesia, a feeling of numbness remains. If pain relief was carried out correctly, without violating the technology of administering the anesthetic, the numbness goes away after some time.
Experts have identified maximum thresholds for each type of anesthesia:
- after application with gel or ointment, numbness disappears in no more than thirty minutes;
- after conduction anesthesia, the numbing effect lasts up to five to six hours;
- after infiltration anesthesia, numbness disappears within three to four hours.
In order to identify the maximum time threshold, it is also necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of each patient: age, weight, etc.
Preventing complications of numbness
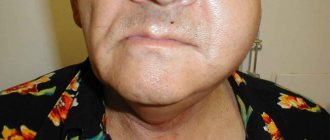
Medicine has encountered cases where paresthesia was accompanied by complications. In some patients, numbness in the chin after wisdom tooth removal or in the cheek after surgery caused permanent loss of sensation in these areas. And sometimes the problem became chronic. Numbness of the face did not manifest itself in the normal state, but under the influence of low temperatures, overwork, and strong experiences, the person again began to experience unpleasant sensations.
This can be avoided if you follow some simple rules:
- Maintain basic oral hygiene and prevent infection from entering the wound, which can cause an inflammatory process;
- Monitor blood pressure. When its levels are high, the expanding vessels can touch the neighboring nerve;
- Take walks, avoid stress and overexertion, do physical exercises;
- Try to eat regularly and properly, avoiding spicy and canned foods, as well as very hot or cold foods;
- Monitor your blood sugar levels. If its amount is reduced, it can cause inflammation of the branches of the facial nerves;
- Do not delay your visit to the doctor if the numbness does not go away.
Patients' lips, chin, and cheeks become numb after a tooth extraction procedure quite often. In the vast majority of such cases, recovery takes 10-15 days. Sometimes the discomfort lasts for a month. If there is no improvement after thirty days, you should visit the clinic where the operation was performed. It is advisable to contact the same doctor so that he can prescribe physical procedures and prescribe the necessary medications. 99% of patients no longer experience any discomfort after proper treatment.
Computer anesthesia
In order to eliminate the possibility of developing complications after an injection, modern dentistry uses computer anesthesia.
Advantages of the technique:
- There is no numbness of soft tissues. Computer anesthesia only numbs the area where the anesthetic is injected.
- Computer anesthesia is painless.
- The pressure of the anesthetic is controlled by a computer, so it is administered at the desired speed and in smaller quantities.
- There is no feeling of gum swelling.
- The influence of the human factor is eliminated due to the fact that the computer controls the entire process.
- The tip is shaped like a pen, which is less intimidating for patients who are afraid of injections.
When does it go away on its own?
Numbness after wisdom tooth extraction is normal. It may appear due to prolonged pressure on a certain area of soft tissue during manipulation.
We invite you to read Mewing: how to hold your tongue correctly to become more beautiful
Under favorable circumstances, this phenomenon disappears within 1-10 days.
Otherwise, persistent paresthesia develops, when the area of the head becomes numb and is not felt by the patient for 2-3 weeks to six months.
What to do if you feel numb
Sensitivity may return several weeks after surgery.
If symptoms persist, the doctor prescribes treatment:
- Physiotherapy. Prescribed to accelerate the recovery of nerve endings and reduce pain. Treatment with high-frequency electric current - exposure to heat leads to relaxation of muscle fibers, improves blood flow, and reduces the inflammatory response. Magnetotherapy - the action of a magnetic field on the affected area has a healing effect and restores nerve cells. Electrophoresis is the introduction of medications through the patient’s skin using electrical impulses, removing inflammation.
- Medicines. A specialist can prescribe drugs to thin the blood, increase immunity, to speed up the blood circulation process - to restore the sensitivity of nerve cells: Piracetam, Actovegin, injections of aloe extract, Dibazol. Taking vitamins B and C accelerates the healing of the hole at the site of the removed eighth tooth.
- Surgical intervention. In difficult cases, when medications and physical procedures do not help, surgical intervention is performed.
It is impossible to get rid of paresthesia on your own. To restore the receptivity of the tongue, you need comprehensive help from a surgeon - dentist, neurologist, neurophysiologist.
It is important to maintain hygiene after surgery: clean the hole in which the removed figure eight was located.
Leftover food can cause infection in the wound, which will lead to inflammation around the removal site. Inflamed tissues compress nerve fibers, and oral sensitivity decreases.
An advanced form of paresthesia leads to further damage to the facial nerves and permanent loss of sensitivity in areas of the face.