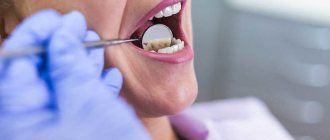
Pus after tooth extraction is an alarming symptom, which is a dangerous deviation from the norm. Ideally, after removal, holes remain that stop bleeding heavily after just a few minutes. The wound may bleed little by little for several more days. After about two days, a blood clot emerges from the hole, which initially protected the open wound from infection. Pain in the area of the extracted tooth can haunt the patient from three days to two weeks, depending on the complexity of the operation.
If the dentist removed the tooth correctly, then the occurrence of purulent processes may be caused by the patient himself. However, pus appears in the socket even when the removal was carried out professionally in all respects, and the patient strictly followed all the instructions.
To understand why suppuration begins after tooth extraction, it is necessary to briefly dwell on the features of this procedure, signs of suppuration, and possible prerequisites that contribute to the formation of an abscess at the site of the removed diseased tooth.
General rules for tooth extraction
The likelihood of a purulent process increases due to the fact that a person is forced to eat regularly, and without chewing this is impossible. Because of this, there is a high probability of mechanical damage to the hole and infection.
If immediately after surgery the gums become inflamed and very painful, this is normal and is not a cause for alarm. But if the hole festers after a few hours, you should immediately contact your dentist.
It is almost impossible to eliminate the purulent process in the gums on your own. Through inept actions, the patient can only cause harm to himself.
To avoid pathological inflammation of the gums after tooth extraction, you must follow these rules:
- Make an appointment only with doctors who specialize in such surgical operations. You should not use the services of a dentist with a dubious reputation.
- Do not rinse your mouth for 24 hours after surgery. This leads to the clot leaving the socket prematurely, opening the way for infection.
- For the first two days you need to refrain from eating solid food. You can eat porridge, purees, grated foods and broths.
- When brushing your teeth, you must refrain from contacting the brush with the gum in the place where the tooth was removed.
- To prevent infection and suppuration of the hole, regularly irrigate the oral cavity with antiseptic drugs.
If pus has formed in the hole after the removal of a diseased tooth, you need to pay attention to this phenomenon, and not think that this is a trifle. Pus in the gums can be a sign of complications and the development of a dangerous disease.
Larisa Kopylova
Dentist-therapist
Only certified specialists with appropriate certificates and extensive practice are allowed to remove teeth. This is justified by the fact that this procedure is a surgical operation during which the soft tissue of the gums, bones of the upper or lower jaw, blood vessels and nerve endings are affected.
Abscess on the gum
An abscess on the gum, which in dental practice is called a periodontal abscess, is accompanied by pain, swelling, and bad breath. Why do purulent abscesses appear and how to get rid of them - read in this article.
What can you do at home?
It is, of course, impossible to cure an abscess on the gum without the help of a qualified dentist.
If a visit to the doctor is delayed or impossible, you can relieve symptoms at home using the following methods:
- cool antiseptic rinses: Chlorhexidine, potassium permanganate solution, Stomatidin, Miramistin, Rivanol;
- cold compresses. Ice can be applied to the affected area;
- taking analgesics. Severe pain can be relieved by drugs such as Nimesil, Ketanov, Solpadeine, etc.).
In case of gum abscess, warm rinses and warm compresses are strictly prohibited. In warmth, microbes multiply more intensively, and there is more pus.
It is imperative to continue brushing your teeth, eliminating excess bacterial plaque. If brushing your teeth is too painful, you should at least rinse your mouth with a paste diluted in water.
Under no circumstances should you open an abscess on your gum yourself! The health consequences can be severe.
Relieving abscess symptoms at home
Local treatment
The goal of local treatment is to open the abscess and remove its purulent contents. The following methods can be used for this:
- removing tartar and cleaning gum pockets from pus – for periodontitis;
- root canal treatment – for periodontitis;
- resection of the apex of the tooth root followed by cleaning out the purulent tumor.
If it is not possible to cure the canals, the apex of the root along with the abscess is cut off;
- removal of diseased teeth and scraping of pus;
- cleaning the tooth socket from purulent plaque if the cause of inflammation is a consequence of tooth extraction.
Abscess treatment
General treatment
After mechanical cleansing of gingival tissue from pus, anti-inflammatory therapy is indicated. It includes:
- taking antibiotics: Amoxicillin, Amoxilav, Dalatsin C, Lincomycin, Clindamycin, Tsiprolet, Ciprofloxacin, etc.;
- applications with healing ointments: Levomikol, Metrogyl Denta;
- antiseptic rinses: Chlorhexidine, Stomatidin, Miramistin, Rivanol, potassium permanganate solution;
- placing a turunda with an antiseptic after cleaning the socket of an extracted tooth.
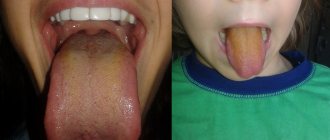
Gum abscess in a child
Periodontal abscesses are uncommon in children. As a rule, they appear due to mechanical injuries, untreated caries or poor oral hygiene.
Children complain of pain in the gums, refuse food and behave restlessly. There is an increased body temperature and swelling of the gums. If you experience such symptoms, you should definitely see a dentist.
An abscess on a child’s gum
Do abscesses on the gums go away on their own?
No. Purulent inflammation cannot go away on its own; you need the help of a doctor. Even if the abscess does not hurt, it must be shown to a specialist.
What complications can there be?
Without treatment, the purulent tumor grows, its contents come out and affect other tissues of the body. This is fraught with acute purulent inflammation of fatty tissue (phlegmon), penetration of pus into the veins of the face (causing phlebitis and thrombophlebitis) and blood poisoning (sepsis). In the most severe cases, death is possible.
Symptoms of the problem
All people who have had their teeth removed know that after this operation the soft tissues swell, and sometimes a slight swelling forms on the cheek. Even with difficult removal under sterile conditions, after a few hours the swelling subsides and the pain gradually subsides.
With infectious complications, patients experience the following symptoms:
- swelling of the soft tissues progresses, it affects the face, seriously changing its outline;
- purulent discharge occurs, which increases in volume, despite rinsing and the use of antiseptic drugs;
- there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth from rotting tissue around the wound left after the operation;
- body temperature rises, reaching high values (39-40 degrees);
- intensifying throbbing pain, which is very difficult to relieve even with potent drugs.
Facial swelling is a clear symptom of a problem
Larisa Kopylova
Dentist-therapist
Many patients do not know what to do when the gums fester after tooth extraction. In all cases, there is only one recommendation - immediately contact the surgeon who performed the operation.
The appearance of pus in the gums could be caused by various factors. Each disease requires specific treatment. Let us dwell on the main reasons why, after a tooth is pulled out, the gums or periosteum fester.
In the video, the dentist talks about the main complications that arise after tooth extraction:
Signs of alveolitis
The most common complication of extraction of a wisdom tooth or any other unit is alveolitis - inflammation of the empty socket (pictured below). It is the undiagnosed and unresolved inflammatory process that subsequently turns into suppuration and entails a host of other unpleasant complications. Inflammation of the gums after tooth extraction is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- pronounced gradually increasing pain syndrome (the pain is pulsating, aching in nature);
- the appearance of an unpleasant (putrid) odor from the mouth, which does not disappear within several days and does not “yield” to hygienic brushing of teeth;
- at the site of the extracted tooth there is purulent exudate (yellowish-brown liquid);
- the hole itself is painful on palpation, hyperemic, swollen;
- If an abscess has formed on the gum, the patient who has undergone extraction may experience swelling in the face (usually on the affected side).
We suggest you read: Tooth hurts with arsenic under a filling. 6 reasons
The course of postoperative alveolitis with a festering socket is also associated with systemic disorders: body temperature rises above 38 degrees, intense headache is present, performance decreases, apathy, lethargy, and weakness in the body appear. Many patients experience chills and muscle pain (signs of general intoxication in the body), and they have difficulty chewing and swallowing food.
The list of signs of an inflammatory process in an empty socket also includes:
- absence of a blood clot in the postoperative wound (the so-called dry socket);
- the presence of a dirty gray plaque on the surface of the healing gum (sometimes it may turn black);
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes.
Important! A cause for concern, indicating that the gums are festering after tooth extraction, is an acute pain shooting into the jaw, which radiates to the temple and gradually spreads along the trigeminal nerve.
In addition to alveolitis, suppuration of the hole after extraction may indicate other dental complications:
- dental cyst (bone fragments remain in the wound);
- osteomyelitis (inflammation of the jaw bones);
- abscess (closed abscess);
- phlegmon (inflammatory process affecting fatty tissue);
- periostitis (damage to the periosteum).
Getting into the hole of infection
This is the most common reason that some time after dental surgery an abscess forms on the gum. The doctor performs various manipulations with the diseased tooth, during which the integrity of the adjacent soft tissues is damaged. If pathogenic microorganisms enter the wound, it can fester within a few hours after the end of the operation.
The infection enters the soft tissue in the following ways:
- with poorly processed tools;
- through the surgeon's dirty hands;
- with leftover food;
- when drinking unboiled water;
- when the patient tries to touch the wound with his finger.
In most cases, the development of alveolitis is preceded by the loss of blood clots from the sockets remaining from extracted teeth. Most often, purulent inflammation occurs after wisdom teeth are pulled out. Access to such wounds is difficult; food debris accumulates in the corners of the oral cavity and saliva saturated with bacteria settles.
There must be a blood clot in the socket of the extracted tooth.
Treatment of alveolitis is carried out in a clinical setting. The doctor opens the wound, cleans it of rot and closes it with special medicines. After this, antibiotic therapy and treatment of the oral cavity with antiseptic agents are prescribed. Advanced alveolitis can lead to dangerous consequences for human health.
First aid at home
Removal of the abscess is carried out only by a specialist, because complications can arise with a dental abscess. Rinsing with herbal decoctions will help relieve suppuration and purulent inflammatory areas. With a purulent abscess, you should be careful so that the upper shell of the abscess does not rupture. The ball with pus is handled carefully without strong pressure. You can alleviate the patient’s condition at home, but in case of purulent inflammation, when the inflamed area has already ruptured, initial treatment at home is mandatory.
Clean the gums from bacteria and plaque using a special antiseptic. The abscess will begin to break out without treatment, and initial treatment of the inflamed dental area with chlorhexidine or furatsilin will prevent the spread of pathogenic microorganisms. Tooth enamel will not be damaged by such actions. If you have a cold, rinsing with antiseptics should be delayed or replaced with a decoction of chamomile or eucalyptus. For abscesses (boils, a bag of pus, purulent blisters), if adults show signs of a cold, aloe tinctures help.
It is impossible to open an abscess even with the help of disinfected needles. Only doctors fight abscesses in sterile conditions.
When removing ulcers, healthy areas of the mucous membrane are protected from purulent discharge. If the causes of inflammation are associated with the installed implant (implantation was carried out with a violation of technology), the doctor should conduct additional diagnostics of the oral cavity. Suppuration can reach the implant.
Read also: Cure for gum disease
Damage to the maxillary sinus
The tooth being removed may have long and strong roots that grow into the walls of the maxillary sinus. If the preparation for the operation is improper (lack of an x-ray), perforation of the maxillary sinus may occur. When the roots are extracted, part of the bone tissue with the mucous membrane comes out. Signs of such an injury are food getting into the nasal passages and air escaping from the wound. The patient experiences difficulty breathing, fever and profuse nasal discharge.
Damage to the maxillary sinus can cause serious complications
Larisa Kopylova
Dentist-therapist
Food that gets into the maxillary sinus rots, and extensive inflammation occurs, spreading to the periosteum, nasal cavity and central ear. In the most severe cases, the rotting contents of the maxillary sinus cause damage to the eyes and brain.
If such symptoms are detected, you should immediately consult your doctor. He will seal the walls of the maxillary sinus and send the patient to an otolaryngologist. The ENT specialist will take measures to remove the purulent mass from the sinuses and prescribe procedures to restore the integrity of the mucous membrane of the nasal passages. If necessary, a course of antibiotics will be prescribed.
What is dangerous if the gums become suppurated?
Incorrect or untimely treatment of purulent discharge from the gums can lead to serious pathologies . For example, the infection may spread to other tissues and lead to osteomyelitis . This disease is treated only in a hospital , as it can lead to blood poisoning , which poses a threat to the life and health of the patient, including death .
Attention! Respiratory failure and pulmonary edema may also occur .
Shrapnel getting into the wound
Old teeth with the nerves removed are very fragile. They crumble when pressed with forceps and when rocked. You need to be especially careful when removing such units. When their roots are removed, fragments of various sizes may form.
A tooth fragment in the socket causes pus to appear
As a rule, it is when the roots become suppurated that acute pain and inflammation occur, which is the reason for the operation. It is the fragments of infected bone tissue that cause the formation of secondary inflammation and the release of pus.
Larisa Kopylova
Dentist-therapist
You can be sure that if the blood clot in the socket is intact, but it has festered, fragments of bone tissue remain in the gum. In modern clinics, such a mistake is excluded from the very beginning, since an image is taken before the tooth is removed and after this procedure. But this is not practiced in most hospitals due to lack of equipment.
Treatment of suppuration caused by root fragments is carried out by a specialist. The cavity is opened, cleaned and treated with antiseptic drugs. Subsequently, the patient is prescribed antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Causes
- In most cases, alveolitis appears due to injury to the walls of the socket. They are quite thin, so if handled carelessly, they can be damaged or completely broken. In addition, when bone tissue is destroyed, debris can get into the wound, which can cause infection. The risk of alveolitis increases significantly when wisdom teeth are removed.
- A common cause of the disease is considered to be insufficient sterility of the tooth, gums, and soft tissues. It is worth noting that even with the use of serious antiseptics it is not possible to achieve absolute sterility. This is explained by the fact that tooth extraction is often prescribed in the presence of purulent complications.
- If the immune system is weakened, the body may not be able to cope with bacteria even when taking antibiotics.
For this reason, it is not recommended to remove teeth during acute infections of the mouth and nasopharynx, as well as during exacerbation of chronic diseases. After the removal procedure, you must avoid contact with patients who have a sore throat, cold or other infectious disease. Moreover, in some cases a preventive course of antibiotics is prescribed. This applies to older people, patients with diabetes, cancer and AIDS. - After a tooth is removed, a blood clot forms in the socket.
If this does not happen, food particles will remain here, which will lead to the proliferation of microorganisms that cause alveolitis. Therefore, before surgery, it is necessary to check blood clotting, and also warn the dental surgeon that you are taking warfarin, aspirin or anticoagulants. - Another cause of alveolitis is a neglectful attitude towards one’s own health. Thus, some patients do not follow the doctor’s recommendations after removal. They don't rinse their mouths, use toothpicks and check with their fingers to see if the area is healing.
Cyst formation
A cyst in the socket can form for many reasons. Most often, dentists have to deal with formations, the prerequisites for the appearance of which are dental fragments remaining in the gums. Thanks to the immune system, such a fragment is gradually overgrown with soft tissue and a cyst is formed. For a number of reasons, the capsule is opened, its contents penetrate into the soft tissues, causing pathological changes in them.
Cyst after an extracted tooth
Rupture of the cyst is accompanied by the formation of an extensive tumor and rapidly increasing pain. Fistulas appear in the gums, through which purulent masses flow. It is impossible to get rid of such a complication on your own. In a dental clinic, the gums are opened and the cyst is removed. The patient subsequently undergoes a course of antibiotics
Gum healing after surgery
The speed of recovery processes after surgery depends on a number of factors:
- Physiological characteristics of the patient.
- The professionalism of the doctor who performed the operation.
- Location of the tooth to be removed.
- Other complications that arose during the operation.
Tooth extraction can be accompanied by various difficulties. There are cases when the coronal part of the tooth is already completely missing, or it is destroyed during the operation. In such cases, the dentist resorts to cutting the gums. Naturally, this leads to a longer healing process.
After the tooth is removed, the hole fills with blood within a few minutes (or up to half an hour if vasoconstricting drugs were used during the operation) and a blood clot appears in it. The clot cannot be removed from the wound , as it serves as a barrier to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms. If it is eliminated, the risk of developing inflammatory processes in the gums and soft tissues of the oral cavity increases significantly.
This is what normal healing of a hole looks like.
Over the course of 2-3 days, the clot changes its color, gradually becoming lighter and forming a kind of fibrin framework, which is the main material for the formation of a blood clot. The thrombus continues to protect the socket from infection and also prevents bleeding from the gums. In order for wound healing to proceed normally, you should leave it alone and not expose the wound to irritation .
Complications from periodontitis
The most difficult operations for dentists are to remove teeth affected by chronic periodontitis. This disease is the formation of purulent sacs at the apex of the roots. For a long time, such formations may not bother a person. But if the tooth has rotted due to general or local hypothermia, a strong blow or a concomitant infectious disease, then it is recommended to get rid of it urgently.
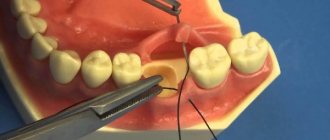
A complication of the operation is inflammation of the periosteum due to purulent capsules remaining on it. The patient feels acute throbbing pain, his temperature rises and his health worsens. To prevent the infection from spreading to neighboring organs, urgent surgery is performed. The doctor opens the gum and removes the damaged bone tissue. After this, the wound is disinfected and sutured. A drain is worn for some time to drain the fluid. The patient is prescribed antibiotics and painkillers.
Prevention
The main task of both the dentist performing the extraction and the patient himself is to create favorable conditions for the formation of a “protective” blood clot in the empty socket. This is the mechanical barrier that protects the postoperative wound from secondary infection and prevents inflammation and suppuration of the gums from developing.
So, in order to minimize the risk of post-extraction complications, it is necessary:
- thoroughly treat the wound with antiseptic solutions, remove bone debris and tooth fragments from it;
- if the indication for surgery is a purulent complication of advanced caries, the dentist must remove the granuloma and, conversely, not perform any rinsing (so as not to remove the blood clot);
- To prevent the protective blood clot from dissolving due to exacerbation of chronic diseases or as a result of infectious “attacks,” the patient is shown intramuscular injections of antibiotics, which alternate with injections of these drugs directly into the gums.
The danger of postoperative alveolitis lies in the high risk of further spread of infection, the consequences of which can be respiratory failure and pulmonary edema. If left untreated, the inflammatory process from the empty socket can spread to neighboring teeth, affect soft tissues, and lead to osteomyelitis.
Thus, at the first “signals” indicating that the postoperative wound is abscessing, you should not self-medicate, but should immediately seek qualified medical help. Strict adherence to all the recommendations given by the dentist at the end of the extraction is the best prevention of alveolitis after tooth extraction.
Independent measures
If after the operation the hole begins to fester or exhibits the above-described symptoms of infection, then you need to contact the dentist as soon as possible . Before visiting the dentist, you can take a number of independent preventive measures. However, it is important to understand that not all means are acceptable for use in a given situation.
First of all, you should remember that you cannot use hydrogen peroxide and soda solution for rinsing your mouth . In addition to the beneficial antiseptic effect, these drugs pose a danger in that they can eliminate a blood clot that performs a protective function. Subsequently, the gums will be completely defenseless against infection.
Rinsing and analgesics bring only a temporary effect.
To relieve inflammation and speed up wound healing, you can use a number of proven folk methods. These include a solution of calendula, a decoction of chamomile and St. John's wort, boiled sage and others.
However, when using natural antiseptics, it is worth remembering important rules:
- Do not wash the blood clot out of the wound ; just hold the solution in your mouth for a few minutes and spit it out;
- also, you should not pick out the remains of a blood clot from the hole , especially using a cotton swab or toothpick;
- It is advisable to apply the solution several times within an hour until signs of improvement appear.
In case of acute pain, the use of analgesics is acceptable. However, they should not be used several hours before going to the dentist. It is important to remember that remedies to relieve pain and inflammation have only a temporary effect and do not eliminate the cause of the infection itself. A visit to the dentist is mandatory.
Home treatment
If purulent exudate flows from an empty hole, you should rinse your mouth several times a day with an infusion of oak bark, decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, sage, calendula), and a soda-saline solution (½ teaspoon of each powder is diluted in a glass of water). You can apply tea tree oil directly to the inflamed gum.
What you should not do on your own:
- rinse your mouth intensively (this can lead to washing out and dissolving the formed blood clot), just take a small amount of the prepared solution into your mouth and hold it against the inflamed gum for 1–3 minutes;
- “suck out” the half-dissolved clot from the hole, even if it has turned black or has the “wrong” color;
- warm the affected area (this measure will only increase the intensity of the inflammatory process);
- drink Aspirin (will increase local bleeding);
- take antibiotics yourself.
Read also: Antibiotics in dentistry after tooth extraction
After preliminary consultation with a doctor, you can take an analgesic tablet (Ketorola, Pentalgina, Naiza) - these drugs will temporarily relieve pain. It is necessary to understand that this is a symptomatic measure to alleviate the general condition, and you still cannot do without full-fledged complex treatment of alveolitis.