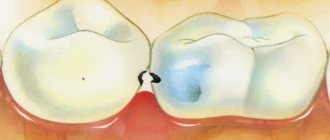
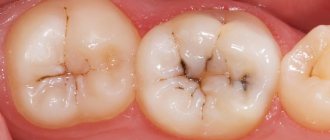
Risk factors
Pulpitis is an inflammatory disease in which the pathological process occurs in the neurovascular bundle of the tooth.
Pathology occurs when pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into a specified area. In children, due to the structure of their teeth, pulpitis develops much more often than in adults. The causes of the disease are the following factors:
- caries in advanced stages;
- enamel damage;
- temperature and chemical damage to teeth;
- infectious pathologies of a chronic nature;
- violations during the filling process.
In young children, pulpitis develops quickly, which is associated with such structural features of the teeth as loose connective tissue, increased volume of the pulp chamber, small size and width of dentinal tubules.
Note! Weakened immunity is also a predisposing cause of the development of dental disease. This condition often occurs after ARVI, chicken pox, or tonsillitis.
When the integrity of the hard tissues of the tooth is violated, microorganisms penetrate into the pulp chamber, causing an inflammatory process.
What is pulpitis:
Features of the disease in childhood
With pulpitis of primary teeth, the disease can occur in acute or chronic form .
The main feature of the pathology at this age is a good outflow of fluid from the inflamed pulp, which is why pain sensations are blocked. This is why children do not immediately complain of pain, but only at an advanced stage of the disease, when the pulp cannot be restored. In the acute form of pulpitis of primary teeth, the child periodically experiences pain, the greatest intensity of which is observed at night. A fluid consisting of blood flowing from the pulp vessels gradually forms in the pulp chamber. Subsequently, purulent masses appear here, which is associated with the collapse of the pulp tissue.
In the chronic course, pain, painful reactions to temperature, and blood flow from the affected tooth are observed.
Pulpitis of permanent teeth is usually observed in adolescent children. Typically, the inflammatory process develops against the background of medium or deep caries. This form of the disease can also occur in both acute and chronic forms.
In acute pulpitis of permanent teeth, complaints of spontaneous pain of an acute pulsating nature are observed; in chronic pulpitis, the pathological process can develop with the release of putrefactive masses with an unpleasant odor.
About childhood pulpitis:
Prevention of childhood pulpitis
Treating pulpitis in baby teeth is difficult and expensive, so it is best to avoid it. The following preventive measures will help with this:
- Start oral hygiene from the eruption of the very first tooth, and gradually accustom the child to it.
- Brush children's teeth with special toothpastes containing age-appropriate fluoride.
- Avoid giving your child too many sweets, especially sugary drinks. The most dangerous thing is to give a child sweets from a bottle - because of this, the front teeth are often affected by caries, and then pulpitis.
- Make sure your child's diet includes plenty of fresh vegetables and fruits. Solid foods are especially beneficial - they strengthen teeth and help remove plaque.
- Every six months, take your child to the dentist for preventive examinations so that the doctor can notice and treat caries in time.
- At the first signs of even mild dental damage, do not let the process take its course, but take the child to the dentist.
These measures will help you prevent pulpitis and keep your child's baby and permanent teeth healthy.
Symptoms of pulpitis in a child
The manifestations of pulpitis in children include the following:
- pain of varying severity. In each child, the inflammatory process of the pulp proceeds differently: some feel constant pain, others do not feel discomfort throughout the entire acute period of the disease;
- unpleasant sensations when a diseased tooth collides with a healthy one, as well as during the process of chewing food;
- swelling of the gums;
- disturbance of appetite and sleep;
- temperature rise to 38-39 degrees;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- the appearance of bad breath;
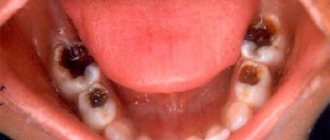
- crown destruction;
- deposits on teeth.
Important! The specific symptoms of pulpitis in children depend on the form in which it occurs.
Causes of pulpitis in children
Most often, according to dentists, this very unpleasant disease in childhood is caused by:
- If caries treatment is not carried out on time - in this case, microbes developing in the carious cavity and tooth tissue disintegrating under their influence provoke the active release of toxins. Under their influence, the inflammatory process of the pulp most often begins, which, if left untreated, can lead to very serious consequences.
- An acute infectious disease suffered by a child - during the course of an infection, tooth pulpitis in a child, as a rule, occurs against the background of decreased immunity and the appearance of a large number of bacteria.
- Injury to a baby tooth - this can be either an accidental damage to the tooth during play or rest, or too rough treatment of the oral cavity in the presence of caries, or even a careless action of the dentist;
- Medical errors in the treatment of caries - inflammation of the pulp can develop under the influence of incorrectly selected filling material or as a result of treating the oral cavity with too strong antiseptics, for example, alcohol, as well as due to overheating of dental tissues during the preparation of a carious cavity.
Incidence of pulpitis
Many parents do not take their children to the dentist, believing that pulpitis cannot develop in a child at 2 years old. Mothers think that if they don’t give their baby sweets, then caries won’t affect the enamel. Unfortunately, they are wrong. Tooth pulpitis can strike a child at 2, 3, or 5 years of age.
- At 2 years of age, pulpitis affects the baby’s front baby teeth;
- From 3-4 years of age, children more often suffer from pulpitis in the back teeth. Often a 4-5 year old child comes to the dentist crying from pain in his molars. Surprisingly, such inflammations occur several times more often than pulpitis in the front teeth of children.
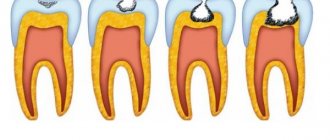
Types of disease
Pulpitis occurs in different variations, depending on which certain manifestations are observed.
| Type of pulpitis | Subspecies and main manifestations |
| Spicy | The focal form of acute pulpitis is rare and is characterized by damage to only one tooth. In this case, the inflammatory process quickly progresses and becomes diffuse. The diffuse form is characterized by the spread of the inflammatory process to the periodontium. In this case, pain occurs when chewing or eating cold or too hot foods. The throbbing pain becomes especially pronounced at night. |
| Chronic | This type is observed much more often than the acute form of the disease. Chronic pulpitis can occur in a fibrous form. In this case, the carious cavity is small in size. The affected tooth often bleeds. Pain with this type of pulpitis occurs extremely rarely. The gangrenous form of chronic pulpitis is accompanied by such manifestations as a feeling of fullness in the diseased tooth, the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the oral cavity, the appearance of gray plaque on the enamel, and enlargement of the postauricular and submandibular lymph nodes. The hypertrophic form of pulpitis is the rarest type of pathology. Its main features are exposure of the pulp and its increase in size, pain when chewing, and bleeding from the pulp. |
Traumatic | This type of disease occurs due to trauma, in particular a tooth fracture. When part of the crown breaks off, the pulp becomes infected through the wide dentinal tubules. |
Treatment methods for baby and permanent teeth
There are several ways to treat pulpitis in children. Their effectiveness depends on the degree of neglect of the pathological process.
Conservative
The goal of this treatment method is to preserve the pulp. To do this, special antiseptic agents are used to destroy pathogenic microorganisms. After this, the canals are filled.
Biological method
This treatment method is a type of conservative therapy. First, the inflamed area is opened, and the bottom of the cavity is filled with a mixture that includes artificial dentin.
After the material has dried, sealing is done using phosphate-cement spacers.
Amputation method
This method, which is also called vital, involves removing either the coronal part of the pulp or the neurovascular bundle completely, without affecting the periodontium.
Vital amputation visually:
Devital
This is the most radical treatment method. The indication for this type of intervention is chronic inflammation in an acute or fibrous form against the background of deep caries damage to primary molars.
To kill inflamed tissue, use an arsenic-based paste. If the roots have not yet formed, a mixture of phenol and formalin is used instead of arsenic paste.
The medicine is applied for one to two days, after which the mortified pulp is removed. After performing the manipulation, a tampon soaked with resorcinol - formaldehyde liquid is placed into the cavity. Thanks to this, the healthy state of the growth zone of the developing tooth is maintained.
Pulpotomy in one visit:
How to treat pulpitis of baby teeth
If you suspect that your son or daughter is suffering from this particular illness, then the best thing to do is to seek professional help as soon as possible. Because the disease is quite serious, and it requires correct diagnosis and qualified medical intervention.
There is no need to remove the tooth at all. Moreover, early removal can lead to the formation of an incorrect bite. The course of treatment of pulpitis in children largely depends on the stage of tooth development at which it is detected.
The fact is that the pulp can be completely removed only in the formed roots (and this takes several years from the moment the tooth erupts). Therefore, in most cases, the doctor removes the pulp only partially. As a rule, carious lesions are removed simultaneously with its part located in the crown of the tooth.
This procedure is carried out after an anesthetic injection. After that, a medicine is placed at the bottom of the cavity and at the mouths of the canals, designed to disinfect the remaining tissues. Or, the pulp is first mummified, also through the application of drugs, and then removed.
Over time, such a “gasket” of medications is replaced or left under a permanent filling.
In case of pulpitis of milk teeth, first of all, it is necessary to eliminate the inflammatory process and prevent complications in the form of periodontal damage, which can cause improper formation of permanent teeth. There are 3 main methods in total.
Biological method of treating pulpitis in children
Several years ago, dentists began to practice conservative methods of treating pulpitis in children. This conservative therapy does not require surgical intervention, is easier for the baby to tolerate and causes minimal complications.
Conservative treatment of pulpitis of primary teeth is carried out in stages:
- The doctor opens the inflamed cavity.
- Covers the bottom of the gum and pulp with a special mixture consisting of Shostakovsky balm, calcemin and artificial dentin.
- After the mixture dries, the dentist seals the tooth using fluorine cement or phosphate cement spacers.
Doctors are ambivalent about such a procedure. Some consider biological treatment of pulpitis in children to be an excellent way to relieve the child of pain and create the most favorable conditions for the development of the apices of the roots of permanent teeth.
Many dentists believe that it is the conservative method of treating pulpitis of baby teeth that can provoke various periodontal inflammations.
In any case, treatment of pulpitis of primary teeth requires repeated visits to the doctor and a serious approach. Therefore, be persistent and patient, and also try to set up your child correctly so that every trip to the clinic does not become stressful.
Please note that there is no general approach here. The inflammatory process occurs differently each time. And only a doctor can decide how to treat pulpitis of a baby tooth in each specific case.
Possible mistakes when treating pulpitis
Unfortunately, it is not at first glance that tooth pulpitis in a child is a simple ailment. Incorrect treatment can provoke nightmares such as periodontitis, periostitis and even acute polio.
The most common mistakes when treating pulpitis in children are:
- Incorrect assessment of the condition of the pulp and, consequently, partial removal of inflammation. In this case, the baby will very soon suffer from a new exacerbation.
- Loose bandage when removing pulp. In rare cases, doctors do not apply a temporary bandage with arsenic tightly enough, which can lead to burns and necrosis of the tissues of the cheek, tongue and mucous membranes.
- An overdose of arsenic can cause acute periodontitis, which requires longer treatment than pulpitis in a child.
- Trauma to the periodontium with a root needle. Incomplete cleaning of root canals during the treatment of acute or chronic pulpitis in children can also provoke periodontitis.
Treatment of pulpitis: how to adjust a child
Pulpitis of baby teeth causes a lot of trouble for the baby. There is no need to aggravate the already difficult days of the child; parents should definitely prepare him for a visit to the dentist.
Talk to the baby. Explain that the doctor will treat tooth pulpitis carefully and the patient will not feel pain. It is important that the child does not associate going to the dentist with torture chambers. Choose a positive doctor whom you trust, and dental treatment will become an exciting attraction.
The main task of parents is not to let the disease take its course. Since chronic pulpitis of the baby tooth, which is most often seen in the photo, can lead to further spread of the inflammatory process and damage to the rudiments of permanent teeth.
And don’t forget that preventing trouble is always easier. Therefore, do not allow pulpitis. Ensure that your child brushes their teeth correctly and regularly using high-quality oral hygiene products. And be sure to visit your dentist regularly.
Ways to prevent
To prevent the development of this dental disease in children, you must adhere to the following rules :
- brush your teeth with a properly selected toothbrush and toothpaste twice a day;
- rinse your mouth with warm water after every meal;
- regularly visit the dentist for preventive purposes and consult a doctor if the slightest complaint occurs;
- limit solid foods that can injure teeth;
- use dental floss and mouth rinses from the fourth year of life.
Parents need to regularly examine the child’s oral cavity, assess the condition of enamel and teeth, and determine the freshness of breath.
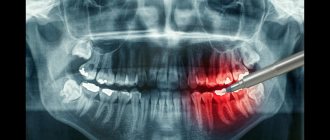
History of treatment of childhood pulpitis:
Symptoms of pulpitis
Pulpitis of baby teeth can be acute or chronic. According to statistics, pulpitis in a child 4-7 years old in acute form is less common than in chronic form. The acute form of this disease has 2 stages: purulent and serous. Each form has its own symptoms. The transition time from one stage to another takes no more than a day, often several hours.
In the serous form, the pain is usually mild. During this phase, people are least likely to see a doctor. In the purulent stage, the pain becomes stronger, but also not always. With good immunity, a large carious cavity through which pus comes out, pain may be absent. You can suspect pulpitis of baby teeth if:
- the baby experiences intense pain when chewing;
- his temperature rose;
- When examining the oral cavity, purulent exudate is observed;
- the child complains of pain.