Content:
- Causes of the anomaly
- What does a “shark” smile lead to?
- When to see a doctor
- When to hesitate to see a doctor
- How is the treatment carried out?
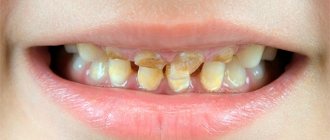
The situation when a molar has erupted, but the milk tooth is in no hurry to leave its place, dentists call a “shark” bite. This is due to the fact that sharks also have units arranged in two rows. In humans, such an anomaly does not look aesthetically pleasing at all. Parents usually get very scared when they see a “double” smile on their child. Should I be concerned if a tooth comes out but the baby tooth does not fall out, and what could this lead to? Let's figure it out together.
Possible deviations from the norm
The process of replacing baby teeth with permanent teeth is often marred by some difficulties and deviations from the norm. Parents need to be prepared in advance for such situations in order to react and provide timely assistance.
The causes of the pathology can be both natural factors and inattention to the child during this period. It is important to monitor what is happening and at the first signs of disturbances, consult a dentist.
Incorrect drop sequence
The order in which baby teeth are lost is established by nature, but there are situations in which this sequence is disrupted. In such cases, it is necessary to visit a specialist and consult on this issue. Most often, the violation does not pose any threat, but a timely visit to the orthodontist will not only be beneficial, but will also calm parental worries.
INTERESTING: at what age do children lose their baby teeth: timing and order of change to permanent units
Premature loss of baby teeth
If a molar does not appear in place of a fallen milk tooth for a long time, we can talk about such a deviation as premature tooth loss. When and why does this happen? The causes may be maternal toxicosis, genetic predisposition, infections suffered by the child, or rickets.
READ ALSO: differences between molars in children and baby teeth
In addition, the problem may indicate the presence of pathologies:
- Retention. It consists of a delay in the eruption of the permanent dentition.
- Adentia means the complete absence of a bite due to the death of its rudiment while still in the mother’s womb.
How soon should you sound the alarm? If, after the loss of a baby tooth, the eruption of a permanent tooth is not observed for 9-12 months, you will need to consult a doctor.
The baby tooth is loose, but does not fall out, and a new one is already growing
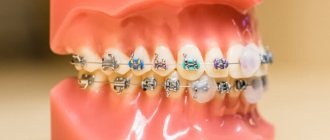
The pathology is called “shark teeth” and is more common than other abnormalities. In such cases, the baby tooth is still loose, not thinking of leaving its place, and the permanent tooth is already erupting nearby. Most often, the second row is observed on the inside of the jaw and in appearance resembles a shark’s mouth.
READ ALSO: Can a 5-year-old child cut his permanent teeth behind his baby teeth? A deviation when a molar grows in, if there is a loose one, does not cause any particular difficulties. If you notice that the old tooth has not fallen out, but a new one is already growing, there is no need to panic, but if a change does not occur within 3 months, you need to visit a doctor (we recommend reading: what to do when a child is cutting his first teeth?). READ DETAILS: what to do if a child’s teeth grow in two rows?
Other pathologies
In addition to the most common pathologies, there are other disorders of the process of changing teeth:
- Curvature of teeth. It occurs due to the early loss of teeth, while the permanent ones do not yet begin to grow. In such cases, neighboring teeth are displaced and occupy the resulting voids. At this time, the new tooth, which begins to grow, turns perpendicular to the others, is placed crookedly, moving forward beyond the row.
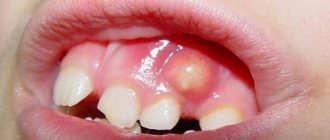
- The appearance of a hematoma. A rare pathology formed in the form of a red or bluish bubble on the edge of the gum. You can relieve pain with the help of gels and pastes.
Also, some children may have a fever and excessive pain. If the child feels unwell, you should visit a specialist who will give competent recommendations.
Causes of the anomaly
If the permanent tooth is erupting but the baby tooth has not fallen out, it can be assumed that the child is not eating enough solid food. With a deficiency of chewing load, the roots of temporary units are in no hurry to dissolve.
The diet of modern children is indeed too “gentle”, one might even say refined. It consists of products that have undergone step-by-step heat treatment. Chewing them requires almost no effort.
If parents think that children need to be given soft and thoroughly steamed food, then they are mistaken. To change teeth in a timely manner and form a correct bite, you need to eat a lot of fresh vegetables and fruits, and other foods that require careful chewing. Then the problem of preserving primary canines, incisors and molars for too long will not arise.
Another possible cause of the problem described is the presence of scars on the gums. If in the first years of life the baby has undergone dental surgery or received a serious injury, a burn to the oral cavity, scars may form on his gums. They consist of very dense connective tissue that prevents teeth from erupting.
Reasons for delay
- There is not enough calcium in the body. The cause of the shortage was not necessarily the presence of pathology. Perhaps the baby was born prematurely, not having time to receive all the necessary microelements, or the tooth did not advance to the required level, or the mother did not eat well during pregnancy and did not consume foods containing calcium. In case of congenital calcium deficiency, the baby will have pale skin, brittle nails, and slow hair growth. In most cases, it is enough to switch the child to a balanced diet. It is very important that it not only includes foods high in calcium, but also excludes those that interfere with its absorption.
- Past infectious diseases. Perhaps, due to a serious illness, your baby has expended all the strength necessary to build a molar.
- Inflammatory processes in baby teeth, caries. In advanced conditions, the molar tooth germ is damaged. This leads to a delay in the growth of the permanent tooth, and it can also come out incorrectly, with an inclination. And this can lead to the formation of an incorrect bite.
- Impact of mechanical injuries. Perhaps the baby had a jaw injury, which caused the rudiments to shift. Now surgical intervention is needed to correct the situation.
- Adentia or retention.
Sometimes the reason why a tooth does not grow is adentia - a disease that can be either congenital or acquired. In the case of congenital pathology, the culprit may be a hereditary factor, as well as smoking or drinking alcohol by the mother during pregnancy. Such a phenomenon as acquired adentia is typical in cases when a molar tooth is removed or when, due to infectious processes in a milk tooth, pathogenic microflora penetrates the molar rudiment and thereby destroys it.
When should you start worrying about delayed growth of molars:
- If in the near future after a baby tooth falls out, your little one doesn’t even have a hint of a permanent tooth, it’s too early to worry. Sometimes it takes a whole year for a molar to appear.
- Of course, there are tables that indicate the approximate timing of the appearance of permanent teeth. However, due to the fact that all children are individual and their physiological characteristics may differ, an error of even one and a half years is acceptable.
- If you are still worried, it is better to see a specialist. He can easily determine whether the baby has edentia. To do this, he will need an x-ray of the child's jaw. In addition, the baby can have a digital photograph taken, which will be less dangerous in terms of radiation exposure and more informative.
What to do if the diagnosis is confirmed? You must understand that this is not a verdict yet. The child will be able to receive special plates with artificial teeth, which will also be responsible for the formation of the correct bite in the baby. It is better not to delay the installation of such a device. You must understand that the baby may begin to have complexes, his bite will form incorrectly, and he will not be able to fully eat food.
This diagnosis is made when there is a serious delay in the eruption of a permanent tooth. If we are talking about complete retention, then in the picture you can see the presence of a tooth germ. However, for some reason it does not erupt from the gums. As a rule, this phenomenon is caused by the removal of a baby tooth for medical reasons ahead of schedule or by too deep localization of the molar rudiment.
Partial retention may also be diagnosed. In this case, the upper part of the tooth pecks, and the lower part does not come out for a long time.
To be honest, when my son’s teeth were falling out, I didn’t worry at all and didn’t look for information about the age when which molar should erupt. Once, my son had a baby tooth removed ahead of schedule (the tooth could not be treated). The doctor immediately warned that a molar would not appear there any time soon. That's why I wasn't worried. And all the other teeth were quickly replaced by molars, and there was no need to consult a doctor for advice.
What does a “shark” smile lead to?
Should you be scared if a new unit comes out, but the milk unit does not fall out? This situation should alert parents. Double dentition can lead to problems with articulation and diction. Then the child will have difficulties with the correct pronunciation of sounds and words.
Also, many patients with the described anomaly have difficulty eating food - they feel uncomfortable biting off hard foods, and when chewing them, small particles often get lodged under the gum. This means that the child will get used to swallowing poorly chewed food. This leads to disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, including flatulence and abdominal pain.
It happens that children who have double units in several places at once begin to lose weight. This is again due to improper chewing of food. During a meal, they swallow large pieces and because of this they swallow a lot of air. Therefore, they often have the illusion of satiety - a feeling of fullness when very little has been eaten.
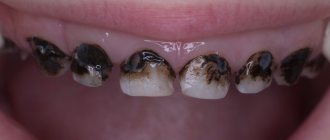
Among the dental complications caused by untimely change of units:
- caries;
- inflammation of the gums;
- deposition of a large amount of soft plaque.
Therefore, you should not put off visiting the dentist. The doctor will conduct an examination and decide whether to remove the extra unit.
When to see a doctor
Doctors believe that a “shark” smile can last up to two to three months, then it is necessary to take action. If the baby tooth does not fall out within the specified period, it needs to be removed. If you do not do this, the complications described above may occur.
But what’s even worse is that the child’s bite may be disrupted. The permanent unit will take the wrong position or be at the wrong angle. Then you will have to correct its position using plates or braces, and this is always difficult and time-consuming.
It is important to know! If a permanent tooth has come out, but the baby tooth has not yet fallen out, you can monitor the situation for several weeks. It is important to ensure that the child carefully maintains oral hygiene. If after two or three months nothing has changed, you need to make an appointment for your baby to see a dentist. But this recommendation is relevant only if the little patient is not bothered by anything and does not complain of toothache.
no permanent tooth buds
Permanent teeth.
The process of replacing baby teeth with permanent ones is very interesting. Some time before a baby tooth falls out, its root begins to dissolve (root resorption occurs), and the tooth begins to become loose. The more the root is absorbed, the more the tooth wobbles. Eventually, it falls out on its own or is removed by the dentist. Simultaneously with the resorption of the roots of the baby tooth, the permanent tooth slowly grows.

Rice. 4. Approximate timing of eruption of permanent (molar) teeth.
The pattern of eruption of permanent teeth is also only indicative (Fig. 4). But the sequence of this process should normally be certain. The first permanent molars (“sixes”) appear first at the age of 6-7 years. They erupt behind all temporary teeth, in an “empty” place where there was no milk tooth before. Next, the replacement of baby teeth with permanent ones occurs in the same order in which baby teeth appeared. The incisors begin to wobble and change - first, two on the upper and lower jaws (6-8 years), and then two more (7-9 years). After this, the premolars are replaced. The first premolars (“fours”) are replaced at the age of 9-11 years, then the second premolars (“fives”) must change until the age of 12. Until the age of 13, the fangs are replaced. Behind them, at the age of 14 years, second molars (“sevens”) appear, which they also erupt in the empty spaces behind the last existing teeth. The last to appear are the third molars, the so-called wisdom teeth (“eights”). This can happen from the age of 15 until late old age, or it may not happen at all (lately, the absence of the rudiments of “wisdom” teeth has become increasingly common).
Summarizing all of the above, I would like to draw your attention to the fact that you should carefully monitor the appearance and change of teeth in a child. It is important to pay attention not only to when and in what sequence the child’s baby and permanent teeth erupt, but also to what location and position they are in (so as not to develop malocclusion in the child). The best way to do this is to regularly visit the pediatric dentist for a preventive examination. In addition, we must not forget about caring for the baby’s teeth and the rules of oral hygiene. Be sure to brush your child's teeth immediately after teething. It is wrong to think that if a child is breastfed, then he does not need to brush his baby teeth. There are special devices and methods for cleaning the baby’s mouth, which a dentist can tell you in detail.
When to hesitate to see a doctor
If a “shark” problem appears and the child complains of pain, the gums are inflamed, swollen, you need to immediately get dental care. Also warning symptoms are:
- bad breath;
- bleeding of the affected gums;
- separation of pus in the area of inflammation;
- severe discomfort while chewing food.
You should not wait a day if the child has a predisposition to malocclusion, for example, if he has previously undergone treatment for malocclusion or one of the parents wore braces. In all these situations, removal should be carried out as soon as possible. This measure will be a good prevention of possible complications.
How is the treatment carried out?
When choosing treatment tactics, the dentist takes into account:
- how old is the patient;
- how long ago the permanent unit emerged;
- how much the molar crown appeared;
- what condition is the milk unit in;
- does the child have any complaints;
- general condition of the dentition;
- the patient has a predisposition to dental anomalies.
After conducting an in-person examination, the dentist decides whether to pull out the interfering tooth or leave it and wait until its roots resolve on their own. In the first case, local anesthesia is administered and removal is carried out; in the second, the doctor tells you when the baby needs to come for a second examination. Thus, if you deal with the problem of a “shark” smile in a timely manner, it will not cause negative consequences.
What can you do
It is possible to influence the process of tooth development. The first recommendation of dentists is to spend time on the condition of the milk to prevent the development of infectious diseases. It is necessary to provide the child with nutrition, in particular calcium, so that the body has enough vitamins for the growth of the radical row.
If there are injuries to the oral cavity at an early age, you need to contact a medical institution for advice. It is necessary to restore the functionality of the gums in time before the development of new teeth. In severe cases, radical treatment methods will be required.
It will be possible to determine the period of development of a molar on an individual basis only by contacting a dentist. If there are no signs of development of a permanent series, the help of a specialist is necessary.
There is a system for replacing teeth that requires control. First, the front baby teeth in the bottom row fall out. There are factors that influence the described process.
If the cause of missing teeth is an infectious disease, it is necessary to restore the child’s immune system. There may be delays in the appearance of teeth up to six months. You need to calm the child down and not worry yourself; stressful situations can make the situation worse.