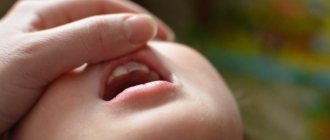
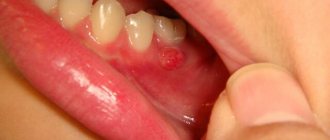
What is flux in a child and what does it look like in the photo?
Flux (periostitis) is a purulent inflammation of the periosteum covering the bone of the upper or lower jaw. As a result of progression, the lesion can spread to nearby tissues. Flux causes serious discomfort to the child and causes increased irritability.
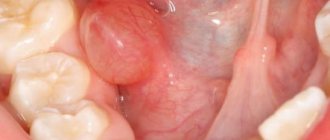
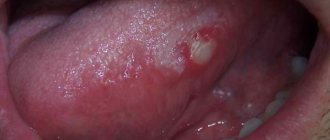
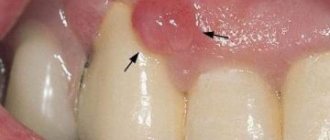
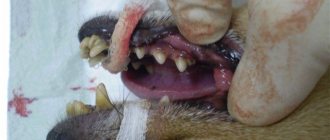
The first sign of the disease is the formation of an abscess on the surface of the gum. The round formation that appears is white on a rich red swollen background. Sometimes flux occurs directly on a baby tooth. The acute form of the pathology, in the absence of timely treatment, becomes chronic. Below, for clarity, are photos of flux in a child.
This is what gumboil looks like on a child’s gum in the photo.
Diagnosis of the disease in childhood
Diagnostic measures regarding gumboil include visual inspection, collection of clinical data, and X-ray examination. Laboratory examinations, which allow us to establish the stage and type of the inflammatory algorithm, will help determine the final diagnosis.
Before visiting the dentist, it is strongly recommended not to use painkillers because this reduces the sensitivity of the teeth. Next, the dentist will be required to carry out the most thorough examination of the oral cavity to determine visible lesions. In addition, specialists apply different temperatures, namely cold and heat, to the area of the dental nerve in order to determine the threshold of susceptibility.
In certain situations, in the process of determining the flux in the gum area, the dentist stimulates the teeth with a slight discharge of electric current. An X-ray examination should be considered an indispensable part of the diagnosis of periostitis. As you know, with the help of a tooth image, a specialist will be able to determine the exact extent of the purulent lesion and determine the location of the source of pain.
Reasons for appearance
Flux in a child can occur for a number of reasons. These include:
- failure to maintain good oral hygiene. Not all preschool children take care of their teeth, as a result of which plaque accumulates in the gum pockets and food particles get stuck. This can cause inflammation;
- soft tissue injury. Children are known lovers of putting everything in their mouths. Foreign objects can disrupt the integrity of soft tissues. As a result, the likelihood of pathogenic microorganisms being introduced into the resulting wound increases;
- advanced form of caries (pulpitis). By destroying the enamel, the pulp is affected, which leads to the destruction of the bone structure and suppuration. To avoid it, it is necessary to promptly treat carious lesions;
- medical errors. Flux can appear when the technique of root canal treatment is violated or the cavity is not cleaned after tooth extraction. In such situations, pathogenic microorganisms easily penetrate deeper;
- pathologies of ENT organs. Inflamed tonsils and adenoids are a common occurrence among preschool children. They act as a source of infection, which in case of weakened immunity provokes the appearance of flux. With sore throat, the gum pocket often becomes inflamed, resulting in the formation of periostitis.
Flux can occur both due to poor oral hygiene and due to injury to the mucous membrane
First aid if a problem occurs
If a child develops flux, what should you do? In this case, surgery is most often used. That is, the flux is opened so that it is possible to drain the pus. Depending on the severity, the dentist may prescribe drugs from the antiviral or antibacterial line. It is very important to fully comply with all instructions, since otherwise you can observe the reappearance of pus.
How to treat flux in a child at home?
Experts also point out the possibility of providing first aid to a baby if a pus ball appears. The recommendations are as follows:
- When a temperature appears, it is necessary to give the child medications to help reduce it. It can also relieve any pain that occurs.
- Puffiness and swelling can be relieved by antiallergic medications.
- The use of cold compresses is necessary.
These are the instructions that doctors recommend following. However, when studying information about a problem such as flux, you can come across recommendations from traditional medicine. Although doctors categorically do not recommend home treatment. And yet this phenomenon occurs.
Main symptoms and signs of periostitis
Flux in a child 6 years of age and younger occurs with pronounced symptoms. The main signs indicating the development of pathology include:
- Painful sensations in the oral cavity, intensified by eating food (at the beginning of the onset of the disease they are moderate, but as they progress they become intense).
- The appearance of a characteristic ball (accumulation of pus) in the gum area.
- Increased body temperature (up to 37.5-38°C).
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck.
- Redness and swelling in the gum area.
- The appearance of bad breath.
Young children aged 2-4 years with the development of flux may become capricious and refuse to eat. It is difficult for them to explain what the reason is; many parents mistakenly attribute this to bad behavior. Pay attention to other possible symptoms.
The main symptoms are pain and fever
If flux occurs on the upper jaw, then swelling may affect the cheek and parotid area. If all of the above symptoms are detected, you should not delay a visit to a specialist. Timely treatment guarantees the absence of negative complications.
Symptoms
At the initial stage of periostitis, which usually does not last long, symptoms may be absent. The progression of the disease leads to the child experiencing pain when eating, fever and general malaise.
In acute periostitis, symptoms occur:
- pain in the affected tooth of a pulsating and aching nature;
- pain increases with tapping and eating;
- gum tissue turns red and swells;
- an abscess appears on the gum.
A clear symptom of flux formation is the appearance of pronounced swelling on the cheek and nearby areas on the side of the diseased tooth. If left untreated, swelling spreads throughout the entire face.
Diagnostics
Doctors are able to recognize periostitis in children based on a visual examination of the oral cavity. The disease occurs with pronounced symptoms, so there are no difficulties in making a diagnosis.
In some clinical cases, X-ray examination may be required to determine the extent of damage to teeth and soft tissues. If complications are suspected, laboratory diagnostics are prescribed - a general blood test. Based on the results, the most appropriate treatment regimen is selected.
Classification
Based on the nature of the course and symptoms, periostitis in children is classified into three stages.
- Serous. The non-purulent stage of the disease, spreading not only to the tooth tissue, but also beyond it. The tissues of the gums, jaw and periosteum around the affected tooth become swollen. The serous stage can develop with periostitis of primary teeth, even at the stage of the appearance of the first teeth.
- Spicy. When therapeutic measures are taken at the serous stage, the process begins to transform into a purulent form. Between the jaw bone and the periosteum there is an accumulation of exudate (discharge with blood), in which, under the influence of infection, the purulent process begins. The acute stage is dangerous with a high risk of damage and subsequent detachment of the periosteum tissue from the bone. If treatment is refused, the disease quickly begins to progress. The baby's condition is deteriorating greatly. The consequence may be complete loss of teeth, osteomyelitis of the jaw and abscess.
Chronic periostitis is extremely rare. The cause of the pathology is predominantly mechanical trauma to the jaw. Its peculiarity is that the entire pathological process is asymptomatic. Several months may pass from the onset of the disease to the acute stage. Periodically, the child may experience exacerbations with mild symptoms. The danger of chronic periostitis lies in the high probability of damage to adjacent teeth and jaw bones.
What is the danger of flux in young children?
Some parents believe that baby teeth do not need to be treated, associating this with the fact that they will soon fall out anyway. As a result, dentists are faced with an advanced form when flux occurs in preschool children. Milk teeth are especially susceptible to carious lesions, which provoke the appearance of periostitis.
In addition, refusal of treatment can lead to serious complications: the infection can spread to the root molar or internal organs of the child. Some children experience acute purulent periostitis, which occurs with severe deterioration and requires urgent medical attention.
Untreated gumboil can lead to tooth loss
Other possible complications include adentia and phlegmon. With flux, the inflammatory process spreads in the bone tissue, which destroys the rudiments of permanent molars and increases the likelihood that they will not grow in this place.
It is not difficult to suspect the development of complications. As a rule, during treatment, after opening the flux, the symptoms begin to rapidly disappear: after a few hours, the temperature drops and swelling disappears. If symptoms persist and the child's condition worsens, there is a high chance that complications have developed.
Features of the disease
Periostitis is an inflammation that occurs in the tissues of the jaw with characteristic damage to the jaw periosteum. It is natural for the disease to develop rapidly and increase the affected area. The pathology is accompanied by a purulent process, which is localized in a specific area. As a result, a visually noticeable swelling of the cheek is formed - gumboil.
According to the etiology of development, periostitis of the jaw bones in children develops as a consequence of untreated dental pathologies and mechanical damage to the gums or teeth. This type of periostitis is called odontogenic. The cause is predominantly the penetration of infection into internal tissues and the subsequent development of a purulent process.
Periostitis of a child’s tooth progresses quickly. Within 24 hours, the baby may develop severe flux, and after another 1–2 days, the infection can spread deep into the tissue or enter the blood. Acute purulent periostitis in a child is fraught with serious consequences: phlegmon, abscess, sepsis and death.
Treatment options for flux (periostitis) in children
If you consult a dentist in a timely manner (immediately after the first symptoms appear), conservative treatment will be prescribed. It has a positive result. Its main task is to preserve the tooth so that there are no problems with the formation of the bite.
In an advanced stage, with a large accumulation of pus, surgical intervention may be required. During this procedure, the specialist makes an incision in the affected area and inserts a drainage to remove the pus. Next, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed.
As practice shows, children rarely undergo surgical intervention; most often it is possible to get rid of the problem with the help of conservative therapy. Let's take a closer look at what it is.
If the form is advanced, surgical intervention is required
Conservative treatment, which medications are effective?
Conservative treatment includes taking painkillers and antibacterial drugs along with anti-inflammatory drugs that promote speedy recovery. Most often, flux is caused by staphylococci and streptococci, which respond well to treatment with antibiotics. The child may be prescribed a medicine from the tetracycline group or the amoxicillin group.
In addition, it is important to treat the oral cavity with antiseptic solutions. To do this, the doctor may prescribe a solution of chlorhexidine (use a ready-made pharmaceutical preparation) or miramistim. Both remedies relieve inflammation well and are used 2-3 times a day.
If the disease has become chronic and often worsens, the child may be additionally prescribed vitamin complexes and immunomodulatory agents.
Why shouldn’t you treat flux at home without seeing a doctor?
You should not self-medicate. If you notice symptoms in a child that resemble flux, it is important to contact an experienced specialist. He will conduct an examination and prescribe appropriate treatment. Medicines should be selected in accordance with the child’s age, symptoms and the nature of the pathology. Self-medication can lead to a number of negative consequences, worsening the child’s condition.
Antibiotics are prescribed to the child to kill the infection.
Treatment with folk remedies, what to rinse with, what to use?
Traditional medicine recipes are not highly effective in treating flux, but can alleviate the baby’s condition and be used as additional therapy. It is worth considering that many natural ingredients can provoke an allergic reaction. Common folk remedies include:
- Soda solution. It is characterized by an anti-inflammatory effect. To prepare the solution, dissolve half a teaspoon of soda in 250 ml of warm boiled water. Rinse your mouth with the resulting product for several minutes 2-3 times a day.
- Herbal decoctions. Many medicinal plants are good antiseptics and eliminate signs of inflammation (relieve soreness and swelling). Among them: calendula, cloves, sage, linden, chamomile and others. To prepare the decoction, place a few spoons of the selected plant in a saucepan, add 0.5 liters of boiling water and leave to simmer over low heat for 15-20 minutes. Rinse your mouth with the resulting decoction for several minutes 2-3 times a day.
- Propolis tincture. Propolis is a well-known natural antiseptic. To treat the affected cavity, take 3-5 drops of tincture, dissolve in 250 ml of warm water and rinse your mouth 2-3 times a day.
Prevention is the best way to avoid flux development
We treat children from 3 to 8 years old
Even at a young age, children are not immune from periostitis. Treatment of this disease has its own characteristics in children of different ages.
- A three-year-old child is still too young to rinse his mouth with something inedible, as there is a high risk that he will swallow the solution. For such children, infusions and decoctions of herbs that are diluted in a safe concentration are used to treat inflammation. For a 3-year-old child, it is important to consult a doctor immediately to save a bad tooth. After all, the change of teeth will not happen soon, and tooth extraction threatens malocclusion in the future.
- When the child is 4 years old, it is allowed to cauterize the source of infection with a solution of iodine or Lugol. A 4-year-old baby has the patience to carry out this painful but effective treatment.
- At 5 years old, a child is almost an adult, but a certain amount of time must pass before teeth change. If a tooth has to be removed, a temporary removable denture is placed. Implantation at this age is carried out in extremely rare cases.
- A 6-year-old child begins to change teeth to permanent ones. Therefore, in almost 100% of cases, in a 6-year-old child, a diseased tooth is removed, and prosthetics are not performed. Treatment at home is carried out with stronger painkillers and broad-spectrum antibiotics.
- At the age of 7, the change of teeth is in full swing, but the child’s activity also increases significantly, as do his capabilities. Therefore, the risk of flux occurring on a tooth increases several times.
- At the age of 8 years, children become more relaxed in terms of physical activity, but rarely agree to brush their teeth correctly. Therefore, the greatest risk for the appearance of flux is improper hygienic treatment of the mouth and teeth. Establishing this process will reduce the risk of periostitis several times.
Prevention methods
To avoid the appearance of flux, it is enough to carry out preventive measures:
- monitor how the child maintains oral hygiene;
- use high-quality toothpastes in accordance with the baby’s age;
- bring the child to the dentist for examinations every six months;
- promptly treat carious lesions;
- strengthen the immune system.
Introduce healthy foods into your diet, minimize the amount of carbonated drinks and confectionery products.
Should we panic?
The occurrence of flux should not lead to parents panicking and having dark thoughts. Research shows that timely action eliminates the likelihood of developing serious pathologies. As a rule, when the doctor opens and removes the pus, following the necessary requirements, all symptoms go away within a couple of days.
It is very important to understand that you should not expect self-improvement without intervention and help when flux occurs. Doctors note that pus may not always break out on its own, and an autopsy or puncture without a doctor can result in an even worse development of the disease.
Based on all that has been said, the occurrence of flux in a child cannot under any circumstances be ignored, much less neglected. Such neglect can lead to the child suffering from problems with teeth and gums in adulthood. And that's the best case scenario. He may also be left without a tooth or suffer irreversible changes in the shape of his bite - in the worst case.
Treatment
Periostitis of the jaws in children is treated taking into account the following factors:
- severity of the inflammatory process;
- type of periostitis;
- severity of the process;
- child's age.
Treatment of periostitis is carried out until all symptoms of the pathology are eliminated. Serous flux in children is treated from 3 to 5 days, acute purulent periostitis - up to 10 days . These are average treatment durations. The individual characteristics of each child play an important role.
In case of purulent periostitis, it is necessary to cut the gum and then drain it.
REFERENCE: How to carry out the drainage procedure - the tip of a rubber strip is inserted into the cavity formed after removal of pus through the incision. The procedure will prevent the edges of the wound from sticking together, and normal outflow of fluid will occur.
A baby tooth that has become a source of infection is almost always removed during gumboil. They try to save permanent teeth if possible. The dentist will assess the potential risks; in some situations, removal may not be necessary. Then the oral cavity is sanitized.
Periostitis of the jaw, view from the inside.
After surgery, the doctor prescribes procedures that are a continuation of treatment. They can be carried out at home; parents should strictly adhere to the doctor’s recommendations:
- Taking antibiotics in a strictly prescribed dosage.
- To relieve pain and reduce inflammation, drugs such as ibuprofen and paracetamol are indicated.
- Antiseptic solutions – for rinsing the child’s mouth. You can rinse with solutions of furatsilin, chlorhexidine, miramistin, but only if they are prescribed by a pediatric dentist.
- Traditional medicine - rinsing with soda solution, propolis tincture, herbal decoctions (chamomile, calendula are suitable for children).
Prevention of flux
As practice shows, it is always easier to prevent any problem than to deal with it and its consequences. There are certain rules that will not be difficult for either the child or his parents to adhere to. If they become the norm in everyday life, they will help in the future to avoid problems not only with flux.
- According to statistics, the main cause of gumboil is caries. It doesn’t matter whether it was undertreated or neglected. Only regular visits to the dentist will help you avoid it.
- Oral hygiene. Brush your teeth morning and evening with a properly selected brush. For each age, the hardness and length of the bristles of the brush are determined. Toothpaste is also important. Don't chase brands, give preference to natural ingredients.
Teeth brushing technique - After your child has eaten, teach him to rinse his mouth with warm water.
- Don't be afraid to have your teeth professionally cleaned. Plaque and tartar are harmful bacteria.
- It is better to remove a diseased tooth in time than to wait for it to spread infection and cause complications.
- A child's diet should always include solid vegetables and fruits. Apples and carrots are not deficient, but contain a whole vitamin complex. In addition, during chewing, the teeth self-clean, the gums are massaged and the osseous-ligamentous apparatus is strengthened.
Apples are healthy and help teeth cleanse themselves. - Do not forget to maintain your child’s defenses at the proper level. A good strong immune system can fight any infection.
A child has a problem with his gums: what to do in this case?
The main contraindication is heating the inflamed area. Warmth will only create a favorable environment for bacteria to multiply.
At the dentist's appointment, an initial examination is carried out, after which an x-ray examination is prescribed. Parents should remember that such a serious disease does not go away on its own. If acute pain and other symptoms of periostitis appear at night, you must call an ambulance. The child will receive emergency care in the surgery department.
The treatment regimen for periostitis largely depends on the course of the disease and the general condition of the patient. Surgical procedures are carried out in several stages. First, the flux is dissected and the purulent discharge is drained. The procedure is performed under anesthesia. In some cases, tooth root removal may be necessary.
During the postoperative period, a course of treatment using anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics is prescribed. Physiotherapeutic procedures show good results during the recovery period.
In order to prevent the occurrence of flux, you must adhere to the following rules:
- Bring your child to the dentist for examination at least twice a year;
- treat caries promptly;
- teach your child the correct technique for brushing teeth;
- purchase a suitable brush and toothpaste;
- introduce more vegetables and fruits into the diet;
- strengthen the child’s immunity.
Under no circumstances should the disease be neglected. After all, every adult knows that neglected pus can cause consequences such as blood poisoning or peritonitis. Parents who are especially worried about their children may think after the above that a child can develop gumboil due to any little thing. In fact, the reasons come down to a not-so-long list:
- ignoring the rules of oral care or its poor quality;
- caries can provoke the development of inflammation in the gums and periosteal tissue;
- infections in damaged gum tissue, which can be caused by a fall or external impact;
- inflammation of the soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- low level of professional training of pediatric dentists;
- past diseases of infectious origin;
- genetic predisposition.
Treatment of flux on a child’s gums can be carried out either with surgery or with the use of medications. The second option will be longer and more complex. It also includes local treatment and an individual dosage regimen.
A timely visit to a doctor will help you choose adequate treatment. However, every parent, having discovered gumboil on the child’s gums and the child’s lack of mood, tries to correct the situation. However, there are rules that cannot be broken. We will consider them further.
If a child has flux, what should you do? In this case, surgery is most often used. That is, the flux is opened so that it is possible to drain the pus. Depending on the severity, the dentist may prescribe drugs from the antiviral or antibacterial line. It is very important to fully comply with all instructions, since otherwise you can observe the reappearance of pus.
How to treat flux in a child at home?
Experts also point out the possibility of providing first aid to a baby if a pus ball appears. The recommendations are as follows:
- When a temperature appears, it is necessary to give the child medications to help reduce it. It can also relieve any pain that occurs.
- Puffiness and swelling can be relieved by antiallergic medications.
- The use of cold compresses is necessary.
These are the instructions that doctors recommend following. However, when studying information about a problem such as flux, you can come across recommendations from traditional medicine. Although doctors categorically do not recommend home treatment. And yet this phenomenon occurs.
Parents should know what can lead to periostitis in a child. With this information, flux can be prevented by avoiding these conditions.
What are the causes of the disease?
- Mechanical damage to the cheek or gum itself.
- Formation of boils.
- Frequent caries.
- Lack of proper oral hygiene.
- Failure to comply with the rules of asepsis and antisepsis during dental treatment.
- Inflammation of the gum pocket.
- Infectious processes in the body affecting the throat, for example, flu or sore throat.
- Incompletely treated teeth, for example, a canal that is not completely filled.
We suggest you read: A white spot on a child’s gum hurts.
It is also worth considering that there are factors that put a child at risk, that is, that increase the risk of gumboil:
- hereditary predisposition;
- weakened immune system;
- ignoring stones formed on the teeth;
- excessive consumption of soda, as well as other sweets that provoke the development of caries;
- regular colds.
Treatment of gumboil gumboil
Some parents mistakenly believe that when a baby tooth changes color or decays, it is not worth much attention because new ones will grow. It is necessary to understand that with the development and spread of the pathological process, permanent teeth may no longer grow healthy.
You should not self-medicate, as a small child will not be able to completely rinse out all the pus. Under no circumstances should you use warm compresses - their effect can activate the inflammatory process. An attempt to open an abscess is especially dangerous; this threatens infection in the bloodstream, blood poisoning, and the development of purulent processes in the temporal and cervical region.
So, a child has flux, what should you do? First of all, determine where exactly the problem occurred. If the disease develops on the baby’s baby teeth, then treatment usually comes down to their removal.
However, the results of studying the formation of a child’s bite indicate that untimely tooth loss can lead to irreversible changes. Therefore, if the treatment is promising, dentists do not neglect it. After all, healthy teeth from childhood guarantee their safety in the future.
Prevention of flux in a baby: what should be done?
Like many diseases, flux comes in an acute form, which, in the absence of proper treatment, eventually becomes chronic. Symptoms of the acute stage of the disease:
- Pain syndrome. Acute pain intensifies when pressing on the inflamed gum or tooth (when chewing, talking).
- Increased body temperature. The body's response to inflammation varies, from low-grade fever (37°C) to high fever (39°C).
- Swelling of the cheek. Due to tissue swelling, facial asymmetry is disrupted. The inflamed side feels hot and pasty to the touch. Depending on the location of the inflammation, swelling may spread to the lower eyelid, lips, and chin.
We suggest you read: If my upper palate hurts in my mouth, what and why, reasons, what to do, what to do, how to treat
It often happens that the treatment of the acute form is not completed, but only until the pain syndrome is eliminated. In this case, the disease may transition into a sluggish, chronic form. The insidiousness of this stage of the disease is that it can occur for a long time without obvious symptoms and spread to neighboring areas.
The prerequisite for the occurrence of gumboil is inflammation of the gums.
Children under 6 years of age are at particular risk of developing sluggish flux due to their not yet fully formed immunity. Symptoms to watch out for in children:
- hardening or inflammation of the gums;
- periodic pain in seemingly healthy teeth.
Considering that flux is caused by a bacterial infection (most often staphylococcus or streptococcus), it responds well to antibacterial therapy. Most often, antibiotics are used to treat flux:
- group of amoxicillins (Amoxicillin, Amoxiclav);
- tetracycline group (Doxycycline);
- group of fluoroquinols (Ciprofloxacin).
Despite the fact that modern antibiotics have a wide spectrum of action and the likelihood of quickly defeating the infection is very high, the medicine must be selected by a dentist. He prescribes the drug depending on the clinical picture, medical history, age and condition of the patient.
At home, the child’s condition is alleviated using folk remedies. Let's look at the most effective of them.
If you are not allergic to bee products, natural propolis will help cope with gumboil
| Procedure | Active substance | Medicinal properties | Cooking method | Periodicity |
| Rinse | Salt, soda | They have antibacterial properties. Helps reduce swelling and pain. | Dilute 2 teaspoons of the substance in a glass of warm water. You can alternate solutions or use a two-component mixture. | 3-4 times a day. |
| Dried sage, oak bark, lemon balm, chamomile | They are natural antiseptics and prevent the progression of the disease. | To get a glass of infusion, you need to pour boiling water over 1 tablespoon of dry herb and let it brew for 15-20 minutes. | ||
| Alcohol tincture of calendula | They have a good anti-inflammatory and calming effect. | Dilute one teaspoon of tincture in a glass of warm water. | ||
| Compresses | Garlic | Thanks to the phytoncides found in garlic, this compress relieves pain and reduces inflammation. | Pass a clove of garlic through a garlic press (or grate it), wrap it in gauze and apply to the inflamed area. It begins to act in 15-20 minutes. | As pain occurs. |
| Soda | Reduces swelling and relieves pain. | Wrap a teaspoon of soda in a cloth, apply to the sore spot, and leave for 20-25 minutes. | ||
| Propolis | Has a strong bactericidal and bacteriostatic effect. | Chew a small piece of propolis for 5-10 minutes. |
All solutions should be made immediately before use. You only need to rinse your mouth with warm water, and then refrain from eating for at least half an hour.
If a child's flux is accompanied by a fever, you can give him a medicine based on paracetamol or ibuprofen. In this case, the antipyretic will not only normalize body temperature, but will also have an analgesic effect.
When treating any disease, experts highlight actions that should never be performed, as this can lead to even greater complications. If a child has flux, it is prohibited:
- warm the affected area;
- take painkillers;
- arbitrarily prescribe antibiotics and other medications;
- touch the pus ball that appears, especially with unwashed hands;
- Use constant mouth rinse as a remedy for inflammation.
If the ball nevertheless bursts and pus flows into the oral cavity, then you should definitely consult a doctor, and as quickly as possible. Since, once inside, the infection can spread throughout the body. Please note that when removing flux at the dentist, you must stop taking aspirin.
We do not provide photos of the pathology for aesthetic reasons. In this case, you should not refuse to use popular antiseptic solutions that your dentist can select. Among the most popular:
- chlorhexidine solution;
- "Miramistin";
- furatsilin solution.
It is very important to use these drugs under the strict supervision of an adult, since their ingestion can harm the child’s gastrointestinal tract.
Parents also need to be aware that treatment methods for children of different ages differ in their methods.
- Treatment at the age of three years cannot be undertaken by parents. It is better to entrust it to a specialist, for which you need to contact him immediately.
- Reaching the age of four is accompanied by an increased level of patience and the possibility of using such treatments as cauterization with iodine solution (Lugol).
- At the age of five, dentists sometimes remove the diseased tooth. And in its place a temporary prosthesis is placed, which is removed when the permanent tooth erupts.
- The period from six to eight years is the age when the change of teeth enters the active phase and the child’s activity increases. The latter increases the likelihood of gumboil occurrence. However, at the same time, treatment becomes easier due to the child’s understanding of the need for the measures taken.
In any case, no matter what age the child is, flux treatment is very painful. So if there is an opportunity to avoid a problem, then you need to take advantage of it.
To avoid the need for flux treatment, the most effective approach is prevention:
- One of the important aspects of prevention is the treatment of any diseases of the oral cavity until complete recovery.
- Careful attention to oral hygiene is required.
- Regular visits to the dentist to remove stones and promptly treat signs of tooth decay.
- Strengthen your immune system and consume enough fresh vegetables and fruits.
Failure to comply with the rules and regulations can lead to the fact that the flux can become chronic. The first manifestations of the disease cannot be ignored. Indeed, in this case, the doctor can cope with the problem without much effort and time, and there will be no consequences at all.
If the problem is neglected, the child may lose not only a baby tooth, but also the appearance of new permanent ones. A very difficult problem is the treatment of gumboil.
A doctor can diagnose its development during a routine examination. In order to definitively establish the diagnosis, the dentist may order an x-ray.
The treatment regimen for flux is based on the course of the disease, additional symptoms and the general condition of the child.
- Since the process is accompanied by the accumulation of pus, antibiotics will definitely be used. But you should not use this method of treatment on your own; if necessary, a test is taken to determine the sensitivity of bacteria to the drug. The child may be prescribed Amoxicillin, Ampiox or Amoxiclav.
- Use of gel-based ointments for external use. They promote rapid healing and have an analgesic effect. So the child may be prescribed Cholisal or Metrogyl Denta.
- If necessary, surgical intervention is prescribed, which consists of sequential procedures:
- the child is given local anesthesia;
- an incision is made in the gum;
- a drainage is inserted, which does not allow the wound to heal immediately;
- purulent contents are gradually released through it;
- The child may be prescribed mouth rinses with herbal decoctions or solutions, such as soda-salt.
- Sometimes it may be necessary to remove the roots of a tooth;
- during the recovery period, physiotherapeutic procedures are recommended to help heal the wound.
We invite you to read: Enteroviral vesicular stomatitis - treatment of hand-foot-mouth syndrome with exanthema
Traditional methods
Often doctors, in addition to drug treatment, prescribe the use of traditional medicine.
- When flux is diagnosed in children, treatment at home can help reduce the severity of symptoms and alleviate associated symptoms. Sometimes it happens that periostitis is tolerated in a mild form; in such cases, traditional medicine methods are sufficient. But even then it is better to show the child to the dentist and be under his supervision.
- The use of an antiseptic - chlorophyllipt solution - will help to cope with the disease. To do this, you will need to add a tablespoon of the drug to 200 ml of water. Rinse your mouth with the prepared solution up to four times a day.
- Applying ice will help reduce pain. It is necessary to use specially designed pads filled with a salt solution or gel. As they heat up, you need to cool them in the refrigerator.
- If there is gumboil on a child’s gums, propolis tincture will help. It will quickly relieve inflammation and also disinfect the oral cavity. To prepare, add five drops of tincture to a glass of warm water. Rinse the mouth with this solution.
- You can make lotions. Cotton swabs are moistened in a solution of soda with the addition of iodine and sea salt.
- Garlic tincture has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- A decoction of sage, chamomile, oak bark, string and calendula has antiseptic properties. It is important to use freshly prepared products.
- Tincture of sage, St. John's wort, and eryngium has analgesic properties.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=subscribe_widget
Often parents do not know how to behave in such a situation. And there are times when they unknowingly harm a child. I present to your attention five points that are unacceptable in helping a child with gumboil:
- Use of antibiotics or analgesics. The use of any medications is permissible only after a doctor’s prescription. In addition, antibiotics can also kill beneficial oral microflora.
- Allow the baby to touch the bump. This can lead to infection, as well as to the fact that this swelling will burst and pus will begin to come out.
- Apply a heating pad or compress. The warming procedure negatively affects the inflamed area, in particular because it promotes the rapid proliferation of bacteria.
- Use aspirin after making an incision on the gum. This drug increases bleeding.
- You cannot be inactive and refuse to visit the dentist, especially if the lump has burst.