1747
The success of orthodontic treatment primarily depends on the correct diagnosis. It is on this basis that the patient will be prescribed treatment.
For this purpose, a wide variety of techniques are used to accurately identify the degree of discrepancy in the development of the dentofacial apparatus.
What is an orthodontic diagnosis?
Modern orthodontic diagnostics is a combination of all the necessary studies that allow us to determine the cause and effect relationships of the disease and prescribe the correct treatment for bite pathologies.
The final and complete diagnosis in orthodontics is made on the basis of anamnesis, preliminary clinical examination of the oral cavity, blood tests, functional tests, x-rays, as well as the opinions of related specialists, such as gnathologist, osteopath, neurologist, ENT doctor, dentist - orthopedist (prosthetist) and some other specialists.
Algorithms for setting and principles for formulating an orthodontic diagnosis include not only an assessment of the upper and lower dentition, but also determination of the size of the jaws, the condition of the mandibular joints and masticatory muscles.
In turn, it is extremely important to note that pathologies and diseases of the masticatory muscles and TMJ joints, which negatively affect the bite, can be caused by disorders in the spine and other large joints and skeletal muscles of the body. The most typical cases are combined (connected) disorders in the cervical spine, adjacent trapezius muscles, TMJ joints, facial and chewing muscles, and crooked dentition.
Accordingly, modern and effective diagnostics for installing braces should be carried out on the basis of an interdisciplinary approach.
Diagnostics in orthodontics
All advanced anthropometric, radiation and clinical methods for diagnosing dentoalveolar anomalies in orthodontics have clear indications and provide the most important thing - the correct diagnosis of occlusion.
Many patients are interested in: “What are the best diagnostic methods in orthodontics? How is differential (comparative) diagnosis of various forms of deep, cross, distal and mesial bite carried out?
As already mentioned above, a complete diagnostic examination before treatment of occlusion and placement of braces is based on an interdisciplinary approach and can be divided into the following areas:
- Examination of the dentition and oral cavity
- Blood tests to identify hidden sources of inflammation and hormonal imbalances affecting the bite, jaw joints and chewing muscles
- Jaw joint studies
- Research of masticatory and facial muscles
- Examination of adjacent organs and tissues not included in the dental system, but affecting the bite. For example, cervical spine, neck and shoulder muscles, etc.
How is a patient examined in dentistry?
Examination of a patient in a dental clinic begins with collecting an anamnesis. The doctor is interested in the patient’s complaints and conducts a visual examination. The doctor clarifies:
- is there pain, what is its intensity, how often does it occur;
- how long ago the symptoms of the disease appeared;
- Do you have increased tooth sensitivity to cold/hot/sour/sweet foods?
At the same time, he pays attention to existing fillings, crowns, previously installed dentures and implants. The doctor evaluates the correctness of occlusion, the presence of defects in the dentofacial apparatus, and injuries to the hard and soft tissues of the oral cavity. If necessary, the dentist will refer you for an x-ray examination (indicating which picture to take - targeted or panoramic), computed tomography (in difficult cases).
Based on the results of the studies, the dentist makes a final diagnosis and draws up an action plan.
Modern diagnostics of occlusion
Orthodontic diagnosis of bite before installing braces consists of mandatory and recommended additional examinations. Additional examinations of crooked teeth and the oral cavity before braces are prescribed to clarify and supplement already identified or obvious bite pathologies. Most additional checks are associated with gnathological, neurological and osteopathic methods of diagnosing certain pathologies affecting the bite and crooked teeth. Below we indicate the clinical protocol for gnathological-orthodontic examination and diagnosis used by orthodontists in France, Israel, Austria and Germany before treating malocclusion with braces and other orthodontic equipment.
Mandatory examinations:
- Clinical examination of the oral cavity, filling out a questionnaire, photographs of the oral cavity and face
- Casts and diagnostic models
- Blood tests
- K.T. skull, including the area of the jaw joints
- Applying a facebow and diagnosing jaw models in an articulator
- Determination of periodontal and hygienic status of the oral cavity
- Consultation with an orthopedic dentist (prosthetist)
Additional examinations:
- Dynamic MRI of the TMJ (mandibular joints)
- Consultation and opinion of an osteopath and/or reflexologist
- Electromyography of masticatory muscles
- Computer axiography
- CT scan of the cervical spine
- Neurologist's report
- TRG in lateral or frontal projection with angle calculations
Diagnostics before braces
Immediately before installing braces, the orthodontist provides the patient with a complete diagnostic case, final diagnosis and treatment options, including financial details. In 75% of cases after diagnosis, orthodontic treatment in adult patients is carried out with braces, with the installation of a metal or ceramic (sapphire) bracket system.
How do modern methods of orthodontic diagnostics differ from traditional methods of examination before installing braces used in Russia? Why is such a thorough and, probably, expensive diagnosis of bite in orthodontics necessary?
When answering these questions, it is necessary to note the following important nuances:
- In more than 85% of cases, malocclusion and crooked teeth are the result of pathologies located outside the dentition. In other words, these are manifestations of disturbances in the size and position of the jaws relative to the base of the skull, diseases of the masticatory muscles and mandibular joints, as well as problems with the spine, neck and shoulder muscles. The above situation is often aggravated by the patient's hormonal, neurological, psychological and osteopathic problems.
- Only 10-12% of orthodontic diseases lie in the area of curvature of the dentition itself with displacement of individual teeth, and can be relatively easily and quickly eliminated with both braces and aligners.
- Taking into account the above factors, at least eight out of ten orthodontic patients require modern gnathological-orthodontic diagnostics to make the correct diagnosis and correct gnathological-orthodontic treatment
- Unfortunately, traditional orthodontic diagnostics in Russia does not take into account and does not provide all the necessary studies, which leads to complications after treatment such as:
- dislocation and loosening of teeth
- recession (recession) of the gums, with exposed teeth
- TMJ pain and dysfunction
- myalgia and hypertonicity of masticatory muscles
- lack of correct occlusal (chewing) contact between the upper and lower teeth
- After a comprehensive gnathological-orthodontic diagnosis, the patient may be warned that in some clinical cases, even correct orthodontic treatment is only an intermediate stage and does not provide the necessary aesthetic correction of the dentition and good occlusion of the teeth. It provides safe alignment of the dentition, improvement of the condition of the jaw joints and masticatory muscles, as well as the most favorable conditions for further gentle dental prosthetics with ceramic veneers and occlusal onlays or crowns.
It goes without saying that having all the information about the upcoming orthodontic treatment, which may not be final, but only an intermediate stage before prosthetics, helps the patient make the right and informed decision about starting such treatment.
What is included in a clinical examination?
After interviewing the patient, a clinical examination is prescribed using special devices and equipment. These methods allow you to study the anomaly in detail and completely recreate the full picture of the pathology.
Do you want to know what an orthodontist treats? Read our new publication.
In this article we will discuss whether myogymnastics for the face is effective.
Here https://orto-info.ru/zubocheliustnye-anomalii/okklyuzii/pravilnyiy-prikus-u-cheloveka-raznovidnosti-i-foto.html we have collected photos of what a correct bite looks like in a person.
X-ray
X-ray examination is used in dentistry to study the structure and condition of the bone tissue of the jaw and teeth. It allows you to build a competent treatment plan and predict its results.
For radiological diagnosis of dentofacial anomalies, the following radiological methods :
- Dental radiography. Refers to the intraoral diagnostic method, which is carried out using a special apparatus in the form of a tube, which is brought up to a distance of 5 cm from the cheek and a projection is made at a right angle.
Using this device, you can identify the abnormal location of the roots of the teeth, changes in bone and periodontal tissue, determine the presence of tooth buds and the stage of their formation.The only drawback of the technique is its limited localization. The device allows you to take clear pictures of only 2-3 teeth and no more.
- X-ray of the palatal suture . Necessary to determine the degree of ossification and structure of the palatal suture. To do this, use a device with close-focus shooting capabilities.
- Tomography of the temporomandibular joint . Necessary to determine the ratio of these elements in the treatment of malocclusion. It is carried out using a dental x-ray machine.
- Orthopantomography . Allows you to obtain a panoramic image of the problem jaw with a detailed image of each element.
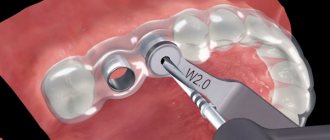
Using models
One of the mandatory diagnostic methods for orthodontic treatment is examination using diagnostic models . This method consists of taking impressions from both jaws of patients and making control working models based on them.
To give the models precise occlusion, it is registered using a heated wax plate. In the future, this plate is used to accurately model the jaw relationship.
What analysis methods are used when studying diagnostic models, watch the video:
Simulation allows you to choose the right method of hardware treatment. Let's look at some of them.
Functional
Functional methods include methods for detecting chewing tests and determining the degree of functionality of various muscle groups .
In orthodontic practice, the following methods are used for this:
- Masticationography. Allows you to accurately determine the type of bite by the degree of participation of certain muscles of the lower jaw in closure and lateral movements. For this purpose, a pulse-type device is used, which records the received data in the form of a curve.
The work of the muscles is judged by its deviation. The device is an elastic balloon that is attached to the lower part of the chin.When the mouth opens and closes, it responds to movement and transmits impulses to the kymograph.
- Graphic accounting. Allows you to determine the activity of the mandibular muscles during chewing. Just like in the previous version, the same apparatus is used, which displays the results in the form of a curve.
When the jaw is lowered, the rubber balloon contracts, causing the scribe to rise. The more the jaw participates in the movements, the higher the level of the curve.If there is no pressure, the scribe goes down. During immobility, the scribe produces a straight line. When diagnosing, pay attention to the wave transition angle and its maximum value.
- Electromyography. It is a study of the excitation potential of muscle fibers using a multichannel electromyograph.
The device allows you to determine the functionality of the muscular system of the jaw at rest, during excessive and natural tension.To do this, electrodes are fixed to the area being examined, through which current is applied to the muscles.
Craniometric
If the methods listed above are diagnostics, mainly based on morphological characteristics, then craniometric ones make it possible to determine malocclusion using the ratio of the proportions of the facial region and the upper part of the head to the planes of the jaw.
Mask model
It is used to accurately determine facial asymmetry, taking into account three planes mutually perpendicular to each other . The planes used are the tragus, the medial line running along the palatal suture, and the frontal plane.
To determine asymmetry, a glass cube was initially constructed with a mask model fixed in it. The mask was made according to facial proportion standards. During diagnostics, the horizontal plane must coincide with the surface of the cube.
Based on the discrepancy between the dentofacial apparatus and the other edges, an anomaly is judged, which is localized along a line asymmetrical to the plane.
Gnatostatdevice
This device is a further development of the mask model, which turned out to be very bulky and inconvenient to use. Subsequently, the cube with the mask was replaced with a special device - a gnathoscope.
It is used to determine a horizontal line that runs along the line of the eyes. The median one is localized in the area of the palatine suture, and the frontal one runs along the central part of the face. The device consists of an impression tray, a metal rod and several movable arrows.
The device is fixed using movable arrows, defining the main planes with them.
Deviation in the area of the median plane indicates asymmetry in the transversal plane, and deviation along the horizontal line indicates prognathism and sagittal asymmetry.
If the upper canines are located in front or behind the horizontal plane, then this is considered a deviation. The narrowing or widening of the jaw is determined by the midline. The vertical line reveals the degree of occlusion displacement.
We will tell you how the bite is determined during edentia in the next review.
Our next article is about the pros and cons of using orthodontic trainers for children.
At the link https://orto-info.ru/sistemyi-vyiravnivaniya-zubov/breketyi/rezultatyi-lecheniya-foto-do-i-posle.html we have posted a selection of photos of how the face changes after wearing braces.
Photostat
With this method, the diagnosis of deviations in the development of the dentofacial apparatus is revealed using photography . For this purpose, a Simon photostat is used, in front of which the patient's head is fixed motionless.
Before shooting, control points are marked, which are the orbital line, ear points, and the lower corner of the jaw. The device has internal on-screen markings of asymmetry measurement planes, which are aligned with the marked points.
Using the finished image, a possible deviation is determined.
Diagnosis is carried out not only by three planes, but also by the angle of the jaw. The deviation of this indicator upward or downward is evidence of the presence of prognathia or progeny.
Teleradiography
It is the most revealing and informational research method. It is an X-ray image of the patient's profile, which displays the skeleton, its structure and the contours of the soft tissues.
The procedure is carried out using X-ray equipment placed at a distance of no more than 1.5 m from the head. In this case, the X-ray film should be pressed as tightly as possible.
For accurate design, it is recommended to apply approximate plane lines to the film.
Based on teleradiography data, the relationship between the bases of the upper and lower jaw is judged. The study also allows us to identify the inclination of the teeth in relation to the base of the skull and the general row.