Preoperative preparation of the patient
Vertical or horizontal osteotomy of the jaws is performed on patients only after a thorough examination of the medical history. The doctor also reviews the results of blood tests.
In dentistry, there are the following recommendations for patients before jaw osteotomy:
- Radical intervention is not carried out for patients who have suffered a viral infection 2 weeks before the planned operation;
- the slightest signs of the patient’s discomfort are the reason for postponing radical intervention;
- a person is prohibited from consuming food, alcohol and pharmaceuticals 20 hours before osteotomy;
- The patient's oral cavity must be sanitized and free of removable dentures and orthodontic appliances.
The price of surgery to correct a malocclusion varies depending on the complexity of the operation, the location of the pathology, the prevalence of the maxillofacial anomaly and the qualifications of the dental surgeon.
Osteotomy of the lower and upper jaw as a method of maxillofacial surgery for correcting occlusion
Malocclusion is not only an aesthetic problem, but also negatively affects a person’s health and functioning. The anomaly can cause speech impairment, lead to tooth loss and the development of pathologies associated with the digestive system due to poor chewing of food, so bite correction is necessary.
It is not always possible to achieve a positive effect with the help of braces, mouth guards and other dental structures. Then they resort to surgical intervention. Thanks to modern technologies, operations to change mesial occlusion or other jaw disorders and align teeth are completed quickly and with minimal inconvenience for the patient.
Benefits of the procedure
Compared to other procedures prescribed to correct malocclusion, osteotomy has the following advantages:
- restoration of chewing functions, which has a positive effect on a person’s quality of life;
- reducing the likelihood of tooth decay, which occurred due to incorrect jaw position;
- correction of the oval of the face, thanks to which you can improve a person’s appearance and make him more attractive;
- restoration of symmetry of the lower and middle parts of the face;
- eliminating the effect of a “toothless” smile, when the crowns are completely hidden by the lips when opening the mouth;
- elimination of the phenomenon in which, when a person smiles, the lips do not cover the gum line;
- reducing the likelihood of developing various jaw pathologies, including diseases of the temporomandibular joint;
- elimination of post-traumatic defects.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Sectoral osteotomy of the anterior maxilla
Osteotomy is resorted to in extreme cases, when orthodontic treatment does not eliminate existing defects in the structure of the facial part of the head. The operation carries a certain danger. Medical errors made during osteotomy lead to infection of the body, blood poisoning and other, more serious consequences.
Indications and contraindications for surgical correction of bite
Correction of the bite surgically is indicated in cases where:
- there is strong facial asymmetry;
- the structure of the dentition has a pronounced deviation from the norm;
- as a result of uneven distribution of the load on the upper and lower jaws when eating food, discomfort occurs;
- there are severe disturbances in the functioning of the speech apparatus;
- alveolar processes are deformed;
- lips do not close completely;
- the tongue is located atypically in the oral cavity;
- there is deformation of the cranial vault and congenital anomalies in the development of the jaw;
- chin dysplasia is observed;
- severe trauma to the facial skeleton occurred.
- pathological disorders in the functioning of the endocrine, cardiovascular, central nervous and immune systems;
- diabetes mellitus;
- infectious diseases;
- tuberculosis;
- HIV;
- mental disorders;
- oncology;
- blood diseases, including blood clotting disorders;
- pathologies of bone tissue.
In children and adolescents
Osteotomy of the upper and lower jaw has age restrictions. This applies to children and adolescents. At a young age, surgery is not performed, since the jaws are still growing and the bite is not fully formed. For patients over 60 years of age, surgery may be contraindicated, but everything is determined by the individual characteristics of the person.
In some cases, surgical correction of a child’s bite before its formation is complete may be indicated. Maxillofacial surgery in children is resorted to if pathological changes in the jaws are severe, and other treatment methods cannot give the desired result (look at the photo).
In adults
For adults, surgical intervention is a reliable and quick way to cope with the problem of mesial occlusion and other similar jaw defects. Moreover, methods such as wearing braces, mouth guards and other dental structures complicate a person’s life and often turn out to be useless.
Modern dentistry offers several options for operations to correct jaw problems, depending on the complexity of the defect and individual characteristics:
- Genioplasty. Aesthetic shortcomings are eliminated. During the intervention, the chin part is shifted to the midline.
- Osteotomy of the upper jaw. Together with the jaw, the teeth and palate are correctly positioned. To do this, incisions are made above the teeth and under the eye sockets, and the jaw itself is fixed with special splints.
- Osteotomy of the lower jaw. To put it in the correct position, a cut is made in the bone behind the molars. The jaw is held in place using titanium plates until the bone tissue grows.
- Segmental osteotomy. Allows you to correct your bite by moving part of the jaw along with the teeth.
When is a bite corrected surgically?
Correcting the bite surgically allows you to eliminate any defects in the structure of the maxillofacial apparatus. The doctor can correct:
- malocclusion;
- discrepancy between the sizes of the upper and lower jaws;
- incorrect position of the jaws relative to each other;
- abnormalities of the jaw joints.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with what painkillers for toothache.
Incorrect bite is not just an aesthetic defect of the face. An anomaly in the structure of the jaw is a serious deviation that can lead to serious consequences:
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. This is due to the fact that the patient cannot eat properly and chew food.
- Apnea. Due to improper closure and position of the jaws relative to each other, sudden cessation of breathing may occur.
- Dental problems. The abnormal position of the teeth causes uneven distribution of the load in the dentition, as a result of which the enamel is subjected to intense abrasion, the teeth crumble and fall out.
- Violation of diction and articulation. An incorrect bite prevents the patient from communicating normally and leading a full life.
- Headache, toothache and joint pain.
Correcting the bite surgically allows you to eliminate all of these problems, restore self-confidence and improve your general condition.
Preparing for surgery
An important step before osteotomy is preparation for it. It includes several main stages, compliance with which will allow you to avoid complications during the operation and in the postoperative period, and will also ensure the achievement of maximum effect:
- Anamnesis collection. Initially, the attending physician should be informed by the patient about the presence of any chronic diseases in order to adjust the course of treatment. It is also important for him to understand what caused the malocclusion, whether it is a congenital or acquired anomaly. Plus, you should report any allergic reactions to medications, since surgery is performed under anesthesia.
- Treatment of existing diseases. During the period of an infectious disease, such as influenza, ARVI or tonsillitis, the use of surgical methods is contraindicated, as there is a risk of infection.
- Teeth straightening. Often, the patient wears braces for 8–16 months before osteotomy.
- Computer modelling. This allows you to predict the position of the bones and the final result, as well as all the details of the upcoming operation.
Immediately before correcting the defect, the patient is required to:
- 8–10 hours before the start of the intervention, stop eating food to prevent it from entering the respiratory tract;
- Before the operation itself, you should not drink liquids;
- Smoking and drinking alcoholic beverages are prohibited 12 hours before surgery;
- From the moment of recovery from acute respiratory infections, at least 2 weeks must pass before osteotomy can be performed.
How is the operation performed?
The surgical intervention itself, or rather, its features, directly depends on the jaw that is planned to be operated on:
- Lower jaw. The operation is performed inside the oral cavity. The advantage of this is that postoperative scars and scars will not be visible on the face. First, an incision is made in the mucous membrane and periosteum. It is carried out along the pterygomaxillary fold. Then the boundaries of the incision are expanded to provide access to the jaw. After this, the plates are sawed using a special saw, the fragments of which are separated on both sides. Next, the jaw is set in the required position and fixed with titanium screws.
- Upper jaw. Osteotomy is performed under endotracheal anesthesia. The incision of the mucous membranes and periosteum is made slightly above the fold of the maxillary junction, and the boundaries are moved apart. Then markings are applied on the jaw walls in front and on the sides on both sides. In accordance with the markings, sawing is carried out, and the resulting fragments are installed in a new position and fixed with titanium mini-plates.
Rehabilitation period
Rehabilitation is a rather difficult and long period after surgical correction of the jaw. It can be divided into several stages:
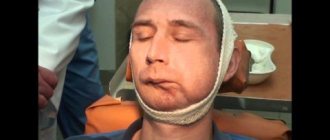
- The first day after surgical alignment of the bite. During this time, a compression bandage is applied to the patient to fix the cheeks and chin. The patient is prohibited from opening his mouth wide, chewing too hard and blowing his nose sharply.
- The first few days after correction. To prevent the development of infection, a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
- The entire rehabilitation period. The dentist observes the new formation of the bite.
- 10–14 days after surgical correction of the lower or upper jaw. During this period, the sutures are removed and the elastic bands are attached to the braces.
- Three to four months after osteotomy. The screw fastenings are removed from the jaw apparatus.
- the appearance of bruises;
- swelling;
- speech disorders;
- difficulty eating;
- numbness in the area of the incision, as well as in the lips, chin and tongue;
- pain when opening the mouth;
- bleeding from the wound;
- brushing teeth becomes problematic;
- the temperature may rise.
All this greatly complicates a person’s ordinary life. However, the effect achieved as a result of the operation justifies all the attendant difficulties in restoring the upper or lower jaw.
Postoperative period
After the osteotomy, the patient must be kept in a hospital for three days. Complications can extend this period up to 10 days. Doctors will judge the final success of the operation only six months after it was performed.
On the first day, doctors will secure the jaw with a pressure bandage and remove it after 24 hours. During rehabilitation, the patient will be prescribed antibiotics to avoid infectious diseases. Special elastic bands will be placed between the teeth to better hold the jaws together. Postoperative sutures are removed after 14 days, and fastening screws only after three months.
Swelling of the tissues will persist for one month, and impaired sensitivity of the chin will be present for four months from the date of jaw surgery. These symptoms are not complications and will gradually disappear as recovery progresses.
At the moment, jaw surgery is recognized as one of the safest for patients, and the positive effects after the necessary operation are very noticeable, both in terms of living comfort and aesthetics.
Radical correction of bite during orthognathic surgery
Most people are horrified by the word “surgery.” If a dental patient suddenly finds out that he is undergoing orthognathic surgery, this news is unlikely to make him happy. We propose to find answers to the questions of whether surgical interventions of this type are really necessary, whether it is possible to do without them, and what their possible complications are.
Reasons for the popularity of orthognathic surgery
Over the past 15 years, orthognathic surgeries have become very popular. They allow you to quickly and effectively eliminate many advanced cases of facial abnormalities (skeleton or teeth). Previously, surgical interventions of this kind were used for serious disorders of the function of organs located in the facial area (impaired chewing or swallowing, narrowness of the airways, congenital maxillofacial anomalies). Now, such operations are increasingly used to eliminate aesthetic defects associated with facial disproportions or an unattractive smile. Patients' demands for the results of such manipulations have also increased: many agree even to extreme measures in order to quickly tidy up their appearance.
Modern dentistry has recently collaborated closely with maxillofacial surgery and orthodontics, which has made it possible to accurately predict the results of surgical interventions. Often, in large centers of maxillofacial surgery, during orthognathic operations, ultra-modern technologies are used, such as virtual modeling of the facial profile, cone CT, and the use of CAD-CAM technologies in the manufacture of splints.
For the successful outcome of such an intervention, detailed planning and accurate calculation of all its stages are especially important. The introduction of virtual techniques allows you to prevent inaccuracies during the execution of operational stages.
The highest demands are placed on surgical interventions on the face, since a deviation from the parameters of even 1-2 mm leads to pronounced aesthetic defects in appearance.
If, for example, the lower jaw is brought forward just a millimeter, this will lead to difficulty closing the lips of such a patient. If the jaws are not brought forward enough, this will further age the patient and lead to recession of the lips.
When the upper jaw drops excessively, the patient acquires a repulsive “gummy” smile, and when it rises excessively, the smile becomes “toothless.” It is now clear how accurately all operations in the area of the face and jaw of any patient must be performed.
Who undergoes jaw surgery?
The term "orthognathic" comes from the Latin words for "straight" and "jaw."
This area of surgery is a type of plastic surgery and requires the highest qualifications of an orthodontic surgeon.
Typically, such interventions are needed to restore an aesthetic smile and achieve harmonious facial proportions. It is no secret that orthodontic manipulations on a patient’s jaws and teeth often take months, or even years. At the same time, the use of various devices requires the patient’s patience and significant financial investments. In addition, not all facial defects can be corrected conservatively.
A variety of non-surgical treatments are often powerless and pointless for severe pathologies of the dental system.
However, untreated malocclusion pathologies are not only an unpleasant external defect. Such disorders (usually congenital) lead not only to problems with diction or chewing food, but also to respiratory problems, rapid tooth decay and constant pain in the jaw area.
But such unpleasant and even dangerous phenomena disappear after surgery and the associated movement of the jaw bones (one or both) in the desired direction (forward, backward, down or up).
Indications for osteotomy
Incorrect mesial bite leads to impaired diction, pain in the temple area, rapid abrasion of tooth enamel, and diseases of the digestive system. An operation to change the position of the lower jaw is indicated in the following cases:
- frontal open bite – incomplete closure of lips, difficulties with diction,
- chin dysplasia – leads to an unaesthetic appearance,
- lateral open bite – accompanied by chewing difficulties,
- underdevelopment and overdevelopment, incorrect position of the jaws,
- open bite – determined by the slit-like interdental gap.
Contraindications to the work of a maxillofacial surgeon include blood clotting disorders, infectious diseases, diabetes, and endocrine pathologies. The operation is also not performed on patients with cancer, HIV, or adolescents under 16 years of age. Before the procedure, the oral cavity must be sanitized, soft plaque, stone, and carious lesions are removed.
Types of orthognathic operations
In this type of surgery, several types of surgical interventions are used, depending on the type and severity of jaw closure disorder and bite pathology. The orthognathic section of surgery is considered particularly complex and responsible.
Errors during surgery affect the appearance of patients and seriously disrupt the most important functions of normal life (breathing, chewing, pronouncing sounds).
Most often, the patient undergoes the following types of interventions:
- Osteotomy in the upper jaw. In this case, intraoral manipulations are performed on this bone. The surgeon makes incisions behind the patient's eye sockets and moves the upper jaw (including the palate and teeth) in the desired direction. Then the jaw is fixed with a special splint in the selected position.
- Mandibular osteotomy. In this case, the bone is cut behind the molars. The jaw is then moved and placed in the intended position. The unusual position of the mandibular bone is fixed using titanium plates. After the required volume of bone tissue has grown, the plates are removed.
- Aesthetic genioplasty. This corrects the symmetry of the face. Its difficulty lies in separating and correctly positioning the chin part ideally along the midline.
What you need to know before orthognathic surgery
Such surgical interventions are performed as planned. The patient is usually familiar with the stages of the upcoming operation and its results. Important information before orthognathic surgery is that:
- Patients who have had viral infections later than 2 weeks before surgery are not allowed to undergo surgery. Otherwise, the operation has to be postponed.
- Any ailment of the patient (nausea, vomiting, fever, high blood pressure, sore throat, etc.) requires rescheduling the operation.
- The night before, it is prohibited to take food later than 20 hours and liquids after 22 hours (8 hours before the intervention).
- It is necessary to abstain from smoking on the day before surgery (an interval of at least 12 hours).
- Taking liquids or food before the intervention is strictly prohibited. This restriction is important to prevent food from entering the respiratory system and causing the risk of death.
- It is necessary to remove contact lenses, dentures and jewelry, and wash off makeup.
- It is important to tell the doctor about all medications the patient is using. Some of them may be incompatible with anesthesia or lead to postoperative complications.
Some nuances of the operation
Let's try to answer questions that patients may have before orthognathic surgery:
- it is performed only in a hospital using general anesthesia;
- its duration depends on the complexity and volume (about 4 hours on both jaws, about one and a half hours on one jaw, about 6 hours for manipulations on the chin);
- thanks to internal incisions, the patient does not receive visible scars on the face;
- wound healing usually occurs in 10 days, and for jaw fusion it takes from 2 (lower jaw) to 4 months (upper jaw);
- Postoperative stay in the clinic is usually 2-3 days.
Rehabilitation after orthognathic surgery
Even before surgery, the patient should be aware of the following postoperative changes in his well-being:
- sore throat;
- nasal congestion and swelling;
- swelling and cyanosis in the cheeks and lips;
- nausea;
- Difficulty speaking and communicating (usually goes away within a week);
- discomfort and pain during oral hygiene in the first days;
- nausea:
- a feeling of numbness in the area of the surgical field for 1-5 months;
- slight weight loss (up to 10%).
Usually, 20 days are enough for many to regain their well-being. After the operation, the patient is given elastic reinforcements on the inner surface of the operated jaw. This is necessary for correct occlusion and sufficient mouth opening.
For the first postoperative week you can eat only liquid food, and then for 4 weeks the food should remain soft and sufficiently crushed.
It is especially important to follow all medical prescriptions in the postoperative stage.
Lower jaw
Since local anesthesia is used for the operation, the presence of an allergy to the drug used is first determined. Osteotomy of the lower jaw begins with a small incision of the mucous membrane in the angular part. Next, the necessary manipulations with the bone tissue are carried out, with preliminary cutting of the jaw bone. Spreading and fixing of individual fragments is used.
After which, the same manipulations are performed on the second side of the jaw. As a rule, swelling on the face persists for 1 month. Loss of sensitivity in the chin can last about 3-4 months. The condition is considered natural and does not require medical intervention. If the outcome is favorable, the patient is discharged from the hospital 3 days after the operation.
Orthognathic surgery and possible complications
Such operations are considered safe and are extremely rarely accompanied by any complications. The possibility of complications during anesthesia is the same as with any other operation.
However, like any intervention in the body, orthognathic surgery may be accompanied by the following complications:
- swelling of the face;
- development of infection (the risk is high due to the maximum speed of blood flow);
- malocclusion due to resorption of the cartilage of the lower jaw (occurs with chronic inflammatory processes in the jaw joints);
- jaw fracture due to previously undetected bone defects:
- persistent numbness of the face (a consequence of damage to the facial nerve);
- poor fusion of jaw fragments or fracture of titanium plates (after violation of the regime and premature load on the jaw bones, such as early chewing or teeth grinding).
You need to know that loss of facial sensitivity (chin or lips) is normal after surgical procedures.
It can last from two months to one and a half years. Then the person may begin to feel “pins and needles”, which will signal the restoration of sensitivity and nerve conduction. Unfortunately, about 5% of patients complain that they lack normal facial sensitivity even after a long period of time after orthognathia.
Facial expressions and lip motility should not be affected after surgery. Such phenomena indicate serious complications and ill-conducted intervention.
Indications for surgery
The most common indications for such surgical interventions are:
- significant anatomical imbalances of the jaw in combination with anomalies of the dentition;
- gross violation of the jaw relationships, excessive or insufficient growth of one of them, violations of the closure of lips or teeth (“bird face”, significant mandibular massiveness, “gummy smile”, etc.);
- results of illiterate operations for the treatment of various congenital facial anomalies (“cleft palate”, “cleft lip”).
Indications for use
Osteotomy is performed to correct the bite, correct congenital anomalies and eliminate the negative consequences of surgical facial plastic surgery. As a rule, it is used for surgical treatment of the upper or lower jaw, but if necessary, it can be double-jawed. Based on the operating parameters, a complete or fragmented operation is distinguished.
The main indications for the correction procedure include:
- malocclusion;
- protrusion of the jaw;
- rapid development of jaw elements;
- improper distribution of chewing movements;
- congenital underdevelopment of the jaw system;
- unnatural arrangement of teeth.
A pathology such as malocclusion is amenable to orthopedic treatment and comes down to correction with the help of plates. In more advanced cases, surgery is used, which is used for fractures and injuries of the lower and upper jaw according to the Lefort type. The technique used to eliminate pathology depends on the severity of deformation changes and the location of the main defect.
Contraindications
But not all patients can undergo such manipulation. It is contraindicated for people:
- under 18 years of age;
- with unprepared dentition;
- general contraindications to any surgical interventions (serious pathologies of the blood, heart or blood vessels, severe diabetes, acute conditions or infections, oncology, etc.)
Such interventions are intended primarily to correct skeletal deformities.
Corrected dentition relationships are essential for the success of such operations.
Therefore, it is first necessary to carry out orthodontic treatment of the patient using one of the selected methods (prosthetics or installation of braces). Sometimes wearing braces lasts up to one and a half years. The system is removed only after surgery, which increases the patient’s chances of 100% treatment success.
Often, surgical methods are first performed to prepare the dentition for surgery (tooth extraction, frenulum correction, restoration of normal nasal breathing, crown exposure, minor osteotomy, partial tongue resection).
Advantages of osteotomy
This operation has a number of advantages:
- After osteotomy, patients are pleased to note the fact that it has become much easier for them to chew and bite food. Chewing functions improve overall, which has a very positive effect on the patient’s standard of living.
- Eliminate and minimize years of tooth decay and excessive wear.
- Osteotomy is also aimed at correcting the oval of the face. After it, the appearance of the face improves, a small chin looks much better, the jaw no longer protrudes, and the bite is normalized. A beautiful appearance makes a person much more confident.
- This operation helps restore the symmetry of the lower and middle parts of the face. The face looks symmetrical and beautiful.
- Osteotomy helps people suffering from a “toothless” smile. When such people smile, their teeth are completely covered by their lips. It doesn't look very aesthetically pleasing. After the operation, the smile becomes beautiful, the teeth are visible.
- In other situations, when smiling, the lips do not completely cover the gums. It also doesn't look very nice. This problem can also be easily dealt with using the procedure described above.
- Few people know, but with the help of such surgical intervention you can reduce the risk of developing temporomandibular joint disease and other jaw ailments.
- After facial injuries, post-traumatic defects often remain on it, which can greatly spoil the appearance of the victim’s face. Such defects can also be treated with osteotomy.
Before deciding on the procedure described above, you need to consult with specialists who will tell you exactly whether such a serious operation is necessary or whether the problem can be dealt with differently. In some cases, surgical intervention is not necessary, since a person often invents problems for himself that actually do not exist. The doctor decides whether or not to perform the operation only after a thorough examination of the patient.
Share link:
What will you need in the hospital?
Regardless of the clinic where the operation is performed, patients usually need to have the following with them:
- documents (passport, referral for surgery, test data);
- slippers and suitable clothing (tracksuit, robe), excluding clothing worn over the head due to possible postoperative pain and swelling of the face;
- hygiene products (towel, comb, soap, toothpaste, brush);
- cup-type sippy cup with a spout for feeding (for postoperative swelling of the lips);
Although the orthodontic treatment industry has achieved tremendous development, for some dental pathologies any conservative treatment may be ineffective.
Thanks to orthognathic operations, it is possible to reduce the time and consolidate the results of treatment for the most serious maxillofacial anomalies.
Sources used:
- “Outpatient surgical dentistry” (Bezrukov V.)
- British Orthodontic Society
- “Propaedeutics of surgical dentistry” (Soloviev M.)
Article rating:
Mandibular osteotomy without braces Link to main publication
Related publications
- Place braces in Moscow
MAXILLOCRANIAL ANOMALIES
Such developmental defects are called “anomalies of maxillo-cranial relationships.” Pathologies arise due to disturbances in the intrauterine development of the cranial bones and facial skeleton. With a mild form of asymmetry and incorrect position of the jaws, they do not cause much discomfort, so they can be classified as aesthetic problems. However, in the vast majority of cases, these are serious pathologies that noticeably change the proportions of the face and cause disturbances in speech, chewing and swallowing food. Due to the incorrect position of the jaws in relation to the skull, the load on the joints, muscles and individual groups of teeth increases.
For information about prices and treatment times, call:
+7
or fill out the feedback form:
Classification of maxillofacial anomalies
- Jaw asymmetry. This pathology includes a number of jaw deformations. The common thing is that there is a discrepancy between the right and left parts of the face, which can cover both a separate zone and the entire half of the face. The jaws can be moved in different directions: sagittal (back and forth), transversal (left to right) or vertical. There are several types of pathologies: with a displacement of the midline of the upper/lower jaw (or both jaws), with an isolated displacement of the chin, the lower edge of the jaw and other parts.
The presence of asymmetry can also be determined visually during examination. It is enough to draw an imaginary line in the middle of the face to detect the displacement and inconsistency of its two parts. The specific problem area is best identified with a wide smile. If at the same time the gums are exposed more strongly and the smile line on the right side changes, then the asymmetry is precisely on the right side. To confirm the diagnosis, an X-ray examination is performed at the clinic. If the x-ray is uninformative, then they resort to other diagnostic methods - orthopantomography, teleradiography and computed tomography.
- Prognathia and progeny. This pathology is characterized by the protrusion of one of the jaws forward, which disrupts the closure of the teeth in the anterior region. The protrusion of the upper jaw is called prognathia (distal bite). In this case, there is an increase in all parameters of the jaw and its anterior position relative to the skull. Visually, this is manifested by a protrusion of the middle part of the face, a change in profile and a shortened upper lip. Due to the fact that the lips do not close, the upper front teeth are visible. With this pathology, the functions of chewing, speech and normal breathing are impaired.
The anterior position of the lower jaw relative to the base of the skull is called progeny (mesial occlusion). As in the case of prognathia, the reasons for its development may be maternal illness during pregnancy, birth injuries, artificial feeding, irregularities in the timing of teething and other factors. This pathology can be determined by the concave middle part of the face, the forward chin and lower lip, the recession of the upper lip and the presence of a gap between the jaws.
- Retrognathia. An anomaly in which one of the jaws moves backward. With maxillary retrognathia, there is a posterior position of the upper jaw, which is manifested by retraction of the middle part of the face and protrusion of the chin. With the lower (mandibular) the lower jaw shifts back, which causes the middle part of the face to stretch and the chin to recede. You can learn more about this pathology in the article Retrognathia on our website.
Treatment of craniomaxillary anomalies
As in other cases, treatment regimens and methods are determined individually based on the clinical picture. For example, in case of asymmetry with a displacement of the midline, an osteotomy is performed to correct the position of the jaw fragment. More problematic is the elimination of displacement of both jaws, since two operations will be required at the same time. For chin asymmetry, surgery (genioplasty) is also performed. Correcting displacement in the lateral sections is a less complicated procedure and involves removing excess bone tissue.
For the treatment of prognathia and retrognathia, there are also proven and effective methods. Their choice depends not only on the severity of the pathology, but also on the period in which treatment measures are carried out - during the process of jaw growth, during the period of mixed dentition or with already formed dentition. For moderate violations, correction is performed using braces. In complex cases, surgery may be required. Prevention of maxillocranial anomalies should include ensuring the normal course of pregnancy, breastfeeding, weaning the child from thumb sucking and other bad habits.