Prostheses with attachments - features and advantages of designs with locking fastenings
Attachments in dentistry are a separate type of fastenings in removable and partially removable prosthetic devices. Essentially, this is a locking mechanism that includes two main elements: the first is fixed on the abutment tooth, stump inlay or crown, and the second on the orthopedic structure. At the moment of fixation, the parts are connected and snapped together, ensuring reliable fastening of the device in the mouth. According to many patients, dentures with this type of fastening are more comfortable to wear, cause less discomfort and fit securely in the mouth. Later in this material we will take a closer look at what it is, what pros and cons are typical for this type of prosthetics.
Pros and cons of clasp dentures with locking fastening
Advantages
- Reliable fixation in the oral cavity
- Excellent aesthetics (fasteners are not visible when smiling)
- More physiological distribution of the load over the supporting teeth compared to dentures with clasp fixation (this makes the chewing process more comfortable)
- Low risk of breakdowns
- Ease of use (prostheses with attachments are easy to remove and put on)
- Miniature (clasp dentures for the upper jaw with locks, unlike dentures with clasp fixation, do not cross the palate)
Flaws
- The need to grind often healthy teeth for crowns (usually 4 abutment teeth are covered with crowns)
- Complexity of manufacturing (requires highly qualified orthopedist and dental technician)
- High cost (in Moscow - from 40 thousand rubles)
- The need to periodically replace the fastening element on the removable part (since the lock parts wear out over time and the prosthesis no longer fits tightly in the mouth)
Disadvantages of classic removable dentures
Standard models of plate dentures usually provide for fastening using clasps - a special wire structure made in the form of hooks. Two phenomena can provide additional fixation strength:
- cohesion – tight contact of the structure due to the repetition of the anatomical shape of the patient’s jaws,
- adhesion - the effect of suction of the prosthesis to the palate or alveolar arch of the lower jaw.
However, this is often not enough for a strong and reliable fixation. Then the patient has to resort to the help of auxiliary means - fixing creams and gels. The massive palatal bridge of dentures for the upper jaw significantly complicates and prolongs the process of adaptation, distorts taste sensations and impairs diction. As for the lower jaw, here the area of contact between the prosthesis and the alveolar process is smaller, which leads to rapid loosening of the structure. There is a risk of the prosthesis falling out during active use of the tongue, for example, when talking or eating.
Classic dentures can fall out while eating
In this regard, the most advantageous option may be a clasp prosthesis. It lacks a massive palatal overlap, which ensures the proper level of comfort. Today, this is one of the best constructive solutions to the problem of partial edentia (there are no complete clasp dentures). Separately, we can highlight a model with a splinting effect - it allows you to secure the remaining loose teeth in the desired position. It is worth noting here that the “clasp” can be either on clasps (hooks) or on attachments - the latter option is certainly more preferable.
What is special about attachments?
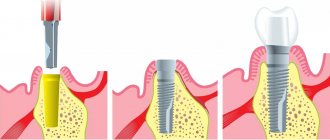
Currently, in dentistry there are several types of locks for installing orthopedic devices. However, the essence of the work of the fastening system comes down to one thing - fixation is ensured by snapping two independent elements together - one on the prosthesis, the other on the supporting tooth.
We can immediately classify them according to the method of manufacturing the mechanism. Thus, a distinction is made between precision and semi-precision attachments. In the first case, the system is created in a factory, and the elements are attached to the prosthesis by welding. The latter are created in a dental laboratory. Specialists model and cast parts based on previously taken impressions of the patient’s jaws1.
Cost of clasp dentures with locks
The price of locking prosthetics depends on several factors and is determined individually after consultation with an orthopedic doctor. The cost is affected by:
- the volume of the defect that needs to be filled, i.e. on the number of lost teeth in a row;
- the number of crowns that need to be installed on the supporting teeth;
- the need for unilateral or bilateral jaw prosthetics - filling a bilateral defect will be more expensive than a unilateral one.
The final price of services also includes intermediate work - taking impressions of the jaw, making a model of the jaw, casting the frame. The cost will be affected by the volume of material required for the manufacture of the prosthesis and the composition of the alloy from which the main load-bearing element - the arch of the prosthesis - will be made.
The dental clinic "Academy Dent" in Moscow rarely performs clasp prosthetics with locks, but if necessary, then at a high professional level. The clinic’s specialists have undergone training and internship abroad and use the latest techniques. The high competence of our clinic’s orthodontists allows us to find the best solutions for each patient.
Our specialists work with complex cases that require a special approach. When installing a clasp denture, specialists conduct a detailed diagnosis of all existing disorders, study the structure of bone tissue and the characteristics of the dentition. Then the configuration of the prosthesis is carefully selected so that it serves the client as long as possible.
Attention is paid to the integrity of the patient’s own teeth. Prosthetics are performed taking into account all the client’s wishes and individual anatomical and physiological characteristics.
Our dentistry uses modern equipment and the latest pharmaceutical and technological developments, which improve the quality of services and improve the final result. In addition to correcting existing problems, prevention of complications in the future is carried out. A positive atmosphere and cozy environment only improve the final result.
What types of attachments are there?
Currently, there are many types of locks used to secure prosthetic devices. Below are the main types of attachments:
- intraradicular – remain hidden inside the abutment tooth or artificial crown, which allows achieving the highest aesthetic standards,
- foliar – fixed from the outside, which gives the required degree of mobility,
- root pins – attached directly to the tooth root,
- crossbar - characterized by the presence of a special valve in its design,
- spherical - the element that is fixed on the support is made in the shape of a ball,
- rail - a part intended for fastening to a tooth or crown, made in a T-shape, which makes it possible to increase the friction force,
- rod - implants are connected to each other by a horizontal beam, which is fixed on the prosthesis using special grooves.
On a note! Attachments are widely used in orthodontics. So, for example, similar fastening systems can be found on mouthguards; they are often used to fix aligners. In this case, we are talking about special convex elements that are fixed on crooked teeth and allow the corrective structure to be more securely attached to the jaw.
Also, attachments can be hard, medium hard or soft - the choice of one or another option largely depends on the individual characteristics of the clinical picture. For the convenience of specialists, such elements can be marked in different colors. When creating such parts, metal, plastic, or a combination of both are used.
Advantages of designs on attachments
According to numerous patient reviews, models with attachments are much more convenient in many aspects. Here are the main advantages of such a fastening system:
- the ability to achieve impeccable aesthetics, since such fastenings are practically invisible on the teeth,
- high level of comfort - dentures are easy to take off and put on, allow you to maintain the proper level of hygiene, since they are easy to clean,
- in the event of a breakdown, you can easily replace the damaged element without the need to correct the entire device,
- guarantee increased strength and stability of the structure,
- provide a relatively uniform distribution of the chewing load.
These prostheses guarantee increased strength and stability of the structure.
“By the way, I just recently made myself a prosthesis with locks. Much more convenient than on hooks - this is my personal opinion. Firstly, the attachments are not visible at all, the smile looks natural and natural, nothing catches the eye. Secondly, getting used to it was much easier and faster, now I don’t experience any discomfort. Of course, I would like to undergo full-fledged implantation, but it costs money. So as a temporary solution, this is the best option.”
Yulia Sergeevna K., Krasnodar, from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru
Despite the abundance of unconditional advantages, this fixation system also has its disadvantages. More details about them in the next section.
Main types of clasp dentures
The most famous removable design is the clasp denture. At the base there is a strong arch made of a metal alloy, onto which other parts are attached: artificial gums made of nylon or acrylic, tooth crowns.
in the photo - a clasp prosthesis with a locking fastening
With careful execution, the technician is able to create a reliable and comfortable bridge with additional fastening. It can be used to reconstruct the upper or lower jaw to support a weakened row.
The main types of clasp dentures:
- on clasps;
- on attachments;
- on telescopic crowns;
- splinting.
Structures of this type can also be classified according to the materials from which they are made:
- metal-free;
- acrylic;
- metal;
- metal-ceramic.
Modern clasp dentures are miniature in size, easy to fix and do not require special care. They are recommended if the patient is uncomfortable using a removable jaw.
At the same time, the dentist makes the design comfortable, which does not affect the ability to chew or pronounce different sounds correctly. Fixed on the inside of the tongue, it is not noticeable during a conversation and does not catch the eye of the interlocutor.
Clasp dentures with clasp fixation
The simplest and most inexpensive is a clasp prosthesis with clasp fixation. It is recommended for the restoration of chewing teeth, provides reliability, excellent pressure distribution when chewing food.
Its main feature is fastening with special clasps. These are miniature metal tendrils with which the product clings to the supports.
Clasp dentures with clasps are ideally installed on the lower jaw. But one of the disadvantages is that the metal tendrils can fall into the visible zone of a smile.
Therefore, modern models are made from translucent nylon, which matches the natural color of the gums.
Clasp dentures with attachment locks
Miniature-sized locks are called attachments. This is a more modern type of prosthetics, which allows you to install clasp-type dentures on the upper jaw or front teeth.
ball type lock fastening
They are put on the support units and securely hold the structure when chewing. One part of the lock is located in the base, the second is built into the body of the support. When put on, they are connected and held in place by grooves.
Types of micro-locks for clasp structures
The attachments are located in different parts, which allows you to firmly fix the locking clasp prosthesis. Based on the type of fastening and structure, they are divided into several types:
- rail;
- crossbars;
- rod;
- spherical.
Read Allergy to dentures - symptoms, treatment, what to do if it occurs
At the same time, a prosthesis with micro-locks can be made from different materials to ensure its aesthetics.
Telescopic fixation
The modern type of prosthetics involves installing the prosthesis on supporting units or pre-prepared pins. The technique helps to adjust the height of the teeth, which is important for serious row defects.
The telescopic fixation system is widely used in European and American practice. But the manufacture of the structure requires precise calculations and high skill of the orthodontist.
Fastening the clasp denture on telescopic crowns
If it is necessary to straighten the dentition, a clasp denture on telescopic crowns is used . It provides for fastening the structure using retractable frames.
To do this, after preparation, caps made of a metal alloy are attached to the supporting units, onto which artificial crowns are subsequently placed. At the same time, strength and reliability are achieved due to the perfect alignment of the grooves.
Splinting type of prosthesis
With gum disease and chronic periodontal disease, a person experiences weakening of the mucous membrane. It sags, causing teeth to become loose.
There is a threat of loss of healthy units; severe swelling prevents the installation of a removable bridge. In such a situation, a splinting clasp prosthesis is used on the lower or upper jaw.
Unlike other types of structures, it has an additional metal arch that supports problem areas on the inside of the tongue.
How to properly care for a prosthesis and how long it will take to get used to it
Food particles often get trapped under the denture, which can cause an unpleasant odor and inflammation of the mucous membranes. The disease can also occur with dry mouth, using an antiseptic solution with alcohol, or smoking. Therefore, daily care of the clasp prosthesis includes:
- The structure should be thoroughly cleaned 2 times a day using a non-abrasive paste and a soft brush;
- several times a week, the prosthesis is soaked in an antiseptic solution for 15 minutes;
- Be sure to rinse your mouth after a cup of coffee or tea to prevent the base from darkening;
- It is necessary to regularly visit the dentist for professional cleaning and adjustment of the clasps.
On average, it takes at least a month to get used to a clasp-type denture design. If a person is still bothered by pain, swelling of the mucous membrane and other unpleasant symptoms, it is necessary to correct the product.
To quickly adapt and use the clasp clasp prosthesis comfortably, dentists give a number of useful tips:
- Before fixing, soak the product briefly in clean water;
- the first days do not take it off at night;
- Drink hot drinks 2-3 times a day to soften the gums;
- During the day, make mouth baths with sage, chamomile, and calendula;
- at home, read aloud any texts or poems to improve the pronunciation of sounds;
- For 2 weeks, follow a diet of liquid and soft food, give up crackers, seeds, and hard meat.
The clasp system for fixing clasp dentures requires certain skills from the patient. Therefore, in the first days you need to take them off and put them on in front of the mirror.
Clasp prosthesis with a locking fastening has a strong metal base. This makes it look neater and thinner than a removable jaw. The dentist can simulate any thickness of the bridge to eliminate discomfort
Arc placement options
Complex structures additionally have a metal arc. It connects the parts of the base that make up the clasp prosthesis. This enhances the strength and quality of the fit, eliminating accidental slippage and movement. It is made from cobalt alloy for durability.
The arch of the clasp prosthesis can be positioned as follows:
- in the region of the back of the palate;
- in the middle part of the upper jaw;
- behind the front teeth.
Depending on the anatomical structure of the oral cavity, the dentist can make one of the arch options:
- A palatal arch is formed on the upper part, which connects the lateral parts of the structure with healthy front teeth. Its thickness is no more than 0.6 cm, which better regulates the load when chewing and does not affect the pronunciation of sounds.
- Transverse arches are made in the back of the prosthesis at the level of the chewing “sixes”. More often, a clasp removable denture is made in this way for the upper jaw to ensure maximum rigidity. Among the disadvantages is an increased risk of vomiting.
- If additional gum splinting is necessary, a horseshoe arch is recommended. With its help, the dentist releases the back of the palate and distributes pressure along the dentition. This is good support for defects and curvatures.
Read Dentures with suction cups - how to use them, storage and care of such dentures
Among the options for eliminating complex anomalies, a transverse arch is recommended, the support for which is molars and premolars. The dentist calculates its location down to the millimeter to prevent compression of the mucous membrane and its rubbing.
Indications for installing devices on locking mounts
In dental practice, there are situations when it is simply impossible to do without a locking type of fastening on a prosthesis. Here are the main indications for installing the structure on attachments:
- excessive demands on aesthetics if the patient’s work involves public speaking and constant communication with people,
- loss of all molars on one or both sides,
- almost complete edentia, in which the remaining teeth cannot provide stabilization of the structure during chewing,
- curvature of individual teeth, preventing the free removal and fixation of the prosthesis,
- noticeable shrinkage of the alveolar ridge,
- flat sky,
- malocclusion,
- abrasion of enamel and reduction in crown height,
- periodontal tissue diseases,
- diabetes.
Loss of all molars on one side is an indication for use.
Also, such systems are recommended in cases where the patient has certain pathologies of the heart and blood, which are accompanied by periodic bleeding of the gums. A denture with attachments may be the best choice for a patient suffering from bruxism - unconscious grinding of teeth at night.
Are there any contraindications
Despite the abundance of advantages, prosthetic structures with locks have a number of installation restrictions. Here are the main contraindications:
- the supporting elements are severely damaged and will not be able to provide reliable fixation,
- there are pockets of inflammation on the roots of the remaining teeth,
- severely exposed roots are a consequence of periodontal disease,
- small crown height (up to 5 mm),
- Parkinson's disease, arthritis and other diseases that limit the mobility of the hands and significantly complicate the process of removing and installing a prosthesis with a complex attachment mechanism.
You should not resort to this type of prosthetics if you do not have the opportunity to see your dentist at least once every six months. It is also necessary to provide high-quality oral care, including before installing an orthopedic device. To do this, experts recommend undergoing professional cleaning to remove plaque and deposits in advance.
SELECTION OF LOCK FASTENERS
To correctly select a locking device that is appropriate for the clinical situation, the following factors must be taken into account:
- type of locking design
- locking functionality
— mechanism for connecting the matrix and patrix
— availability of space necessary for installing the lock fastening
- price
1. Types of design of lock fastenings:
Fig.2 Fig.3
Intracoronal locking fastenings - the matrix is included in the artificial crown (tooth) or installed in the hard tissues of the abutment tooth and does not protrude beyond the contour of the tooth (Fig. 2). The main advantage of intracoronal locking fastenings is that the chewing load is distributed along the longitudinal axis of the abutment tooth. The disadvantages of such fastenings appear when the size of the crown of the abutment tooth is insufficient to accommodate the matrix and lead to an excessive increase in the contour of the crown. In such cases, the anchorage of choice is the extracoronal anchorage.
All intracoronal locking fastenings are rigid, which explains the need to connect at least one more adjacent tooth to the abutment one.
In the case of a small height of the supporting teeth, in order to ensure sufficient stabilization of the prosthesis, it is necessary to use anti-tip devices and milled lingual overlays.
Extra-coronal locking fastenings - the matrix of extra-coronal locking fastenings stands behind the contour of the crown of the abutment tooth (Fig. 3), it is installed by welding/soldering with the frame or cast together with the frame of a fixed prosthesis. The advantages of this type of locking fastenings are: preservation of the normal dimensions of the crown of the abutment tooth, no need for massive grinding of hard tissues, and a fairly easy way to insert dentures.
Extracoronal anchorages can be rigid, but most are labile. Labile extracoronal locking attachments allow for various types of mobility of the matrix and patrix, which leads to a redistribution of the load between the tissues of the prosthetic bed and the periodontium of the supporting teeth. However, in order to prevent overloading of the abutment teeth, it is advisable to connect adjacent teeth to the abutment teeth.
The disadvantage of extracoronal locking fastenings is that it is difficult to maintain oral hygiene in the area of installed locking fastenings - it is necessary to instruct patients in the use of dental floss and other additional hygiene products in order to prevent the accumulation of plaque and the formation of tartar.
Root and intra-root button-type locking fastenings:
To install root and intra-root locking fastenings, special preparation of the supporting roots is required. The matrix or patrix can be installed by soldering/welding to the root part or cast together with a reproduction of the root post (Fig. 4). Intra-root locks such as Uni-Anchor or Direct O-Ring are cemented into the root canal without making an individual root post (Fig. 5). The matrix of intra-root locking fastenings such as Swiss Logic and Zest is installed within the space created in the support root (Fig. 6). In the manufacture of “overdentures” type prostheses on implants, factory-made screw-on heads with button fastenings are used (Fig. 7).
Button clasps ensure a good level of oral hygiene. Another advantage of button-type locking fastenings is the better ratio of the crown and root parts of the supporting teeth, provided by the low profile of the supra-root part, which minimizes lateral loads when using the prosthesis.
Beam lock fastenings:
Bar locking attachments are located above the edentulous areas of the alveolar process and connect the supporting teeth, roots (Fig. or implants (Fig. 9). Removable bridges, partial dentures or overdentures cover the beam and are connected through the matrix to its retention elements.
or implants (Fig. 9). Removable bridges, partial dentures or overdentures cover the beam and are connected through the matrix to its retention elements.
The main advantage of beam-type locking fastenings is the ability to combine “problematic” supporting teeth (roots) into one functioning group and subsequently exclude supports from it without significant alteration of the prosthesis.
When designing removable dentures with fixation on beam-locking fastenings, it is necessary to take into account the condition of the mucous membrane of the edentulous alveolar process to ensure normal oral hygiene.
Alternative options
If you want to save a little on removable prosthetics, then it makes sense to give preference to a model with locks - clasps. These can be parts made of metal, plastic or rubber that surround the crown or abutment tooth, thereby ensuring fixation of the orthopedic apparatus. They are not as aesthetically pleasing and convenient as attachments, but to this day they remain the most common option for attaching clasp dentures.
This is what a prosthesis with clasps looks like
It is worth noting that the best solution to the problem of partial and complete adentia is dental implantation. Only by replacing dental roots with full-fledged titanium analogues can you completely restore the functionality of the dental system and stop atrophic processes in bone tissue. Today, this is the most optimal option for restoring a smile, especially since modern dentists increasingly give preference to one-stage treatment protocols - in the shortest possible time and without the need for bone tissue augmentation.
Read more about implantation with immediate loading in our special material >>>
Clasp dentures: price 2020
The cost of a clasp denture for any jaw depends on many factors: the quality and type of material for the base and crowns, the type of fastening, and the qualifications of the dentist.
The most expensive type are structures on implants: in the complete absence of dentition, at least 4–6 pins are required per jaw.
The cost of a clasp denture with clasps
Clasps are a more budget-friendly method of fastening. The average price may vary by region and clinic:
- One-sided clasp denture for 3–6 teeth – up to 30,000–40,000 rubles.
- Replacement in case of complete absence of teeth – up to 55,000 rubles.
- Complete denture on implants – from 130,000 rubles.
- Bridge structure – 25,000 rubles.
- Clasp prosthesis Quadrotti - from 35,000 rubles.
in the photo there is a Quadrotti clasp prosthesis.
With the additional installation of a metal splint, the cost increases by 5000–7000 rubles.
Read Prosthetics of primary teeth in children: types of children's dentures, indications for prosthetics
Price for clasp dentures with micro-locks
The best dental prosthetic designs with micro-locks are offered by German manufacturers who work only with high-quality metal-ceramics.
The cost of dentures of this type starts from 45,000 rubles for a one-sided model. It increases to 90,000 rubles for a removable jaw from Bredent.
Popular manufacturers of lock mechanisms
Today, there are several leading companies in the production of prosthetic devices and their components. These include the following representatives of the orthopedic products market:
- Bredent is a German company that specializes in the development and production of high-quality sphere-shaped attachments,
- Rhein-83 - a manufacturer from Italy produces vertical and spherical locking fasteners for orthopedic devices,
- Cendres metaux Sa dental - a company from Switzerland produces almost all types of attachments for dentures.
Comfort, aesthetic appearance and ease of care are the key criteria that a modern, high-quality denture must meet. Designs based on attachments have received special recognition from both specialists and patients. Overall, this is a more advanced and improved option that solves many of the problems of removable prosthetics.
- Perevezentsev A.P. Attachments in implantology, 2004.