Key Aspects
The retention period is the final stage of treatment of a dental anomaly, which follows the active treatment and serves to consolidate the achieved movement.
The tendency of teeth to return to their previous position after correction is explained by several reasons, primarily by different rates of bone resorption and formation.
Bone tissue in the area of compression is absorbed faster than new tissue is formed in the area of tension. Because of this, after treatment is completed, the teeth may begin to shift back to their original position.
Another reason for relapse is the fact that transformations in bones occur faster than in soft tissues.
Elastic deformations that persist in periodontal tissues and periodontal collagen fibers force the alveoli, along with the teeth, to partially return to their previous position.
The following factors also contribute to relapse:
- Dysfunction of masticatory and facial muscles.
- Bad habits of children, the ongoing formation and growth of the bones of their dentofacial apparatus.
- Unstable occlusal relationships of the upper and lower teeth (mismatch of cusps and cavities).
- Discrepancy between the sizes of the upper and lower segments of the dental arches in the frontal region.
- Premature contacts of teeth (super contacts).
- Pathological changes in periodontium.
Conditions of stability
In order for the position of the teeth to be stable after movement, the following conditions must be ensured at the end of treatment:
- The first molars are in the 1st class according to Engle.
- Stable multiple fissure-tubercle contacts have been achieved.
- The overlap of the incisors is normal (there is no sagittal fissure).
- The roots of the teeth are parallel (according to x-ray results).
- There are no gaps between teeth and no rotation of individual units.
- The incisor torque is normal (no tilt back and forth).
- The interincisal angle corresponds to the norm (130°-140°).
- The width of the dental arch along the canines is unchanged.
The mechanism of bone tissue restructuring during tooth movement and some nuances.
Visit here to learn more about orthodontic teeth traction.
At this address https://orto-info.ru/ortodonticheskoe-lechenie/osnovnoy-period/distalizatsii-molyarov.html we will consider the apparatus used for distalization of molars.
The importance of consolidating the result
From all of the above, it follows that for a successful, predictable result of correction, the active treatment stage must be followed by a retention period.
The importance of consolidating the achieved results during orthodontic treatment is obvious. In the absence of retention, the likelihood of relapse is very high. According to some studies, it reaches 60%. There was no relapse in only 20% of the analyzed cases.
Even a partial return of teeth to their previous position negates the time and money spent on treatment. To avoid this, the doctor must properly plan and carry out the final phase of treatment, and the patient must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations.
The latter is especially important if a removable device is used, which can be removed by the patient himself.
Strict adherence to the wearing regimen is the main condition for the successful stabilization of teeth after treatment.
Retention period results
You will not see visible results, but your teeth will acquire a stable position. To do this, the structures must be put on a maximum of 24 hours after the braces are removed and the duration of the retention period of orthodontic treatment recommended by the doctor must be observed.
You will need to visit the dental office periodically so that the orthodontist has the opportunity to monitor the progress of the final stage. It is very important to maintain good oral hygiene. Now there are various specialized products designed specifically for the retention period.
Some people wonder if there is an alternative to wearing retainers. Here we can answer unequivocally - there is and cannot be an alternative. Neglecting to wear retention devices is unacceptable, as it can lead to the return of malocclusion and repeated curvature of the teeth.
In this article, we tried to convey to you the importance of the retention period and told you what devices are used to consolidate the results obtained. In conclusion, we present to your attention a video through which you will learn how a permanent retainer looks and is installed.
Designs used
For retention, devices specially designed for this purpose are used (they are called “retainers”), as well as those used for orthodontic treatment (braces, trainers, positioners, activators, bionators).
In general, the term refers to all devices whose main purpose is to stabilize treatment results.
But often it is understood as only one of the most popular types of non-removable retention devices - a wire lingual device. It will be discussed in more detail below.
Retainers
The main criterion for classifying devices is removability and non-removability. Fixed retainers are attached to the lingual surface of the teeth using adhesive or composite.
These include the following designs:
- Wire or fiberglass.
- Lingual on rings.
- Clasp lingual.
Indications for the use of fixed devices:
- consolidation of results after treatment of inclination and crowding of incisors, true diastemas;
- preservation of space after removal of permanent or baby teeth;
- implantation planning.
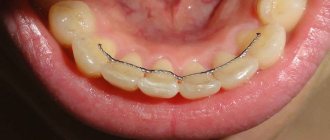
Wire lingual appliance
This most popular type of retainer is a single or twisted wire, bent to the shape of the dentition and secured to the palatolingual surface of the teeth using a composite.
Typically, the device is used to retain anterior teeth. Metal wire can be replaced with fiberglass thread (Ribbond, Fiber Splint). The wire can be bent exactly to the shape of the lingual surface of individual teeth (zigzag) or straight. The second one is used more often.
Wire devices are installed in the lower third of the crown. Possible installation schemes:
- from fang to fang;
- from the 2nd premolar to the 2nd premolar (in the absence of the 1st premolar;
- from the 1st molar to the 1st homolar (in the absence of the 2nd premolar).
When installing a retainer, it is first secured with a ligature to the treatment device. The latter is removed after the composite mass has hardened (in about an hour).
Advantages of wire lingual retainers:
- simplicity, compactness, low price;
- aesthetics (absolutely invisible);
- efficiency, securely fix teeth, prevent not only linear or angular displacement, but also rotation.
Flaws:
- complicate oral hygiene (flosses cannot be used);
- create the possibility of periodontal complications due to tissue compression and blocking the physiological mobility of individual teeth relative to each other, and therefore the maximum time of use is limited to 5 years.
Removable retainers include plates, mouth guards, as well as structures whose main purpose is treatment, and not consolidation of its result.
Mouthguards
Retention trays are structures made of transparent elastic polymer (polycarbonate), installed on the entire dentition and covering each tooth, rigidly fixing its position.
Mouthguards are made using a plaster model of the dentition. To cast the latter, an impression is required. The material for making mouth guards is round or square polymer plates, which, after heating, are used to compress the plaster model in a vacuum former.
If necessary, artificial teeth can be included in the mouthguard to preserve space in the dentition or hooks for attaching intermaxillary traction. For erupting teeth, a section can be cut out.
The doctor determines the wearing mode based on the clinical situation. Sometimes constant wear is indicated, in other cases the mouth guard is worn all night and worn for several hours during the day. The total duration of wearing is also individual and can be several months or more.
Advantages of the cap:
- ease of use (can be removed at any time for eating or caring for teeth);
- good aesthetics due to transparency;
- efficiency and reliability.
Flaws:
- does not prevent tooth rotation;
- There may be a violation of the wearing regime due to removability.
Plates
The devices are removable basic polymer plates with clasps and other elements - a vestibular arch, a tongue rest, pelotes, etc.
Advantages of plates:
- structural reliability and efficiency, especially after expansion of the upper jaw;
- do not interfere with micromovements of teeth and their optimal occlusal relationships;
- can be used in people with parafunctions (bruxism).
Flaws:
- Higher price than mouth guards and fixed wire devices;
- covering the palate (creating discomfort);
- visibility due to wire elements, as well as the risk of injury to the gingival papillae and damage to the enamel.
Types of structures
Parents are often faced with the question of which design to choose to make the child as comfortable as possible. A special classification will help with this, which divides all devices into several groups and characterizes the devices. In addition, the choice of design should be based on the degree of discipline of the child and the aesthetic parameters that are characteristic of one or another design option. All types of retention devices are divided into the following types:
- removable;
- non-removable.
Under the removable ones, special plate structures are raised, which are fixed on the upper or lower jaws using a special plastic base and with clasps. In some situations, clasps are not required. If necessary, special arches or dental drops are added to the design. This allows you to speed up and improve the overall result.
Fixed devices have the form of soldered rings with crowns and soldered beams. In some cases, industrially manufactured retainers can be used. Some specialists can use plate devices in an inactive state for treatment. For example, it is practiced to use orthodontic appliances as retainers, but without further activation.
After treatment of malocclusion pathologies, you can use a special device with a rubber traction, gradually releasing the pressure. It is highly not recommended to use a non-removable mouthguard in such a situation, since this can provoke the development of dental caries, as well as the appearance of new anomalies and other complex disorders.
Estimated timing
The time it takes to consolidate the result depends on a number of factors:
- Type and severity of the anomaly. In particular, treatment of severe crossbite, deep bite, open bite and distal bite should result in long-term retention.
- Structures of rebuilt bone tissue. For example, correction of the temporomandibular joint requires longer retention than correction of dental misalignment.
- The speed of movement of teeth or dentition during treatment. It is believed that the slower it is, the lower the risk of relapse.
- Achieving conditions for stability of teeth and rows. For example, if during the correction of crossbite it was possible to ensure a stable illusion (multiple tubercular-fissure contact), then relapse is unlikely.
- Depending on the patient's age.
The standard ratio of the duration of consolidation of the result to the treatment time is considered to be 2:1. That is, the retention period should be 2 times longer than the treatment time. If a small correction force was used and the movement speed was low, a 1:1 ratio can be used.
There are also supporters of the point of view that when moving slowly and ensuring stable occlusion, retention is not required at all.
In some cases, if it is impossible to achieve stable stabilization, it is necessary to resort to lifelong wearing of devices.
Indications for orthognathic surgery and possible complications.
In this publication we will tell you what you should not eat with braces on your teeth.
Here https://orto-info.ru/ortodonticheskoe-lechenie/podgotovitelnyiy-period/konsultatsiya.html find out how much an orthodontist consultation costs.
Reasons for relapse
In some cases, even treatment with retention ends in relapse. The reason for this may be the following factors:
- Failure of the patient to comply with the doctor's recommendations. Most often this is a violation of the wearing regime of removable devices.
- malfunction not corrected in a timely manner .
- Transition to the retention phase with unfinished treatment. In particular, without achieving stable occlusion.
- Incorrect treatment. For example, relieving crowding without providing adequate space in the row, which causes the teeth to tilt forward.
- Correcting one anomaly (in particular, crowding of the anterior teeth), but ignoring another (for example, violation of the occlusion of the posterior teeth).
Measures to help combat relapse:
- Preservation of the original shape of the mandibular dentition.
- Maintaining intercanine distance.
- Use, if necessary, fibrotomy (dissection of periodontal fibers to prevent relapse of rotation).
- Separation (division) of the lower incisors along the proximal surfaces.
- Grinding of occlusal surfaces of supercontact teeth.
When consolidating the result, it is necessary to take into account the following points and patterns:
- The length of the lower jaw dentition decreases with age.
- Advancement of the lower incisors threatens stability.
- Knowing the position and condition of the roots allows you to choose the optimal method of correction and retention.
If all measures to combat relapse prove futile, the patient is prescribed lifelong retention with non-removable devices.
Expert opinions
Most experts believe that retention is a mandatory phase of treatment, and its duration should be determined depending on the clinical picture.
At the same time, recent studies have led to the conclusion that teeth after certain types of correction are generally characterized by instability due to physiological reasons.
For example, it was found that a recurrence of crowding of lower resources cannot be dealt with by performing a one-time retention. This is due to the fact that with age, the intercanine distance decreases, and as a result, its forced increase in order to prevent crowding is unstable.
In this regard, experts express the opinion that the only solution to the problem in this and similar cases is lifelong retention, that is, wearing the device until the end of your days.
The video provides additional information on the topic of the article.
Time to use retainers
Your orthodontist, after installing a retention device, will observe the behavior of the teeth and make a conclusion about the time of its use. During the first months after braces are removed, you will most likely need to wear them constantly. Later, you will be able to wear the retainer only at night. Over time, the retainer can be worn once or twice a week at night, and after about a year, when the teeth have finally adapted, it can be abandoned altogether.
As a rule, the orthodontist installs a retention device immediately after removing braces. It is important for the patient to understand that this is not a whim of the doctor, but a necessity due to physiological characteristics and many years of experience in correcting malocclusion with braces.