Is it possible or not?
Patients often confuse periodontal disease with periodontitis, so we will consider the features of the process of correcting the bite, taking into account the general features of periodontal tissue diseases. Malocclusion and periodontal pathologies are often interrelated, since the former can trigger the development of the latter and vice versa.
When teeth are crowded and poorly positioned, it is often difficult to clean plaque efficiently even with careful hygiene, as a result of which dental deposits accumulate in hard-to-reach places. Plaque and stone inevitably lead to the development of inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues.
Treating pathology without eliminating the root cause is a waste of time and money, since after the inflammation is removed, it will appear again, since dental plaque will reappear after a while. The first thing to do is contact an orthodontist.
In the stage of exacerbation of the inflammatory process, no one will put braces on you.
In the acute stage of inflammation, no one will put braces on you, since this is a direct contraindication to orthodontic correction. It is necessary to stop the inflammatory process, have your teeth professionally cleaned, and then think about correcting your bite.
Chronic inflammatory process of the periodontium without exacerbations is not an obstacle to the correction of malocclusion. Before starting treatment, the oral cavity must be prepared. Decisions are made on an individual basis, but in most cases the algorithm of actions is something like this:
- supportive therapeutic treatment,
- professional oral hygiene,
- installation of braces.
Diagnosis of periodontitis
Periodontium is a complex of tissues surrounding the tooth and closely interconnected. This complex includes the gums, tooth root cement, periodontium - the ligaments that hold the tooth in the socket, the alveolar bone - the tooth socket. Dental periodontitis is an inflammatory process of the periodontium, that is, all components of the above complex are involved in the inflammation process.
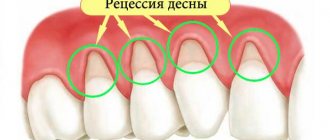
The cause of periodontitis is infection. The accumulation of harmful bacteria causes inflammation of the gums around the tooth and suppresses the immunity of the tissues surrounding the tooth. The development of periodontitis is facilitated by poor hygiene (a lot of plaque on the teeth), malocclusion (disruption of the normal load on the teeth, accumulation of plaque due to crowding of teeth), lack of teeth (the gums in the place of the missing tooth recede, exposing the necks of neighboring teeth). Untreated periodontitis can cause the loss of all teeth.
Treatment of periodontitis should be comprehensive and include many different measures that are aimed at eliminating the cause of periodontitis, restoring the normal functioning of all periodontal elements, as well as preventing the return of the disease. The periodontist must conduct a quality examination to accurately determine the extent of the lesion and prescribe the correct treatment. This is done by examining, measuring the depth of periodontal pockets, and studying the condition of the jaw bones using dental x-rays.
To reliably study the bone tissue around each tooth, as well as confirm the diagnosis of periodontitis, a dental computed tomography (CT) is performed at the Family Dentistry, which is used to create panoramic reconstructions for the upper and lower jaw. The great advantage of this method is the absence of overlap of the lateral surfaces of the teeth and the ability to study the level of the bone both from the outside and from the inside, which is absolutely excluded when performing a traditional panoramic photograph of the teeth.
In this case, periodontist Nogina A.Yu. Upon examination, she revealed swelling of the gums and their blueness, which indicated a disruption of normal blood circulation in the gums and the presence of stagnant processes - these are symptoms of periodontitis. The depth of periodontal pockets reached 8 mm, which corresponds to severe periodontitis.
DETAILS: Lincomycin - instructions for use, price 2020, in dentistry
Important points in occlusion correction for periodontal disease and periodontitis
Bite correction for periodontal tissue pathologies has many nuances :
- the type of malocclusion is not considered separately, but taking into account its relationship with the stage of gum disease,
- the force of pressure of braces on the teeth is reduced, while the retention period is increased (time after completion of the correction, consolidation of the results),
- in the first place is careful hygiene, this is the main condition for a successful treatment result.
Subject to these conditions, bite correction for periodontal diseases will not only straighten the teeth, but also improve the condition of the oral tissues and stop the progression of the disease.
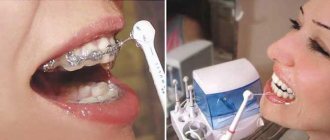
Braces make good hygiene more difficult.
Is it possible to have prosthetic teeth with periodontal disease, which prostheses and prosthetic methods are better?
Periodontal disease is considered one of the most serious dental diseases.
The pathology is characterized by destruction of gum tissue, atrophy of the jaw bone, and tooth loss. Periodontal disease is a complicated form of periodontitis, so it is important to begin treatment immediately after the first symptoms appear. about the treatment of periodontal disease, a review of 16 effective methods
Most orthopedic dentists warn patients that severe gum disease is a contraindication to dentures. Restorative procedures are not performed during exacerbation of periodontal disease.
If adverse symptoms do not appear for a long time, any type of prosthesis can be installed. But it must be taken into account that the service life of installed dental structures may decrease due to the displacement of healthy teeth and progressive atrophy of bone and gum tissue.
Before performing dental prosthetics for periodontal disease, the dentist evaluates the condition of the oral cavity according to several criteria.
Periodontal disease causes difficulties in prosthetics due to tooth mobility
Loose teeth
To hold a clasp or bridge prosthesis, the supporting elements of the dentition must:
- receive nutrition from the nerve;
- securely held by ligaments in the hole
- be healthy (no cavities).
Attaching bridges to shaky teeth is strictly prohibited.
Tissue atrophy
If, despite periodontal disease, the living teeth are securely held in the socket, an implant can be installed. But exposure of the neck of healthy elements of the dentition will be an indication for a gum augmentation procedure.
The orthopedic dentist will also request an orthopantomogram. If the x-ray shows signs of jaw bone atrophy, then bone grafting is performed before prosthetics.
Another difficulty with prosthetics arises from gum atrophy
Modern technologies make it possible to give a positive answer to the question “is it possible to have prosthetic teeth with periodontal disease?” But it is necessary to take a responsible approach to choosing the optimal prosthetic option. You also need to follow all the recommendations of the periodontist regarding gum care.
If a patient with active periodontal disease has lost all his teeth, but wants to restore chewing function and an attractive aesthetic appearance of his smile, it is recommended to install dentures. The advantage of this type of prosthesis is that it can be removed at any time and undergo the required therapeutic procedures.
You cannot leave dentures in your mouth overnight: plaque and bacteria will begin to accumulate under the artificial structure. Eventually, gum disease will progress.
This is what a splinting prosthesis looks like
Bridges
If the patient is missing a front tooth, the doctor will recommend installing a bridge. But it must be taken into account that the supporting elements must be stable. If an inflammatory process develops after prosthetics, the dentist will be able to remove the prosthesis and carry out the necessary treatment.
If you ignore the periodontist's recommendations, the inflamed gum tissue may begin to rot. Eventually, the periodontal ligaments will break down, leading to loss of supporting teeth and the prosthesis itself.
The dental structure can be installed directly for therapeutic purposes. This type of prosthesis not only restores the integrity of the dentition, but also holds living incisors and molars in place. The design can be installed on patients who are missing four consecutive teeth.
Quadrotti prostheses
The structure is made of biocompatible plastic and can be installed in patients with metal allergies or during periodontal disease treatment. The prosthesis is easily removable and looks more aesthetically pleasing than a classic false jaw.
Splinting dentures fix mobile teeth, preventing them from loosening further
Veneers
Microdental dentures are not recommended for gum disease. To install an artificial onlay, the dentist will have to grind off a layer of enamel. Without careful care and treatment, the weakened tooth will fall out along with the veneer.
Considering the low cost, microprosthetics can be performed to restore the aesthetic appearance of the dentition.
Implantation
Considering the high cost of the implant, installation is recommended only after complete cure of periodontal disease. Otherwise, the risk of artificial pin rejection increases. If a chronic disease has caused the jaw bone to atrophy, bone grafting and gum augmentation are first performed.
During the procedures, the patient can have an inexpensive plastic removable denture installed. Once the titanium post is secured in the jawbone, the dental technician will create a metal-ceramic crown. The orthopedic dentist will attach the onlay with special cement. The implant can become the basis for securing a clasp or bridge prosthesis.
We suggest you read: When to pull arsenic out of a tooth
Before installing implants, bone tissue is augmented
According to reviews, dentures installed by patients with periodontal disease last 10-15 years. The service life of implants is 20-30 years. The main thing is to pay enough attention to oral care. Artificial materials accumulate plaque in the same way as natural enamel. Required daily:
- brush your teeth with an individually selected brush and toothpaste;
- use mouthwash after every meal;
- Visit a hygienist once a year.
Those who have removable dentures are recommended to purchase special cleaning tablets. Dental structures should be removed at night and left in the solution. It is also necessary to take the denture to a dental technician for preventive maintenance at least once a year.
Even if the symptoms of periodontal disease have not appeared for a long time, it is recommended to come for preventive consultations with a periodontist annually. It is allowed to use special rinses to strengthen the gums. But you need to make sure that the product does not stain the artificial insert.
Treatment of periodontitis: review of modern methods
Periodontal disease is no longer an absolute indication for prosthetics. Professionals will help you choose the optimal method for restoring the integrity of your teeth.
Periodontal disease is one of the most unpleasant contraindications to many types of dental restoration. This is a disease that causes damage to periodontal tissue and atrophy of the alveolar processes, which significantly complicates the implementation of almost all types of prosthetics. Read about how prosthetics are performed for periodontal disease in our article.
Before describing the types of prosthetics for periodontal disease, you need to briefly talk about the disease itself. Periodontal disease is quite rare (on average, 1 - 8% of patients), and many people confuse its symptoms with periodontitis. These two diseases do have common features, but periodontitis is distinguished by inflammation of the soft tissues, exposure of gum pockets and purulent discharge.
Periodontal disease is not an inflammatory disease, but it leads to a decrease in bone tissue and atrophy of the alveolar processes, and in the absence of surgical treatment, to tooth loss. The causes of periodontal disease are not completely clear today.
In the later stages of periodontal disease (especially the fourth - the most complex) in most cases, teeth are removed and subsequently replaced with a prosthesis.
Before starting dental restoration, it is necessary to carry out comprehensive treatment of periodontal disease, otherwise the orthopedic stage will not make sense.
- Zirconium crowns – placed on ground natural teeth
- Bridges – fixation occurs on abutment teeth or special crowns
- Removable dentures - the prosthesis is fixed using clasps and occlusal pads
- Implantation – installation of prostheses supported by implants
To restore teeth with periodontal disease, it is impossible to use metal-ceramic and porcelain crowns. For minor forms of periodontal disease in remission, zirconium crowns are used, which prevent the accumulation of bacteria and the development of the disease. Often, zirconium crowns are used to replace front teeth with periodontal disease.
They are rarely used (especially in severe forms of the disease), since there is a lot of pressure on the supporting teeth and bone tissue. Often, the use of a fixed prosthesis is accompanied by splinting of the dentition for greater stability of the structure.
In the presence of periodontal disease, the removable structure is made in such a way that the base of the prosthesis has minimal impact on the soft tissues and mucous membranes.
The most common option is a splinting clasp prosthesis, which has multi-link clasps.
This design performs two functions at once: it restores lost teeth and provides a tighter fixation of natural teeth affected by periodontal disease.
Implantation for periodontal disease has a number of nuances. As a rule, all diseased teeth are removed, after which the treatment method is agreed upon. Often the patient requires bone augmentation and soft tissue grafting. Specialists usually perform one-stage or basal implantation.
If you have this disease, you cannot say with 100% certainty which prostheses are better: everything is very individual and depends on the specific clinical case. In terms of functionality and aesthetics, implant-supported dentures are considered the best, however, with periodontal disease, the risk of implant rejection is considered quite high, especially for basal implantation, which in itself is a traumatic and rather risky technique.
If natural teeth are preserved, the optimal solution would be to install a removable denture, which leaves the edges of the gums open. This reduces the risk of inflammation and provides the doctor with good access to the area affected by periodontal disease.
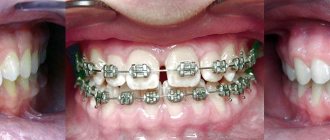
Why do gum diseases develop while wearing braces?
Even if the patient has never known problems with gums, during the period of orthodontic treatment the risk of their occurrence increases, and there are reasons :
- installing braces complicates the process of brushing teeth; with poor hygiene, plaque accumulates in hard-to-reach places - the main cause of gingivitis,
- If the inflammation that has begun is left unattended, gingivitis will gradually turn into periodontitis - the inflammatory process will penetrate deeper into the ligamentous apparatus that holds the tooth. This is accompanied by bleeding, an unpleasant odor, the formation of periodontal pockets, and the accumulation of pus in them.
Periodontal disease and braces are an ambiguous combination, since moving already mobile teeth is a questionable activity, and it is impossible to predict the result. This is a non-inflammatory pathology that has nothing to do with gingivitis and periodontitis. The disease develops slowly against the background of impaired nutrition of tissue cells, as a result of which the gums recede and the teeth become mobile.
Under no circumstances should you begin treatment knowing that you have periodontal disease, periodontitis, or gingivitis. If the doctor and the patient decide to correct the bite, the pathology is first transferred to the stage of stable remission, and only then orthodontic correction begins.
The brace system will be installed after the disease has gone into remission.
Prevention of gum disease with braces installed
Periodontal disease and braces do not have to go hand in hand. There are a number of preventive measures through which both periodontitis and periodontal disease can be prevented.
- High-quality self-cleaning of teeth. It is done not only in the morning and evening, but after every meal. The use of an irrigator is recommended.
- Professional cleaning of the oral cavity. The most common cause of periodontitis and periodontal disease is tartar. Only ultrasonic cleaning will help remove such deposits, which must be carried out once or twice a year as necessary.
- Treatment of the resulting inflammation. If an inflammatory process develops in the mouth while wearing braces, it is better to get rid of it by using antiseptic solutions or taking antibiotics. The dose and duration of use are determined by the doctor.
- Physiotherapy. Laser or electrophoresis helps overcome inflammation.
- Surgical intervention. If the gum is severely detached from the tooth, and the tooth itself begins to stagger, then surgical treatment may be used. The orthodontic structure has to be removed for a while. The gum is incised and the tooth root is cleaned of all deposits that have formed on it.
Prevention of gum inflammation while wearing braces
To ensure that wearing braces is beneficial and does not cause problems, follow the following recommendations :
- After installing braces, the dentist will recommend that you purchase special devices to care for the structure:
- several types of brushes,
- dental floss intended for the care of braces,
- special rinses,
- an irrigator that allows not only to wash away plaque from hard-to-reach areas, but also to massage the gums,
- toothpastes to prevent bleeding gums.
- Be sure to visit your dentist for professional teeth cleaning.
- It would be advisable to take vitamin complexes to strengthen the gums (on the recommendation of a specialist).
The main condition for successful correction is ideal oral hygiene.
Braces for periodontal tissue diseases are installed after a thorough diagnosis, transfer of the pathology to the stage of stable remission and provided that the patient strictly follows the specialist’s recommendations.
The result of periodontitis treatment
Competent treatment of periodontitis takes from 5 to 14 days and consists of the following procedures:
- X-ray diagnostics - allows you to determine the level of bone loss and the size of interdental spaces due to the lowering of the gingival margin.
- Removing microbial plaque - in 99% of cases, the cause of inflammation is bacterial deposits (sub- and supragingival), so treatment begins with eliminating the root cause.
- Local anti-inflammatory therapy - the use of antiseptics, antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - Metrogyl denta, Ortofen, etc.
- Physiotherapeutic treatment of periodontitis - electrophoresis, darsonvalization and other physical methods that reduce the inflammatory reaction.
- General therapy - strengthening the immune system (vitamin therapy), taking antihistamines - Suprastin, Tavegil.
- Home care - use of toothpastes with enzymes and natural plant ingredients - Lacalut Fitoformula, Parodontol Active.
You can get rid of periodontitis once and for all only if you follow all the doctor’s recommendations. Self-medication is the cause of constant relapses.
Vector therapy
A universal method that is prescribed both at the initial stage of inflammation and for chronic periodontitis. It is carried out using the Vector ultrasound machine. A special scaler attachment creates ultrasonic vibrations that cleanse the gum pockets of toxins and pathogenic bacteria. As a result, the gums become denser, bleeding and suppuration stop.
One session of Vector Therapy is enough; it is recommended to repeat the procedure after 6 months.
Painless and most effective procedure. The laser beam completely removes tartar, pus and soft plaque from the periodontal space. The biofilm where colonies of pathogenic microorganisms live is destroyed. In addition, the laser polishes the enamel, and fewer bacteria accumulate on the smooth surface.
A positive result is achieved after the first procedure
A mandatory component for chronic generalized periodontitis (CGP). The doctor prescribes applications of anti-inflammatory ointments and gels (Cholisal, Kamistat, Asepta, etc.), taking antibacterial drugs (Levomycetin, Levomekol, Summamed).
Special collagen films are also used, which promote the regeneration of periodontal tissue. In the most advanced cases, an antibiotic injection is given into the gums.
Surgical intervention is indicated for severe periodontitis, when conservative methods have proven ineffective. The following operations are used:
- curettage – scraping of deep subgingival deposits with hand tools (hooks, excavators, curettes), carried out with or without opening the gums;
- flap surgery - a small incision is made near the edge of the gum, then the doctor moves the flap, removes the infected granulation tissue under the gum and eliminates periodontal pockets. After this, the wound is sutured;
- gingivotomy - removal of the inflamed and overgrown edge of the gum or gingival papilla. It is used to eliminate the source of infection, as well as for cosmetic purposes.
DETAILS: Correction of bite in dogs Ukraine
Surgical methods are painless as operations are performed under local anesthesia.
This is the final stage for those patients who are missing some teeth. The goal of orthopedic treatment is to restore chewing function, relieve increased mechanical stress in certain areas of the periodontium and prevent displacement of the remaining teeth. For this purpose, crowns, bridges, clasp or plate nylon prostheses are used.