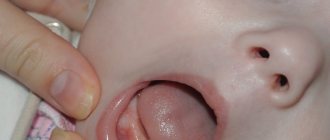
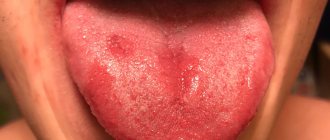
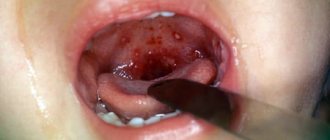
Warts most often form on the surface of the skin, but it also happens that they affect the tongue. Another name for growths is papillomas. Both on the skin and on the tongue, warts (a photo of the neoplasm is presented below) appear against the background of the development of an infectious disease in the body. Papillomas can occur in people of any gender and age.
Types of warts
The tongue is an organ whose surface is covered with papillae. At the initial stage of growth, papillomas can be confused with them. Over time, they form into new formations that are clearly felt and visualized with the naked eye.
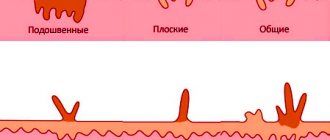
Warts on the tongue (photo below) are divided into 2 types:
- Flat. Such neoplasms have a round shape. Their contour is clearly defined, and it has a more pronounced shade than the surface of the skin. These warts on or under the tongue are flat in shape. They protrude only slightly above the surface of the skin. In the process of eating food, they are not damaged or only slightly injured. However, flat warts on the tongue require treatment in any case. In the presence of multiple tumors, their surgical removal is indicated.
- Pointed. If the warts under the tongue on its root or surface have a similar shape, it is customary to talk about condylomas. Such neoplasms protrude strongly above the skin. They are attached to the tongue with a light pink stalk. Their upper part looks like a papilla. When condylomas grow, they look like cauliflower inflorescences. Most often, such warts are localized on the root of the tongue (a photo of the affected organ is presented below) and on its lateral part. Less commonly, condylomas appear on the root near the throat. Such growths are constantly injured, and therefore there is a risk of their degeneration into a tumor. They significantly impair the quality of life, making it difficult to eat and talk.
You should consult a doctor if even one wart appears on the tongue. This is due to the fact that growths are not always benign.
Types of benign tumors of the tongue
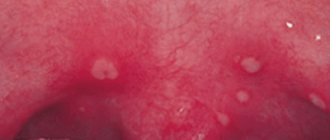
Papillomas on the tongue are multiple or single formations of pale pink color, round or elongated, rarely growing to large sizes
The clinical course of a tongue tumor and the characteristics of its growth are associated mainly with the type of tissue from which it originates. The presence of epithelial, muscle, glandular, and adipose tissue in the tongue structure, as well as the possible entry into the tongue tissue during embryogenesis of the rudiments of other tissue structures (bone, cartilage, thyroid tissue) determine a wide variety of clinical forms of tongue tumors. Most often dentistry encounters vascular tumors of the tongue (angiomas). The second place in prevalence is occupied by papillomas, the third place by fibroids of the tongue.
Papilloma . This tumor of the tongue grows from the stratified squamous epithelium of its mucosa. Most often it occurs on the back and tip of the tongue. Papillomas are multiple or single formations of pale pink color, round or elongated, rarely growing to large sizes. The appearance of keratosis on the surface of the papilloma, as a rule, indicates its malignant degeneration. In some cases, spontaneous involution of papilloma was observed.
Adenoma . Formed from the glands of the tongue mucosa. Cystoadenomas are more often observed on the tip of the tongue. In the area of the root of the tongue, polyps from the heterotopic gastric mucosa may appear.
Botriomyxoma . The tongue tumor is flat or spherical in shape, in rare cases divided into several lobules. Initially it is red in color, but over time it becomes brown. In its growth it can reach the size of a walnut. The surface of botryomyxoma can be smooth or coarse-grained, often covered with crusts. Factors that provoke the formation of this type of tongue tumor include trauma and tongue fissure.
Fibroma . A round tumor of the tongue of elastic consistency, growing from connective tissue cells. Fibroids can grow on a stalk. Its color often does not differ from the color of the mucous membrane, in other cases it has a yellowish or whitish tint.
Retention cyst . Most often located on the lower surface of the tongue in the area of its tip. It has a multiple character. This tumor of the tongue develops from the nunnia glands located in its superficial muscle layer.
Lipoma . A tumor of the tongue developing in the submucosal layer with a lobular structure and a soft-elastic consistency. It is most common on the undersurface at the back of the tongue. Lipoma is characterized by slow growth and painless course.
Myoma . A tumor of the tongue that occurs when the cells of its muscles proliferate. It often has a size of up to 1 cm and a dense consistency, but can grow to a significant size. Covered with mucous membrane. It is usually localized on the upper surface of the tongue. In some cases, small papillary outgrowths are observed on the surface of the fibroid.
Neurofibroma . They develop from the tissues of the nerve branches passing through the tongue, most often in the posterior half of the tongue. This type of tongue tumor occurs in rare cases and is characterized by slow growth. May be accompanied by various pain sensations.
Hemangioma . Tumor of the tongue, originating from the tissues of blood vessels. Associated with a violation of embryogenesis, more often observed in girls. This tongue tumor is usually detected at birth or in early childhood. Capillary hemangioma appears as red spots of various sizes and shapes that do not rise above the surface of the tongue. The spot turns pale when pressed.
Cavernous hemangioma is a tumor of the tongue with a bluish-purple color and soft consistency. Often rises above the surrounding mucosa. Characterized by deep germination into the underlying tissues. Pressure on the tumor leads to a decrease in its size, which quickly recovers when the pressure is removed. Vascular tumors of the tongue may be accompanied by bleeding, most often caused by injury.
Lymphangioma . It grows from the walls of the lymphatic vessels of the tongue and appears in the first years of a child’s life. It can cause diffuse damage to the tongue, leading to its significant enlargement. Local lesions are represented by growths of a warty structure with vesicular elements and are most often located along the upper surface of the root or tip of the tongue. When injured by food or teeth, this swelling of the tongue often becomes inflamed.
Struma of the tongue . A rare tumor of the tongue that arises from cells of thyroid tissue that enter the tongue as a result of impaired embryonic differentiation. It is a node localized at the root of the tongue with a diameter of up to 3 cm.
Causes
If warts appear on the tongue, this indicates the activity of papillomavirus in the human body. Normally, it is present in every second inhabitant of the planet. In this case, the virus should ideally be in a dormant form. Under the influence of various unfavorable factors, against the background of which there is a significant weakening of the body’s defenses, it becomes more active. Then the papillomavirus begins to multiply rapidly, affecting the upper layers of the skin. It is against the background of its active life that pinkish or white warts form on the tongue or other parts of the body.
The following categories of people are at risk:
- The body of which experiences a pronounced deficiency of vitamins, macro- and microelements.
- Suffering from chronic pathologies. The risk of papillomavirus becoming active forms increases with exacerbations.
- Have undergone surgery in the recent past.
- Those suffering from HIV.
- In the recent past, they have been ill with pathologies of an infectious nature.
- Regularly experiencing stress.
- Smokers.
- Regular abuse of alcoholic beverages.
- Taking hormonal medications for a long time.
In addition, the virus can become active during menopause, pregnancy and breastfeeding.
In a dormant state, the pathogen can remain in the body for up to 5 years. At the same time, its carriage is not dangerous for others. Infection of other people can only occur if the virus is active and multiplying rapidly.
Polyp on the tongue - what is it?
A tongue polyp is a dense, tuberous neoplasm on a wide stroma. The polypous lesion rarely has a long stalk. Such growths can occur under the tongue. Given the high risks of injury under the influence of temperature, food and mechanical factors, the polyp is unstable and prone to infection and bleeding.
The main tumors are adipose tissue, lymphatic and blood vessels, muscle fibers, and epithelial cells. Thus, polyps constitute a whole group of benign tumors of the tongue, including tongue papillomas, retention cysts, fibromas, and botryomycomas.
Pathological neoplasms are rarely encountered in dental practice. Against the background of polypous lesions of the tongue, combined pathologies are often diagnosed in the form of anomalies of the osseous-facial bones, cartilaginous apparatus and tongue.
Routes of infection
The pathogen is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person. But this requires close contact with an infected person.
Routes of infection:
- Sexual. The virus is transmitted even through oral sex; the risk of infection is especially high if the partner already has warts on the tongue.
- Domestic. You can become infected by using personal hygiene items of a sick person.
- While kissing.
- In the process of childbirth. In such cases, the virus is transmitted from mother to child. If a woman does not treat the infection during pregnancy, after birth the baby will soon notice warts on the root of the tongue and on the cheeks.
In addition, self-infection cannot be ruled out. It occurs when the integrity of the skin of the lips, cheeks or tongue is damaged. In such cases, the virus begins to spread to healthy tissue.
According to statistics, the pathogen is most often transmitted through sexual contact. However, it is able to maintain vital functions for a long time, especially in warm rooms with high humidity.
Why can shoots appear under the tongue?
The formation of a growth on the tongue in humans is often associated with infection with the papilloma virus.
Infection occurs in two ways:
Warts or papillomas do not form immediately, so it is not possible to determine the culprit of the infection. HPV “dormants” in the body for months or years. When favorable circumstances occur, the strain becomes active and releases pathological elements onto the skin or mucous membranes.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with the Taste of blood in the mouth, causes and solutions
If growths appear under the tongue, this may indicate poor hygiene. A similar problem is faced by parents of small children who taste toys and surrounding objects.
A number of other factors contribute:
- frequent stress;
- deficiency of nutrients;
- overwork;
- microtraumas on the tongue;
- oral contact with a carrier of the virus.
Natural movements of the tongue contribute to the spread of infection in the oropharynx. After additional infection, warts may appear on the lips or cheeks.
Associated symptoms
As mentioned above, the cause of warts on the tongue is the human papillomavirus. As the latter progresses, the number of neoplasms increases.
In addition, patients complain of the following conditions:
- In the process of swallowing food, severe discomfort is felt.
- The presence of painful sensations. They appear when warts become damaged or come off the tongue completely.
- Bleeding. They also occur when a wart is torn off or damaged.
- Burning.
- Voice change.
- Disruption of the digestive system.
- In rare cases, breathing becomes difficult.
Regular injury to papillomas and condylomas poses a danger to human health. This is due to the fact that frequent violation of their integrity can lead to the development of a malignant process.
Symptoms of benign tumors of the tongue
A tumor of the tongue that has reached a significant size in its growth can cause changes in speech and difficulty chewing and swallowing food.
A small tumor of the tongue does not cause any discomfort in the patient and for this reason may remain invisible. As the tumor grows, the patient experiences a sensation of a foreign body on the tongue. Most often, tongue tumors are painless formations. Pain may occur when the tumor is compressed and injured during chewing or talking. A tumor of the tongue that has reached a significant size in its growth can cause changes in speech and difficulty chewing and swallowing food.
A sharp change in the characteristics of a tongue tumor (color, consistency, surface), the appearance of rapid growth or germination into neighboring tissues indicate malignancy of the tumor with the development of tongue cancer. It is also possible that an inflammatory process may occur, usually resulting from injury to a tumor of the tongue. Inflammation is manifested by typical symptoms: swelling, pain and redness of the formation. In some cases, inflammation of the tongue tumor is accompanied by necrotic changes.
Diagnostics
If warts appear under the tongue, on the side or on its surface, you should consult a dermatovenerologist. Many people mistakenly come to an otolaryngologist or dentist, which is incorrect, since these specialists do not treat papillomavirus.
The dermatovenerologist will conduct a primary diagnosis, which consists of interviewing and examining the patient. After this, he will schedule a comprehensive examination, including:
- Blood analysis.
- Bacterial culture.
Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor will draw up a treatment regimen for warts on the tongue. The cause of the disease is a virus, and therefore a specialist may additionally refer you for a consultation with an infectious disease specialist.
Diagnosis and treatment of papillomatosis in the mouth
The diagnosis is based on visual examination data. For small tumors, additional studies are not carried out. Large and bleeding growths on the side of the tongue and in any part of it require taking a biopsy and transferring the material for examination of tumor tissue.
To eliminate harmful HPV, specialists prescribe antiviral medications. Patients apply them externally and use them internally. The progress of treatment should be supported by constant sanitation of the mouth. If positive dynamics cannot be achieved from drug therapy, the doctor may suggest more aggressive measures to influence the strain.
If the wart does not create inconvenience and does not grow, symptomatic treatment with constant monitoring of the patient’s condition is sufficient. To relieve a burning sensation in the mouth caused by papilloma. the use of an anesthetic is indicated. In advanced cases, the patient is offered surgical intervention.
We suggest you read What to do to get rid of toothache
An operation performed to remove a growth on a child’s tongue can be dangerous for the child’s body. Since the manipulation is performed under local anesthesia, respiratory arrest is possible. In connection with this treatment of a small patient, only experienced, qualified doctors should be involved.
Drug treatment
It is important to understand that any drugs are effective only at the early stage of the disease. As a rule, doctors prescribe the following remedies to eliminate warts on the tongue:
- "Isoprinosine." This drug is an immunomodulator. Its active components help enhance the production of interferon. In addition, they suppress foci of pathology. According to the instructions, Isoprinosine should be taken twice a day for 14 days. By decision of the doctor, this period can be increased to 1 month. Treatment with this drug is suitable for both adults and children over 4 years of age.
- "Interferon". This is an antiviral agent. Its active substance also helps strengthen the body's defenses, thereby increasing its resistance to pathogenic microorganisms. The duration of treatment of warts with Interferon is up to 2 months. It can be used even in infants.
- "Complivit." This is a multivitamin complex designed to strengthen the body's defenses. You need to take 1 tablet per day. Duration of treatment - 1 month. On the pharmaceutical market, Complivit is sold for different ages.
- "Acyclovir". An antiviral drug that helps destroy pathogens. According to the instructions, the product must be taken 1 tablet every 4 hours (the night period is not taken into account). The duration of treatment is 5 days.
- "Panavir". Available in the form of ointment and solution for injection. This is a modern antiviral and immunomodulatory drug. Its use is contraindicated for pregnant and breastfeeding women, as well as persons under 18 years of age.
This treatment regimen can be changed or expanded by your doctor. The specialist always prescribes medications taking into account the individual health characteristics of the patient.
What treatment do doctors prescribe?
Depending on the diagnosis after examination or laboratory tests, the doctor will prescribe treatment:
- orasept, hepilor, angilex, miramistin, givalex, rotokan, strepsils, chlorhexidine, furatsilin, chlorophyllipt in order to kill harmful microorganisms with antibiotics and also clean the oral cavity with antiseptics
- macrolides, penicillins, tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones, epithromycins to kill bacteria
- Zovirax ointments, acyclovir, herpevir in the presence of herpes infection
- lornoxicam, voltaren, cholisal, ketoprofen to get rid of irritation
- kamistad, strepsils “Plus”, lidocaine to relieve pain;
- immunostimulants Tamilad, methyluracil, pyrogenal, as well as complex vitamin preparations to improve the body’s immune response
- pyrazinamide, rifampicin, isoniazid, streptomycin for tuberculosis
Grouping all the above drugs, we can distinguish the following types of drugs used:
- Antibiotics.
- Antiviral.
- Immunostimulating.
- Antituberculosis.
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Anesthetics.
- Antiseptics.
Depending on the complexity and nature of detection on the tongue, as well as on the presence of concomitant diseases, the doctor prescribes a complex for treatment.
Methods for removing papillomas
In many cases, drug treatment for warts on the tongue does not lead to the desired result. If the tumor is benign, it can be removed in one of the following ways:
- Laser. The method does not require preparation. The average duration of the procedure is 20 minutes. First, the doctor treats the tongue with an anesthetic, then burns out the papillomas. The final step is to use an antiseptic solution. There is no bleeding during the wart removal process. The method is considered safe and extremely effective. After laser removal of papillomas, the virus does not spread to healthy tissue.
- Cryodestruction. The method requires preparation: before the procedure, it is necessary to cure all existing pathologies of an infectious nature. Algorithm for removing warts: the doctor treats the tongue with an antiseptic solution, and then treats the neoplasm with liquid nitrogen. Then the procedure is repeated several times. Anesthesia is not required for this method.
- Electrocoagulation. Before the procedure, it is also necessary to cure all infectious diseases. First, the doctor heats the device to the required temperature, then treats the tongue with an anesthetic. After this, he touches the warts with an electrode. This method is not advanced. Currently, laser removal or cauterization with liquid nitrogen is increasingly preferred.
In some cases, traditional surgical excision of warts is performed. It is performed under local anesthesia. After administering the anesthetic, the surgeon excises the tumor using a scalpel. The wound is then disinfected and stitches are placed on it. The latter are removed after 2 weeks.
Traditional methods
It is important to understand that the use of unconventional methods does not eliminate the need to seek qualified medical help. This is due to the fact that warts on the tongue are constantly exposed and regularly injured, due to which a benign process can turn into a malignant one. The use of traditional methods is permissible, but only at an early stage of development of papillomas and after permission from the attending physician.
The most effective recipes:
- Take 1 chicken egg and separate the white and yolk from each other. The first one must be thoroughly beaten. After this, you need to lubricate the affected area of the tongue with protein foam. The procedure can be performed every 20 minutes. As a rule, warts begin to dry out and decrease in size. After about 2 weeks they disappear completely.
- Take 20-30 g of chestnut and pour 200 ml of boiling water over it. Let the product sit for 6 hours. After this, it must be consumed orally daily. In this case, the product must be held in the mouth for several seconds before each sip. The duration of treatment is 14 days.
- Soak a piece of sterile napkin or cotton wool in castor oil and apply to the wart. Try to keep the product on your tongue for at least a few minutes. When the cotton wool or napkin is completely saturated with saliva, remove the swab. The duration of treatment is 7 days.
- Mix strawberry, hawthorn and St. John's wort leaves in equal quantities. Then the grass must be poured with boiling water. Let it brew for half an hour. It is necessary to use the product before each meal in the amount of 3 tbsp. l. The duration of treatment is 7 days.
Regular use of these recipes will help cope with early manifestations of papillomavirus on the tongue. When the growths are multiple and large, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Neoplasm Clinic
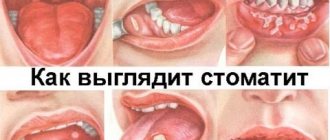
Sometimes papillomatosis can be confused with other oral diseases. Most often, with stomatitis.
There is a certain set of signs to suspect a wart:
- discomfort when swallowing;
- bulge on the mucous membrane of the tongue;
- bleeding due to traumatization of the growth;
- can increase in number and volume , merging with each other;
- an increase in the size of several papillae on the mucous membrane of the tongue.
Note! Any neoplasm in the oral cavity that does not go away within 2 weeks requires immediate medical attention.
Prevention
In order to prevent infection and prevent the virus from activating, it is necessary to regularly follow some recommendations:
- Observe hygiene rules. Teeth and tongue should be cleaned of food debris daily.
- Avoid getting into stressful situations. It has been proven that prolonged stay in such a state increases the risk of the virus transitioning from a latent form to an active one.
- Regularly carry out activities aimed at strengthening the body's defenses. First of all, you need to give up bad habits and follow the principles of proper nutrition.
- Treat all identified diseases, especially infectious ones, in a timely manner.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- Properly organize a regime of active activity and rest. It is important to remember that the duration of night sleep should not be less than 8 hours. In addition, short breaks should also be organized during the day.
If a sexual partner has been diagnosed with human papillomavirus, treatment must also be mandatory. In addition, during therapy, sexual contact with an infected person must be excluded.