Why do ulcers appear on the gums and how are they treated?
When painful ulcers appear on the oral mucosa, in most cases this indicates the presence of pathological processes in the body. Patients who experience such unpleasant phenomena complain of severe discomfort, which is especially acute when eating and performing hygiene procedures. There are many varieties of such formations and no fewer reasons that can provoke the problem. Read further in this article about what this can mean if ulcers appear on the gums, as well as how to cure the pathology.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures aimed at eliminating the pathology are selected based on the factors causing the anomaly. At the initial stage, the small patient is prescribed antibiotics, antiallergic drugs, drugs that relieve inflammation, swelling, and bleeding. At the same time, the wounds are treated with antiseptic agents. Ultrasound therapy is also performed.
A wound on a baby's gum requires constant treatment and rinsing with disinfecting solutions. Since he himself does not yet know how to do this, parents should make lotions with a weak saline solution, lubricate with Metrogyl gel, Cholisal, Kamistad, Kalgel.
Chlorhexidine solution, Lugol spray, Ingalipt are also used to rinse the gums. These medications qualitatively eliminate the formation of bacteria and fungal infections. If the problem is caused by an infectious disease, Remantadine, Acyclovir, Interferon are prescribed. Zavirax ointment and Megasin also help well for healing wounds.
You should not ignore the occurrence of wounds on the gum tissue in a child. It is advisable to immediately contact a specialist so that the infection process does not progress too deeply. The doctor will determine the cause of the pathology and prescribe adequate treatment.
What types of ulcers are there on the gums?
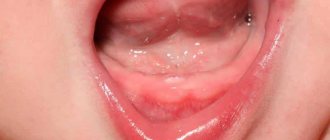
The appearance of even a small ulcer on the mucous membrane will immediately make itself felt. Anyone who has already encountered a similar problem knows how much trouble this symptom can cause. Among the accompanying manifestations, the following problems are usually identified:
- severe discomfort, especially when eating or talking,
- swelling of the mucous membrane in the affected area,
- painful sensations due to mechanical irritation,
- formation of small cracks on the gums,
- general loss of strength and weakness of the body.
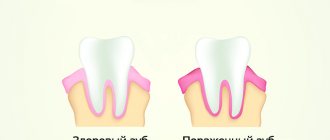
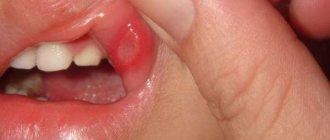
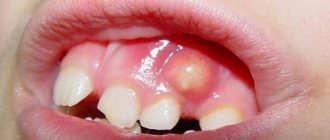
The appearance of ulcers is usually preceded by swelling and edema. After some time, a small white bump appears on the mucous membrane, filled with liquid exudate. After some time, the bubble bursts, and in its place an open wound forms - an ulcer. Similar tumors can appear on the inside of the cheeks, lips, palate, gums and even on the tongue.
Why can ulcers appear on the gums?
However, in some pathological conditions, ulcers may have distinctive features. So, for example, against the background of the development of syphilis, wounds of a round shape and with slightly raised edges form in the oral cavity. In this case, the central part is usually red with a slight grayish coating. But necrotizing gingivostomatitis is accompanied by the appearance of ulcers with uneven outlines and a greenish coating. In this case, the gums become very inflamed and begin to bleed. As part of diagnosing the disease, the doctor must take into account the visual characteristics of the rash, as well as the accompanying symptoms that the patient complains about.
More serious causes of the formation of wounds on a baby’s gums are the following diseases:
- Syphilis, which causes sores to appear on a child’s gums. This characterizes the initial period of development of the disease. In this case, deepened ulcers with significant redness are noticeable. Infection can occur in young children (even infants).
- Infection with Koch's bacillus leads to tuberculosis, in which a noticeable symptom is ulcerative lesions of the oral mucosa. In this case, the wounds on the gums hurt a lot and bleed.
- HIV infection of a baby is also determined by the presence of the listed symptoms.
- Diabetes mellitus is always accompanied by damage to the mucous membranes of internal organs.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract provoke the formation of wounds on the gum tissue.
- Endocrine disorders are accompanied by wounds and ulcers of the oral mucosa.
- In renal failure, there is usually the presence of wounds in the gum tissue.
Causes of the disease and characteristic symptoms
When a white purulent ulcer appears in the oral cavity, a lot of questions involuntarily arise, mainly regarding where the sore came from and what to do with it now. The most harmless cause of neoplasm is ordinary damage to the mucous membrane, including after tooth extraction. The problem can also arise due to rubbing with an orthopedic design, injury from the sharp edge of a crown or filling or braces, or the use of a toothbrush that is too hard. However, in some cases, such a symptom directly indicates a pathological condition.
When ulcers appear in a child's mouth
The most common pathological cause of mouth ulcers in children is stomatitis. The development of its aphthous form can be triggered by many different factors:
- suffered a stressful situation,
- chronic constipation,
- permanent injury to the mucous membrane,
- disruptions in the endocrine system,
- a sharp weakening of the immune system.
Acute form of aphthous stomatitis
Other common causes of this symptom, experts in the field of pediatric dentistry and pediatrics include childhood infectious diseases. In this case, whitish spots appear on the gums. With the development of diphtheria, the oral mucosa becomes covered with a thin film of a yellowish tint; against the background of chickenpox, the entire body, including the internal surfaces of the oral cavity, is covered with a scattering of small bubbles with liquid exudate, and angina is characterized by erosive lesions in the throat and tonsils.
White rashes surrounded by inflamed tissue are characteristic of the catarrhal stage of measles. Similar neoplasms appear when the herpes virus is activated - papules burst, and in their place painful wounds remain, which take quite a long time to heal. Another common cause of the appearance of a similar symptom in children is necrotizing gingivostomatitis, an infectious disease accompanied by swelling of the soft tissues, the formation of ulcers, the appearance of bad breath and fever.
Why can ulcers appear on an adult's gums?
As noted above, the appearance of a painful ulcer on the oral mucosa does not always indicate any pathological processes. Such a neoplasm may well be the result of a banal injury to the mucous membrane from the sharp edge of a crown, an incorrectly fitted filling or a fixed orthodontic appliance.
“Once I discovered such a ulcer on my gum. I won’t say that it hurt a lot, but it caused irritating discomfort. I first rinsed my mouth with chamomile, but nothing went away. The next day I decided to make an appointment with the doctor. It turned out that it was due to an incorrect bite that the crown was clinging to the mucous membrane. In general, it's okay. They prescribed me an ointment, and in just a couple of days everything went away.”
Antonina F., 32 years old, Moscow, from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru
However, in some cases, mouth ulcers indicate the presence of a specific problem in the body. Thus, chronic stomatitis often occurs in adult patients - this disease is one of the common causes of the formation of ulcers on the gums. When the pathology worsens, aphthae go away on their own within a week, however, in some cases, painful neoplasms can persist for longer than a month. Of course, such a situation requires immediate medical intervention. If no attempts are made to solve the problem, the disease will soon develop into an ulcerative form, which, in turn, is characterized by pronounced clinical manifestations and acute intoxication processes1.
If the pathology is not treated, it can develop into a chronic form.
In addition to the potential causes listed above for children, the following factors can cause a similar symptom in adult patients:
- tuberculosis - the disease may be accompanied by the formation of peculiar tubercles on the oral mucosa. The ulcers are painful and sometimes bleed.
- HIV - a similar symptom occurs in about a third of patients,
- syphilis - aphthae with a white coating are formed,
- oncology - ulcers often do not cause any discomfort, but take a long time to heal,
- deficiency of vitamins and beneficial microelements - in some cases leads to the formation of plaque and the appearance of sores on the gums.
Even if mouth ulcers do not cause much discomfort, you should definitely see a doctor. Essentially, these are open wounds on the mucous membrane, which create favorable conditions for infection to penetrate the soft tissues. In addition, in some cases they signal the development of pathological processes. Even if the problem is in the sharp edge of the tooth, crown or filling, all this requires immediate correction.
Reasons for the appearance of lesions
Causes of development of inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity:
- decreased immunity;
- hypovitaminosis;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- damage to the mucosa;
- tumors;
- prosthetics;
- poor quality oral hygiene procedures;
- chronic diseases;
- syphilis;
- AIDS;
- smoking;
- hormonal changes;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- stress;
- allergic reactions;
- irradiation;
- tuberculosis;
- helminthic infestations;
- use of immunosuppressants and steroids;
- dental problems: caries, periodontitis, deposits on teeth.
The appearance of ulcers on the gums of a child occurs when baby or permanent teeth erupt. To rule out serious infections, you should consult a doctor.
White plaque on the gums, tongue and small sores in children are a characteristic sign of candidal stomatitis. In newborns, this is a common phenomenon that occurs when passing through the birth canal, which is densely populated with fungi of the genus Candida.
Choice of treatment tactics
We have figured out the main reasons for the formation of ulcers on the mucous membrane, and now it’s time to find out how such symptoms are treated. So, how to treat such pathological manifestations? To prescribe the necessary therapy, the doctor conducts a thorough examination of the patient. Only by knowing the exact cause of the formation of ulcers can a correct therapeutic plan be drawn up. So, for example, treatment of aphthous stomatitis in a child usually takes place in 7-10 days, but in severe cases it may take 3-4 weeks. Experts, as a rule, prescribe rinsing with antiseptic agents: “Chlorhexidine” or “Furacilin”. Immunomodulatory drugs are also prescribed to restore the body's defenses.
Chlorhexidine is often prescribed to treat pathology
Herpes infection requires taking specialized medications, one of which is Acyclovir. Antihistamines and vitamins are also prescribed - always vitamin C. In the event that the occurrence of ulcers is caused by a disease of internal organs or systems, targeted medications are prescribed as part of treatment for adults and children. In some situations, when ulcers are accompanied by pain, painkillers are additionally prescribed.
How to treat ulcers on a child’s gums
How to treat gingival lesions? The principle of therapy depends on the cause of the formation of ulcers and the child’s health condition. Based on the table, you can create an accurate treatment for gums for a particular disease.
| A dental disease that occurs with the appearance of ulcers on the oral mucosa | Treatment principle/drugs |
| Aphthous stomatitis | 1. Intraoral baths every 4 hours with a solution of chamomile and oak bark. 2. Orally – antiallergic drugs (“Suprastin”, “Cetrin”). 3. A course of multivitamin complex. |
| Viral stomatitis | 1. Local applications with Cycloferon and Solcoseryl ointments. 2. Rinse with an aqueous solution of chlorhexidine. 3. Orally – antiviral drugs (“Valtrex” or “Viferon”). 4. After meals - “Vitrum kids” or “Complivit asset”. |
| Necrotizing periadenitis | 1. Rinse with Rotokan or Stomatofit solutions 3 - 5 times a day. 2. Local treatment of ulcers with Metrogil Denta gel up to 2 times a day. 3. Orally – broad-spectrum antibiotics (strictly as prescribed by the doctor). 4. Nutrition correction. |
| Decubital ulcer | 1. Frequently rinse your mouth with a solution of chamomile and oak bark. 2. Lotions with vitamins A and E (2 times a day after brushing your teeth). 3. Giving up bad habits (gnawing on foreign objects). |
| Afty Bednar | 1. Changing the HW technique. 2. Weaning a child off thumb sucking. 3. Giving up bad habits. 4. Individual selection of oral hygiene items. 5. Wetting the ulcers with a 0.05% chlorhexidine solution. |
| Gum injury | 1. Elimination of damaging factors. 2. Intraoral baths with antibacterial agents (“Miramistin”, “Chlorhexidine”). 3. Applications with vitamins A and E. |
| Hypovitaminosis | 1. Change in food quality. 2. Eating plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables. 3. Consumption of pharmaceutical vitamin complexes and minerals. 4. Use of toothpastes with vitamins and other biologically active substances (“Splat baby”, “Lacalut teens 8+”, “Junior New Pearl”.) |
The child's body is very sensitive to the effects of medications. In order not to harm the health of your baby, after detecting signs of illness, it is recommended to consult a doctor as soon as possible for proper treatment of gums.
Traditional methods of therapy
So, we found out how to get rid of mouth ulcers. Now let's talk about what traditional medicine offers us in this regard. Almost all pathological conditions, during the development of which such sores form on the oral mucosa, require saturation of the body with vitamin C. It is also useful to rinse the oral cavity with moods and decoctions of medicinal herbs. Such rinses help relieve swelling and inflammation, but this is not a panacea, but only maintenance therapy. The use of such prescriptions must be agreed upon with the attending physician. Here are the most common and proven recipes:
- Calendula is often used to treat canker sores. A tablespoon of dried flowers is poured into a glass of boiling water and left for about an hour. It is recommended to rinse your mouth with the prepared solution 3 times a day,
Calendula tincture will relieve pain - To alleviate the condition of viral stomatitis, including herpetic stomatitis, it is recommended to use a solution of potassium permanganate. A small amount of it, literally at the tip of a teaspoon, is dissolved in a glass of plain water. It is recommended to rinse your mouth with this solution every 3 hours,
- Another great remedy is a simple co-solution. To prepare it, just dilute half a teaspoon of salt and soda in a glass of water.
Remember: any independent attempts to speed up the healing of oral ulcers are fraught with serious complications. Before you begin treatment at home, you should first visit a doctor and determine the true cause of the problem.
- Barer G.M., Ionov V. State of microbiocinosis of the oral mucosa in chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis, 2007.
Causes
Harmless sores occur for several reasons. The most common is stomatitis:
- Catarrhal - gums turn red due to non-compliance with personal hygiene rules.
- Aphthous - occurs when immunity decreases, stress, or hormonal imbalance. Aphthous stomatitis can develop into a chronic disease.
- Fungal (thrush) - a whitish coating appears on the mucous membrane, after removal of which ulcers can form.
- Allergic – when a certain pathogen enters the oral cavity, an allergic reaction occurs in the form of aphthae.
- Viral (vesicular) - characterized by the appearance of a blistering rash, after which ulcers form.
- Herpetic - transmitted by airborne droplets. The appearance of ulcers is preceded by blisters with watery contents.
There are other causes of ulceration of the mouth and gums. These include:
- Necrotizing periadenitis is a complication after inflammation of the submandibular lymph nodes.
- Trauma – damage to the gums during dental procedures, spicy food, a damaged tooth or crown.
- HIV infection - the appearance of ulcers due to decreased immunity.
- Syphilis is a white coating without pronounced pain.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - ulcers appear when the acid-base balance is disturbed.
- Kidney dysfunction – disorders of the excretory function prevent the kidneys from removing fluid, which causes numerous ulcers.
- Pathologies of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus) - hormonal imbalance provokes the development of aft.
- Hypovitaminosis, vitamin deficiency - an excess or lack of vitamins leads to the formation of ulcers.
- Anemia – lack of iron leads to ulceration of the oral mucosa.
- Leukoplakia is a lesion of the oral mucosa, expressed by the appearance of white ulcers that become denser over time.
- Bad habits – smoking, alcohol and coffee abuse.