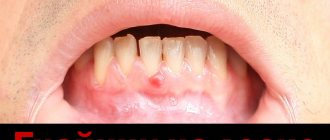
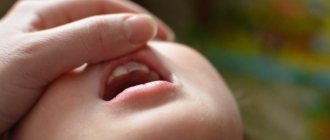
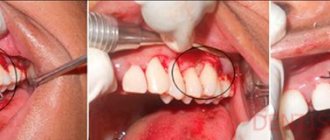
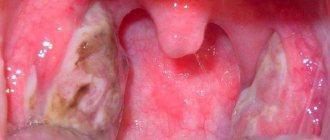
A wound to the gum is a problem that arises for many reasons and always causes severe discomfort to a person. Sores can make it difficult to eat, interfere with normal sleep and worsen the general well-being of both adults and children. Treatment of such pathology is always complex, using drugs from various drug groups.
It is important to understand that long-term non-healing wounds on the gums are always a symptom of some problem in the body, both dental and general somatic. If such wounds on the gums are left untreated, serious complications may develop with the addition of purulent processes.
Types of wounds on the gums
Depending on the cause of the wound on the gum, there are several types of it. For example, as a result of injury or the development of a herpetic infection, blisters appear, which subsequently burst to form erosions and ulcers. With aphthous stomatitis, aphthae are formed on the mucous membrane - flat wounds with a white coating and clear edges.
A wound on the gum near a tooth that does not heal for a long time, periodically disappearing and appearing, is called a fistula. It occurs due to chronic inflammation in the tissues surrounding the tooth. At the top of the fistula there is an opening through which exudate exits.
Ulcers with uneven edges, filled with soft plaque, are characteristic of the ulcerative form of gingivitis or stomatitis. In case of gum injury, scratches or small hematomas are visualized with damage to the integrity of the mucous membrane.
Main types
The main cause of sores in the mouth is stomatitis. There are several types of it:
- chronic stomatitis appears with constant biting, malocclusion, poorly made dentures;
- chemical stomatitis is caused by the appearance of burns in the oral cavity as a result of exposure to chemicals and drugs;
- allergic stomatitis occurs when the body is sensitized to various allergens;
- fungal stomatitis appears when affected by microspores of candidiasis, etc.
Causes
There are many reasons for sores on the gums. These include:
- Various dental diseases - stomatitis, gingivitis.
- Hypovitaminosis.
- Traumatic damage to the mucous membrane.
- Oncological diseases of the oral cavity.
- Having bad habits, such as smoking.
- Poor-quality dental fillings or errors in the manufacture of dentures.
- Taking certain medications.
- The period of treatment of oncological diseases (chemo- and radiotherapy).
- Certain diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Helminthiases.
- HIV infection.
- Diabetes.
- Complications after tooth extraction.
- Hormonal changes in the body.
Ulcers on a child’s gums usually occur with the development of stomatitis or as a result of injury to the mucous membrane by foreign objects. Children tend to taste everything, which increases the likelihood of infection or injury to the oral cavity.
Oncological diseases
One of the most serious causes of wounds is gum cancer. It is characterized by the presence of a chronically non-healing ulcer, accompanied by swelling and pain. Externally, you can see increased pigmentation with a pronounced vascular pattern and red spots.
Regional lymph nodes enlarge, the patient’s general well-being suffers - weakness appears, body temperature rises to low-grade levels.
Hypovitaminosis
Hypovitaminosis is understood as insufficient intake of vitamins into the body. With hypovitaminosis, general and local immunity deteriorates, the ability of the mucous membrane to quickly recover is affected, which is why wounds take longer to heal and a bacterial infection is more likely to occur.
Ulcerative gingivitis
Ulcerative gingivitis is an inflammatory lesion of the gums, which occurs with the formation of erosions, ulcers and tissue necrosis. A symptom of necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis is sharp pain that makes eating difficult. An unpleasant odor appears from the mouth, the gum tissue is hyperemic, swollen and bleeding.
Characteristic are ulcers in the area of the gingival papillae and the apex of the gingival margin, around which a border of necrotic gray-white tissue is visualized. Removal of plaque is accompanied by bleeding.
Ulcerative gingivitis usually develops against the background of catarrhal inflammation. Provoking factors can be dental plaque and stones, multiple untreated caries, as well as chronic trauma to the mucous membrane.
Stomatitis
Stomatitis is an inflammatory disease of the gum mucosa that occurs for many reasons. There are several forms of stomatitis:
- Aphthous - accompanied by small ulcers (aphthae) covered with a dense white coating. Aphthae are always painful.
- Herpetic - provoked by the introduction of the herpes virus, characterized by the appearance of multiple blisters on the gums, lips and cheeks.
- Catarrhal - most often occurs in children as a result of insufficient oral hygiene.
- Allergic – develops in response to the introduction of an allergen into the body.
Stomatitis is both an independent pathology and a symptom of a disease. Most often, it occurs as an independent nosology due to poor oral hygiene, chronic trauma, or the introduction of pathogenic microorganisms. In addition, stomatitis can be caused by various immunodeficiency conditions.
With aphthous stomatitis, single or multiple oval ulcers appear on the mucous membrane of the gums, in the center of which there is a white coating. The mucous membrane is painful and bleeds.
Injuries
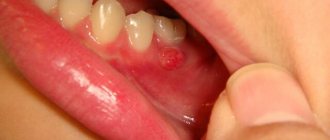
In adults, a wound on the gum due to trauma to the mucous membrane can occur as a result of improper use of dental floss or a toothpick. In addition, damage develops if a person is accidentally injured by hard food.
Injured gums: how to treat scratches, cracks, cuts and other damage
The oral mucosa has a thin and delicate structure and is sensitive to damaging factors. Any slightest crack or scratch on the gum will cause significant discomfort and will be a reason for urgent treatment, since any open injury is a kind of entry gate for infection.
First of all, this problem affects young children, who often damage the mucous membrane with foreign bodies.
Causes of scratches on gums
The periodontal tissues and periosteum of the lower and upper jaw are in close contact with the mucous membrane of the gums. Mucosal tissue not only plays a protective function, but also serves as a conductor for metabolic reactions.
The tooth is nourished due to reliable blood supply and innervation in the gums, and any slightest damage will always result in a painful sensation. Thanks to this, the dentist can determine the location of the lesion and its parameters.
A scratch, be it a microcrack that is not visually visible, is a reason to seek specialized medical help. In the oral cavity (on the surface of the tongue, cheeks) there is a large amount of foreign microflora, which, if they get into the scratch itself, cause serious problems for the teeth and the body as a whole.
There are three reasons that cause gum damage:
- Mechanical factor - when the oral mucosa is damaged by hard food during eating (for example, when the gums are crushed with hard food: crackers, sweets, seeds) and during therapeutic measures (the gums are damaged during dental treatment - touching with a needle, drill, etc.). Mechanical damage (scratches) is more often caused by young children who carry unknown things to their mouths, gnaw or chew them.
- Chemical factor - when the mucous membrane is exposed to various chemical compounds (acids, alkalis).
- Thermal factor - ingestion of too hot food or water causes burns, and exposure to cold damages teeth.
One should take into account the fact that the mucous membrane becomes more susceptible when the human body’s immunity is reduced. Typically, this condition is caused by concomitant diseases: diabetes mellitus, HIV infection, benign and malignant neoplasms, sexually transmitted diseases.
In children
Since gum scratches more often occur in children who want to “taste” everything, their parents should carefully examine the oral cavity every day for the presence of such scratches.
In children, the immune system is still weak and the protective mechanism in a small body may not work, and then a small scratch may be complicated by swelling and redness of the soft tissues around the lesion.
Externally, the child will be restless due to soreness in the mouth.
The teenage generation has a high risk of bruises (street fights, football, bad falls). Vivid symptoms of damage include severe pain in the mouth, bleeding gums, a knocked out tooth, etc.
Complications after gum injuries
If you do not properly care for the oral cavity, as well as ignore a scratch on the gum, serious complications will always follow - infection in the scratched gum and the occurrence of an inflammatory reaction. How to understand that a complication has appeared?
- If a scratch has a whitish tint and its edges rise above the level of healthy tissue, this is a guarantee of a foreign infection.
- If the healthy tissues around the lesion are red and there is also swelling, this is evidence of inflammation (the body’s response to the introduction of a pathogen into a painful wound).
- If pus is released from a scratched gum, then an intoxication syndrome may occur in the body (fever, increased general weakness, increased pain in the mouth, a feeling of brittle bones).
- If there is a throbbing pain in the damaged areas, radiating throughout the jaw.
Cyst in a child's mouth
If symptoms are detected, you should immediately contact your dentist, because the infected exudate from the scratch gets into the roots of the teeth and deep into the gums, causing local complications (stomatitis, gingivitis). Since the mucous membrane is supplied with blood, its flow causes the infectious process to become generalized.
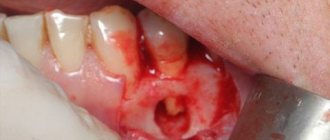
Treatment of scratches and wounds on the gums
What to do if you cut your gum? If the scratch is without foci of inflammation and other signs of complications, then you can get by with treatment at home using traditional medicine and the use of local antiseptics. Treatment of with chlorhexidine or furatsilin when rinsing promotes healing of the scratch and will become a serious obstacle to infection.
Treatment activities will include:
- drug treatment;
- folk remedies for wound healing;
- surgical care.
Drug treatment of injured areas
Many dentists do not advise self-medication and delaying consultation, especially when the child has cut the gum. At the stage of specialized care, the doctor will examine the surface of the mucous membrane, the nature of the cut in the gums and tell you how to treat it.
For difficult-to-heal mouth ulcers, dentists use ointments with an antiseptic effect :
- gel "Metrogil denta";
- gel "Cholisal";
- "Levomekol" (antibacterial agent);
- medicinal paste “Parodontocide”;
Metrogyl and Cholisal
For deep cuts, in order to prevent purulent infection, antibiotics :
- penicillin antibiotics (Amoxiclav);
- tetracyclines (Doxycycline, Tetracycline);
- tyrothricins (Grammidin).
Along with antibiotic therapy, anti-inflammatory treatment is indicated, including the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs :
- Ketorolac;
- Nimesulide;
- Diclofenac.
This therapy is aimed at reducing the inflammatory response and pain.
A frequent question: “What to do when you scratch your gum, it’s swollen and you have bad breath?” If the gums are scratched and have an unpleasant odor, this indicates an infection in the mouth. If there is a complication, then surgical intervention , the purpose of which is to release pus from the scratch and then treat it with local antibiotics.
Folk remedies for wound healing
If the patient has scratched his gums, but does not want to seek medical help, a solution may be to take folk remedies that will quickly eliminate signs of inflammation and relieve tissue swelling.
- Dried St. John's wort in combination with flax seeds and oak bark will cope with an infection in the mouth. By killing the infectious agent, this decoction will restore beneficial microflora. Use 1 time per day for a week.
- Pieces of propolis relieve the inflammatory reaction. Used in alcohol infusion or made in the form of plates, attached to the inflamed area of the gums for 30 minutes. Use daily until inflammation disappears.
- Compresses with calendula have a similar effect to propolis.
- Using a solution of potassium permanganate to relieve inflammation, 2 times a day, for a week (especially for pulpitis, stomatitis, gingivitis).
Treatment of scratches in a child
Since children are susceptible to infection, self-medication is not the right solution. If a child exhibits the corresponding symptoms of gum damage, you need to contact a dentist to decide on further treatment measures.
Even a microcrack in children is an indication for consultation. The doctor will examine you and tell you how to treat the inflamed scratch.
Features of oral care
Proper oral care is vital. Taking into account the peculiarities of care, you can avoid diseases of the teeth, gums, throat and their complications.
A competent approach to oral hygiene includes:
- Choosing a quality toothbrush to clean hard-to-reach areas and minimize the risk of injury while brushing your teeth.
- Rinsing with medicinal solutions (rinse your mouth with Colgate mouthwash, Forest Balm, etc.).
- Refusal of dental sticks as hygiene products, or their replacement with dental floss.
- Visit the dentist once a year. Removing tartar when identified. Examination of gums.
- Vitamin therapy.
- Proper nutrition (refusal to hard and hot foods).
- Rejection of bad habits.
If the patient has damaged the gum with a toothbrush or the gum has cracked due to a lack of vitamins due to a concomitant disease, it is necessary to immediately clean the teeth and treat the scratch with an antiseptic (chlorhexidine, furacilin).
If gum inflammation develops in the future and pain increases, you should consult a dentist. With a calm course, a non-inflamed scratch will resolve on its own, but only if the rules of oral hygiene are observed.
Source: https://DesnaZub.ru/zabolevaniya/travmy-carapiny-treshhiny-porezy
Treatment of gum wound
Treatment of wounds of the oral mucosa depends on the cause of their occurrence and the degree of damage to the soft tissue. Treatment is always complex, including internal and external medication. As an additional measure, treatment with traditional methods can be carried out.
Drug therapy includes the prescription of drugs of various groups:
- Antibacterial.
- Antiviral.
- Painkillers.
- Wound healing.
- Anti-inflammatory.
To relieve pain and accelerate wound healing, local drugs such as Metrogyl Denta, Cholisal, Kamistad are prescribed. For bacterial infections, the use of antibacterial drugs and treatment with antiseptic solutions - Chlorhexidine, Furcillin, Miramistin - are indicated.
To treat a viral infection, antiviral drugs are used - Zovirax, Acyclovir and others.
For severe pain, lidocaine-based anesthetic gels and sprays are applied topically. It is necessary to prescribe healing agents - Solcoseryl, vitamins B1 and B6, sea buckthorn oil.
ethnoscience
Traditional methods include rinsing the mouth with decoctions of medicinal herbs:
- Calendula tincture - add 1 tablespoon of the prepared pharmaceutical product to a glass of warm boiled water.
- St. John's wort tincture - add 40 drops of the drug to 1 glass of water.
- Infusion of oak bark - pour a tablespoon of dry plant into a glass of boiling water and infuse.
- Rinse with saline solution - add a tablespoon of salt to a glass of water.
Treatment with traditional medicine methods should serve as a complement to basic drug therapy.
Treatment of wounds on the gums in children
In children, healing of any wound on the gum occurs faster than in adults. This is due to the higher ability of the mucous membrane to heal itself.
Antihistamines are prescribed - Zodak, Fenistil or Diazolin. Wounds are treated with an antiseptic solution - Miramistin or Chlorhexidine. To speed up healing and relieve pain, keratoplasty agents are applied - Cholisal, Solcoseryl or sea buckthorn oil. During illness, it is necessary to maintain oral hygiene and clean it after each meal.
Non-dental diseases
An ulcer on the gum is a common symptom of non-dental diseases. Erosions often occur in patients with the following diagnoses:
- tuberculosis;
- syphilis;
- cancer;
- diabetes;
- renal failure;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- blood diseases.
The listed diseases require complex treatment in a hospital setting. The sooner the patient contacts a specialist, the more optimistic the prognosis.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Analgin for toothache - does it help and can it be taken in different ways?
Prevention
Measures to prevent wounds on the gums are simple:
- Careful oral hygiene in both adults and children.
- Hand washing before eating.
- Chewing hard foods carefully.
- Elimination of toothpicks and proper flossing technique.
- Regular visits to the dentist.
- Strengthening the immune system.
Self-treatment of ulcers on the gums is only possible if the cause of their appearance is a minor injury. If the wound does not heal for more than 7 days, you must consult a dentist for diagnosis and selection of the correct treatment.
Author: Yulia Khaimanova, dentist, especially for Karies.pro