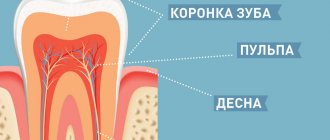
About the illness
There is no medical diagnosis of thrush as such. There is a certain type of stomatitis that is caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida. At least a dozen candida are known that can cause inflammation of the oral mucosa. They live everywhere - in the environment, in the mouth, in the intestines, in the vagina of girls.
Candida are permanent inhabitants of the human body, but they go into “conflict” only when something changes in their living conditions - humidity, body temperature. Thus, while the child is healthy, the fungi behave quite peacefully, but as soon as he gets sick, the immune system begins to weaken, candida activates and becomes aggressive. This is how the disease begins, popularly called thrush. The name is very accurate, since the white sores visually closely resemble curdled milk particles.
In the mouth, thrush develops when saliva loses its bactericidal properties.
It’s no secret, says Komarovsky, that saliva is quite active against a wide variety of microorganisms, and if its biochemical parameters are normal, it can easily cope with candida. But if saliva becomes thicker, or it is not produced enough, then stomatitis will not have to wait long.
In newborns, thrush in the mouth is often a consequence of passage through the mother's birth canal. There, colonies of Candida of different species are a completely normal phenomenon, but a child’s saliva immediately after birth does not yet have strong bactericidal properties, and the immune defense is still imperfect, local immunity is not sufficiently developed. As a result, the baby's mouth is covered with white spots, it hurts him to suck, and he gets worried.
Typically, stomatitis caused by candida is not particularly dangerous.
But in some cases, with severe and extensive damage, inflammation can spread to the larynx, and this is fraught with sore throat.
Why do babies get thrush in their mouth?
What causes thrush in the mouth? During the period of breastfeeding, the baby is just beginning to develop stable immunity. Every day the baby encounters a variety of microorganisms living in the environment. An underdeveloped immune system increases the likelihood of infection in a newborn.
A disease such as thrush can affect children not only in the first months after birth, but also during intrauterine development. It is caused by fungi of the genus Candida, which live in the body of every person. However, under unfavorable circumstances, rapid growth and reproduction of these microorganisms begins.
Thrush in newborns also often appears after contact with adults. A child can become infected from them through a kiss. The main reasons for the development of candidiasis in children:
- Prematurity. Children who are born prematurely are more susceptible to infection with thrush. This is due to the immaturity of the immune system.
- Artificial feeding. Mother's milk has a unique composition, including substances that help strengthen the newborn's immunity. Children who are bottle-fed do not receive these substances, because... The mixtures contain only nutritional components. In addition, infant formula has a higher sugar content than mother's milk, and these are favorable conditions for the proliferation of fungal infections.
- Avitaminosis. Vitamins are necessary for the body for the proper functioning of all systems, including the immune system. Insufficient supply of these components causes developmental disorders.
- Surgical operations. Any intervention is stressful for the human body. Surgical procedures are especially difficult for infants. To avoid complications in the postoperative period, children are prescribed a course of antibiotic therapy. They help stop the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria, but under their influence the child’s own microflora is also destroyed.
- Pathologies of the endocrine system, hormonal disorders, abnormal metabolic processes. All these conditions lead to decreased immunity.
- Injuries to the oral mucosa. Scratches and wounds in the mouth create favorable conditions for bacteria to penetrate and multiply.
- Infection during childbirth. If the mother has the disease, the risk of transmitting the infection to the newborn during childbirth increases significantly.
- Non-sterile bottles, toys. Infection can occur in everyday situations if the child’s immunity is weakened.
- Regurgitation. Constant regurgitation of food often leads to the development of thrush in young children.
- Poor hygiene. Maintaining hygiene is necessary for both mother and baby. A woman should thoroughly wash her breasts and hands, and take care of the cleanliness of the baby’s mouth from the first days after birth.
- Period of teething. At this time, local immunity in the oral cavity weakens, so the risk of disease increases.
Causes
Saliva, according to Evgeniy Komarovsky, begins to lose its bactericidal protective properties when it dries out. This can happen for a number of reasons:
- The baby is in a room that is too hot and dry.
- Mom and dad rarely take the baby out for a walk.
- The baby screams often and for a long time, while he inhales mainly through his mouth, which is why the saliva dries up.
- The child has a runny nose, nasal breathing is difficult, he has to breathe
Candida is very contagious, and therefore there may be other causes of stomatitis.
A one-month-old baby can “catch” an infection from a pacifier or dishes held by a person suffering from thrush. Even a mother can become this person. It can also be caused by being in close proximity to a young cat or puppy (parents love to photograph babies this way). Even frequent regurgitation can lead to stomatitis if parents do not remove milk from the mouth.
Children under one year old often begin to suffer from oral thrush when they understand how to put this or that object into their mouth and actively practice it. And babies older than one year can get sick from eating unwashed vegetables and fruits and improperly cooked meat.
What does Dr. Komarovsky advise?
Komarovsky believes that if thrush appears in the mouth, you should not be treated with medications if it is at an early stage. To improve the health of a small patient, it is enough to increase the humidity in the room and ensure that the child breathes through his nose and not his mouth. That is, when the humidity in the room is normalized, the proliferation of fungi will stop and the whitish coating will disappear. But this can only be achieved if the immune system can cope with the disease.
If a child of the first year of life who is breastfed has plaque only on the tongue, then there is no need for treatment.
But when rashes appear on the cheeks, you need to start treatment, the main method of which is to restore the bactericidal properties of saliva. In this case, it is necessary to wipe the stains with a 2% soda solution.
If saliva loses its protective properties, thrush may appear. The main reason for this can be called overdrying of the mucous membrane, which can occur due to the fact that the air in the house is dry and the baby rarely walks.
Treatment and prevention according to Komarovsky
Thrush requires special attention when ulcerative lesions are observed not only on the child’s tongue, but also on the inner surface of the cheeks. The first case cannot be considered a disease at all, says Evgeny Komarovsky, since for a child who is breastfed or fed with adapted milk formulas, this is a variant of the norm, and nothing needs to be done about this plaque.
If white ulcers are found on the cheeks, we can talk about stomatitis as such and begin therapeutic actions.
First of all, Evgeniy Komarovsky proposes to return the necessary protective properties to saliva so that it can cope with the raging fungus of the genus Candida. To do this, you should buy a room thermometer, hang it in the children's room and make sure that at any time of the year or day, the air temperature does not exceed 18-20 degrees Celsius.
The second necessary purchase is a humidifier with a hygrometer. Using a humidifier, you need to increase the relative humidity in the child's room. A hygrometer will allow you to monitor its level. The humidity at which saliva does not dry out and does not lose its bactericidal properties is 50-70%.
The child should walk a lot in the fresh air.
And while he is outside, the room must be ventilated and wet cleaned at least once a day. There is no need to add detergents containing chlorine to the water. Dust should definitely be removed from the nursery every day, and all “dust collectors”, which are large soft toys and books, should be removed altogether from the room where a small child sleeps and spends a lot of time.
The child must be given enough water, because a lack of fluid in the body also causes saliva to dry out. If the baby drinks milk, you should give him a few sips of water so that there is no milk left in the mouth and does not create a favorable environment for the proliferation of yeast-like fungi.
The white sores themselves on the baby’s gums and cheeks should be treated with a two percent soda solution. It’s easy to prepare it at home: take 2 grams of baking soda per 98 ml of boiled water.
Electronic kitchen scales are found in almost every home today, and calculating the required amount of a substance is not difficult. If there are no scales, then take soda on the tip of a knife, in water - a little less than half a glass.
Dr. Komarovsky's advice for treating thrush in children
General recommendations and preventive measures
Taking into account the fact that many internal and external factors contribute to the development of thrush, special attention should be paid to the true causes of candidiasis. According to Dr. Komarovsky, this reason is a decrease in the protective function of the child’s saliva . This happens most often if the baby’s saliva is very dry, says a famous pediatrician.
Saliva with normal levels should contain colonies of beneficial bacteria, which are responsible for inhibiting the growth of pathogenic flora. When their number declines and the antimicrobial properties of saliva fade, pathogenic bacteria begin their harmful actions, dooming the child to pain from stomatitis or thrush.
Thus, it can be assumed that the prevention and treatment of thrush in a baby will come down to the elementary restoration of the immune properties of salivary fluid, that is, to reducing its dryness.
To achieve this, you need to take walks in the fresh air every day, regularly carry out wet cleaning of the apartment, monitor the microclimatic parameters of the room (air humidity should be at least 60–70% , temperature should not exceed 23 degrees). You should not wrap your child in warm clothes if the room is warm enough; overheating can cause harm. Timely cleaning of the baby's nasal cavity will allow him to avoid breathing difficulties, and the mucous membrane will remain moist.
It is necessary to prevent your child from crying for a long time. When a child cries for a long time, his mouth becomes dry.
Pediatrician Komarovsky is confident that the presence of a small white coating on the tongue of a baby under one year old, as a rule, is not a pathology and soon goes away on its own without treatment. There is a myth among the fairer sex that the name thrush is associated with breastfeeding. In fact, this opinion is far from the truth, but you should not be alarmed if you discover a white tongue on a newborn. You need to fuss if the rash and plaque spreads to the inside of the cheeks - this is definitely thrush.
For the most part, treatment of candidiasis in the mouth of children is effective even without prescribing a group of medications, if you adhere to a certain algorithm - moisturize, monitor the cleanliness and humidity of the air.
At the same time, auxiliary techniques will shorten the recovery period. To cleanse plaque on the mucous membranes, you can prepare a soda solution, which is dipped in a sterile bandage or cotton wool, and then the affected areas of the mouth are treated without sudden movements. Of course, before doing this you need to make sure your hands are clean. A teaspoon of 2% soda diluted in a glass of warm water is one of the safe ways to get rid of fungal candidiasis. The high efficiency of this method lies in the formation of an alkaline environment that is not intended for the existence of fungi. This procedure is carried out twice a day an hour before feeding the baby.
Recognized folk recipes made from anti-inflammatory and bactericidal herbs - chamomile, sage, calendula - help treat candidiasis. Lotions with sea buckthorn oil work great .
The solution is suitable for washing the mother's nipples before feeding, as well as for treating the nipple.
Honey has proven itself to be the best in the fight against thrush. You can treat problem areas with honey solution instead of soda. Before using such a folk recipe, you should make sure that the child is not allergic to bee products.
It is highly not recommended to give antibiotics to children without a doctor's prescription. Without identifying the causes of the disease, treating a child with antibiotics is extremely dangerous. Hardening the body, proper nutrition of the mother with the inclusion of vitamin-rich foods in the diet will serve as reliable protection against thrush.
If you discover thrush in a baby, you cannot stop breastfeeding . With the relief of symptoms, the child will begin to feed on mother's milk without any difficulties.
Drug therapy
With a complex form of candidiasis, the child may require drug treatment.
Among the antifungal agents approved for use after 12 months are:
If the disease cannot be treated and the infection has spread to the intestines, to the genitals, oral antimycotics are called upon to help: nizoral, candida, flucanozole .
What can't you do?
You cannot burn white spots in your mouth with iodine or brilliant green, as well as alcohol and alcohol solutions.
You should not give antibiotics to a child with oral thrush, or apply antibiotics directly to oral ulcers.
Do not remove plaque from the cheeks and tongue mechanically or manually.
You cannot take a child to kindergarten with signs of stomatitis, because in one day in the group he will infect up to 70-80% of his peers with candida.
During treatment, you do not need to give your child sweet foods; Candida loves sweets. A nursing mother should exclude sweets from her diet.
You will learn more about fungal infections in the mouth in children from the following video.
medical reviewer, psychosomatics specialist, mother of 4 children
Just yesterday your little one was laughing, giving you smiles, willingly playing and sucking milk, but today he began to behave completely differently: refuse to eat, began to cry and be capricious? We recommend looking into your baby's mouth. If you see a white coating there, you should know that this may be the first sign of a popular disease of the 21st century called thrush.
There is no need to worry too much, since it is quite easy to cure the disease at an early stage. But if you ignore the symptoms that appear, getting rid of the disease will be much more difficult. In this article you can familiarize yourself with why thrush occurs in a child, with the recommendations given by Dr. Evgeniy Komarovsky, preventive measures, characteristic manifestations and treatment.
Thrush in newborns in the mouth - causes, symptoms, treatment, prevention
Any mother is pleased with the healthy appearance of her baby, when he reacts animatedly to the game, greets him with a cheerful smile, and eats with pleasure.
But the baby's playful mood is replaced by capricious crying and anxiety caused by the appearance of ordinary thrush.
This common disease requires timely identification and treatment, as it causes discomfort during sleep and interferes with feeding the baby.
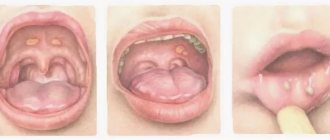
Thrush appears when microorganisms of a fungal nature, called candida, actively multiply in the child’s mouth. Therefore, the medical synonym for thrush is candidiasis. When the disease occurs, the baby's tongue, gums and inner cheeks become covered with a white coating, first in the form of a milky film, and then in the form of flakes similar to curdled milk.
Due to inexperience, young mothers at the first stage of the onset of the disease find it difficult to recognize it, since the white coating looks like clots of milk in the baby’s mouth left after feeding.
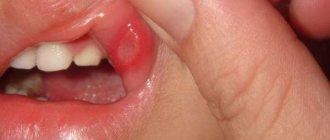
Candidiasis can be easily distinguished from milk residues if you try to remove the plaque with a cotton swab. Red spots will be visible under the plaque - this is the beginning of the inflammatory process, confirming the onset of the disease.
If the white spots do not disappear on their own, they noticeably increase, and with the appearance of plaque the baby cries and refuses to eat, then there is no doubt about the occurrence of thrush.
Why do babies get thrush?
The fungus Candida albikans lives in every human body, including a newborn. The following conditions contribute to its active growth:
- violation of the hygienic regime (insufficient care of nipples and mammary glands, use of nipples and bottles, toys without boiling treatment);
- use of formulas containing excess sugar or sweetened water when feeding;
- decreased body resistance during teething, dysbacteriosis or colds;
- the mother has a disease;
- treatment with antibiotics that kill beneficial bacteria that slow down the proliferation of the fungus.
When thrush appears, it is important to determine the cause of its occurrence. Eliminating the cause will affect the effectiveness of treatment and the choice of preventive measures.
What happens if thrush is not treated?
Milk plaque in a baby’s mouth does not go away on its own. Over time, it increases, an inflammatory process develops under the white greasy film, and red spots of plaques form. The mucous membrane is broken and bleeds. Small wounds in the oral cavity become “gates” for the entry of other infections.
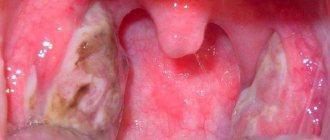
In advanced cases, a dense film of plaque covers the baby’s entire mouth from the inside, spreading to the mucous membrane of the inner surface of the throat. Bleeding cracks appear on the lips and gums.
The baby cannot swallow and suck without pain; he constantly screams and refuses to eat.
The child’s temperature rises due to anxiety and emotional stress.
How to treat thrush
When thrush appears in an infant, there is no need to panic. This disease is easily curable, but requires regular procedures until the symptoms completely disappear.
The baby must be shown to a doctor. Only he will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment with medications. As a rule, these are antifungal drugs with nystatin. The doctor will determine the dose of the drug and the duration of treatment.
There are treatment methods that can be carried out independently before visiting a doctor. This alleviates the baby’s condition and slows down the growth of the fungus. To treat damaged areas in the baby’s mouth, use a solution of ordinary table soda or honey.
Using soda solution
1 tsp. Stir table baking soda until dissolved in 200 ml of boiled water. Wrap a gauze napkin or bandage around a finger that has been previously washed with soap.
Using a finger dipped in the resulting liquid, try to carefully treat the mucous surfaces of the oral cavity and the surface of the tongue. In this case, do not remove the coating, but simply moisten it with the solution. If the plaque is disturbed, the bleeding plaques will become a source of infection, and the fungus will easily penetrate inside.
The baby may interfere with the procedure by refusing to open his mouth on his own. Then you need to press the child’s chin with your thumb and hold it until the treatment is completed.
The soda solution is used for several days in a row, 4-5 times a day. In order to prevent further infection, only freshly prepared solution should be used.
Uses of honey
This method of treating thrush is only suitable if the baby is not allergic to honey. If the child has not been given honey before, then treatment should be started with great caution.
To treat the inner surface of the mouth for thrush, use a honey solution prepared from 2 parts warm water and part honey. The procedure must be carried out in the same way as when treating with soda, and with the same frequency.
For treatment to be effective, you need to follow simple rules:
- Before giving it to the baby, the pacifier must be rinsed each time in either a soda or honey solution;
- Bottles and nipples used for feeding should be constantly sterilized by boiling, and the same should be done with toys;
- Before each breastfeeding, the mother must treat her nipples using the above solutions.
With proper hygienic care and regular treatment, thrush stops bothering you after 3-4 days. If the disease goes away before the treatment prescribed by the doctor ends, it still needs to be completed. This will prevent symptoms from returning in the near future.
Why is thrush prevention necessary?
The likelihood of a child developing thrush remains until he reaches six months of age. Until this time, the immune system is weakened, the body does not resist infections. Therefore, it is important for adults to strictly adhere to the rules for caring for a child in the first months of life.
All items that are used for playing or feeding a child are subject to hygienic treatment. If they are made of a material that cannot be sterilized, then they are treated with a soda solution.
The mother must constantly monitor the cleanliness of the breasts and nipples and prevent cracks from appearing on the nipples.
After feeding, it is advisable to offer the baby to drink warm water to remove any remaining milk from the tongue or gums. Milk residues become a breeding ground for fungus. After burping, you also need to give the baby water.
Other forms of thrush in children
Thrush in girls needs to be treated especially carefully. If the oral cavity becomes infected and there is no careful care, the fungus spreads through bathing water to the genitals and causes a disease such as vulvitis.
When the genitals become infected, redness appears in the labia area. This disease cannot be treated on your own; you must seek help from a specialist. Correct and timely treatment will prevent the consequences of infection, manifested in the fusion of the labia.
The fungus that causes thrush can also develop in all newborns in the groin area, in the anus, on the shoulders, back, and on the skin of the hands. Then red spots with regular, clear boundaries appear, the skin becomes dry, rough and itchy. If treatment is not started, pockets of erosion will form, grow and cause discomfort and anxiety due to itching and burning.
There are cases when the infection spreads to the eye area. The result is swelling of the mucous membranes, redness, photophobia and tearing. If, with thrush in the mouth, the fungus gets inside when swallowing food, then intestinal candidiasis begins, the signs of which are increased formation of gases, stool disturbances and the presence of white curdled flakes in the stool.
Due to the ease of treatment, thrush in newborns cannot be classified as a complex and dangerous disease, but it can cause discomfort in the child due to painful or itchy sensations, disrupt his proper nutrition, wakefulness and healthy sleep, and affect his emotional state.
Why does thrush occur in a child?
The scientific name of the disease is candidiasis, but it is popularly called thrush. It is a lesion of the skin and mucous membranes by yeast-like fungi Candida albicans. Fungi are opportunistic organisms that live in the body of a child and every adult in normal quantities. But after creating good conditions, they begin to multiply and create unpleasant symptoms. The cause of the development of the disease is always the weak immunity of small crumbs. Let's find out what factors contribute to a decrease in the body's protective functions and can cause thrush. These include:
- cracks and injuries in the oral mucosa;
- burns and other damage to the skin;
- disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract (most often dysbacteriosis), regurgitation;
- long-term therapy with hormonal and antibiotic drugs;
- lack of hygiene or poor compliance with it;
- overeating sweet mixtures;
- eating a lot of sweets (for older children);
- period of teething;
- absolutely any inflammation, colds, infections;
- vitamin deficiency, metabolic disorder;
- prolonged stay in a damp room, wearing diapers.
Pediatricians, including Dr. Komarovsky, say that oral thrush most often develops:
- in a premature baby,
- in children after operations.
Also at risk are infants who do not receive all the nutrients and vitamins found in their mother’s breast milk, since artificial formulas are used for feeding. Fungi can be transmitted during childbirth if a woman has not cured genital candidiasis. Most often this is what happens.
Causes of thrush in a child's mouth
Excessive proliferation of yeast-like fungi Candida albicans causes damage to the mucous membranes. This phenomenon is called thrush. Fungi are a component of the opportunistic flora of a newborn’s body; they are also found in acceptable quantities inside adults. From the moment good conditions appear, they begin to reproduce , creating unpleasant sensations. The starting point for the development of candidiasis is often the infant’s poor immunity.
Factors that contribute to a decrease in the immune function of the body, and, consequently, the development of thrush, are divided into endogenous and exogenous.
Endogenous causes
- Abnormal intrauterine development of the fetus. Due to prematurity, the child does not always fully develop physiological functions that could counteract the proliferation of candida fungi. Thrush is more common in children who are bottle-fed, and this leads to a deficiency of enzymes that the newborn receives from mother's milk.
- Complications after surgical interventions.
- Deficiency of vitamins and microelements.
- Hypotrophy . Chronic eating disorders are accompanied by a reduced body mass index in children in the first months of life.
- Anemia. A condition with a characteristic decrease in the level of hemoglobin in the blood, simultaneously with a sharp decrease in the number of red blood cells.
- Rickets. Hypovitaminosis state, there is a decrease in the level of vitamin D in the plasma and bone structures, calcium-phosphorus metabolism is disrupted, bones become fragile, the nervous system suffers, and malfunctions in the functioning of internal organs occur.
- Dysbacteriosis . Violation of the quantitative and qualitative composition of the intestinal microflora, changes in its bacterial habitat.
- Acute or chronic infections.
- Metabolic disorder. Disruptions in carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism.
- Endocrine diseases, including diabetes and prediabetes.
- Frequent regurgitation, vomiting.
Exogenous causes
- Mechanical or chemical damage to the child’s oral mucosa. The delicate tissues of the mucous membrane of a newborn are easily injured, due to the fact that blood flows there intensively. Microtraumas disrupt the integrity of the surface epidermal layers and make way for pathogenic microbes and fungi, which from their usual habitats (skin, mucous membranes) enter the child’s body. An important role in this process is played by the maturity of the oral mucosa, as well as its level of moisture. Almost all newborns have poorly hydrated oral mucosa. The dry shell causes inflammatory processes and fermentation due to the increased acidity of saliva. All these factors affect the child’s oral health.
- Long-term use of antibacterial drugs . Under the influence of antibiotics, the vital activity of many beneficial microorganisms that are responsible for the proper functioning of the intestinal flora is inhibited. Enzymes destroyed by antibiotics can no longer synthesize essential vitamins. Their lack negatively affects the body's protective barriers. The stability of the intestinal microflora guarantees the required level of acidity, which contributes to the prevention of such troubles as thrush. Hormonal and immunosuppressive drugs, along with antibiotics, sharply suppress the child’s immunity, which also leads to complex forms of candidiasis.
- Quick transition from natural feeding to artificial feeding. Mothers who early began to accustom their child to ready-made formulas, especially with a large amount of fast carbohydrates, deprive the baby of the opportunity to receive protective antibodies along with breast milk. The high sugar content in such mixtures disrupts the acidic environment of the mouth and provokes the proliferation of fungi.
- Increased level of pathogenicity and virulence of strains of yeast-like fungi. By associating with other fungi, viruses and bacteria, fungi of the genus Candida albicans increase their negative impact on the weakened body of the child. For a newborn, infection inside a hospital or maternity hospital poses a great danger; a large number of pathogenic fungi circulate within the walls of medical institutions, capable of living in the environment for a long time. Nosocomial strains are characterized by resistance to most antimycotic and disinfectant substances.
- Fungal diseases of the mother . If a mother is diagnosed with vulvovaginal candidiasis during pregnancy, that is, the vaginal walls are affected by fungi, the risk of intrauterine and intrapartum infection of the fetus increases. It is possible that a newborn may become infected during the postpartum period through milk or nipples. Pregnant women are difficult to treat and often suffer from relapses.
- A baby can also become infected through direct contact with a nurse or doctor, or relatives who are carriers of candidiasis. The presence of superficial forms of candidiasis, with the manifestation of fungus on the nails and skin, facilitates the method of transmission of the disease. The fungus can be picked up through dirty hands, a ventilator, an endotracheal tube, bedding, and toys.
Komarovsky: thrush in a child’s mouth, symptoms
The famous pediatrician Evgeny Komarovsky constantly shares useful information about various diseases, their prevention, treatment, etc. Naturally, the doctor could not forget about thrush. He says that in addition to external and internal factors, saliva is to blame for the development of oral thrush. The fact is that it dries out, thereby reducing its protective properties. Saliva contains beneficial bacteria that prevent the growth of fungal agents in the mouth. When the quantitative indicator decreases and saliva is not able to fight microbes, opportunistic microorganisms begin to develop, causing thrush.
The mild stage of the disease is recognized by cheesy formations in the form of separately located plaques on the tongue, cheeks (inner side). In most cases, the disease does not bother the baby very much, and the temperature does not rise. If you detect white plaque in a timely manner, getting rid of it will be quite simple. To remove stains, use either a cotton swab or a sterile bandage, which is wrapped around one or two fingers. In mild cases, the gums become slightly swollen and red, and the oral mucosa becomes dry and smooth.
If there is no treatment, the disease manifests itself in moderate severity. Then the areas affected by fungi appear as formations in the form of yellow films. The infection also spreads to the baby's lips. The plaque must be removed very carefully, and it is better to entrust the procedure to doctors, since wounds remain under the tubercles, causing pain. Typically, a sick child has a low-grade fever, an irritable state, he is nervous and capricious. Often babies refuse to eat or suck on bottles of milk.
A severe form of thrush has an extremely negative effect on the entire oral mucosa. Individual cheesy islands combine to form a single film that covers the cheeks and tongue, gums, walls of the pharynx and lips. It is prohibited to remove it, since the procedure is very complicated and causes pain. If you try to remove the plaque, bleeding erosions and wounds will remain underneath it, so it is better not to touch them. The child is in a state of malaise due to high fever and pain in the mouth. Therapeutic therapy takes a long time and includes various treatment methods (local, general). For infants, this stage of thrush presents a difficult challenge.
Thrush in a child’s mouth: treatment according to Komarovsky
Thrush is a disease that can strike a child in the first weeks of his life.
It is provoked by special fungi that live inside the newborn’s body. If favorable conditions are created for them, they begin to actively manifest themselves, causing the baby to become restless. The very concept of thrush does not fit into medical terminology . The disease got its name because of such a pronounced symptom as a white coating on the mucous membrane of the mouth or genitals. In medical reference books the disease is listed as candidiasis.
Most pediatricians can always give advice on how to avoid contracting thrush, what to do if the disease cannot be avoided, what medications help alleviate the child’s condition, and what preventative measures are necessary. An experienced specialist, whom young parents turn to, is ready to share comprehensive information about fungal infections. He will conduct the necessary research, and if necessary, draw up a competent treatment strategy for the baby, at the slightest suspicion of candidiasis.
Evgeny Komarovsky is extremely popular among mothers . The authority of this talented specialist is not in doubt among parents, which is why there are so many calls to the pediatrician regarding various diseases of newborns.
Among other issues, Komarovsky pays a lot of attention to consultations on fungal diseases of the oral cavity: stomatitis and thrush.
Many years of experience and accumulated experience allow him to help young mothers identify the causes of thrush, advise rational treatment and preventive measures.
Treatment and prevention from Komarovsky
If you suspect you have thrush, you should only seek the help of a good doctor. Dr. Komarovsky advises to activate and restore the functions of saliva: both bactericidal and protective. In this case, the parents' responsibilities include:
- carrying out wet cleaning;
- support of normal temperature conditions (in the range of 20–22 degrees Celsius);
- Cleaning the baby's nose so that breathing occurs easily and nothing interferes with it.
By the way, parents should be careful and prevent the mouth from drying out, which occurs after screaming or crying for a long time. Clothes play a big role. It is not recommended to wrap your children up and create high humidity, since fungi love to live in such conditions. If children are fed artificially, it is better to give them some water after each meal, and it is recommended to give about two spoons. Using this method, you can remove leftover food from your mouth.
Even more interesting:
Causes of sores on the labia
Manifestation of thrush
On the child's genitals
This type of thrush is not as common as in the mouth, but can still develop in a child. Obvious signs are redness and swelling of the genitals, burning and itching. In boys, inflammation of the foreskin, head of the penis, and scrotum is noted. In girls, the vagina and vulva are affected. Discharge from the genitals has a consistency reminiscent of cream or cottage cheese. The smell is either absent or similar to sour fermented milk product. If the disease was diagnosed on time, local treatment - ointments, creams, vaginal suppositories and tablets for girls - will be sufficient. If the symptoms were ignored, the treatment will take longer. Often, in addition to topical medications, systemic antimycotic drugs and drugs that strengthen the immune system are used.
On the skin
If Candida fungi have attacked the skin, most often they will choose areas that rot quickly and easily as a cozy and comfortable place: intergluteal folds, folds in the groin area, armpits. Sometimes the infection spreads to the back, skin of the arms, legs, and neck. The disease manifests itself in the form of painful wet spots that are red in color or small blisters. After a certain period of time, the bubbles burst, the affected areas unite and form fairly large areas. You can also recognize thrush in a child due to the following manifestations:
- clearly visible limitation of healthy skin and erosive areas of crimson color;
- the presence of a white coating on the rash;
- damp and even varnished surfaces of areas affected by candida.
In infants, the skin in the anal area most often suffers, since it is very sensitive and delicate. For the purpose of prevention, all pediatricians and Dr. Komarovsky recommend leaving the child without a diaper in order to avoid the formation of suitable conditions for the life of fungal agents. In addition to the skin, yeast fungi can establish and organize colonies on the nails. This type of such a popular disease begins to develop due to high humidity and local injuries. The infection can be noticed due to swelling and hyperemia in the places where candida penetrates the nail plate. With candidiasis, a change in the structure of the nail occurs: it becomes duller, thicker, and brown grooves are formed on top, located transversely. It is worth noting that there is no purulent discharge.
Thrush in the corners of the mouth
This form of the disease often occurs due to the spread of yeast from the child's mouth. Sometimes it develops as an independent disease, then the main cause is a lack of vitamin substances, in particular vitamin B2, which is called riboflavin. It is easy to recognize the infection: the skin in the corners of the mouth cracks, peels, becomes dry, and takes on a reddish color. (It happens that nearby areas serve as localization sites). Candidiasis is the second name of the disease. It often bothers young children. It is quite rare in adults. If it occurs, it occurs in females with a weak immune system.
What is candidal cheilitis?
People are willing to ask about this form of the disease on forums on the Internet. Dr. Komarovsky answers all user questions, including this one. Cheilitis is also called cheilosis. The infection is reflected in the form of inflammation of the mucous glands of the lips, a red border that can peel off and be swollen. Unpleasant characteristic symptoms are thinning of the skin, the presence of pus, burning sensations, yellow scales, the edges of which are raised. The causes of the disease are chemical damage, injuries, bad habits, allergic reactions to cosmetics. Parents, do not treat your child’s thrush on your own!
If you find any suspicious symptoms, take him to the hospital immediately. The doctor will examine you with his experienced eye, prescribe an examination, and then draw up a detailed individual treatment plan. All treatment recommendations listed in the article are provided for informational purposes only. If you have questions, ask our specialist! Let's fight fungi together!
Thrush in a child is a fairly common occurrence. Depending on the cause that causes it, certain types of course of this condition differ. Treatment methods for thrush are prescribed depending on the above factors.
How to cure oral thrush in a baby?
The choice of treatment method depends on several factors. The doctor must take into account the child’s age, the severity of the disease and the location of the fungal colony in the body. Therapeutic measures should be aimed at eliminating the source of the disease, only in this case the treatment will be effective.
Thrush on the tongue of a baby is the most difficult to treat, because... Severe forms of candidiasis require the use of medications. Most pharmaceuticals have contraindications for use in childhood and therefore cannot be prescribed to children. Most often, thrush in infants is treated with folk remedies and topical medications.
General recommendations
In order for the treatment of thrush on the lips, gums, palate and tongue in children to be effective, it is necessary not only to use medications, but also to create favorable conditions for fighting the fungal infection. Parents should adjust the child’s diet and avoid giving him sugary drinks, especially before bedtime. Children should be walked for at least 3 hours every day. It is important to monitor the temperature in the room where it is located and maintain an optimal humidity level.
Children are usually prescribed topical medications, taking into account their age. During a visit to the pediatrician, the mother must inform him about all existing chronic and genetic pathologies in the child. This information is extremely important because each medicine has contraindications for use in certain conditions and diseases. In addition, you should tell the specialist about the medications your baby is taking so that the doctor does not prescribe incompatible medications.
Preparations for oral administration
With repeated infections and severe forms of candidal stomatitis, topical medications may not have the required effect, so doctors prescribe medications for internal use. These medications destroy fungus throughout the body, regardless of its location. Oral medications have a more pronounced effect and prevent re-infection.
In childhood, antifungal drugs can be used, the main component of which is fluconazole. They can be purchased at the pharmacy in the form of capsules (Diflazon, Kandizol, Flugal), syrups (Mikomax) or tablets (Futsis). When the active substance enters the digestive tract, it is absorbed into the blood and distributed throughout the body, eliminating sources of pathology.
Pharmaceutical products for topical use
Oral antifungal drugs are generally not used in infancy. Thrush in infants is treated using local agents that allow you to influence the cause of the disease without harm to the body. The most commonly used topical medications for treating children are:
- Cholisal (gel);
- Vinylin (balm);
- nystatin ointment;
- Levorin (suspension for treating the oral mucosa);
- Kanesten (solution);
- tannin solution.
These drugs are used to treat inflamed areas of the mucous membrane of the palate, tongue and lips of a newborn in accordance with the instructions. The daily number of procedures depends on the age of the child and the drug used.
Traditional therapy
Traditional methods of dealing with the symptoms of thrush on the tongue are often the most acceptable, especially when it comes to treating infants. However, their use should be previously agreed with the pediatrician. Most often, parents use the following home remedies:
- Soda solution. It is prepared by dissolving 1 tsp. soda in 1 tbsp. warm water. For these purposes, only boiled water is suitable. The tongue, cheeks and gums are treated with a swab soaked in soda solution at least 5 times a day.
- Infusion of medicinal herbs. You should combine 1 tbsp. plants such as chamomile, sage, oak bark and calendula. Pour boiling water over this mixture and leave.
- Honey with raspberry juice. Boil honey and raspberry juice three times, taken in equal proportions. Cool the paste and apply it to the inflamed areas of the oral mucosa.
- Zelenka. This substance helps get rid of thrush in a few days. When breastfeeding, the mother needs to treat her nipples with brilliant green before feeding. You can also lubricate the child’s mouth in areas affected by fungus with brilliant green.
What is this?
This disease has the scientific name Candidiasis. Accordingly, its causative agents are called certain fungi belonging to the “Candida” variety.
They are deployed in a wide variety of areas, live in the air, on the human body, and are located in the surrounding space and water.
Due to the presence of certain system failures, the growth and reproduction of fungi of this genus is activated.
This disease in a child’s oral cavity becomes a consequence of dysbiosis, a decrease in the level of immune defense and hormonal imbalance.
It is immunity that causes the manifestation and spread of candidiasis. There are some differences between the problem of this type and regurgitation, which is also observed in humans in childhood.
Causes and symptoms
Medical practice identifies some of the main causes of these problems in childhood:
- violations of the normal level of immune defense of the child’s body;
- development of dysbacteriosis;
- infection with harmful microorganisms that are infectious in nature;
- change for the worse in the normal hormonal levels of the child’s body;
- the presence of other health problems in the child’s oral cavity.
In medical practice, the following pronounced symptoms of this phenomenon are noted:
- the appearance of red spots on the cheeks of an infant;
- the appearance of a white coating on the affected areas several days after the appearance of redness;
- after some time, red spots grow, they begin to turn white and yellow;
- The size of the affected area increases over time from several millimeters to several centimeters.
Separation of fungal plaque occurs with great difficulty; scarlet areas may bleed and their area may increase. The severity of the disease is directly proportional to the size of the affected area.
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms and signs of intestinal candidiasis can appear both together and individually. The following characteristic manifestations of the disease can be distinguished:
- the presence of stool with a liquid consistency;
- the presence of white inclusions in the feces in the form of curdled flakes;
- increased gas formation (flatulence);
- discomfort after eating;
- rumbling in the stomach;
- sleep disorders.
In some cases, with intestinal candidiasis, the child develops general weakness, increased fatigue, and body temperature may rise. When examining the anus, small moist formations in the form of lumps can be detected. Children who are able to describe their condition complain of heaviness and pain in various parts of the abdomen. Newborns show anxiety and react to discomfort by crying frequently.
In the case of the development of an invasive (diffuse) form of intestinal candidiasis, the patient develops diarrhea with blood and mucus, damage to the kidneys, liver, and stomach. This condition is extremely rare in children. According to statistics, it is diagnosed in 1 case out of several thousand.
At home
The following methods for treating this disease at home are recommended:
- Immediately before eating, the child’s tongue should be lubricated with honey to create a favorable environment for treating the disease.
- After eating, you need to give the child a glass of water and wash off the remaining milk from his tongue.
- At the beginning of such a disease, it is necessary to treat the affected areas of the tongue with salt water. To prepare it, you need to mix a spoonful of salt with a glass of water at room temperature.
- It is also recommended to force the child to drink water with honey, 100 grams per day.
You can also take some plants internally: aloe juice, calendula tincture, chamomile decoction. Therapy with similar methods at home takes at least two weeks.
Medication
Treatment with medications involves the use of the following:
- Fluconazole capsules in an amount of no more than one per use, is contraindicated in children under one year of age;
- Candida solution with a concentration of 1%, instillation is performed once a day;
- cyanocobalamin ampoules, one per day, complete treatment of the entire space of the oral area;
- use of Duflucan capsules for treatment, mixed with cyanocobalamin and lubricated the affected area once during the day;
- The mouth is completely lubricated with Nystatin solution once a day.
A combination of folk and home treatment methods gives good results; it is not recommended to use medical products without a doctor’s prescription.
Candida for thrush
It is quite simple to distinguish candida from the problem described. The milk disappears over time, but the red growths remain. Moreover, they only increase in size over time.
The clinical stage of thrush is determined quite easily.
Its pronounced symptoms are:
- a white coating appears on the baby’s tongue in the mouth, which can be removed with a finger;
- the taste of such a coating is sour, with added sweetness;
- The temperature does not rise in such a situation.
The problem does not go away on its own; long-term treatment is necessary until it is completely eliminated.
Complications and consequences
The action in question has some difficulties, which generally boil down to the following:
- The disease may develop into a chronic form with an uncertain course.
- Ulcers appear on the tongue, which subsequently grow into a separate disease.
- Speech disturbances appear in the child.
- An unpleasant odor from the affected area is often observed.
- The child becomes irritable and whiny.
- Persistent changes in the normal state of the acidic environment in the patient’s mouth occur.
You can read what drops are used for sinusitis in adults with antibiotics at the link.
And you can find out the answer to the question - how to relieve toothache at home during pregnancy - here.
Symptoms and forms of the disease
The first signs of thrush in newborns can appear in the first month after birth. Symptoms that should alert parents:
- The child’s habitual behavior changes
- The baby turns away from the mother's breast and does not want to suck milk from the bottle
- The child is restless, cries often, cannot sleep
- Frequent regurgitation appears
- Weight loss due to refusal to eat
A specific picture of candidiasis in young children can be detected by examining the oral mucosa. The variation in manifestations will largely depend on the form of thrush and the stage of the disease.
- The mild stage begins with small red spots on the walls of the mouth, which over time are joined by cheesy white plaques. After removing the plaques, hyperemia is recorded. The mild form does not cause pain to the child.
- With the development of a moderate degree of the disease, a thick cheesy coating is found in the child’s mouth, formed as a result of the combination and enlargement of plaques. After removing several plaques, you can see bloody erosions. At this stage, unpleasant symptoms increase: burning of the mouth and tongue, pain while eating.
- During the severe stage of thrush, intense bleeding of ulcers joins the general symptoms; the disease spreads to the surface of the tongue, affecting the tonsils, gums and palate. A white film of a cheesy consistency affects the entire oral area, including the throat and lips. Symptoms expand with elevated temperature, dysbacteriosis, enlarged lymph nodes, and general malaise.
Infants are most often susceptible to oral candidiasis, which occurs in the following forms:
- Glossitis is infection of the pharynx by pathogenic fungi.
- Stomatitis is a fungal infection of the oral cavity.
- Seizures - fungi multiply on the corners of the mouth, forming cracks and painful cracks.
- Fungal cheilitis is a candidal infection of the lips.
Like many other diseases, thrush has two courses:
Prevention measures
Experts recommend the following preventative measures for this condition:
- Compliance with all oral hygiene instructions.
- Frequent walks in the fresh air.
- Constantly maintaining vitality and performing hardening procedures.
- Proper care for the child’s mouth area.
- Eliminating the smoking habit of parents.
- Regularly undergoing preventive examinations with a doctor to prevent such a problem.
- Removing plaque that appears again on the tongue with hygienic brushes.
- Regular and timely implementation of the procedure for sanitation of the baby’s oral cavity.