Medical certificate
Stomatitis is an inflammatory process in the oral cavity, accompanied by the appearance of small ulcers and aphthae on the surface of the tongue, gums and the inside of the cheeks. This is a fairly common disease. It is characterized by speech impairment in the patient against a background of painful sensations. At the same time, eating and drinking cold or hot drinks becomes very difficult.
Dentists classify stomatitis as a separate disease. After tooth extraction, it can also occur for a number of reasons, both on the part of the doctor (treatment errors) and due to the fault of the patient himself (improper oral care).
Treatment
Medicines are prescribed by a dentist . It is not recommended to engage in treatment on your own. To prescribe drug therapy, it is necessary to determine the type of the disease.
You can buy ulcer cleaning products at the pharmacy. The plaque that has formed on the ulcer itself prevents its healing. Special ointments will clear plaque. Pastes are also used that cover the ulcers with a film, thereby protecting the damaged mucous membrane from external irritants - food and bacteria.
Anesthetic drugs are prescribed when the manifestation of stomatitis is too painful. Some products containing benzocaine, lidocaine, Kalanchoe juice, trimecaine and others will reduce the sensitivity of ulcers before eating. Available in the form of aerosols and pastes.
Doctors recommend antibacterial cleaners, rinses with chlorhexidine, as well as antiviral drugs - terbofen, bonaftone or oxolinic ointment.
To restore epithelium damaged by numerous ulcers, use sea buckthorn oil or propolis. Tooth extraction is often accompanied by an aphthous type of disease. These remedies help quickly restore the mucous membrane.
Types of stomatitis
Depending on the type of infection, several types of lesions are distinguished. The most common are the following:
- Catarrhal stomatitis. This is the most common form of the disease. It is characterized by increased salivation, the appearance of swelling of the mucous membrane, and the formation of a yellowish or white coating on it. Stomatitis is accompanied by bad breath and bleeding gums.
- Candidal stomatitis. Occurs due to the activation of fungi of the genus Candida. The patient feels a burning sensation in the larynx, and a coating of cheesy consistency forms on the mucous membranes. In rare cases, the ability to taste food is lost.
- Aphthous stomatitis. It develops against the background of a genetic predisposition, gastrointestinal diseases, and allergies to anesthesia. The disease manifests itself in the formation of ulcers on the mucous membranes of the mouth, which is accompanied by pain and weakness.
Separately, stomatitis after wisdom tooth removal should be highlighted. This is a common occurrence that also requires qualified medical care.
Forms and varieties of the disease
There are different forms of damage, the most common of them are as follows:
- catarrhal The most common variant of the course of the disease in the early stages, the main symptom is intense salivation, swelling of the mucous membrane, and bleeding gums. The main causes are caries, lack of proper oral hygiene, infection,
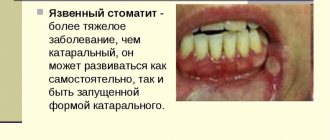
- ulcerative This type of stomatitis most often affects patients with disorders of the gastrointestinal tract,
- aphthous form. Occurs from an infectious lesion, gastrointestinal diseases, an allergic reaction to anesthesia preceding tooth extraction. Characteristic symptoms: mouth ulcers, general weakness, pain while eating,
- candidal stomatitis. The peculiarity of the disease is that the disease {amp}amp;#171,selects{amp}amp;#187, patients from two age categories: preschool children and the elderly. In its advanced form, the disease deprives the patient of the ability to distinguish the taste of drinks and food, leads to a significant decrease in body tone,
- herpes stomatitis. Occurs due to the herpes virus.
The reason for its appearance is enterovirus. From a medical point of view, it is a complex virus that localizes and develops in the gastrointestinal tract.
There are three main ways the virus can enter the body:
- along with raw water,
- as a result of insufficient heat treatment or consumption of unwashed products,
- from sick animals,
- violation of personal hygiene rules.
Risk group, children under 3 years of age, adult patients suffering from enterovirus are rare. The likelihood of contracting a variant of the disease increases in the first few days after tooth extraction.
Regardless of the cause, the symptoms are similar and include:
- bubble formations in the mouth, causing discomfort when chewing food,
- there is significant redness of the mucous membrane,
- Having removed the plaque from the cheek, you will find redness underneath, and in the later stages of the disease, bleeding areas,
- Bad breath occurs, and hygiene measures become more painful; any touch to the mucous membrane causes discomfort and pain.
Depending on the type of infection, several types of lesions are distinguished. The most common are the following:
- Catarrhal stomatitis. This is the most common form of the disease. It is characterized by increased salivation, the appearance of swelling of the mucous membrane, and the formation of a yellowish or white coating on it. Stomatitis is accompanied by bad breath and bleeding gums.
- Candidal stomatitis. Occurs due to the activation of fungi of the genus Candida. The patient feels a burning sensation in the larynx, and a coating of cheesy consistency forms on the mucous membranes. In rare cases, the ability to taste food is lost.
- Aphthous stomatitis. It develops against the background of a genetic predisposition, gastrointestinal diseases, and allergies to anesthesia. The disease manifests itself in the formation of ulcers on the mucous membranes of the mouth, which is accompanied by pain and weakness.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Articaine with epinephrine Forte instructions for use: indications, contraindications, side effects - description of Articaine with epinephrine Forte solution for injection.
40 mg 0.01 mg/1 ml: 1.7 ml cartridges 10, 50 or 100 pcs., 1 ml or 2 ml amp. 5, 10, 100 or 250 pcs. (41896) - directory of drugs and medicines. Separately, stomatitis after wisdom tooth removal should be highlighted. This is a common occurrence that also requires qualified medical care.
Mistakes of patients and doctors
The human factor works always and everywhere, including in the doctor’s office. Stomatitis after tooth extraction can occur due to the fault of a dentist, even with extensive experience. We are talking about the following situations:
- use of non-sterile instruments during tooth resection;
- leaving root fragments in the hole;
- incorrect tooth extraction.
After tooth extraction, the doctor always gives recommendations to the patient regarding oral care in the next few days. For example, refusal to frequently rinse or palpate a blood clot at the site of the manipulations. Neglecting these tips can lead to stomatitis.
Main reasons
There are many such factors, the most common of which are:
- infection through unsterile dental instruments,
- violation of the rules of oral hygiene after tooth extraction,
- allergic reaction to anesthesia,
- after a tooth was removed, its fragments remained in the gums,
- weakened immune system at the time of visiting the dentist,
- wisdom tooth removal,
- food from dirty dishes,
- genetic predisposition,
- contact (kiss) with a person who has already become infected with stomatitis, at least approximately coinciding with tooth extraction.
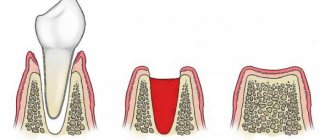
The oral mucosa is a vulnerable place for infections. Especially after dental procedures, when the mucous membrane is damaged and the gum tissue is deformed. Pathological microorganisms can cause infection under the influence of the following factors:
- absence of a blood clot at the site of the extracted tooth;
- weakened immune system;
- allergies to anesthesia and other drugs that the doctor uses during treatment.
Clinical picture
Stomatitis in the mouth after tooth extraction manifests itself with a pronounced clinical picture. First, the patient experiences swelling of the gums, redness, and increased pain after eating. As the disease progresses, new signs appear:
- headache;
- burning in the mouth;
- swelling of the mucous membranes, cheeks and tongue;
- the appearance of erosions and ulcers;
- increased salivation;
- temperature increase;
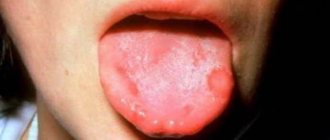
- the appearance of a white or yellowish coating on the tongue;
- enlargement of lymph nodes due to their inflammation;
- loss of appetite;
- fast fatiguability;
- gagging after eating.
If the above symptoms occur, you should immediately contact your dentist.
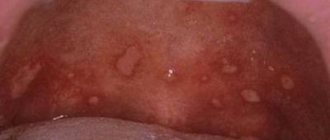
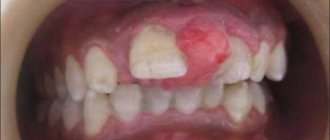
What do ulcers look like with stomatitis?
Sores are either oval or round in shape. In the middle they have a grayish or whitish color, and externally they have a red edging. The tissue around such formations appears healthy.
The patient finds it very difficult to eat, and the ulcers cause unpleasant pain.
Interesting to know: If a person has high immunity, stomatitis can occur in a mild form with the formation of just one ulcer.
Associated symptoms:
- temperature increase;
- inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- headache;
- loss of appetite or vomiting after eating;
- weakness in the body or irritability;
- and even constipation.
In addition, increased saliva production and heavy coating on the tongue are possible.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of stomatitis after tooth extraction is based on a physical examination of the oral cavity and a study of the patient’s medical history. In the presence of white plaque, erosions and ulcers, the procedure does not require much time. However, in young patients, diagnosis can be difficult due to the inability of the child to talk about his feelings. Parents should be attentive and monitor the child’s health after tooth resection.
During the examination, additional blood tests may be required to determine glucose, and bacterial culture from the affected area to identify the causative agent of the disease. Based on the test results, the dentist prescribes therapy.
Drug therapy
After tooth extraction, stomatitis on the gums, tongue and inner surface of the cheeks is accompanied by rather unpleasant symptoms. However, for modern medicine its treatment does not present any particular difficulties. For help, you should first contact a dentist. In rare cases, additional consultation is required from specialized specialists: a gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, immunologist, etc. A similar need arises when the course of stomatitis is accompanied by other chronic diseases against the background of decreased immunity or hormonal imbalances.
Regardless of the form of stomatitis after tooth extraction in adults and children, treatment begins with the following procedures:
- Professional sanitation of the oral cavity.
- Treatment of affected areas with antiseptics.
- Rinse.
In the aphthous form of the disease, therapy involves the use of drugs and immunomodulators that act locally on the inflammation. In the case of candidal stomatitis, agents that destroy fungal colonies are prescribed. For the catarrhal variety of the disease, therapy begins with eliminating the underlying disease that led to the formation of ulcers in the oral cavity.
Some patients try to overcome the disease on their own and take antibiotics. However, after a while they notice that there is no visible improvement. Stomatitis is viral in nature, so antibacterial agents in its treatment are ineffective. Antibiotics can only help with its infectious form.
How to treat stomatitis after tooth extraction? There are no drugs that can completely get rid of it. However, it is possible to stop local rashes on the oral mucosa with the help of medications and traditional medicine recipes.
To eliminate stomatitis, local antiseptics are usually prescribed. They are available in the form of rinses, aerosols and ointments. The drug Hexoral is particularly effective. The aerosol has an antimicrobial and analgesic effect. The spray is sprayed onto the affected areas of the mucous membrane twice a day. It is better to perform the procedure after eating. Hexoral is also available in tablet form.
Special products are recommended for cleaning ulcers. However, their healing may be delayed due to existing plaque. Therefore, additional help from gels may be required to eliminate it. After cleaning the hole from plaque, you need to start using ointments to form a film on this area. It will protect the damaged mucosa from pathogenic flora and food particles.
In case of painful stomatitis, the dentist prescribes anesthetics. They allow you to reduce sensitivity, including before eating. Lidocaine, Trimecaine, and Benzocaine are particularly effective.
Treatment of damaged areas with iodine helps to heal wounds. The procedure should be repeated for two days. Some patients prefer brilliant green to iodine. In fact, this approach is wrong. Zelenka helps dry out the oral mucosa. It is not suitable for the treatment of infectious and inflammatory processes.
To treat ulcers and canker sores, dentists recommend oxolinic ointment. However, it is important to understand that for use on mucous membranes, drugs are best used in gel form. Ointments do not have the desired effect, they are washed off almost instantly with saliva and do not have time to be absorbed.
To summarize the above, we can imagine several drugs used in medical practice today for the treatment of stomatitis:
- "Viferon gel" and "Cholisal gel". These are antiseptic drugs prescribed to speed up the recovery processes on the mucous membrane.
- "Actovegin gel", "Solcoseryl gel". These remedies are especially effective for the aphthous type of stomatitis. They accelerate the regeneration processes of the mucous membrane and have a positive effect on erosive rashes in the mouth.
- "Miramistin". It is used for rinsing and has a pronounced antiseptic effect.
The choice of a specific drug, as well as its dosage, is determined by the doctor.
Professional care and disinfection
Treatment of stomatitis that occurs after tooth extraction begins with the elimination of concomitant diseases in the oral cavity and professional teeth cleaning. Then it is necessary to disinfect the surface of the mucous membrane using antiseptics:
- soda solution;
- brilliant greens;
- hydrogen peroxide;
- potassium permanganate solution;
- "Chlorhexidine";
- "Miramistina";
- "Furacilina".
This will minimize the number of pathogenic microorganisms, which will speed up recovery. Before treating stomatitis with any medication, you must obtain permission from your doctor.
Hydrogen peroxide
Help from traditional medicine
In addition to drug treatment of stomatitis after tooth extraction, there is also a non-drug option, the effectiveness of which is often not inferior to pharmaceutical products. However, before starting to use traditional medicine recipes, it is important to consult a dentist. It is important to consider that with the candidal form of the disease they will not bring any benefit at all. In most cases they have an antiseptic effect. Therefore, the fungal flora is not properly influenced.
On the positive side, sea buckthorn and rosehip oils, vanillin, and propolis have proven themselves in the treatment of stomatitis after tooth extraction in adults. Other popular traditional medicine recipes include the following:
- Various infusions. As the main ingredients you can use calendula, oak bark, St. John's wort, sage or chamomile. Brew a few tablespoons of the dry mixture with 0.5 liters of boiling water and let it brew. Rinsing allows you to relieve unpleasant symptoms and get rid of microorganisms that cause inflammation. Procedures can be repeated several times a day.
- Compresses. For preparation, you can use a mixture of chopped garlic with yogurt or raw potatoes. To prepare the last recipe, just wash, peel and grate one tuber. You can then apply it to the affected areas for a few minutes.
- Rose hip decoction. This drug is taken orally. The decoction has a positive effect on the immune system, improves the body's resistance to various diseases due to its high vitamin C content.
It is important to understand that using exclusively traditional medicine recipes does not cure stomatitis after tooth extraction in a child or adult. Only complex therapy helps to get rid of the disease and its symptoms.
Why shouldn't you self-medicate?
The course of stomatitis causes a lot of inconvenience to the patient; it is not difficult to get rid of the disease so that the patient quickly seeks help from specialists. Therapy includes:
- preventive cleaning of the oral cavity,
- treating the area affected by the disease using antiseptics,
- rinsing.
If stomatitis is ulcerative or aphthous, then the basis of treatment will be anti-inflammatory drugs and immunomodulators. If we are talking about the candida variety of the disease, the doctor will prescribe antifungal agents. It is important to be aware that infectious and viral stomatitis are fundamentally different diseases and are treated differently. Antibiotics are effective against the infectious form, but they are useless against the viral form.
Pain relief is required at all stages of treatment. The following means will help achieve the desired effect in this direction:
- Lidocaine,
- Trimekain,
- Benzocaine.
Properly selected toothpaste helps achieve the effect. In the context of this situation, it should have an analgesic and antibacterial effect. The following ointments should be considered as auxiliary methods:
- oxolinic,
- tebrophenic acid,
- bonaftone.
When applied topically to the mucous membrane, only gels and rinses can provide the desired effect. Creams are not suitable; they are washed off with saliva faster than they can be absorbed. For local exposure, the following are most often used:
- antiseptics (Viferon-gel),
- drugs that stimulate the regeneration of the mucous membrane (solcoseryl, actovegin),
- antiseptics (Miramistin). This is especially true for herpetic stomatitis.
Along with medications, traditional methods are also widely used. So, to combat this disease they use:
- sea buckthorn oil,
- calendula infusions,
- rosehip decoction. It should be used not only for rinsing, but also to drink,
- solutions based on potassium permanganate or soda. Their concentration should be weak so as not to cause additional damage to the mucous membrane already affected by the disease.
Treatment with folk remedies is not considered a priority. Sometimes they provide an occasional effect, but you should not pin your hopes on alternative medicine.
The disease is dangerous and can lead to serious consequences. If the problem made itself felt after tooth extraction.
Do you feel nervous before visiting the dentist?YesNo
Having lost time on fruitless attempts to get rid of the disease on his own, the patient, contrary to logic and common sense, himself stimulates the development of the disease. On the other hand, modern medicine has an impressive range of means and methods to cure this disease that occurs after tooth extraction quickly and without discomfort for the patient. The determining factor in the context of upcoming therapy is timely seeking help.
Stomatitis, a treatable, albeit insidious disease. Professional treatment and diagnosis will help you avoid the consequences. As soon as you notice symptoms of the disease, visiting a doctor becomes a priority.
Consequences of the disease
In the photo, stomatitis after removal of a wisdom tooth or molar looks quite unpleasant. However, not all patients seek medical help after detecting signs of the disease. Lack of timely treatment can lead to negative consequences.
Pathogenic microorganisms very quickly begin to produce toxins or poison of biological origin. Such substances, entering the blood or stomach, poison the body. The person's health deteriorates. Weakness, headaches and joint pain appear, and appetite worsens. The clinical picture may be supplemented by stool disorder and fever.
Other complications may also occur, ranging from inflammation of the throat to destruction of the jaw bones and infection of the circulatory system. That is why treatment of stomatitis after tooth extraction should begin immediately after confirmation of the diagnosis by the dentist.
Prevention methods
Stomatitis is a disease that is characterized by relapses. Therefore, the basis of prevention is proper oral hygiene, normalization of diet, and strengthening of the immune system. Doctors also advise adhering to the following recommendations:
- Oral hygiene should be adequate, but should not be overzealous. It is enough to brush your teeth regularly and visit the dentist once a year. If carious processes or other diseases are detected, they must be eliminated immediately.
- It is recommended to remove allergenic foods from the diet. You will also have to give up hard, spicy foods. They irritate the mucous membrane, which can provoke a recurrence of stomatitis after the removal of a wisdom tooth or molar unit.
- Incorrectly installed braces or dentures often cause ulcers and sores in the mouth. Therefore, before installing corrective systems, it is important to take a responsible approach to choosing a dental clinic and the doctor directly.
If stomatitis appears after tooth extraction, you should not self-medicate or neglect the problem. Only qualified and timely medical care can eliminate the disease.
Causes of stomatitis in adults and its types
In adults, stomatitis most often develops as a result of weakened immunity and the activation of viruses, bacteria and fungi as a result. The development of stomatitis is provoked by a lack of substances such as iron and zinc in the body. Another common cause of stomatitis is various injuries to the oral cavity resulting from chemical, thermal or mechanical exposure.
Stomatitis can take various forms:
The variety of types and forms of stomatitis emphasizes the fact that it is important not to self-medicate, but to immediately contact a doctor in the department of therapeutic dentistry who can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment, since its tactics may vary depending on the type of stomatitis.