1023
Periodontal disease is a disease that occurs infrequently - it is diagnosed in only 3 people out of 100.
But the consequences of the disease are dire - in the absence of proper treatment, a person can lose all his teeth.
Implantation today opens up many opportunities for replacing elements lost due to pathology. Let's consider all aspects of the operation for this unpleasant diagnosis.
The insidiousness of pathology
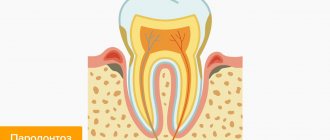
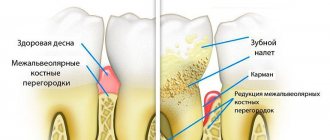
Periodontium is a collection of tissues (periodontium, tooth enamel, dental pulp, gums, alveolar processes, dentin, cement). All these components surround and hold the tooth in its socket.
With periodontal disease, due to insufficient oxygen supply, pathological changes occur in periodontal tissue.
The neck of the tooth is exposed, uniform destruction of bone tissue develops, and the enamel becomes thinner. It is impossible to cure this disease completely; it is only possible to stop its further development.
Not so long ago, doctors considered the implantation of a rod for periodontal disease to be a pointless waste of effort and money. There was an opinion that with this pathology the system would not be fixed firmly and would simply fall out . Risks were associated with low bone volume and possible inflammation of the gums around the artificial tooth.
Fixed dentures are also not a panacea for the disease, due to ongoing bone degeneration. It is not uncommon for an installed bridge to fall out after just 2 years.
To minimize these complications, comprehensive treatment is necessary:
- therapeutic,
- orthopedic,
- surgical.
Therapeutic treatment involves taking medications and physiotherapy. The drugs used in treatment are anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins, hormones.
Physiotherapy includes short-wave ultraviolet irradiation and electrophoresis. Gum massage is also an important part of pre-therapy.
Orthopedic treatment includes splinting mobile teeth, when they are tied together with a bottom thread or using fiberglass.
Periodontal disease always leads to tooth loss; over time, the neck of the tooth becomes increasingly exposed and bone tissue decreases. In this regard, after complex treatment and removal of teeth that cannot be restored, artificial roots are installed.
Is it possible to have implantation?
Today, carrying out an implantation procedure if a patient has periodontitis or periodontal disease is a difficult task. This is due to the severe inflammation that necessarily accompanies this disease.
Next, we will consider the main problems that the specialist and the patient may encounter during the operation.
Bone disorders
Lack of bone tissue and its fragility require a procedure to build it up. This takes at least 5-6 months. This is a full-fledged surgical operation that requires a fairly large investment of money.
Mobility
If teeth are severely loose, they must be removed. The period of tissue restoration takes up to six months, so implantation will have to be postponed.
Inflammation
With periodontal disease, all tissues surrounding the tooth are susceptible to inflammatory processes, which can affect the reliability of the implant and its further survival.
Rejection
Unfortunately, even after an implantation operation, the doctor cannot give a 100% guarantee of a successful result. The proximity of the tissues in which the inflammatory process occurs can affect the outcome of the entire work.
The patient may encounter the above situations if implantation is performed using the classical two-stage method, since in this case the bone tissue must meet strict requirements in terms of volume and quality.
Methods used
Clasp removable dentures, which previously were the only way to restore the dentition, do not prevent the progressive destruction of periodontal disease.
Therefore, implantation is not only indicated, but is the only possible way to restore dental functions. Modern dentistry offers three methods:
- The classic method, in which the pin is installed in the upper layer of bone tissue.
But this method is not always effective, since the process of bone loss continues after surgery. Even sinus lifting doesn't help. Its duration is also not in favor of the method. 4 to 5 months must pass before the procedure is completed. And all this time there will be no load on the bone, which will also affect its condition. - With the express method, implantation is carried out in one stage. This technique requires careful adherence to technical nuances. The advantages include low trauma and low risk of infection.
- Basal technique. The entire procedure can take only 3 to 5 days. This provides immediate loading, which is very important for the bone. This technique involves installing a rod into the deepest – basal layer of bone, which is characterized by its high density and resistance to degeneration processes.
The basal method is also supported by the fact that artificial roots can be installed at an angle. This increases the area of contact between the surface of the system and the bone tissue.
What risks exist with conventional implantation against the background of periodontitis and periodontal disease?
The main risks of this type of implantation have long been known:
- High probability of rejection . If this process occurs in the area of the front teeth, re-implantation will be more difficult and less effective.
- Implant instability . The bone surrounding the artificial root is porous and cannot support stress. The implant becomes mobile, which leads to discomfort and possible breakage of the prosthesis.
- Inflammation of the gums . Infection of soft tissues contributes to disruption of the gingival contour and exposure of the abutment. This is not aesthetically pleasing and is fraught with the spread of infection to deeper layers.
Therefore, in case of such pathology, alternative methods of implantation are used.
Requirements for systems
The choice of implant for periodontal disease is influenced by two factors:
- form . The structures must have a wide coil diameter and an elongated, conical shape that can penetrate into the deep layers of the bone;
- covering . It should prevent the proliferation of pathological microorganisms and promote rapid and high-quality fusion of the bone and the rod.
To achieve good gingival aesthetics, platform switching technology is used.
Almost all modern models are made of titanium alloy. This bioinert material almost never causes allergies or rejection.
But if an allergic reaction still occurs, you can choose designs made of corundum ceramics and zirconium.
The most popular systems used for periodontal disease are models from Alpha Bio, Straumman, Nobel Biocare, Astra Tech.
Options for restoring chewing function
When all teeth are removed due to gum problems
After extraction of hopeless units, there are 2 ways to restore chewing function:
- Installation of a complete removable denture.
- Prosthetics on implants.
Complete removable dentures are one of the ways to restore chewing function.
Removable dentures are cheaper, but have a number of disadvantages:
- long-term adaptation;
- the mobility of the prosthesis causes discomfort when eating;
- aesthetics are far from natural;
- chafing gums;
- lack of natural load on the bone will lead to irreversible atrophy.
Implantation for periodontitis is the right decision. The infection is localized in the periodontal tissues, and the inflammation covers only that part of the jaw on which the teeth are preserved. After removing the latter along with the infected tissues, osseointegration will be complete .
When most of the teeth need to be saved
You can install bridges or artificial crowns on implants. The disadvantage of the first option is the gradual destruction of the supporting units, which are pre-ground. The annual percentage of their loss under bridges is 30%. Therefore, doctors adhere to a rational strategy:
- at the initial stage of the disease, drug therapy is carried out;
- Titanium rods are installed in empty spaces in the jaw.
If a specialist has doubts about the advisability of preserving the remaining teeth, then they are subject to removal followed by implantation.
Basal method
Basal implantation allows you to load the artificial root in the shortest possible time. The load that is transferred to the bone during periodontal disease is very important. In this way, blood circulation processes are stimulated, which means that the supply of oxygen to bone cells and surrounding tissues increases.
Under conditions of periodontal hypoxia, such changes have a beneficial effect on the treatment of periodontal disease and prevent bone atrophy. In addition, improved blood circulation allows tissue to grow around the system and it integrates faster.
The technique involves implantation not into the spongy, but into the basal, denser layer of bone, which does not undergo resorption. This ensures instantaneous loading.
With the basal technique, the doctor selects designs of different shapes and structures. Each of them has its own function and features. The following types of systems are used:
- compression They are positioned in narrow spaces, affecting spongy tissue. The special structure of the structures makes it possible to compact the cancellous bone, thereby creating a stable layer and ensuring primary stability;
- basal - they are screwed into the basal bone.
By combining basal and compression models , the doctor opens up a wide field of maneuverability. Such structures can be installed not only straight, but also at an angle, close to each other, or when the bone volume is insufficient.
The doctor selects a whole set of systems of different shapes, lengths, widths and threads. An individual design appears with the main component – the prosthesis.
What is bloodless implantation and its technique.
Let's find out here whether implantation can be performed if you have diabetes.
At this address https://zubovv.ru/implantatsiya/metodiki/lazernaya/innovatsionnyiy-podhod.html we offer a selection of positive and negative reviews about laser dental implantation.
Is implantation possible for severe forms of periodontal disease and periodontitis?
It’s sad, but dentists’ assurances that after certain preparation the implantation will be successful are not confirmed in practice.
Let's explain why:
- To restore the volume of bone tissue, surgery will be required. It costs money, requires several months of rehabilitation, but the most unpleasant thing is that it does not guarantee regeneration of the bone structure, and in case of granulating periodontal disease and generalized periodontitis it is not used at all;
- with a large affected area, the inflammatory process can affect not only the upper layers of the gums, but also the basal ones. In this case, even single-piece implants with an angular multi-unit abutment, used in basal implantation, cannot always provide reliable support.
Advantages and disadvantages
The use of the basal technique for periodontal disease has many advantages:
- no need to build up bone tissue;
- treatment according to individual characteristics. To reduce the healing period and ensure uniform loading, structures that differ in shape, length and thread will be selected;
- short treatment process;
- bone tissue is restored due to stimulation of blood circulation;
- few contraindications;
- resistance to microorganisms - since the rod is installed in the deep layers of the bone, access of microbes and bacteria to it is difficult, which means the risk of rejection is minimal;
- it is possible to restore the tooth immediately after removal;
- can be performed with significant bone atrophy;
The disadvantages of the technique include the lack of qualified specialists. There are very few truly professional doctors who have undergone specialized training and know all the nuances of the basal technique, and the chances of falling into the hands of an unprofessional are very high.
To become a real professional, you need to study at the International Foundation of Implantologists, and studying there is not cheap.
In addition, the doctor must not only be a surgeon and orthopedist, but also be able to simulate treatment using special computer programs.
Periodontal disease – is implantation possible?
Periodontal disease is a disease of the dental-ligamentous apparatus of a non-inflammatory nature. The reasons for it are not fully understood. Risk factors are heredity, decreased immunity, systemic diseases of the body. The disease manifests itself as a deficiency state in which tissue nutrition is disrupted and atrophy occurs.
You can understand that a patient has periodontal disease by external signs:
- Recession of the gingival margin.
- Wedge-shaped defect.
- Blueness or whitishness of the mucous membrane.
- Bleeding may occur.
According to the patient's complaints - sensations of itching, burning, numbness of the gum mucosa. It is not difficult to recognize periodontal disease using an orthopantomogram. The bone descends and its density decreases.
Obviously, in such cases, installing an implant involves serious risks. It is impossible to cure periodontal disease completely (that is, the tissue damage that has already occurred cannot be restored). However, its development can be stopped. Complex therapy includes antibiotics, local procedures, and sometimes injections into the gums are required. Ultrasound has proven itself well in the treatment of periodontal disease.
After a course of periodontal treatment, the patient has a chance of successful implantation. The doctor will be able to determine the possibility of surgery based on the results of the examination.
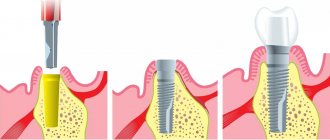
Stages of implementation
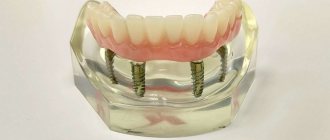
Basal implantation includes 4 procedures:
- diagnostics and preliminary preparation;
- modeling;
- implantation of rods;
- prosthetics.
Let's look at each stage in detail.
- Diagnostics takes place in one to two days. At this stage, the doctor comprehensively examines the patient, examines the bone tissue and oral cavity, and during this period a computed tomography is performed.
During the consultation, the doctor asks the patient about chronic diseases and gives recommendations on preoperative actions. At the same time, the necessary tests are taken, including a blood test.The patient undergoes examination by a specialized doctor. Moreover, the initial consultation can take place not only in the doctor’s office, but also via video link, and files with CT data can be sent by email.
This method is convenient if the patient lives far from the clinic, in another city or region, and traveling every time is inconvenient. At the preliminary stage, comprehensive treatment of periodontal disease and removal of teeth that are unsuitable from a functional and aesthetic point of view are carried out.
- At the computer modeling stage , the doctor evaluates the atrophied bone, selects a place to install the system so as not to touch important nerves, and selects the optimal design.
To do this, the data obtained from the computed tomography scan is saved to a computer. The further treatment process is simulated using special software. It is sometimes supplied by manufacturers along with systems. - Installation of the structure is carried out by cutting or puncture. Piercing is often used for periodontal disease, as it is suitable for patients with weak gums. The entire procedure can be performed without stitches.
- 3 days after implantation, the prosthesis is installed .
It is made using impressions taken from the patient’s teeth. This prosthesis is made of plastic and is temporary. You need to wear it for about 3 years until it loses its appearance. Only after this time, permanent crowns are installed, which will last at least 20 years.
The video presents the stages of implantation for periodontitis and periodontal disease.
Stages of tooth restoration for periodontal problems
Before starting surgery, a specialist will examine the oral cavity to find out whether it is possible to install implants for periodontal disease and assess the possible risks. The prosthesis is installed only if there are no contraindications. The operation consists of several stages:
- Instrumental diagnostics. Panoramic photographs of the jaw are taken. The optimal method of implantation, as well as its size and shape, is selected.
- Sanitation. Before the procedure, caries, pulpitis must be cured and inflammatory processes in the soft tissues of the oral cavity must be eliminated. If necessary, antibacterial therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures are carried out.
- Removing loose teeth or eliminating their mobility using splinting - joining each other from the inside of the row with a special strong thread.
- Implantation. Installation of the metal rod and fixation of the abutment are carried out during one visit to the dentist. If there are no contraindications, experts give preference to the transgingival method of implantation for periodontitis. In this case, rehabilitation takes less time. Immediately after the procedure, impressions of the jaw are taken to make the prosthesis.
- Prosthetics. The installation of the structure is carried out 4-7 days after implantation of the rods, which stimulate bone tissue, accelerating the process of its regeneration.
Diagnostics is carried out in just 1-2 days, with the help of which the doctor conducts a comprehensive examination of the patient. He models his bone tissue and oral cavity, using CT. The specialist must know about the possible chronic ailments of his patient in order to give the necessary recommendations on further actions before the operation. The patient undergoes tests, where blood counts are of great importance.
After the examination, the patient must have all loose teeth removed. Using computer modeling, the doctor can see bone atrophy. He selects a place to install the system, selecting the optimal design without damaging important nerves.
All data through the program allows you to select further treatment. Installation of implants is done using punctures or incisions. For patients with weak gums, piercings are better suited. They are performed without incisions and subsequent suturing.
After three days, the patient is given temporary dentures, which are made after an impression of the patient’s teeth is taken. The structure is made of plastic. After some time, you can begin installing permanent crowns. They will serve the patient for about 20 years.
Dental implantation for periodontal disease is associated with risks of disease progression. Its effectiveness depends on a number of factors:
- stages of the disease;
- therapy methods;
- quality of materials used;
- doctor's professionalism;
- compliance by the patient with all the specialist’s recommendations.
In case of generalized periodontitis and granulating periodontal disease, such a procedure is not carried out, and prosthetics have to be abandoned. Over time, the inflammatory process penetrates into the basal layers of tissue, and even one-piece implants cannot guarantee reliable support.
Features of rehabilitation
For the operation to be successful, you must follow all the doctor’s instructions and recommendations:
- Carefully care for dental structures. Particular attention should be paid to the back of the artificial tooth;
- Be sure to clean the interdental spaces. You can use dental floss, but not everyone knows how to use it and injures their gums. The optimal solution is to use an irrigator or a dental brush;
- Once every six months, carry out professional teeth cleaning , your own and artificial ones.
- do not drink alcohol, do not smoke, avoid sports and heavy physical activity during the first postoperative period.
- rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions , take prescribed medications.
During the postoperative period, a gentle diet is important, excluding foods that irritate the oral mucosa.
What is periodontitis - why are there difficulties when installing implants?
The disease is characterized by inflammation of periodontal structures, which leads to disruption of the periodontal junction and destruction of the alveolar process of the jaw. Periodontal tissues include:
- outer cementum layer of the root;
- periodontal ligaments;
- bone bed (alveolus);
- gums.
The listed elements hold and absorb the tooth. Inflammation leads to weakening of the periodontal ligaments, destruction of the bone, which threatens the loosening and loss of units .
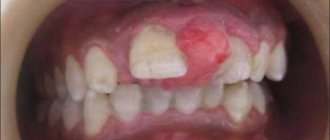
Each stage of periodontitis is characterized by certain symptoms:
- At the initial stage, the pathology is manifested by swelling, redness, and bleeding of the gums. Moderate vascular changes are clearly expressed in the oral cavity, which triggers atrophic processes in the periodontal structures. A decrease in bone volume is detected in the interdental septa, and periodontal pockets of varying depths are formed.
- The medium and severe stages are accompanied by active bone resorption, exposure of the necks of the teeth, and deformation of the interdental septa.
Possible complications after implantation of titanium roots due to inflammation of the tissues of the dental system:
- insufficient stability of the implant in atrophied bone;
- infection of the mucous membrane over the structure;
- peri-implantitis due to damage to the bone bed;
- rod rejection.
Risks and complications
Implantation during pathological processes in the periodontium can cause the following complications:
- Bleeding during surgery. It is eliminated using hemostatic techniques.
It can also occur with high blood pressure, fear of surgery, or if blood clotting is impaired. The solution to the problem is different in each case, some are helped by taking sedatives, others by taking blood pressure-lowering medications. - Pain . If it occurs during surgery, the doctor increases anesthesia. In the postoperative period, pain is considered normal; the doctor always prescribes strong painkillers.
- Swelling is also considered a natural reaction of the body to injury. They usually last no more than a week; to reduce swelling, short-term application of cold to the area is recommended.
- Elevated temperature can be both normal and a sign of complications. If it does not go astray and remains around 38 degrees, you should consult a dentist.
- The patient himself is most often to blame for suture dehiscence
- Implant rejection. In this case, it is removed and a new one is installed after a month or two.
Absolute and relative contraindications to simultaneous dental implantation, features of its implementation.
In this publication we will tell you what dental implants are and what their cost is.
Here https://zubovv.ru/implantatsiya/metodiki/chem-mini-otlichayutsya-ot-obyichnyih.html we offer detailed information about prosthetics on mini-implants.
What types of implantation are in demand for periodontal diseases?
Depending on the severity and extent of the pathological process, the following may be used:
- All - on -6 with immediate load. Allows the prosthesis to be secured to 6 implants. The process of their installation is planned based on CT results and is highly accurate due to the use of a special template during surgery. The presence of six supports helps to distribute the load more evenly when chewing.
- All - on -4 with the installation of Zygoma zygomatic implants . The prosthesis is fixed on two regular and two long implants, screwed into the atrophy-resistant zygomatic bone. Thanks to this, from the first minute the implants receive high primary stabilization.
- Individual basal implantation . Used for moderate to severe periodontitis. It can be used both for the restoration of several teeth and the entire jaw. The production of individual implants is carried out in the laboratory using 3D printing (based on the patient’s CT data).
Answers on questions
Many patients are interested in some questions regarding implantation for periodontal disease:
- Is it true that pathology is a direct contraindication to implantation?
Periodontal disease certainly complicates the surgical process, but if the correct tactics are chosen, the protocol is followed and preliminary treatment is carried out, the procedure can be carried out.At the same time, in order to correctly distribute the load on the teeth, you need to install splints. They fix loose teeth.
- Will the system fully function?
If it was installed in compliance with all requirements, and the patient continues comprehensive treatment of periodontal disease, while following the doctor’s instructions, the structure will fully perform the functions of a real tooth. - Should I try to save my loose teeth?
This is quite possible if the pathology is at an early stage. Comprehensive treatment should be carried out, including orthopedic treatment, consisting of splinting.
Is it possible to place implants with periodontal disease?
Periodontal disease is a chronic disease of periodontal tissues in which bone resorption occurs around the tooth roots. It occurs extremely rarely - in 1-7% of cases. It differs from periodontitis in the absence of an inflammatory process and its generalized nature (the problem concerns the entire jaw, and not a separate area).
Causes of the disease:
- deterioration of metabolism, which negatively affects the blood supply to soft tissues;
- osteopenia - pathologically low density or mass of bone structures, leading to resorption;
- dysfunction of the nervous and immune systems;
- atherosclerosis;
- diabetes;
- genetic predisposition;
- mechanical damage, dental trauma.
Stages of periodontal disease:
- Mild - asymptomatic, with only occasional itching in the gums, discomfort while eating, and occasional bad breath. Determined by a panoramic radiograph - shows bone resorption of less than ⅓.
- Medium - manifested by frequent itching, exposure of the necks of the teeth. The image reveals bone resorption up to half of the tooth root.
- Severe - there is loosening and protrusion of teeth, an abundance of plaque and deposits, bad breath, a reaction to thermal irritants and solid foods. The x-ray shows resorption at the level of ⅔ of the tooth.
Implantation for periodontal disease is a reliable way to restore lost teeth and save the remaining ones. Due to the absence of an inflammatory process in this disease, there is no need for preliminary therapy. Before implanting titanium rods, the main task is to identify and eliminate the cause of jawbone recession and remove teeth that cannot be saved.
Obstacles to implantation may include:
- the impossibility of detecting and treating diseases that cause bone loss - implants are placed only if you are confident that the required volume can be maintained.
- hereditary factors or diabetes mellitus are involved in the development of periodontal disease;
- health problems that increase the risk of structural failure;
- poor oral hygiene, bad habits.
Experts' opinions
Prosthetists believe that the installation of removable or partially removable dentures is a fairly effective and inexpensive method of restoring teeth in case of periodontal disease compared to implantation.
However, experts point out significant disadvantages of this procedure. In particular, we are talking about the inconvenience and unreliability of prostheses, which can become deformed after a short time.
In addition, bone tissue continues to decrease due to uneven load. Experts are confident that only implantation and removal of diseased teeth will help fight the consequences of periodontal disease.
It is quite logical that when amputating a problematic tooth, the infection that provokes the development of periodontal disease is eliminated. All this creates favorable conditions for subsequent fusion of the bone with the system. And bone tissue atrophy stops due to the newly emerged chewing load.
Why did the doctor recommend removing my entire loose teeth and performing implantation?
There are several reasons for this. The onset of inflammation around the tooth root can be cured only at the initial stage. Unfortunately, patients come to our clinic only when obvious problems appear - tooth mobility and pain. Time is lost, and it is impossible to restore the destroyed tissues. Your teeth will continue to become loose.
A conservative method of eliminating this deficiency is to secure a splint (removable denture) or bind the teeth with a reinforcing thread. In the center there is one or more teeth affected by periodontitis, at the edges there are healthy ones that serve as support. During the chewing process, the entire load is directed onto them, and they will not last long in this position.
What we have:
- an attempt to preserve teeth that are unfit for function in order to maintain the aesthetics of a smile;
- destruction of at least two healthy supporting teeth that regularly experience unusual loads.
We should not forget about atrophy, the process of which does not stop for a minute, because loose teeth in the jaw are only nominally present and do not fully function.
What will we get if we place implants:
- with the removal of the root, the source of infection disappears, periodontitis is cured;
- the implant functions and regularly loads the bone, stimulating its blood supply;
- a crown made of zirconium dioxide, ceramics or metal-plastic is made in the image and likeness of a person’s own teeth: shape, size and shade of enamel.
A smile becomes aesthetically pleasing; nutrition is not limited to pureed soups and cereals. A person lives a full life.
Reviews
Implantation is the only method that effectively combats such terrible consequences of periodontal disease as missing teeth. And even a small amount of bone tissue is not an obstacle to surgery, because you can use the basal technique.
In the comments to the article, you can tell your story of struggling with this disease. Have you resorted to implantation or are you using removable or partially removable structures? Write, your reviews about this or that treatment method will be interesting to us and our readers.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter.
Tags implantation periodontal disease
Did you like the article? stay tuned
No comments yet
Periodontium is in danger
Periodontal disease is a pathological disease that affects nearby dental tissues – periodontium.
The disease is characterized by loss of gums, as well as exposure of tooth necks and roots. During the course of the disease, the inflammatory process and pathological periodontal pockets are not observed. Periodontitis is a common periodontal disease that differs from periodontal disease by the presence of an inflammatory course and deep periodontal pockets. The inflammatory disease is accompanied by bleeding gums, pain and tooth loss at the last stage of development.
As is known, in severe stages of such gum diseases, partial or complete loss of teeth is observed. To eliminate a cosmetic defect, dentists recommend prosthetics. To choose the right treatment tactics, a highly qualified specialist must take into account several nuances:
- nature and stage of the disease;
- type of bite;
- structural features of the upper and lower jaw.
Caring for implants after installation
After surgery, it is important to follow all doctor's recommendations. This will speed up engraftment and minimize the risk of complications. Home care tips:
- Brush your teeth thoroughly twice a day on both sides.
- To clean the interdental spaces, use floss, a single-tuft brush or a special brush.
- An irrigator will be a good alternative to the usual rinsing after cleaning. A jet of liquid, supplied under pressure, will remove food debris from hard-to-reach places and provide a massage to the gums.