Description
Pyogenic granuloma.
This is a benign neoplasm of the skin or mucous membranes of a vascular nature. Externally, it is a round formation (papule) with a diameter of up to 1.5 cm, bright red, cherry or black-brown in color. The tumor volume is filled with small vessels and capillaries surrounded by connective tissue. The surface is easily damaged and bleeds profusely. External examination, dermatoscopy, and histological examination data help determine the type of tumor. If the filling does not undergo spontaneous regrowth, surgical treatment (electro-, cryo- or laser coagulation) is indicated.
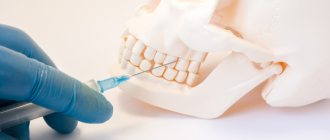
Removal of tooth granuloma
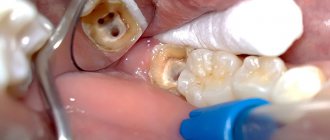
Treatment through surgery must be used if conservative treatment is ineffective, which often occurs with serious destructive processes in the periodontium and bone tissue. All surgical procedures are performed only under local or general anesthesia.
There are several techniques for performing the operation, but at stage 1, surgical opening of the gums is required to drain the purulent contents. Then drainage is introduced into the lesion, leaving it for up to 3 days for the gradual release of pus.
At the same time, treatment with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers is prescribed.
Next, the granuloma is removed using one of the selected techniques:
- Cystectomy.
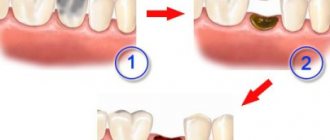
Cystectomy involves resection (excision) of the root apex. First, a piece of gum tissue is peeled off, providing access to the top of the tooth, after which the granuloma is removed along with part of the root.
After resection of the root apex, the resulting cavity is filled with synthetic tissue substitutes, and the tooth is filled. The operation lasts about an hour.
- Cystotomy.
This method is suitable for removing large granulomas and involves gradual removal of the lesion. First, an artificial channel is created between the source of suppuration and the oral cavity, through which all the pus comes out and is absorbed into cotton swabs. After complete cleansing, active antibacterial treatment of the cavity is carried out, and sutures are applied. Bone tissue gradually grows, filling the cavity freed from pus. The procedure is lengthy, but is tolerated quite easily by patients.
- Hemisection.
The procedure is performed only on multi-rooted teeth. With this surgical technique, the granuloma is eliminated along with the removal of the root and crown fragment. The operation is considered uncomplicated and allows partial preservation of the tooth and its functions, which makes it possible to further carry out full aesthetic prosthetics.
The method is indicated only if the remaining roots and crown are able to withstand the intended load.
- Removal of a tooth
They try to remove a tooth with a granuloma in extreme cases, and only if other measures are ineffective, in the following conditions:
- destruction or cracks in the root;
- pronounced destruction of the pulp and crown;
- dense filling of root canals.
After the tooth is extracted, all the contents from the source of suppuration exit through the hole in the socket, that is, the resulting granuloma is completely eliminated after tooth extraction and antiseptic treatment. At the site of the removed root and tooth, the wound heals and the periodontal tissues are completely restored. After a few months (you should wait for complete healing to occur), you can put a pin for the new tooth.
Surgical treatment is accompanied by the simultaneous use of:
- antibacterial and painkillers in tablets or injections;
- local anti-inflammatory and painkillers: dental gels Metrogyl Denta, Cholisal, Oralcept spray;
- rinsing with antiseptic solutions (Romazulan, Chlorhexidine).
Additional facts
In practical dermatology, pyogenic granuloma is found under the name botryomyoma, telangiectatic granuloma, granulation type, hemangioma, eruptive angioma. Inside the tumor node, the connective tissue forms intermediate layers, which determines the most appropriate definition of the pathology from a histological point of view as “lobed capillary hemangioma.” Occurs in adolescents and adults under 30 years of age. It is equally often diagnosed in patients of both sexes. Hormonal changes cause frequent development of the disease in pregnant women (about 5% of cases). Cases of multiple botryomyoma, its subcutaneous or submucosal location, and the formation of vascular formations on the inner surface of the esophagus and intestines have been described.
Causes of granuloma formation on the tooth root
Among the causes of granuloma on the root of a tooth, the main one is considered to be the introduction of pathogenic bacteria into the periodontium (the tissues that hold the tooth in the socket) and its inflammation. This occurs in the following abnormal conditions and pathologies:
- untreated caries or pulpitis (chronic);
- improper filling of root canals - microbes begin to multiply in a poorly sealed cavity at the apex;
- gum injuries and tooth fracture;
- introduction of infectious agents during the treatment of dental diseases (failure to maintain sterility);
- piercing the top of the root canal as a result of a medical error when cleaning the canals or installing a pin;
- periodontal disease, periodontitis;
- an inflammatory process that begins at the root of the tooth under the crown;
- penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the gingival socket after tooth extraction (including milk teeth).
Causes
The etiology of the disease is not fully understood. Assumptions about the mycotic genesis of the pathology, made in the 19th century, have not received further confirmation. Theories that the disease was inflammatory or viral in nature turned out to be unfounded. Botriomycosis is currently one of the angiomas that develop as a reactive process instead of microtrauma. In the genesis of the disease, the following factors are of primary importance: • Mechanical damage to the mucous membranes and skin.
The main factor in the development of the disease.
This is evidenced by the location of neoplasms in those areas of the body that are most susceptible to injury and microflooding: fingers, feet, lips, gums, mucous membrane of the nose and mouth. To start the formation of a granuloma, a small effect is enough: an injection, lascivious and careless treatment of the nail cuticle. • Hormonal imbalance.
According to statistics, most cases of vascular malignant neoplasms are detected in adolescents and pregnant women.
A significant provoking factor is the use of hormonal contraceptives and endocrine pathology. It is important to increase sebum under the influence of hormones and its excessive defatting during puberty, increasing the level of vascular growth factor in pregnant women. • Therapeutic effect.
The likelihood of developing granulation hemangioma increases when taking protease inhibitors, certain antiviral drugs, and retinoids used to treat acne.
Preparations of both systemic (in the form of tablets, capsules, injections) and local (creams, lotions, ointments) actions are important. • Skin diseases.
Patients with dermatoses, inflamed nevus and telangiectatic angioma suffer more often than others without dermatological problems.
Multiple lesions develop at the site of thermal and chemical burns. Irritation of the mucous membrane of the cornea and conjunctiva by chemicals, intolerance to certain components of cosmetics, conjunctivitis and blepharitis can cause the appearance of vascular papules on the eyelids. Giant granulomas develop in bedridden patients in areas of pressure ulcers.
Dental cystogranuloma is a dangerous disease. It poses a hidden threat to your health due to the possibility of many complications. Thus, the result of advanced cystogranuloma can be inflammation of the facial and neck muscles, and in severe cases, the heart.
Jaw osteomyelitis and meningitis may occur. Infection of various organs occurs, which leads to pyelonephritis and infectious myocarditis. This is not a complete list of possible complications.
How dire is the situation and what to do?
Treatment of cystogranuloma is mandatory! The possibility of further treatment, preservation of nearby teeth, the possibility of implantation, installation of removable dentures, etc. depends on how quickly you begin dental treatment. It is very difficult to recognize the disease at an early stage, although it is the early detection of the disease that allows treatment in a conservative, therapeutic way and do without surgical intervention. However, as a rule, this happens very rarely and a granuloma is usually discovered by chance, while solving other problems with teeth, or at the last stage, when all the signs of a granuloma are present: swollen reddened gums, discharge of pus between the gum and tooth, malaise, temperature, sometimes unbearable pain.
Can a dentist help in the early stages of the disease?
Yes, this is an annual dental examination. So, in our dentistry on Festivalnaya you can get an orthopantomogram. This is a panoramic photograph of the teeth of the upper and lower jaw. There is no other way to detect cystogranuloma at an early stage!
This service with current discounts for patients “Dentistry at Festivalnaya” costs 1100 rubles!
Give us a call and schedule a free appointment to receive a referral for an oral exam.
DETAILS ABOUT THE CAUSES OF CYSTOGRANULOMA
The development of cystogranuloma occurs for several reasons
In simple words, this type of dental disease is often called a dental cyst, although this is not entirely true. The cause of granuloma can be ordinary caries. Against the background of a prolonged inflammatory process, many pathogenic bacteria form in the pulp. As a result of this, the pulp dies over time (the necrotic process can occur very quickly). After this, microorganisms begin to attack bone tissue. A new formation already appears there, which is called granuloma.
How does the infection get to the root of the tooth?
At the next stage, the infection in the tooth multiplies, tissue grows at high speed, and pus appears. This is the stage of acute granuloma
. The human immune system weakens. The roots of the tooth are exposed, and the tooth itself becomes mobile.
Attention! Very often, the cause of this whole process can be ordinary tartar. Because of this, periodontal pockets appear through which the infection reaches the tooth root. Where does the infection come from in this case? From the stone itself, which contains a large number of pathogenic microorganisms. As a result of infection, tissue grows, which subsequently fills with pus. That is why it is so important to sanitize the oral cavity and remove tartar on time.
The role of filling methods in the development of the disease
Granuloma often occurs due to poor quality of antiseptic treatment of dental canals. It should be said that there is no unanimity among doctors in choosing methods for filling them. A lot depends on the choice of doctor and the quality of work here. As for outdated techniques, these include filling using resorcinol-formalin.
Secondary causes of granuloma development: inflammation and infections
Any inflammatory process in the tooth: untreated inflammation of the pulp, inflammation in the periodontium, poor quality of antiseptics during treatment - all this can cause granuloma. Secondary causes include colds, climate change (sharp), and physical overload. All this can become fertile ground for the development of the disease. As a rule, people with reduced immunity are at risk.
Treatment of granuloma at different stages of the disease
Treatment for granuloma depends on the stage of the disease. If at the first stage therapeutic treatment is sufficient, then in the acute stage of its development surgical intervention is required. The more advanced the disease, the more difficult and expensive the treatment. Conservative therapy involves taking anti-inflammatory drugs. The primary cause that led to inflammation must also be eliminated. If necessary, the source of infection is removed. At the end of drug therapy, the tooth canal is filled.
Surgery
Surgical treatment for granuloma involves one of three options: opening and drainage of the cavity of the cystogranuloma, resection or hemisection of the tooth. As a last resort, extraction is performed (when it is impossible to save the tooth)
. During resection, the top of the tooth and the cyst are removed. The removed tissue is replaced with artificial one. With hemisection, everything is more complicated: the coronal part and the root itself are removed. Their place is filled with special material and a crown is placed.
Remember that it is very important to treat the tooth in all cases. Several visits to the dental clinic will be required. Choose specialists with experience. Evaluate the result of treatment and possible bonuses that will help you reduce the cost of treatment in the future.
After all, even simple caries that is not properly treated can lead to disaster not only for the tooth, but also for the body as a whole. The best option is to avoid complications, which requires visiting the dentist twice a year or having an orthopantomogram done once a year.
We work from 9.00 to 21.00
seven days a week at Festivalnaya no. 12. Come visit us during happy hours from 12.00 to 16.00 and get a discount on dental treatment of up to 10%. Call +7 (495) 374-51-05 and make an appointment for a free appointment!
During the coronavirus quarantine period, we are working with increased requirements for patient admission: anti-epidemic measures ensure complete safety of dental treatment. Pre-registration for an appointment for patients who are conveniently within walking distance of our dentistry near the Rechnoy Vokzal metro station is made daily from 9 a.m. to 8 p.m. using the dental office’s contact numbers.
Pathogenesis
The development of papules is based on the reactive growth of granulation tissue under the influence of external and internal influences. Granulations consist of newly formed vessels and connective tissue, ensuring rapid wound healing. They create conditions for subsequent epithelization of the wound surface and scar formation. Granuloma is a consequence of disruption of the normal process of granulation formation, excessive development of blood vessels, active division of fibroblasts, and excessive production of connective tissue fibers during injury. The normal thickness of the granulation layer is 1-2. The diameter of the pathological formation can reach one and a half centimeters. The development of purulent granuloma largely repeats the wound healing process. The papule consists of arterioles, venules, capillaries, a small amount of fibroblasts, and connective tissue fibers. The longer the tumor exists, the more connective tissue it contains. The final stage is severe fibrosis of the papule, accompanied by epithelization of its surface.
Unconventional methods of treatment
Traditional methods cannot completely cure granuloma, but it is possible to relieve painful symptoms and reduce inflammation before going to the hospital and during therapeutic treatment of the pathology.
If you suspect a granuloma in adults and children, you should never warm up the sore spot. Hot poultices or compresses provoke the formation of pus and cause it to spread faster.
Rinse
Dentists recommend rinsing with medicinal herbs as an auxiliary therapy for granuloma.
The procedure should be done after every meal, in the morning and before bed. It soothes pain, relieves swelling of the gums and helps eliminate pathogenic bacteria. A proven folk remedy that relieves the signs of granuloma is oak bark .
You need to pour 1 spoon of the product into 250 ml of boiling water in an enamel bowl and simmer in a water bath for 20 minutes. Turn off, add the boiled volume of liquid and strain. The broth is ready for rinsing. Oak bark can be combined with other medicinal plants. It is useful to combine it with sage or chamomile one to one, take a spoonful of the mixture, brew it in a glass of boiling water, leave it, filter it and use it to treat the oral cavity.
Herbal infusions
- The herbal mixture quickly relieves the symptoms of inflammation at the root of the tooth. You will need St. John's wort, rose hips, oak bark, medicinal chamomile flowers, and dried calendula. You need to chop the rose hips, mix the components in equal parts, take a large spoon and pour in 0.5 liters of hot water. Place the broth in a water bath. After 20 minutes, turn off, cool, pass the liquid through gauze and rinse the gums 5 times a day for at least 5 minutes.
- A collection based on walnut leaves has good antimicrobial properties. You need to take a spoonful of the crushed ingredient, add to it the same amount of thyme, oak bark and calamus roots. Stir, pour 1 large spoon of the mixture with a glass of cool water and leave for 2 hours. Put on fire, boil for 10 minutes, cool and filter. Use to rinse gums and as a lotion on a sore spot.
- Exacerbation of granulomatous periodontitis can be treated with a healing infusion of eucalyptus, chamomile and sage. You need to combine the components in a ratio of 1:2:1, brew 1 spoon of raw material in 250 ml of boiling water. Cover with a lid, wrap in a towel and leave for an hour. Use the strained infusion for frequent rinsing of the mouth.
Soda and salt
Rinsing with baking soda has no contraindications. They can be used by adults and children in unlimited quantities to reduce discomfort in the mouth.
- In a glass of warm water you need to dilute a teaspoon of soda.
- For a child, it is recommended to reduce the dosage by half.
- Take a large sip of the solution into your mouth and concentrate it in the area of the inflamed gum.
- Hold for 2-3 minutes and spit out.
- Repeat the manipulations several times in a row.
Sea or regular salt is suitable for rinsing. Mix half a teaspoon of the product in 250 ml of warm water. Use the liquid in the same way as a soda solution. A recipe in which soda and salt are combined one to one is highly effective. A teaspoon of the mixture is poured into a glass of water and used as an antiseptic treatment for the mouth.
After rinsing with medicinal herbs, salt and soda, you should not eat or drink for about half an hour.
Propolis tincture
It is recommended to treat granuloma on the root of a tooth with an alcohol tincture of propolis. To prepare the medicine, you need to pour 0.5 liters of vodka with 30 g of bee propolis, seal the container and place it in a dark place to infuse. After 2 weeks, propolis is completely dissolved, and the tincture is ready for use.
The drug retains its beneficial properties for about a year, so it should be prepared in advance and stored in the refrigerator for various needs. To relieve the inflammatory process in the dental canals, you need to dissolve 1 spoon of liquid in 200 ml of water and rinse the seal on the gum at least 5 times a day.
Calamus root
Alcohol tincture from calamus root is useful. Two spoons of crushed raw materials are infused in 0.5 liters of vodka for two weeks. Then it is filtered and used in the same way as the first recipe. To enhance the effectiveness of treatment, you can mix a spoonful of propolis tincture with 2 tablespoons of calamus root tincture, dissolve it in a glass of water and use the liquid as a rinse and lotion on the gums.
Tincture of calendula
The fragrant orange flowers are an ancient folk remedy against purulent formations and chronic inflammation. Alcohol tincture of calendula is useful for treating the oral cavity . It can be easily purchased at a pharmacy or made at home yourself.
Add 2 tablespoons of dry calendula to 100 ml of medical alcohol and leave in the dark for 2 weeks, periodically shaking the contents of the bottle. Pass the finished drug through gauze and use it in the treatment of various diseases of the mouth and throat. For rinsing, the medicine must be dissolved in water. For 250 ml of liquid, 1-2 tablespoons of tincture are enough.
Celandine
Due to its complex biologically active composition, celandine is widely used in folk medicine. To get rid of granuloma, water and herbal infusions are suitable.
- You need to measure out 2 teaspoons of dried celandine herb, mix with the same amount of lemon balm and pour 200 ml of boiling water in an enamel bowl. Close the container tightly and leave for 3 hours. Then strain and rinse 4-5 times a day.
- To prepare the second recipe, you need to purchase a 30% alcohol tincture of celandine at the pharmacy. Take 1 large spoon of medicine, combine with 1 spoon of glycerin. Mix the ingredients thoroughly until they form a homogeneous consistency. Apply the substance to the sore gum 2 times a day. In the absence of glycerin, it can be replaced with refined olive oil.
Other folk methods
- If you are worried about a sharp, aching pain, but you can’t get to the dentist, you can use agave juice to relieve the unpleasant symptoms. You need to cut off the bottom sheet, wash it, cut it lengthwise and apply the inside to the affected gum. Leave the compress on for 5 minutes, the pain should become less severe. Freshly squeezed plant juice, diluted 1:5 with water, is used as a mouth rinse.
- Plantain quickly relieves pain and relieves inflammation. A spoonful of dry raw material is poured with 250 ml of boiling water, placed in a water bath, filtered after 10 minutes and used as a rinse 4-5 times a day.
To avoid complications, you need to visit the dentist's office at least once every six months . The specialist will examine the gums, clean the tartar and get rid of the initial stages of caries. Healthy teeth are the best prevention of disease. It reliably protects against the development of pulpitis, periodontitis and granuloma.
Symptoms
In 75% of cases, the growth of lymph nodes begins on unchanged skin. Microtrauma, which can lead to the appearance of bothryoma, often goes unnoticed by the patient. In addition to the fingers and oral mucosa, papules may appear on the face, back of the arms, palms, neck, chest and upper back. In pregnant women, fillings are mainly formed on the mucous membrane of the gums of the upper jaw and the inner surface of the lips. The papule grows over several weeks. Maximum diameter 1.5 cm, average 6 It has a round or lobed shape, rich color due to the large number of vessels, a wide base, and less often a short stem. The consistency is soft and elastic. The surface of the blisters is easily damaged, often eroded or scabbed, and may be surrounded by a white border of sloughed epithelium. The node is painless, etc.; it has no nerve endings. Discomfort is caused by the presence of noticeable formations in the arms, neck, shoulders and other parts of the body that cling to clothing, objects and cause severe bleeding when damaged. Botriomics in the nail bed area may peel off from the nail plate during active growth. Having reached a certain size, the papule begins to gradually condense due to the active development of layers of connective tissue until complete fibrosis. Thrombosis and vascularization lead to focal necrosis of purulent granuloma. If the causative factor is eliminated, the formation may disappear on its own. Reversal of granulomas may take several months.
Granuloma of a postoperative scar: causes
Often after surgery, patients complain of a compacted formation in the area of the postoperative scar. A nodule can appear both on the surface of the seam and inside it. The size of the granuloma ranges from a pea to a tumor-like tubercle, and the neoplasm itself is not accompanied by pain, fever or other alarming symptoms.
The reason for the formation of granulomas on the scar is most often the use of non-absorbable suture materials by surgeons. The appearance of a compaction in this case is the body’s reaction to foreign particles in the body. Typically, granulomatous nodules resolve on their own without requiring special treatment.
Also, granuloma of a postoperative scar occurs due to the ingress of starch into the wound, talc, which is used for surgical gloves, foreign microorganisms (with incomplete compliance with the rules of asepsis) and infections.
If the cause of the formation of the compaction is an infection, then the presence of a granuloma will be accompanied by high fever and weakness. In this case, treatment should be carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor.
If the patient experiences pain, fever, severe redness in the area of the lump, and the presence of pus is suspected, then he should undergo a more thorough examination to exclude other, more serious, postoperative pathologies such as a fistula or seroma.
Some granulomas do not manifest themselves for a long time, so for early detection and timely treatment it is necessary to periodically palpate the postoperative suture.
Possible complications
The only significant complication of pyogenic granuloma is severe bleeding, which occurs when the filling is damaged. With prolonged bleeding from several nodes, the patient is at risk of developing anemia. With the external location of the formations, the source of blood loss can be easily determined. Gastrointestinal bleeding may be much more difficult to suspect. Difficulties may be caused by the differential diagnosis of botryomyoma and hemorrhagic ulcer of the stomach or intestine.
Symptoms and possible complications
The symptoms of granuloma are quite obvious, but in most cases patients do not pay attention to them. That is why it is recommended to visit a doctor in the first months after surgery of any kind to examine the sutures.
- redness of the skin of various types from light pink to brown
- the appearance of a pink nodule inside or outside the scar
- roughness of the skin in the suture area
- painful sensations on palpation
- increase in body temperature
- general malaise: increased fatigue, weakness
Diagnostics
Benign suppurative granuloma must be distinguished from several other pathological formations. Here, the appearance of the node, its microscopic structure, and any other data that helps the dermatologist make an accurate diagnosis are decisive: the growth rate of the tumor, the presence of provoking factors, the effectiveness of previous treatment and concomitant diseases. Valuable information can be obtained: When examining the mammary gland using dermoscopy, characteristic signs of an angiomatous neoplasm are revealed (a homogeneous red nodule surrounded by a white rim). As a rule, visual signs are sufficient for differential diagnosis of the disease with various benign and malignant pathological changes of the skin, externally similar to botryomyoma. Tissue collection for histological examination is usually carried out directly during surgery to remove the tumor. This allows you to confirm the diagnosis of botryomyoma and determine the extent of surgical intervention. Pathomorphological examination determines the growth of capillaries and fibroblasts, stromal infiltration of leukocytes. Complex diagnostic cases may require examination by a dermatologist or surgeon. Externally, melanoma without pigment, squamous cell skin cancer, skin metastases from tumors of bones, internal organs and some other malignant neoplasms have a similar appearance to bothrom. The location of lesions between the shoulder blades may be one of the manifestations of Hodgkin's disease, which requires the attention of a hematologist.
Treatment
Medical management of cancer depends on many factors: age, location, heavy bleeding and whether the woman is pregnant. Occasionally, a bleeding finger will need to be removed immediately to make the patient's daily routine easier. The formation of the oral mucosa, which appeared during pregnancy, is recommended to be observed for several months after childbirth. If a pyogenic granuloma persists spontaneously, it is removed during a minor outpatient surgery. Surgical procedures include: • Electrocoagulation.
This allows you to quickly remove pathologically altered tissue with minimal blood loss.
The likelihood of recurrence of botryomyoma after electrocoagulation is lower compared to other surgical methods. Anesthetize with local anesthetics. Using an electrode, the seal is cut off from the surface of the skin at the base. The resulting piece of tissue is sent for histology. • Removal with liquid nitrogen.
Cryotherapy is used only when other methods are not available.
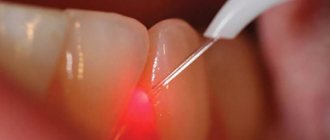
Low temperatures also help reduce bleeding, but this is not as good as electrocautery. Therefore, it is recommended to combine lidocaine with epinephrine to relieve pain. Adrenaline causes a sharp constriction of blood vessels at the injection site, lengthening the time of local anesthesia. • Removing the laser.
Laser coagulation is an almost bloodless method, which, if performed correctly, leaves no visible scars. Blood cells contain the pigment hemoglobin, which absorbs the energy of laser pulses more actively than surrounding tissues. This allows the laser beam to interact with the papule differently. The vascular mass is removed, leaving healthy cells intact. Whatever surgical method is used, at the site of manipulation the rounded wound remains covered with a dark, dense crust. Optimal conditions for epithelization are created below. The scab cannot be removed until the wound has completely healed, otherwise there is a risk of scarring. This is the only limitation of the postoperative period. Conservative treatment is recommended only at the first signs of relapse. In this case, an ointment containing 5% imiquimod is applied topically.
Granuloma of a postoperative scar: treatment
Most often, such granulomas resolve on their own and do not require medical intervention, but sometimes, depending on the location, diameter and type, it causes a lot of discomfort, in which case it needs to be gotten rid of.
Granulomatous compactions impair the function of tissues and organs. A large number of granulomas in one place, compressing nerve endings and blood vessels. Fibroblasts appear around the lesion and scarring forms. Treatment is carried out exclusively in medical institutions, by excision of the connecting tissue of the granuloma and scar.
If the cause of the pathological formation was the entry of non-absorbable suture material into the wound, then after excision the inflamed area is cleaned, removing fragments.
Before the operation begins, the patient is prescribed a series of diagnostic tests, consisting of MRI, ultrasound and, if necessary, mammography. A blood test is taken to rule out infection. The excision itself is carried out using anesthesia or anesthesia.
The operation lasts no more than 30 minutes (depending on the doctor’s qualifications), and is usually discharged the next day. If there is a need to observe the patient, they can wait a couple more days.
After surgery, special antibacterial and anti-inflammatory ointments are prescribed for postoperative sutures.
To avoid re-formation of granulomas and other infectious diseases, regularly treat the seam, remembering to disinfect your hands or wear gloves.
Bibliography
1. Features of angiogenesis in pyogenic granuloma / Guskova O. N., Skaryakina O. N. // Bulletin of new medical technologies. – 2018 – T. 25, No. 3. 2. Pyogenic granuloma as an interdisciplinary problem / Efanova E. N., Rusak Yu. E., Vasilyeva E. A., Lakomova I. N., Keldasova R. R. - 2020. 3. Pyogenic granuloma in the practice of a dermatologist / Tarasenko G. N., Tarasenko Yu. G., Bekoeva A. V., Protsyuk O. // Russian Journal of Skin and Venereal Diseases. – 2020. 4. Dermatovenereology. National leadership / ed. Butova Yu. S., Skripkina Yu. K., Ivanova O. L. - 2013.
What is granuloma?
Granuloma is a small dense nodule that appears against the background of an inflammatory process. This benign neoplasm can be localized not only on the surface of the skin, but also inside many tissues and organs.
Granulomas are formed in the process of absorption of foreign particles and microorganisms by phagocytes - phagocytosis. Most often, the diameter of the inflammatory vesicle reaches 2 mm, but there are also larger formations. The size of the granuloma can vary from small to large, clearly felt when palpated.
The granulomatous nodule consists of expanded mesenchymal stem cells mixed with hematogenous components.
The structure of neoplasms depends on the causative agent of the disease, the body’s immune response and the type of tissue that served as the site of localization.
The formation of a nodule consists of 4 steps:
- Monocyte phagocyte cells accumulate in abnormal tissues.
- Maturation of these phagocytes with further transformation into macrophages (macrophage granuloma).
- Formation of epithelioid compaction due to the maturation and movement of monocyte phagocytes and macrophages.
- Cell fusion and the formation of giant foreign bodies.
According to the factor of occurrence, granulomas are divided into several types. Nodules can be infectious or non-infectious; there are formations of unknown origin.
Infectious granuloma is diagnosed for the following ailments:
Non-infectious granuloma can manifest itself against the background of the following factors:
- drug influence
- foreign bodies that somehow got into the tissue
- dust diseases (talcosis, asbestosis, silicosis and others)
The resulting granuloma is a serious reason to contact the clinic for consultation and a thorough examination.
Learn about postoperative scars from the video provided.