Can a tooth hurt after nerve removal?
The dental nerve, or pulp, is a thin bundle of nerves, ligaments and blood vessels that fills the inner cavity of the tooth. It is responsible for blood supply and sensitivity, helps maintain enamel strength and serves as a barrier to infections. Carious processes in the oral cavity can lead to inflammation of the pulp - the so-called pulpitis. To prevent inflammation from spreading beyond the tooth root, the dentist, under local anesthesia, removes the nerve, cleans the canals and fills the tooth. After this operation, he completely loses sensitivity: he stops reacting, for example, to hot and cold.
It would seem that a tooth devoid of nerve endings is not capable of causing its owner any unpleasant sensations, but despite this, patients who have tooth pain after removal of a nerve still turn to dental clinics. So why does this happen?
Tool breakage in the channel
If a dentist encounters such a complication for the first time as an instrument breaking off in a canal, then in most cases the doctor panics (a psychological factor is triggered - after all, this is a medical error). However, this, although not the most common, but nevertheless quite common operational error, can be corrected using modern technologies and methods, and the tooth can be saved.
If, while cleaning the canal, part of the endodontic instrument breaks in it, then if it is left in the canal, the tooth will begin to hurt either immediately or after some time. This is due to the fact that a piece of an instrument stuck in the canal does not give the doctor access to the apex of the root, which is why a part of the nerve remains there or an infection that has not been washed out, which will certainly begin to multiply and can lead to very big problems in the future.
An instrument breaking off most often occurs due to the doctor’s fault, and the following reasons are possible:
- Excessive pressure is applied to a sharp instrument;
- the technique of using the instrument is violated;
- lubricating gels are not used to prevent “jamming” in the canal;
- Old “needles” are repeatedly used for cleaning and expanding canals (reamers and files), which have gone through many stages of processing and are no longer suitable.
Even narrow and highly curved channels can be worked accurately and correctly, without causing the tool to break off.
To avoid possible future complications, immediate removal of the debris is carried out using various methods. For example, the ultrasonic method of “knocking out” debris is currently being actively used. Another method of extraction is to pass the canal next to the piece of stuck instrument, widen it, rinse it, grab it, and then remove it.
It is also useful to read: Does garlic help with toothache or is it more a myth than the truth?
If extraction is impossible, conservative surgical methods can be used, when the passed part of the canal is filled with cement, and the part where the fragment is located is resected (the tip of the tooth root is cut off).
A questionable method still remains the impregnation method of eliminating complications, when a powerful antiseptic mixture (most often resorcinol-formalin) is poured into the canal over the broken instrument and a filling is placed. Usually, after some time, such patients again turn to the dentist with a question - they say, they had the nerve in their tooth removed, but it still hurts. This method using resorcinol-formalin paste does not always give results; removing the broken instrument from the canal is much more reliable.
How long does a tooth hurt after nerve removal?
It should be noted that pain for several days after removing the nerve and filling the canals is a natural reaction of the body to the intervention. Dentists call this condition post-filling pain. During the procedure of pulp extraction and canal treatment, microtrauma to surrounding tissues is inevitable, so after the anesthesia wears off, the patient may experience discomfort. Normally, they are easily relieved with analgesics and gradually disappear.
The following symptoms indicate complications:
- 5-7 days after removal of the nerve, the tooth still hurts;
- the pain is strong and sharp;
- painkillers do not relieve pain;
- gum inflammation;
- the temperature has risen;
- headache;
- the pain spread to other teeth.
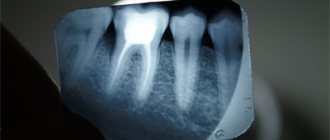
In this case, you should immediately consult a doctor so that he can do an x-ray or CT scan and find out the cause of the complication.
Treatment at home
Without the help of a specialist, symptomatic therapy can be carried out using pharmaceutical medications and traditional methods of therapy.
Medicines
When treating toothache after depulpation, the following drugs are used:
- You need to take medications in accordance with the dosages indicated in the instructions, unless there are contraindications.
Ketanov;
The listed painkillers are available in the form of tablets for oral administration.
You need to take medications in accordance with the dosages indicated in the instructions, unless there are contraindications.
For toothache after nerve removal, it is also recommended to use rinses. These include the drugs Stomatofit, Tantum Verde, Chlorhexidine, Angilex.
Traditional methods
To treat toothaches, it is recommended to use the following methods:
- Rinse with Novocaine. To prepare, mix 200 ml of Novocaine solution (1%), 1 spoon of salt, 1 egg white. Rinse your mouth with the resulting mixture for 5-10 minutes. The product relieves pain and relieves the patient from discomfort.
- Wine with herbs. Add 200 ml of wine and 0.5 cups of dried herbs sage and rosemary to the container. The liquid is boiled for 3 minutes, then cooled and a spoonful of honey is added. The finished medicine is used for rinsing 3 times a day after meals.
- Ice compress. Wrap a few ice cubes in a napkin and place them on your cheek in the area of the sore tooth. Due to the effects of cold, pain sensitivity is reduced and swelling is eliminated.
- Chamomile decoction. Add 5 tablespoons of dried chamomile flowers to 1 glass of boiling water. The liquid is boiled in a steam bath for 30 minutes, after which it cools. A warm mouth rinse is used several times a day.
- Salt rinse. To prepare, add 0.5 tablespoons of salt and soda to 1 glass of warm water and mix. You need to repeat rinsing once every 2 hours.
Self-medication can reduce the intensity of pain, but we must not forget about the need to visit a doctor if the pain intensifies or lasts longer than 10 days.
Main reasons
So why does a tooth hurt after nerve removal? In most cases, this is caused by poor quality work by the dentist. High-quality treatment of canals requires precision, accuracy and excellent mastery of technology, and inattention and careless attitude lead to errors in treatment, which in turn lead to very painful complications.
Here are the possible causes of pain after nerve removal.
The canals are not completely closed with filling material
If the doctor made a mistake when assessing the depth of the canals and did not seal them completely, then over time bacteria can accumulate in the voids and provoke an inflammatory process. This error does not manifest itself immediately: for quite a long time the patient may think that everything is fine. However, sooner or later destructive processes will still manifest themselves - as a rule, sharp pain that appears on its own or when pressing on the tooth. Inflammation in an unclosed canal can lead to destruction of the tooth root, the formation of a granuloma or cyst.
The filling material has gone beyond the root
One of the most common complications is in which, after removal of the nerve, the tooth hurts when pressing and biting food. The situation is exactly the opposite of the previous one: in this case, the cause of pain in the tooth after removal of the nerve is not the lack of filling paste in the canal, but its excess. The paste enters the jawbone, causing irritation, inflammation and the body's immune response to the foreign body. Pain appears immediately after obturation (filling) of the canals, and its intensity directly depends on the amount of paste that has gone beyond the tooth root: the larger the volume of the foreign body in the jaw bone, the stronger the discomfort.
The end of the dental instrument broke off and remained in the canal
This also happens. To extract the pulp and process the canals, very thin instruments are used, which require high precision from the doctor. If manipulations are performed with excessive pressure on the instrument, without the use of a special lubricating gel, or simply carelessly, then the thin end of the endodontic instrument may break off and remain in the root canal. Then access to the canal will be blocked, and its high-quality processing and filling will become impossible. Over time, this will certainly lead to inflammation, pain and destruction of the tooth root.
Perforation of the tooth root occurred during canal treatment
Perforation is a puncture of the root wall during canal processing with an endodontic instrument. It is dangerous in itself: it can lead to inflammation and suppuration of the tissue in the puncture area, but also through the hole, filling material can get into the jawbone with all the ensuing consequences. Due to anesthesia, the patient will not feel the moment of the puncture, but after the effect of the painkillers wears off, he will definitely feel a sharp pain. It is practically not relieved by analgesics.
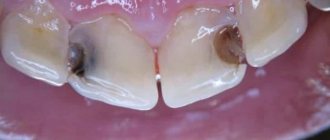
The carious cavities were not drilled out completely
Another “delayed” complication after nerve removal is when the doctor inadvertently leaves caries-affected tissue in the tooth. A filled tooth may not remind you of itself for several weeks or even months, but sooner or later the unpleasant sensations will definitely return. Pathogenic bacteria will continue the process of tooth destruction, affecting healthy tissue, causing inflammation and pain.
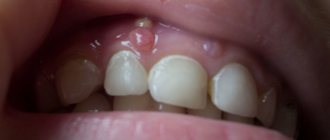
The patient had an allergic reaction to the components of the filling paste
This is the only cause of post-filling complications that does not depend on the actions of the doctor. Individual intolerance to the filling material leads to swelling of the gums, burning, and nagging pain in the area of intervention. After removal of the nerve, the tooth aches, the eyes may become watery, the lips and cheeks may swell, there may be nasal congestion and even a rise in temperature.
What symptoms should you consult a doctor for?
Pain after depulpation may indicate quite serious complications that require medical intervention.
You should contact your dentist if you have the following symptoms:
- Gradual increase in toothache;
- Severe reaction to hot or cold;
- The appearance of edema;
- Redness of the tissues near the diseased tooth;
- Pain in the cheek or jaw in the area of the diseased tooth;
- The tooth hurts and aches for too long.
Important to remember! The appearance of these symptoms is a direct indication for an immediate visit to the dentist. Delay can lead to aggravation of the pathological process. If a tooth hurts badly, do not try to treat it yourself!
What kind of help does the dentist provide?
The method of treatment depends on the nature of the pathology. First of all, the doctor examines the sore spot and identifies associated symptoms. The exact cause of pain when pressing is determined and further treatment is carried out.
Main methods of therapy:
- Repeated depulpation - used if the dental nerve was not completely removed.
- Replacing a filling – used in case of an allergic reaction or root perforation.
- Taking anticonvulsant and antispasmodic drugs is prescribed for pinched trigeminal nerve.
- Opening a purulent formation is performed during the development of periodontitis in order to remove pus and further antiseptic treatment of tissues.