Content:
- What will happen if left untreated?
- Why does it occur
- Classification 3.1. Root 3.2. Residual 3.3. Follicular 3.4. Teething 3.5. Primordial 3.6. Lateral periodontal 3.7. Calcifying odontogenic
- Symptoms
- How to treat 5.1. Surgical treatment 5.3. Conservative therapy 5.3.1. Depophoresis - an innovative method of conservative treatment
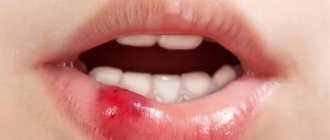
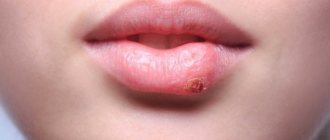
A pathological neoplasm formed in the gum as a result of a protective reaction to infection or injury is called a cyst.
Its appearance is caused by penetration of pathogenic microorganisms through the root canals. As a result, severe inflammation develops. Tissues that are involved in the inflammatory process slowly die. A cavity is formed. Liquid exudate accumulates in it. A cyst in the gum is a way to protect against further spread of the infectious process. A dense capsule appears around the lesion, holding necrotic cells inside. Its dimensions can range from a few millimeters to a couple of centimeters.
If the diameter of a cyst on the gum does not exceed 5 mm, it is called a granuloma. In total, dentists distinguish three stages of inflammation:
- granuloma;
- cystogranuloma;
- cyst.
The sooner the patient seeks medical help, the better. If you postpone treatment until later, you may lose your tooth.
The difficulty is that in the first stages inflammation most often does not manifest itself. But the number of pathogenic microorganisms in the tumor is rapidly increasing. To stop the abnormal process, the body sends immune cells to its source. This negatively affects the functioning of the immune system and leads to its weakening.
Treatment of cysts on the gums -
Sometimes a cyst on the gum opens on its own. This happens when the pressure of the pus reaches a large size and the mucous membrane bursts. In this case, pus breaks into the oral cavity. In this case, a fistula hole will remain on the surface of the gum, from which pus will constantly or periodically be released - after all, purulent inflammation at the apex of the tooth root has not gone away. And even with this development of events, you will still have to visit the dentist to save the tooth.
If the patient immediately goes to the dentist, and the latter sees a bag filled with pus on the gum, the doctor first sends the patient for an x-ray to determine the possibility of saving the tooth. If the image shows that the tooth does not need to be removed and can be cured, then the patient receives standard emergency care on the first visit (the same as for exacerbation of chronic apical periodontitis).
Emergency assistance on the first visit -
We have already said above that usually inflammation at the apex of the tooth root is characterized by a sluggish, asymptomatic course of the inflammatory process. However, in some cases, a sharp exacerbation of the process may occur - with the appearance of acute pain when biting on a tooth and swelling of the gums. Moreover, acute pain always subside when the pus finds its way out under the mucous membrane of the gums. The first thing your dentist should do is open the tooth first (this will allow the pus to drain out through the root canals - see video 1).
Next, if there is a purulent sac on the gum, the patient is referred to a dental surgeon for an incision. How to make a gum incision - see video 2. After this, the tooth is left open for several days, and the patient is prescribed antiseptic rinses, antibiotics, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Second and subsequent visits -
The patient is scheduled for a re-examination approximately 3 days later, and if there is no more purulent discharge from the canals, then mechanical treatment of the root canals continues at this visit. Next, the canals are washed with antiseptics, and the root canals are temporarily filled with special pastes based on a powerful antiseptic - calcium hydroxide. A temporary filling is placed on the tooth. How long a person will go through root canals with medicine depends on the size of the inflammation at the apex of the tooth root.
Under the influence of calcium hydroxide in the root canals, the focus of inflammation is reduced and sanitized. When this happens (this can be seen on an x-ray), the patient can have permanent filling of the root canals with gutta-percha, and then restore the destroyed coronal part of the tooth with a filling or an artificial crown. Read more about filling root canals in the article at the link below.
→ How to fill root canals for periodontitis
What will happen if left untreated?
Ignoring the symptoms of the disease leads to dangerous consequences for health. Thus, the patient may encounter:
- destruction of roots, their strong loosening;
- jaw fracture;
- tumor formation;
- purulent abscess;
- periostat;
- osteomyelitis.
The disease can cause the development of sepsis. This is a very serious condition in which the infection enters the blood and quickly spreads throughout the body.
Will the cyst resolve on its own after tooth extraction?
Purely theoretically, the cyst can resolve, but the percentage of such cases is extremely small. You need to understand that a cyst takes a long time to form: at first it is a small formation (less than 5 millimeters) consisting of granulation tissue (granuloma), and only after a while a capsule with pus and dead tissue is formed. If it was not possible to completely eliminate the problem or the cyst appeared after tooth extraction, expecting it to resolve on its own is at least naive. In most situations, the formation only increases and, if left untreated, can cause much more serious complications, including flux and sepsis.
Why does it occur
Among the main causes of pathology:
- advanced caries;
- jaw injuries;
- illiterate root canal treatment;
- overload of individual units as a result of poorly performed prosthetics;
- congenital anomalies of the upper/lower jaw;
- infections of the nasopharynx and oral cavity.
Regardless of the characteristics of the provoking factor, a gum cyst should be treated under the supervision of a dentist. Self-medication for this diagnosis is unacceptable.
Classification
All cysts that occur in the human oral cavity can be divided into the following types:
- root;
- residual;
- follicular;
- teething;
- primordial;
- lateral periodontal;
- calcifying odontogenic.
Let's talk about each of them in more detail.
Root
It is a consequence of granuloma that appears due to periapical inflammation and necrosis. Located in the area of the apical part of the root. The boundaries of such a structure are easily determined. Its size can be from 2 mm to 3 cm. But even with a large diameter, root formation does not lead to a change in bone volume or displacement of the incisor. Only if a secondary inflammatory process is involved, the disease makes itself known through pain and swelling.
When identifying a disease, you need to understand what led to its appearance and take measures to eliminate the provoking factors. Usually the problem can be resolved with endodontic therapy.
Residual
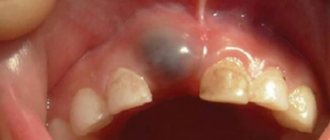
It is also called residual. Appears after removal right in the place where the roots of the torn out unit were previously located. X-ray diagnostics helps determine the presence of a residual structure.
Follicular
It is formed from the tissues of the follicular sac that covers the rudiments. Easily visible in the photo. Often leads to serious damage to premolars and molars.
As a rule, follicular formations quickly increase in size and can spread to adjacent teeth, changing their location and angle of inclination. Traditionally, their treatment involves surgical curettage.
Teething
Appears during the period of eruption of permanent units. Covers the emerging rudiment. May contain blood. Visually resembles edema, swelling. Has a bluish tint.
Sometimes it ruptures spontaneously, spontaneously. Then the person simply notices that the “ball” has disappeared, the liquid has flowed out of it. In rare cases, surgery may have to be performed. During this procedure, the blood sac is opened, and the structures that interfere with further eruption of the molar are excised.
Primordial
Formed on the basis of the tooth germ. Most often diagnosed in the area of the posterior units. This type of formation is prone to recurrence. To cure the primordial structure, it is necessary to curettage the altered tissues.
Lateral periodontal
Rarely encountered in dental practice. It has modest dimensions. Clearly visible on X-ray images. This cavity is called a lateral cavity, since it is fixed to the side of the tooth root.
The tumor can only be removed by curettage. The material obtained during the operation is necessarily sent for histological analysis to ensure that the disease present in the person is benign.
Calcifying odontogenic
Another rare type of cyst. Observed in the lower part of the supporting surface of the jaw. Well visualized on x-rays. There is cloudy contents inside. Its color depends on the degree of calcification.
Immediately after diagnosis, surgical curettage is performed.
Rinsing as a treatment method
In addition to traditional methods for eliminating cysts, there are also folk recipes. The herbs from which infusions and decoctions are made for mouth rinsing have proven themselves to be excellent.
The most common herbs that have medicinal properties are:
- Calendula.
- Chamomile.
- Sage.
- Eucalyptus.
- Millennium.
- Thyme.
- Horsetail.
All of them can relieve itching, pain and swelling. Herbs are also endowed with disinfecting properties; they prevent microbes from multiplying. For treatment to be effective, you need to rinse your mouth for several minutes in the morning and evening.
Symptoms
The disease manifests itself as a dull pain when eating solid food. A fistula may form on the gum. Patients also complain of:
- swelling of the face;
- swelling;
- increased body temperature;
- weakness, decreased performance;
- high sensitivity to temperature changes;
- increased volume and tenderness of the lymph nodes;
- toothache.
If a tooth looks healthy, but pain occurs when pressing on it, you should definitely make an appointment with a dentist. The same must be done if the gum is swollen, swollen, or a fistula has formed on its surface.
Simple tips to help get rid of cysts
To avoid the disease, you need to pay attention to the following methods of treating a cyst in the gum of a tooth using folk remedies:
- Be sure to rinse your mouth with warm water and lemon juice several times a day.
- If your gums are swollen, a solution of cranberry juice and tea tree will help.
- In case of dental granuloma, bergamot oil is effective.
- Sage and iris root will help during rinsing. The ingredients need to be crushed, then take 50 grams of the mixture and simmer over low heat for 15 minutes. Then strain, cool and apply.
- Sesame oil will help reduce the growth of bacteria. Just one teaspoon of the product, which you need to keep in your mouth for five minutes, will cope with the problem.
- Massage with turmeric and table salt relieves pain.
- Melissa decoction is an effective remedy for cysts. You need to pour four tablespoons of crushed lemon balm leaves into 400 g of boiling water and let it brew for about 4 hours. The resulting decoction is filtered and used several times a day.
- Dog nettle tincture will reduce the inflammatory process. To prepare it, you need to pour one tablespoon of nettle into 150 ml of vinegar and simmer under a closed lid for about five minutes. Then cool, strain and use.
- Honey will help soothe the pain. You need to chew honeycombs for 15 minutes a couple of times a day, and then spit them out.
- Plantain has many medicinal qualities. Therefore, you can take a leaf of the plant, wash it thoroughly and chew for 15 minutes, trying to direct it to the place of pain.
- An alcohol tincture with celandine will kill all pathogenic bacteria. To make it, you need to mix celandine juice and alcohol in equal proportions. Next, the tincture is placed in the refrigerator for 7 days, after which a cotton pad is moistened in the solution and applied to the gums.
How to treat
Today, doctors are trying to eliminate the disease without resorting to tooth extraction. The unit is pulled out only if it is completely contained in the inflammatory capsule and its tissue is significantly destroyed.
In other situations, therapy may be:
- surgical;
- conservative.
Surgery
Cystectomy is a procedure aimed at removing the cyst and the changed part of the root apex. The technique is considered highly effective. Its only drawback is its difficulty.
Less commonly, for cystic changes, hemisection is performed. The operation is indicated for complete destruction of the tooth root. During treatment, the dental surgeon removes the capsule with its contents, the altered root and part of the crown. This leaves a serious hollow defect. It is closed by laying special composite materials and installing a crown (if necessary).
Conservative therapy
Does not involve surgery. The doctor does not make an incision to access the capsule. Instead, he drills out the roots and treats them. The fact is that the tip of the tooth root connects to the cyst, so after drilling, the contents of the cavity immediately flow out.
When this happens, a medicinal composition and a special anti-inflammatory paste are placed into the canals. Afterwards the filling is carried out. The disease is considered to have resolved if after six months the treated area is not visible on the image.
Conservative treatment helps most patients, so the main emphasis is placed on it when fighting the described disease.
Depophoresis - an innovative method of conservative treatment
The most modern conservative treatment method is depophoresis. It does not require drilling of channels. The doctor exposes only the mouth of the canal, after which he inserts a thin electrode into it. The second electrode is pressed into the patient's cheek. Then it delivers a weak current discharge, along with which copper/calcium hydroxide passes through the channel. It penetrates even the most inaccessible areas, instantly kills pathogenic microorganisms, and destroys necrotic cells. Depophoresis is repeated three times. This is enough to clean the fabrics. Afterwards the tooth is filled. This technique is very effective. It allows you to get rid of the problem forever in 99% of cases.
Treatment
Sometimes there are situations when the opening of a formation on the gum occurs on its own. The reason for this phenomenon is considered to be too much pressure from the purulent contents, which is why the pus breaks out and periodically comes out of the fistula. In this case, you need to urgently visit a doctor.
Literally 5-10 years ago, a tooth with a cyst formed on the gum was not saved. However, now you can try using a therapeutic method of treatment.
The dentist performs several procedures when a cyst is detected in a patient:
- An incision into the mucous membrane, that is, an opening. Thanks to this, pus drains out, which helps get rid of pain and other symptoms.
- Dental treatment. If periodontitis has led to the formation of a cyst, pulp removal and subsequent treatment, as well as canal filling, are indicated. In some cases, re-treatment is required.
In modern dentistry, several methods of treating cysts are used:
- Therapeutic method . In this case, the crown along with the filling is carefully removed, and the canal is unsealed. Then the doctor pumps out the pus, refills the root canal and installs a filling.
- Surgical method . If the roots have not been filled properly, resection will be required. In other words, part of the root is carefully cut off, which helps avoid re-filling the canals and reinstalling the crown.
- A combination of therapeutic and surgical methods. We are talking about tooth extraction. This is the fastest and most effective way to get rid of a cyst on the gum. The dentist resorts to this solution provided that the tooth is seriously damaged.
Folk remedies
When a cyst forms, some patients prefer alternative treatment. However, you need to understand that such home remedies eliminate pain and relieve inflammation near the tooth for a short time.
For cysts, rinsing with a solution of table salt . You can also use decoctions of chamomile, calendula, eucalyptus and sage. Such infusions have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect.
If there is a cyst on the gum, hot compresses are strictly prohibited, as they contribute to the spread of infection.