Most often, bruises are not a symptom of some disease, but the consequences of various injuries. However, a bruise on the tongue can signal not only a blow or injury, but also the presence of a disease.
In almost all cases, the cause of the bruise lies in the formation of subcutaneous hemorrhage.
Vascular rupture most often occurs due to impact, excessive compression or pinching, and can also signal severe fragility and loss of elasticity of the vessels. In some cases, rupture of blood vessels occurs in hypertensive patients due to a sharp jump in pressure (most often, blood vessels rupture in the sclera of the eye, but in rare cases, small hematomas can occur on other parts of the body). Frequent appearance of hematomas and their large area may indicate a blood clotting disorder. This is a rather serious disease, and in case of severe injury, a person may begin to bleed, including internal bleeding, which without medical intervention can lead to serious blood loss and even death.
Rupture of blood vessels can cause hematomas of varying sizes and severity. For example, a small cerebral hemorrhage is much worse than a huge bruise on the leg after a fall or blow.
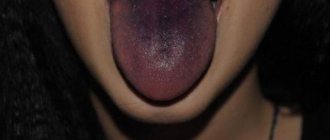
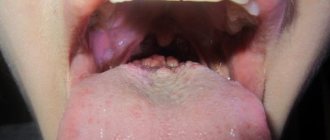
A bruise on the tongue is a fairly rare occurrence. This organ is located in the human body cavity and is protected by the teeth, gums and jaws. Its vessels are strong, and the thickness of the skin allows it to be kept safe. Most often, a bruise forms on the lower part of the tongue, where the tissue is not so well protected. The blood begins to accumulate and forms a hematoma, slightly different from the one that can be seen on the human body. In the tongue, a hematoma is a spherical or ellipse-like swelling in structure without severe swelling of the adjacent tissue.
Causes of hematoma on the tongue
A bruise on the tongue is quite small, but can cause a lot of discomfort. The tongue is the most mobile muscle in the human body. He makes many movements when chewing and swallowing food; instinctively, a person uses his tongue to check the condition of his teeth, gums, and upper palate. Without this organ, it would hardly be possible to determine the taste and temperature of the food consumed.
Injuries to the tongue do not occur as often as injuries to other parts of the body, but due to its increased mobility they bring unpleasant sensations.
Most often, a bruise on the tongue in adults and children appears due to mechanical injury to this organ. It comes in five types:
- injury due to a fall, squeezing or blow to the jaw;
- biting the tongue while falling or eating, drinking liquids, swallowing saliva, talking, laughing;
- injury as a result of an epileptic seizure or sudden convulsions;
- injury as a result of external surgical intervention during surgery on the gum or tooth;
- injury as a result of tongue puncture during piercing.
Bruising as a result of biting is the most common tongue injury. It can appear in both adults and children, including newborns. The tongue of babies is so delicate and fragile that it can be injured even without teeth, but only by slightly biting the gums while crying or feeding.
The cause of a bruise on the tongue may be dental in nature. A chipped tooth or an incorrectly placed filling, or the absence of a temporary filling during tooth treatment can also lead to injury to the tongue. In this case, not only hematomas can occur, but also small cuts and punctures.
Other causes of a bruise on the tongue:
- high sports and sexual activity;
- rough and solid foods with a high content of spicy seasonings;
- burns and injuries when taking liquids and food with high or, conversely, very low temperatures;
- various diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- incorrectly selected piercing accessories;
- in some cases, the appearance of hemorrhage in the tongue may be a symptom of an overdose or become a side effect when taking medications, especially vasodilators;
- in rare cases, hematomas on the tongue are a symptom of certain diseases, including hemophilia and hemorrhagic vasculitis.
Causes of bleeding
The reasons why the tongue bleeds can be different. Some of them are relatively harmless, pass quickly and do not lead to serious consequences. Others talk about serious disorders in the body. A person himself cannot always determine exactly why blood appears on an organ.
Mechanical damage
The most common causes of tongue bleeding are mechanical damage. These include:
- damage from cutlery;
- eating hard foods;
- biting;
- blows to the face;
- dental procedures;
- sharp tooth angles;
- low-quality dentures.
Due to the large number of blood vessels on the surface of the tongue, even a minor injury can cause heavy bleeding. If there are a lot of pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity, a small erosion or ulcer will subsequently form at the site of the wound.
Inflammation or glossitis
Glossitis is an inflammatory process affecting the tissues of the tongue. It appears under the influence of viruses or bacterial microorganisms. Various factors can provoke the onset of a pathological process, from the abuse of bad habits to thermal, chemical or mechanical injuries.
There are several types of disease:
| Type of glossitis | Specifics |
| Deep | The source of inflammation is localized at the base of the oral cavity, which is why the process can spread to the areas of the chin and neck. |
| Interstitial | Syphilitic lesion. If left untreated for a long time, it can become malignant. The mucous membrane of the tongue wrinkles, numerous scars form. |
| Desquamative (geographical) | The tissues of the tongue are loose, the lines are “irregular” and look like a geographical map. Possible causes include helminthic infestation, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, stomach and liver diseases, and hormonal changes. Leads to destruction of the epithelial layer. |
| Gunterovsky | Due to a lack of vitamins, the structure of the tongue changes: from rough it becomes shiny and smooth. |
| Diamond-shaped | Visually, the tongue begins to resemble a diamond due to thickening near the root. Small rashes form - warts and pimples. This happens due to low stomach acidity. |
| folded | Deep folds form on the surface of the dorsum of the tongue. It can only be corrected surgically, but does not affect the functionality of the organ. |
| Villous | There is a proliferation of ulcer-like papillae, which over time become keratinized and visually resemble villi. Possible causes include smoking, long-term use of medications, frequent injuries and chronic oral thrush. |
| Catarrhal | It begins when infection enters microscopic injuries. The tongue becomes swollen, painful, and traces of blood are observed. |
| Ulcerative | It begins against the background of advanced stomatitis or persistent injuries. Numerous painful ulcers form on the surface of the mucous membrane, causing blood to appear on the tongue. |
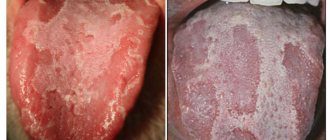
| Candida | Inflammation begins due to the active proliferation of fungi of the genus Candida. They are in the body constantly, but they begin to show activity due to problems with the microflora of the oral cavity or when immunity decreases. The tongue is covered with a dense white or yellowish coating. |
| Atrophic | The tongue swells and increases in size, multiple ulcers appear, and an unpleasant odor appears. The disease usually occurs against the background of advanced forms of gonorrhea, bacterial infections, herpes, HIV or cancer. |
Cracks
Fissures are a fairly common cause of blood on the tongue. They lead to:
- allergies;
- injuries;
- poor quality prosthetics;
- parasitic infection;
- lack of vitamins of groups A, B, PP.
Also, a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane occurs due to chronic diseases of the digestive, nervous or circulatory systems of the body. Due to the constant mobility of the organ, the cracks tend to worsen, causing blood to appear from the tongue. If the muscle is in a calm state for a long time, they gradually tighten.
Chemical or thermal burn
Thermal burns occur frequently, but do not always cause bleeding from the tongue. They are usually of a household nature and occur due to contact with hot foods or drinks. Usually the burned mucous membrane simply turns red, and in this case the tongue does not need specific help: healing occurs without auxiliary measures.
Chemical burns are a consequence of exposure to harmful substances or chemicals. In this case, you must immediately seek help from specialists. When chemicals enter the body, the consequences can be unpredictable.
Symptoms of hematoma
Outwardly, it is very difficult to notice a hematoma on the tongue, since it is most often located on the lower part of the tongue and is not visible either to the victim or to other people.
When struck, the primary pain syndrome can distract attention from the pain in the tongue. But it quickly returns and regularly reminds itself when chewing food, swallowing, drinking and moving the tongue. In most cases, this is a slight aching pain, but with the injury itself you can feel a slight pulsation.
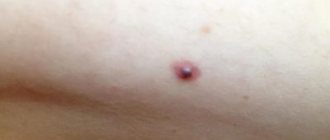
You can examine the affected area in more detail using a mirror. A hematoma is a small swelling, which in color and shape can be compared to a small cherry.
In addition to pain, a person feels difficulty speaking, and some sounds may change.
If the bruise is large and the tongue is additionally injured, an infection may enter the bloodstream.
This is quite dangerous, since microbes from the oral cavity can enter the stomach and intestines, as well as the lungs. With such an injury, there may be a rise in temperature, chills, the tongue swells and becomes very painful, and the lymph nodes in the jaw area may become enlarged.
Most often, an infectious infection of a hematoma occurs when the tongue is bitten with teeth, or when the tongue is pierced incorrectly or insufficiently sterile for piercing.
Methods for treating a bruise on the tongue
In most cases, a bruise on the tongue goes away within a few days and is treated on its own at home, but sometimes a visit to the doctor may be necessary:
- if the hematoma is very large, lasts more than a week and interferes with normal eating and speech;
- if a bruise occurs in the absence of injury, as this may indicate certain diseases of the internal organs or blood vessels;
- with an increase in body temperature, severe swelling of the tongue and the presence of other signs of intoxication of the body;
- with frequent occurrence of bruises on the tongue or a large number of them;
- if after puncturing the tongue pus appears with severe throbbing pain.
First of all, you need to know that a hematoma on the tongue is unlikely to differ in any way from a bruise elsewhere. Therefore, the treatment methods are the same.
A piece of ice will help to avoid hematoma, reduce swelling and pain. It doesn’t have to be applied to the bruise; it can simply be absorbed like candy. A similar procedure should be carried out hourly during the day after injury.
In order for the bruise to resolve quickly, you need to protect your tongue from re-injury. It is advisable not to eat hard and heavy foods for several days, stop smoking, hot and carbonated drinks.
The mucous surface cannot be treated with ointments and gels; known remedies for bruises must be replaced with analgin, ibufen or dolaren tablets.
Rinsing your mouth with a solution of salt, potassium permanganate or chamomile infusion will speed up the resorption of blood clots and tissue healing, and also protect against germs.
Often, the cause of a hematoma on the tongue is domestic trauma, when blood accumulates in the subcutaneous areas, swelling on the tongue appears as a result of submucosal hemorrhage. In other words, a hematoma is a cavity filled with dried or liquid blood that comes from damaged vessels. As the tissue is restored, the blood in the affected area has accumulated in the subcutaneous cavities, the color of the hematoma undergoes such changes - first it is blue, then yellowish-green, and eventually the bruise acquires a pale yellow tint.
Aloe
A paste made from aloe leaves can have a good effect. The pulp of the leaf should be crushed and applied to the blister for 15 minutes. It is recommended to repeat the procedure three times a day.
You should not pierce the bubble with a needle in order to speed up its resorption. On the contrary, before being examined by a doctor, it is necessary to avoid not only deliberate puncture of the blister, but also arbitrary one.
What should you not do when blood blisters appear on your tongue?
Treatment of hematoma on the tongue
If you find a blood formation the size of a cherry on your tongue, it is most likely a hematoma on the tongue, the treatment of which is quite simple. We will describe to you below some general tips on treating a hematoma on the tongue.
Rinsing with a salt solution (7 times a day).
Treatment of hematoma on the tongue is carried out by rinsing with chlorhexidine (7 times a day).
During the healing and treatment of a hematoma on the tongue, do not drink alcoholic beverages, as they can cause swelling and will only worsen the situation.
Do not smoke until the hematoma on the tongue goes away completely.
What to do with a hematoma on the tongue?
It is best to make an appointment with a specialist dentist, he will examine whether there are any complications and prescribe a course of treatment that will speed up the process of resorption of the hematoma. You will probably be prescribed medications such as Diazolin or Nise, but it is better not to self-medicate a hematoma on the tongue without consulting a doctor. Perhaps you just need to drain the blood from the swelling that has formed on the tongue. Here you need to be extremely careful, since an introduced infection can provoke suppuration.
Causes of hematoma on the tongue
A hematoma on the tongue can be caused by biting the tongue, another injury, or too thin blood vessels. Refinement of capillaries can be caused by excessive coffee consumption, which in large quantities has a bad effect on the elasticity of blood vessels, the heart and the nervous system. Therefore, if a hematoma often appears on your tongue, analyze your diet and the medications you have taken recently, maybe this will be the answer to the mystical formations on the tongue.
A hematoma on the tongue (its treatment is mandatory), which occurs without additional complications, usually disappears in 2-4 weeks. It is interesting that bruises in different parts of the body take different amounts of time to heal; for example, a bruise on the leg will take much longer to resolve than an abrasion on the arm. This is explained by the fact that the pressure in the leg area is much greater and the hemorrhage there occurs more violently.
The mucous membrane in the human body performs a sutured, excretory, and absorption function. The mucous membrane of the oral cavity is involved in thermoregulation, and the taste of food is perceived through the taste buds on the tongue. It protects against the negative influence of the external environment, which is manifested by microorganisms, mechanical pollution, and has high regeneration.
More resistant to mechanical, chemical, and temperature irritants than other mucous membranes of the body. The condition of the oral mucosa often indicates the health of the entire body.
Therefore, the doctor often makes a diagnosis using examination of the oral mucosa. A symptom of many infectious, specific, nonspecific, chronic and acute processes in the body can be a change in the integrity and color of the mucous membrane. N
For example, it can be used to determine how the liver functions. A disease such as diabetes mellitus leads to redness on the tongue, dry mouth, cracks, and erosion. Therefore, it is important to know what causes the appearance of blood blisters on the tongue?
How to treat a blood bladder?
General therapy
Depending on the type of pathological condition that caused the appearance of a blood bubble in the mouth, treatment can be carried out with the following medications:
- In case of traumatic formations that go away on their own over time, the oral cavity is treated with antiseptic agents
For candidal stomatitis, antifungal drugs such as Levorin and Nystanin are effective.
For diseases of viral etiology, the treatment regimen includes Viferon, Amoxicillin, Tsiprolet, Azithromycin. To combat gingivostomatitis, where it is expected to remove areas affected by necrosis, antiallergic medications, antibacterial agents, and vitamin complexes are used. In case of traumatic formations that go away on their own over time, the oral cavity is treated with antiseptic agents. If there is pain, the doctor may prescribe Cholisal, Ketoprofen, Voltaren, Lornoxicam, Kamistad. To eliminate tuberculosis, appropriate chemotherapy is prescribed, which includes Rifampicin, Ioniazid, Pyrazinamide.
Local therapy
To speed up the healing process, regularly rinse with antiseptic agents. Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, Stomatidine, Betadine, Miramistin, hydrogen peroxide solution, Iodoform, Chlorophyllipt show good results.
Treatment of the affected tongue with disinfectant solutions should be performed twice a day, at a minimum, but before that you must brush your teeth and remove any remaining food.
It is advisable to eat food after the procedures within 30-60 minutes, which will significantly increase their effectiveness.
Traditional methods
To alleviate the condition, it is good to use healing decoctions based on chamomile, sage, yarrow, St. John's wort, and viburnum fruits.
They are prepared at the rate of 1 tbsp. herbal raw materials per 1 glass of water.
The mixture is brought to a boil and left for 2-3 hours to infuse. Before use you need to strain.
Aloe or Kalanchoe juice has a wound-healing effect.
Oil from sea buckthorn and rosehip also has the same property. They are applied directly to the affected area.
These agents accelerate the regeneration process, prevent the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms and anesthetize the lesion.
A solution prepared from salt (1 tsp), 3 drops of iodine and soda (1 tsp) is a universal remedy in the fight against inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
These components are mixed in one glass of warm boiled water and used for lotions and rinses. It is also good to treat the affected areas with hydrogen peroxide.
What is this symptom?
A blood bubble in the mouth is a bruise, in medical terms, a hematoma. Hematoma is an accumulation of coagulated blood in a limited cavity; it is a hemorrhage resulting from damage to blood vessels or capillaries.
The causes of a blood bladder are damage that differs in the nature of the traumatic factor:
- Mechanical - various objects act as traumatic factors. For example, fish bones when eaten can damage the integrity of the mucosa. Biting while chewing food. Often the seed shell causes damage;
- Chemical - injury to the mucous membrane occurs when eating spicy or salty foods. Heavily salty food irritates the mucous membrane, so it can easily injure it;
- Too cold or hot food and drinks become a thermal factor. For example, we often encounter tongue burns caused by tea.
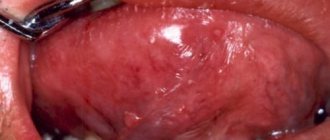
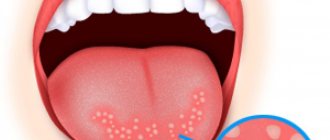
A blister on the tongue looks like a bubble filled with fluid. Contents may vary in color. The serous fluid in the bladder makes it chalky white, indicating the absence of blood, which means that the wound is superficial - there is no damage to the blood vessels.
Healing should be faster. If the liquid is red, then the injury is deeper, and the cavity contains blood, which is less easily absorbed. It is an excellent breeding ground for microorganisms.
Blood blisters can be classified by location:
- blood blister under the tongue;
- on the tongue;
- Blood blister on the side of the tongue.
Bubbles are symptoms of various diseases. If there are a lot of them and they bother you for a long time, you should consult a doctor. They occur with stomatitis, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, and endocrine diseases. If there is only one blister, and there have been no such cases before, then it is probably a bruise.
There is a blood bubble on the tongue, what should I do? Treat, but correctly
The treatment and cause of a blood blister on the tongue are closely related. The main reason for its appearance is trauma to the mucous membrane, a wound. It is important to understand that the course and treatment of a wound depend on several factors. These include the volume of the damaged surface, the fluid content, its nature, and location.
The amount of damage is important because treatment directly depends on it. With extensive trauma, a large, diffuse bruise forms. The larger the volume, the worse it is absorbed, so treatment from conservative can proceed to surgery.
If the area of damage is small, then the bubble on the tongue will be small. It will dissolve easily and quickly. If the volume is large, then the blood in the bruise stagnates and is difficult to resolve. Therefore, you should contact your dentist or maxillofacial surgery where the doctor will help remove the stagnant fluid. Wash the damage with an antiseptic solution, which will promote the healing of the hematoma.
A bruise must be distinguished from a hemangioma or vascular tumor. It occurs more often in children.
The doctor will determine the treatment during the examination. Often a hemangioma is left without specific treatment, but only if it does not continue to grow. If it increases in size, it is removed surgically.
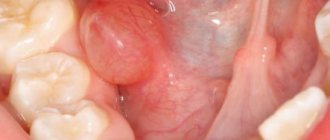
A bubble under the tongue - a ranula - occurs due to damage to the small salivary glands. It is painless, bursts easily, bluish in color, and filled with mucus. The reason is damage to the salivary duct of the gland. If the disease is acute, then the bladder is opened and drainage is installed. If it appears again and again, then excision of the affected gland is used. Many blisters may be symptoms of pemphigus or syphilis.
Small white or red bumps under, on, and on the side of the tongue may be a sign of glossitis. Glossitis is an inflammation of the tongue caused by microorganisms. Symptoms of inflammation are manifested by burning, the formation of tubercles, which turn into pustules. Treatment in this case will be more frequent sanitization of the oral cavity, rinsing with antiseptic solutions.
What should not be done if blisters, including blood blisters, are detected?
- Puncture the bladder yourself or further injure it in some other way. Then it is possible to avoid the addition of microflora or fungal infection, which can aggravate and prolong the disease;
- Leave to chance, without attention to the occurrence of wounds, damage to the mucous membranes of the tongue and mouth. You should consult a doctor to find out the real reasons. The appearance of blisters may be a consequence of injury or a symptom of more serious diseases. Therefore, wounds in the mouth should not be left unattended;
- Panic and attribute fatal diseases to yourself.
What should you do if you find a bubble?
- Rinse your mouth with an antiseptic solution;
- Avoid foods that irritate the mucous membranes - spicy, salty, hot, cold;
- Go to the doctor for a consultation.
Everything is simple and everything is complex. The main thing is don't panic. Go to a doctor to get qualified help that will help you stay healthy and protect you from complications. You will be healthy!
The protective properties of the human body are performed both by individual parts of the body and organs, and by their membranes (covering). The mucous membrane provides thermoregulation, affects taste buds and protects muscle tissue from direct mechanical damage. The oral cavity is completely covered with such a protective mechanism, including the surface of the tongue, which often suffers from spicy, salty foods and accidental injuries. Thanks to food, a person receives all the necessary vitamins, microelements and nutrients, so regular nutrition is an integral part of life for everyone. But what to do when the process of eating, in addition to the obvious benefits, brings pain and discomfort?
A hematoma on the tongue, or a black pimple, is a hemorrhage in the tissue
Pimple under tongue
Hello, I am worried about discomfort in my mouth, the bottom hurts a lot. Something jumped up under my tongue, and most likely I have an inflammation of the frenulum. The photo shows that there are two bubbles and something white between them. And the lower back of the gum hurts. I can't eat or talk. Tell me what I can use to rinse my mouth so that the pain goes away.
Dentist's answer:
Hello, you need to see a doctor, you may need professional treatment. At home, you can rinse your mouth with chlorhexidine 0.05.
Hello, I’m 30 years old, I’ve had allergies for 6 years, my palms were covered with water blisters, there were wounds on my head and they always oozing out, there was swelling on my cheeks, my ears were red, all this was 2 rubles per year, I worked as a nurse in a regiment and after contact with bleach it got worse, I had to quit 1.5 years ago. I was treated by a dermatologist because we don’t have an allergist, we tried everything from Suprastin to Erius, more often we gave Dexamethasone injections, in the month of May an unpleasant feeling appeared in my throat, as if something was bothering me As I always thought I had an allergy, I went to a dermatologist, they prescribed Dexamethasone injections, it didn’t help, they prescribed Erius.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the Department of saliva that occurs when receptors are irritated. Salivation in response to various stimuli. How does digestion occur in the mouth?
I drank it all easier, the lump in my throat didn’t make me feel nauseous, I couldn’t eat all the time, I felt nauseous all the time, my stomach began to hurt, the dermatologist said that I needed an allergist, he couldn’t help, I only went to another city in August to see an allergist, he prescribed me an examination, donated blood everything is normal only (esinophils-7, cholesterol-6.4, bilirubin 14.5), I donated blood for immunoblotting (it showed a food allergy to tomato and crab)
, did an ultrasound of the liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, everything is fine (only deformation (kink) of the gall bladder), ECG is normal, pressure too, ultrasound of the thyroid gland showed (hyperplasia, nodule of the left lobe of the thyroid glands) blood test for hormones showed that everything was normal, FCDS showed that the gastric mucosa was atrophying, with all the examination I went back to the allergist - he prescribed me (hypo-diet, lordestin (drink for 6 months), omez, trichopolum, azitrox for the stomach, atarax, lactofiltrum) I followed the diet very strictly, I took all the medicines, all the wounds went away from my head, my hands became clean, but a lump remained, it was hard to swallow, heaviness appeared in my neck, my neck muscles began to ache, it radiated into my ears and tonsils, I began to eat even less.
Dentist's answer:
It makes no sense to review what is written in correspondence consultation mode! Based on the complaints, I don’t see the need for a serious diet.
The mucous membrane of the mouth is the most resistant surface to many influences. But with injuries or illnesses, the delicate balance is disrupted and inflammatory processes begin. Why do blisters appear under the tongue? In a brief review, we will tell you in detail about the culprits of the disease and how to effectively get rid of the unpleasant manifestation.
Large cyst-wound under the tongue
What is a tongue hematoma
A hematoma on the tongue is a consequence of a ruptured vessel, in other words, hemorrhage occurs in the tissue, causing the affected area to change color and sometimes density. The mucous membrane of the tongue is highly resistant to various damages, and by its external condition it is quite possible to determine problems associated with other parts of the body. Based on analyzes of the oral mucosa, diagnoses of internal organs are made, and close attention to the gums, teeth and tongue is a mandatory part of the general examination in the doctor’s office.
The appearance of bloody blisters on the mucous membrane indicates both minor diseases and serious malfunctions in the functioning of internal organs.
What are the dangers of hematomas, and how to deal with them? These questions are easy to answer by studying the causes of bruises on the tongue.
Types of tongue hematomas and main causes
The nature of a fresh hematoma in the oral cavity
Hematomas on the tongue are nothing more than bruises caused by spontaneous hemorrhage into muscle tissue. Damage and rupture of capillaries or blood vessels lead to a similar phenomenon. Bloody blisters are not dangerous. Normal blood circulation, over time, promotes the resorption of the densified, discolored tubercle. Is it worth worrying about such trifles then? Factors leading to various external damages come in only a few types of origin:
- mechanical;
- chemical;
- thermal;
- combined.
Traumatic hematoma in an accident
Damage of a mechanical nature includes all cutting and piercing objects without exception that cause direct and almost immediately noticeable harm. Thus, food with bones can cause damage to the oral mucosa during chewing. The size of the food is not so important, because even microtraumas violate the integrity of the surface of the tongue.
Hematomas caused by mechanical stress do not pose a threat to human health; the only prescription in such cases is regular rinsing of the mouth after eating.
When salty or acidic substances come into contact with the tongue, an immediate reaction occurs and small ulcers form on the mucous membrane. Chemical damage occurs quite often, especially among lovers of spicy seasonings and oriental cuisine. At least once in their life, every person has been burned by too hot tea or coffee. Wounds from thermal effects take longer to heal than others, because the lesions are of the deepest nature (muscle tissue is covered).
The color of hematomas directly indicates the reasons for their occurrence. The hemorrhage cavity contains liquid blood, which is a favorable environment for the development of dangerous microorganisms and bacteria. Bloody lumps can even be located under the tongue (a part of the mucous membrane that is difficult to reach for mechanical damage).
Hemorrhages on the palate and tongue are manifestations of vascular diseases
If the situation with single bruises is more or less clear, then multiple hematomas cause justifiable concern.
Scattered red formations interfere with eating, swallowing liquids, and even while talking. Such a symptom signals a hidden but potentially dangerous threat. Consulting a doctor in the early stages of unknown diseases will save your money and health. Possible causes of bruises on the tongue may be stomatitis prolonged without treatment, ailments of the gastrointestinal tract, or disturbances in the functioning of the body's defense systems. Determining an accurate diagnosis and prescribing effective treatment will protect your health from the development of serious diseases.
Point hematomas are a sign of problems with the gastrointestinal tract
Tongue hematoma treatment, which includes a comprehensive examination and detailed blood tests, is the most correct and effective. What should you do first when a bruise appears on the front or lower part of the tongue (including the frenulum and lateral surfaces)?
Types of bubbles
Bubbles that form under the tongue are of different origins, differ in color, size and content. Some formations do not require any therapeutic effect, while others are a symptom of serious diseases that require immediate treatment. Based on the nature of the ball formed under the tongue, specialists can make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment.
Bubbles in the sublingual area, depending on the cause of their occurrence, vary in color:
- without changing the color of the mucous membrane - the bubble has a characteristic physiological color;
- red color indicates accumulation of blood inside the bladder;
- white blisters occur with stomatitis;
- a bubble with a blue tint may indicate the formation of a ranula.
Bubbles under the tongue can have different contents. There are bubble formations: with a clear liquid inside, with a blood clot, without content.
Blisters under the tongue differ in size and growth pattern: large, small, medium, growing, blisters that do not change in size.
Treatment of bruises on the tongue
To treat bruises on the surface of the tongue, an integrated approach is required, because a simple symptom can indicate a hidden illness. If bloody blisters appear as a result of a cut or bite with teeth, there is no reason to worry.
The main help at home is careful adherence to all rules of personal oral hygiene.
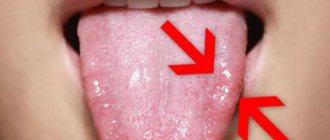
Red dots - petechiae do not hurt, but indicate a weakened immune system
Associated problems, fluid accumulation along the bruise, and compaction of darkened parts of muscle tissue can lead to blood poisoning and the development of a harmful, pathogenic environment for bacteria. If there is the slightest change in the color and shape of multiple hematomas, it is recommended to immediately see a doctor. The size of the damage plays an important role in prescribing effective treatment.
Furacilin for rinsing is an effective remedy
For extremely advanced forms, surgical intervention is mandatory (rinsing and applying ointments do not give the desired result). For small bruises, emergency measures are not required; over time, the blood will resolve on its own. Large volumes of lost blood are much more difficult to remove from the oral cavity, and this situation is fraught with secondary infections.
Treatment of bruises at home brings improvements in the condition of hematomas, but without an accurate professional diagnosis, it is often ineffective.
If bubbles or small lumps appear on your tongue, contact specialists, doctors with many years of experience.
Your health, including your oral health, is only in your hands.
A bruise on the tongue is not only unpleasant, but sometimes also very painful. But the worst thing is that upon discovering it, a person invents an incredible illness for himself and becomes emotionally unbalanced. And this can already lead to much more serious consequences. But is a hematoma on the tongue really not dangerous, or can there still be a reason for nerves?
The tongue and the mucous membrane around it have 5 main functions. Namely:
- protection;
- suction;
- selection;
- thermoregulation;
- taste perception.
It is the protective function that “monitors” that the negative influence of the environment does not cause harm. But we are talking not only about various viruses and microorganisms, but also about mechanical damage. The mucous membrane withstands irritants of all types: from mechanical to temperature and chemical.
Interesting! The mucous membrane of the mouth is endowed with the fastest regeneration.
Often, it is by the mucous membrane that the doctor can determine whether there are serious disturbances in the body’s functioning or not.
Most diseases leave their mark on its condition, for example, in a patient with diabetes mellitus, the tongue will be red, with cracks and erosion. Therefore, any changes in the tongue, and especially a bruise, should cause an urgent visit to the clinic.
Infections
The most likely “provocateurs” of transparent blisters in the oral mucosa in children and adults are cold and hot drinks, as well as rough food. Often microtraumas on the lower lip, cheeks, tongue, palate are caused by poorly polished fillings, poorly fitted dentures, cutlery, etc.
Numerous blisters on the palate, cheeks and mouth are often manifestations of stomatitis, an infectious disease that occurs in acute or chronic form. The most common types of disease are herpetic and aphthous stomatitis. Congenital pemphigus of the oral mucosa is another cause of the problem.
As a rule, this disease is diagnosed in early childhood and “accompanies” the patient throughout his life (it is characterized by a chronic relapsing course). Pemphigus can manifest itself in a simple and dystrophic form (the main diagnostic sign is the symptom of pemphigus). Treatment of the disease is usually symptomatic, in severe cases with the use of corticosteroids (hormonal drugs).
Diet plays an important role in the fight against the signs of this unpleasant disease - the patient’s daily menu should be high-calorie, nutritious, but at the same time salt-free. To relieve discomfort and pain caused by transparent blisters in the mouth, the mucous membrane is regularly treated with local anesthetics.
Blisters in a child’s mouth can “signal” about the Coxsackie virus. In this case, watery transparent blisters cover not only the oral mucosa, but are also found on the feet and palms. Like oral pemphigus, this disease requires exclusively symptomatic treatment - taking painkillers, antipyretics, and preventing dehydration.
Herpetimorphic dermatostomatitis (another name for the pathology is Dühring's disease) is a disease of unknown etiology, manifested in the form of spots, blisters, vesicles on the roof of the mouth and on the skin. Such formations are painful to the touch, itchy, and cause discomfort to the patient. Treatment of the disease is complex, using drugs from the sulfonamide group of drugs. If these do not demonstrate the desired effect, the patient is prescribed hormonal medications.
The herpes virus can provoke the development of not only herpetic stomatitis, but also a more serious illness - shingles. This disease “signals” its appearance by small, extremely painful spots, which over time transform into oral blisters with clear liquid.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the upper extreme tooth on the left
Shingles is a chronic disease, periods of exacerbation of which are associated with the following factors:
- nervous shocks, stress;
- immune disorders (including as a result of prolonged use of various medications);
- various chronic diseases of internal organs;
- oncology;
- chemotherapy;
- chronic fatigue;
- autoimmune diseases.
Treatment of herpes zoster is symptomatic and involves preventing suppuration of blisters with local disinfectants, as well as taking systemic antiviral drugs (Acyclovir and its analogues).
The most traumatic area of the oral cavity is the area of the mucous membrane located under the tongue. There is a high probability of the appearance of bloody blisters of different sizes, colored in a burgundy-red hue. The causes of the problem are varied - from infections and injuries to the delicate mucosa to tumor processes. The appearance of at least one such blister that does not go away for 4–5 days is a reason to seek medical help.
Hematoma on the tongue: causes
There are three reasons for a bruise on the tongue.
If you determine the main one, the doctor will be able to prescribe competent treatment and the problem will disappear in the near future. Among the probable causes of hematoma, the following are worth highlighting.
- Injury to the mucous membrane by mechanical impact on it. Most often, the notorious fish bones and seed husks are to blame.
- Chemical burn. We are not talking about dangerous reagents, but the whole point is overly salted or spicy food. Pepper and salt irritate the delicate mucous membrane, thereby injuring it.
- Thermal exposure is a sip of scalding tea or an ice-cold drink. Most often, they provoke the appearance of hematomas on the tongue.
Type of hematoma based on fluid color
Even before going to the doctor, you can determine the degree of injury and the duration of wound healing based on the color of the liquid in the hematoma. The content may be as follows:
- a milky white tint indicates that the wound is of a superficial type, where the vessels were not affected. There is no blood in the ulcer, only serous fluid. Such injuries heal the fastest;
- red color indicates a fairly deep injury; it is possible that a muscle is affected. Such wounds take longer to heal, the reason being that the blood is much more difficult to absorb. What complicates the situation is that this environment is attractive to various types of microorganisms. It's no secret that the mouth is the dirtiest place in the body. It is in the oral cavity that contains a large number of microorganisms that can cause inflammation.
If the blood bruise is located on the side of the tongue, then this may be a symptom of a dangerous disease: stomatitis, problems with the gastrointestinal tract, disruptions in the endocrine system. This is why you should not put off going to the doctor.
Why is there a problem?
Bubbles on the mucous membrane in the mouth are a common phenomenon, which, as a rule, signals such acute and chronic ailments as:
- disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract;
- endocrine disorders;
- problems with hematopoiesis;
- cardiovascular pathologies;
- respiratory, renal dysfunction.
Bubbles in the mouth appear with hypovitaminosis, during a course of chemotherapy, may indicate the development of a malignant neoplasm, indicate syphilis or immunodeficiency in the body.
Herpetic stomatitis is the most common cause of blisters on the mucous membrane in children. Some lesions of the oral mucosa are amenable to even basic visual diagnosis, but in some cases the patient has to undergo a comprehensive examination to identify the root cause of blisters in the mouth.
Correct treatment
Eliminating the cause means curing the disease faster. This statement is truer than ever. But only if the cause is not a serious illness. It is clear that large hematomas take longer to disappear than small ones. Despite this, even a tiny bruise can be a reason to go to the clinic. The fact is that in order to avoid serious consequences, surgical intervention is sometimes necessary, during which the hematoma is removed. When contacting a doctor, it is better to choose an oral and maxillofacial surgeon.
In order for the hematoma to go away faster, you need to maintain oral hygiene, namely:
- brush your teeth after and before bed, and preferably after every meal;
- if you cannot brush your teeth after eating, chewing gum can perform hygienic cleaning, removing food particles;
- Rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions several times a day.
It must be said that only the attending physician prescribes treatment methods for a bruise. True, most often it is the most common and is based on rinsing. Only if the hematoma grows or conservative treatment fails, something more serious is used.
If
the hematoma has not resolved for a long time or has festered , then surgical intervention cannot be avoided.
The cause of the appearance of a neoplasm, which means a hematoma, is a blockage of the salivary gland duct. It’s good if the bump is small and painless, because in most cases it bursts on its own and heals quickly. True, it is not uncommon for an acute form to occur. In this case, drainage will have to be placed in the duct or the opened gland. If this does not help, the gland will be removed.
Found a hematoma in your mouth? It would be helpful to do the following:
- give up irritating foods: salty, smoked, spicy, etc.;
- rinse your mouth with antiseptic drugs;
- make an appointment with a doctor and be sure to visit him if hematomas appear;
- adhere to medical recommendations.
In addition, when identifying a hematoma on the tongue (blood or regular), you cannot:
- pierce it so that it heals faster (you must remember that it is easy to get an infection into the wound);
- injure in any other way;
- refuse to go to the doctor in the hope that everything will go away on its own;
- panic and invent dangerous diseases and their symptoms.
Oral hygiene and specific medications
If bubbles appear on the tongue, treatment should begin with scrupulous oral hygiene: brush your teeth every time after eating and use a special mouthwash. These steps are often enough to relieve the burning sensation caused by the blisters and resolve them within two or three days.
However, in the case of stomatitis or ulcers of viral origin, it will take about ten days to eradicate the symptoms of the disease, which, however, after the first two days will no longer be contagious.
As for treating blisters on the tongue with medications, it all depends on the reasons:
- antiviral drugs if the blisters are caused by the herpes virus
- antibacterial medications if the blisters are caused by bacteria
- antifungal medications if the infection is caused by fungi
Antimicrobial therapy may be accompanied by painkillers that can relieve pain from ulcers, or antipyretics in case of stomatitis with high fever.
Dangerous consequences
The most common complication that can occur as a result of a hematoma is infection in the wound. If you do not pay attention to this in time, an inflammatory process begins, accompanied by fever, increased temperature, weakness, loss of consciousness and other dangerous symptoms. Moreover, this can harm not only the oral cavity, but the entire body. Although most often, as a result of a bruise, a person simply loses his sense of taste and appetite. It must be said that if the above symptoms are accompanied by numbness of the tongue or jaw and speech impairment, then you need to urgently call an ambulance or go to the clinic yourself.
Most often, bruises occur on children's tongues. Kids are in a hurry, play around, bite themselves or get injured, for example, with a fork. True, adults are not protected from such damage either. Be that as it may, everyone in such situations needs to consult a doctor, and then adhere to the above treatment recommendations. Then the bruise will disappear in a matter of days and without complications.
Therapy methods
If damage to the mucous membrane is detected, there is no need to self-medicate, as it can lead to serious complications.
You should immediately consult a doctor so that he can prescribe the appropriate course. Local therapy is used, which is aimed at pain relief and accelerated healing of ulcers, as well as a general approach that eliminates the cause.
A visit to a specialist is also necessary, because in this matter the doctor adheres to individual treatment, based on the patient’s age, stage of the disease, the presence of contraindications and restrictions.
When treating tongue ulcers in different cases, they resort to:
- antibiotics;
- antiviral drugs;
- immunostimulants;
- anti-tuberculosis drugs;
- anti-inflammatory ointments;
- antiseptics;
- anesthetics.
If you have sores on your tongue, be sure to treat them with painkillers and antibacterial agents, which are available in sprays, rinses and lozenges.
Popular in this group are Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Hepilor, Rotocan, Furacilin, Strepsils, Chlorphyllipt, Rivanol, Givalex, Orasept, Angilex.
Depending on the provoking factor, the following drugs are prescribed:
- Candidal stomatitis is caused by the spread of a fungus, so antifungal agents are necessary for treatment. These include Levorin, Nystatin.
- To combat viruses, in particular in the presence of herpetic sores, Viferon and Zovirax are prescribed. Gels are applied directly to the site of infection, since a huge accumulation of pathogenic cells is observed inside the vesicles. In more severe cases, when the disease is associated with bacterial activity, accompanied by elevated temperature and protracted nature, antibiotics are prescribed: Tsiprolet, Amoxicillin, Azithromycin.
- Gingivostomatitis is also treated with antibiotics, but antiallergic drugs are added during therapy. Vitamins and a high-calorie diet are required. Treatment is accompanied by removal of necrotic tissue under local anesthesia. Damaged areas are treated with antiseptics.
- Treatment of ulcers caused by injuries usually does not require specific therapy, other than local treatment with antiseptics and, if necessary, anesthetics. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed as painkillers. They are taken orally according to the instructions. The most popular are Lornoxicam, Ketoprofen, Voltaren. Cholisal-gel, Kamistad, Lidocaine and Strepsils plus are good for local anesthesia. To activate the immune system, Immunal is prescribed, as well as vitamin complexes.
- For tongue tuberculosis, specific chemotherapy with rifampicin, isoniazid, and pyrazinamide is prescribed. Treatment of infectious diseases: tuberculosis, syphilis and HIV is carried out under the supervision of a doctor in the clinic. Therapy is usually long-term and requires an integrated approach.
Malignant formations are dangerous due to the rapid spread of metastases, so treatment must be carried out promptly. After a series of tests and chemotherapy, the ulcers are surgically removed. Subsequently, it is necessary to regularly undergo a comprehensive examination in order to promptly detect remaining foci of cancer.