A disease such as stomatitis often occurs in newborns and children of primary school age. In addition to the characteristic rash on the oral mucosa, the inflammatory process is accompanied by other symptoms. Only after establishing the etiology of the disease can a specialist prescribe antibiotics for treatment. For stomatitis in children, this group of medications is used exclusively in severe cases. Let's take a closer look at how to properly treat infectious pathology and what drugs are used in pediatric practice.
Causes of stomatitis
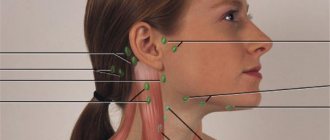
One of the common diseases encountered in pediatric dentistry is stomatitis - an inflammatory process that develops in the oral cavity. The development of the disease is provoked by various pathogenic microorganisms that enter the child’s body in various ways. Harmful bacteria may initially be present in the oral cavity, and with a decrease in the protective functions of the immune system, they begin to multiply, which leads to the development of stomatitis.
The main reason for the development of the disease in babies is poor hygiene of pacifiers and toys. In addition, young children learn about the world through the objects around them and try to put them in their mouths. The injured oral mucosa is the entrance gate for pathogenic microorganisms.
Another reason is long-term antibiotic therapy. At the same time, doctors talk about the development of candidiasis (thrush). Bacterial stomatitis is also common in children. Treatment with antibiotics in this case is carried out after determining the type of pathogen. Pathology can be caused by microorganisms such as streptococcus, staphylococcus and other pathogens of specific infections. The frequent appearance of ulcers indicates the weakness of the child’s immune system.
Causes of stomatitis after taking antibiotics
Taking antibiotics weakens the immune system, which contributes to the development of stomatitis. The most common reasons are:
- changes in the composition of saliva;
- dry mucous membrane;
- immunodeficiency virus (HIV);
- diabetes;
- smoking.
Elderly people are especially susceptible to the disease, as immunity decreases with age.
Symptoms
The manifestation of the disease depends entirely on its type. A common symptom is the appearance of a rash resembling sores on the mucous membrane of the mouth. Young children also experience behavioral changes. Babies become capricious, often cry for no apparent reason and put their fingers in their mouths. This is due to the fact that stomatitis causes unpleasant, rather painful sensations and general discomfort.
The most common type is herpetic stomatitis. The appearance of ulcers on the mucous membrane is accompanied by an increase in temperature and signs of intoxication of the body. If a bacterial infection occurs, the baby may be prescribed an antibiotic.
With aphthous stomatitis in children, it is important to find out the etiology of the disease. Pathology develops against the background of disturbances in the functioning of the immune system. At the same time, the child’s temperature rises, lymph nodes enlarge, and appetite worsens.
The bacterial type of stomatitis is also common in children of different age groups. This type of disease is characterized by redness of the oral mucosa, the appearance of painful ulcers and swelling. Having determined the type of pathogenic pathogen, the doctor must prescribe antibiotics.
Causes
Antibiotic stomatitis appears after taking various drugs. Usually the disease develops from tetracycline and streptomycin. Rarely, allergies to penicillin medications and macrolides occur.
The causes of stomatitis from antibiotics include dosage violations, individual sensitivity to the medication, and improper combination with other drugs. In this case, irritation and redness in the mouth occurs. Some people may develop allergies even to medications that were previously taken without side effects. It all depends on the general condition of the body.
How to treat stomatitis in children?
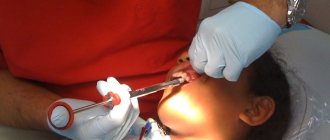
Having discovered ulcers on the oral mucosa in a child, parents should immediately seek medical help. The disease is treated by a pediatrician or pediatric dentist. Therapy consists of the use of systemic and local medications. The use of antibiotics for stomatitis in children is not always advisable. Most doctors try not to use this group of drugs. Treatment is carried out mainly with the help of antiseptics in the form of rinsing solutions. Antiviral and antifungal ointments for treating mouth ulcers are used for herpetic and candidal stomatitis. Anesthetic aerosols are used for severe pain only if the child is over a year old.
What does a specialist follow when prescribing antibiotics to a baby?
Firstly, it is necessary to understand at what stage the inflammation is, and the use of heavy drugs is prescribed only in cases where stomatitis has caused complications in other internal organs.
The second factor is the age and general condition of the child, because everyone suffers from diseases in different ways, and for one organism an antibiotic will play a positive role, while for another it will completely deprive all protective functions.
You also need to take into account possible allergic reactions to one or another component and predict in advance how the baby will react to the new drug. Therefore, if an adult can try to independently select an effective treatment method, then when it comes to children, this is a very serious and long-term strategy that must take into account many factors, ranging from previous diseases to possible internal pathologies. If you have childhood stomatitis, you should not self-medicate , and timely consultation with a dentist and therapist will help you quickly cope with the disease.
And if you and your doctor nevertheless decide on antibacterial therapy, be sure to protect yourself with probiotics and saturate your child’s body with beneficial microflora. Being in a state of stress, many parents let this point take its course, not understanding how it can affect the future condition of the baby.
What antibiotics are prescribed for stomatitis?
A child with symptoms of stomatitis must be examined by a doctor. The decision on the need to take antibacterial drugs is made only after determining the type of pathogen. You cannot do without these medications if the rash quickly spreads across the oral mucosa and the child’s condition worsens. Selecting medications on your own is extremely dangerous.
Antibiotics for stomatitis in children are prescribed taking into account the patient’s age group and the severity of the disease. With the right treatment regimen, it is possible to cope with the symptoms of the disease in a short period of time.
The following medications are effective for stomatitis:
- "Amoxiclav".
- "Amoxicillin."
- "Augmentin".
- "Sumamed."
- "Lincomycin."
How to take antibiotics?
To reduce the negative effects of antibiotics on the body, it is important to follow some rules:
- Drugs must be prescribed by a doctor based on indications, contraindications, age, weight, and tolerance.
- Even if a medicine is strong, this does not mean that it is more effective. Each ailment has its own antibiotics, so you should not ask your doctor for the strongest medications.
- You must complete the entire course for improvements to occur.
- It is necessary to write down or remember what products you were allergic to, especially in children. This information is entered into the medical record to prevent recurrence of negative reactions in the future.
- You should not change the dosage yourself. Smaller does not mean safer.
- You should not skip taking medications. They must be taken at the same time every day.
Is it worth treating stomatitis with antibiotics?
Not every parent has a positive attitude towards treatment with antibacterial medications. Each drug in this category has many contraindications and negative consequences. The last point worries parents the most. The active substances contained in antibiotics negatively affect not only the vital activity of pathogenic agents, but also significantly reduce the number of beneficial bacteria in the body.
The intestinal microflora is mainly affected. Therefore, antibiotics for stomatitis in children are used with extreme caution. After treatment, most patients experience disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system, manifested in the form of dysbacteriosis.
In addition, treating stomatitis in a child with antibiotics can lead to relapse of the disease. This is due to the fact that after prolonged use of bactericidal drugs, the protective functions of the immune system weaken, and the body becomes vulnerable to pathogenic microorganisms. Therefore, before starting treatment, you need to consult a dentist or pediatrician and find out what antibiotics to take for stomatitis. In children, this disease is usually mild and does not require the use of strong drugs.
Types of antibiotics
Treatment of stomatitis with antibiotics in adults and children is carried out in extreme cases:
- there was a transition of stomatitis to a severe form of the disease;
- for systematic diseases of internal organs and systems that provoke the development of stomatitis.
Of the variety of antibiotics, treatment of this disease is usually carried out with the prescription of drugs that have a wide spectrum of action. In order for treatment with prescribed antibiotics to bring maximum effect, a specialist performs an analysis, after which it is possible to identify the sensitivity of pathogenic microflora to certain types of drugs.
After this, when diagnosing “stomatitis,” those antibiotics are determined, the effect of which has the greatest suppression of bacterial activity.
Sumamed
This antibiotic is used when stomatitis in the oral cavity has progressed to a severe form of the disease and the threat of intoxication of the entire body increases. Taking Sumamed allows you to achieve a positive result in the treatment of the disease in young patients:
- For children, this medicine is available in the form of syrup, and for adults, the form of production is tablets.
- The positive side of this type of antibiotic is that it can be used even in infants.
The duration of treatment and the dose of the drug are determined only by the doctor after a thorough diagnosis of the patient’s disease.
Amoxiclav
This antibiotic is widely used to treat dental diseases and its use is especially justified in cases where topical drugs do not bring the desired result. Amoxiclav has a number of advantages over other medications:
- has a systemic effect, that is, it can be used to eliminate the source of infection in the oral cavity and, after achieving the desired result, stop taking it;
- A high effect in the treatment of stomatitis in adults and children with the help of this drug can be achieved due to its inhibitory effect on the synthesis of cells of pathogenic microorganisms.
The release form of amoxiclav is tablets, drops and powder for preparing a suspension. If the need to use this antibiotic is confirmed, the doctor will prescribe a special course of treatment, which usually looks like this:
- for adults and children over 12 years of age, the daily dose of the drug is divided into three doses and is 250 mg;
- Children under 12 years of age are prescribed amoxiclav in the form of syrup or drops, and the dosage is calculated individually by the attending physician.
Augmentin
This antibiotic contains two leaving substances:
- amoxicillin is an antibiotic that helps destroy large accumulations of pathogenic microorganisms in the body;
- clavulanate - refers to excipients that suppress the production of bacterial beta-lactamase, because its presence can disrupt the functioning of the drug.
This combination of components in the drug allows you to quickly and effectively get rid of stomatitis. Most often, this drug is prescribed for severe forms of the disease, when intoxication of the whole body begins. Augmentin is used to treat the oral cavity of young children and adults, and depending on the age of the patient and the severity of stomatitis, the doctor will prescribe one or another form of antibiotic and its dosage.
Amoxicillin
Typically, treatment with this antibiotic is carried out when the site of infection is not the oral cavity, but the internal organs. Amoxicillin is a penicillin drug that does not act on the oral cavity, but on the source of inflammation located in another organ. Stomatitis can be treated with this antibiotic in both adults and children, and the dosage interval is 8 hours.
It is necessary to carry out treatment with antibiotics only after consultation with a doctor, since for some types of stomatitis their use will be ineffective, and incorrect use can lead to the development of side effects.
Antibiotics for stomatitis are a last resort and are prescribed when treatment with rinsing and various physiotherapeutic procedures has not brought any results. If the doctor nevertheless decides to prescribe antibiotics to the patient, it is necessary to carefully consider the proposed treatment regimen and the indicated dosage of the drug, especially for young children.
"Sumamed" for stomatitis
Sumamed, an antibiotic developed on the basis of azithromycin, is considered an effective drug from the group of macrolides. The active substance actively suppresses the development of gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms. According to reviews, this drug (when used correctly) is well tolerated by children. It can be used for the treatment of dental and ENT diseases as prescribed by a specialist.
The drug is produced in the form of a suspension, which has a pleasant taste, and tablets. The dosage is calculated depending on the child's weight. In the form of a suspension, the medicine can be taken for no more than five days, and in tablets - no more than three. The daily dosage must be determined by a doctor.
Is Augmentin effective for stomatitis?
The antibacterial agent "Augmentin" is a semi-synthetic penicillin. For the treatment of stomatitis, it is prescribed in the form of tablets, suspension or syrup only in severe cases. The active components of the drug are substances such as clavulanate and amoxicillin. The strong composition allows you to achieve significant improvement in your condition within 2 days.
The drug can be used to treat babies from 2 months, but only as prescribed by a doctor. "Augmentin" in the form of a suspension must be prepared immediately before starting therapy. Only the attending physician can calculate the dose for a child.
Stomatitis appeared after antibiotics in a child
It is worth separately considering the development of stomatitis, which appeared after the use of antibiotics in a child. Due to weakened immunity, the body's resistance decreases due to prolonged use of antibacterial agents. The mucous membrane becomes unstable to all kinds of viruses and bacteria . As a consequence of this, stomatitis develops. In this case, relapses cannot be ruled out.
In this case, it is simply necessary to take immunostimulating and various antiviral medications. Antiviral drugs are best used in the form of ointments. To do this, you need to blot the oral cavity with gauze and apply a small amount of ointment to the mucous membrane. The antiviral drug should be used to treat the affected areas 3-4 times a day.
Immunostimulants should be used as additional immune restoration and to prevent relapse. Parents should definitely consult a doctor.
To eliminate the symptoms of stomatitis, you need to rinse your mouth with antiseptics daily.
Which antibiotic is better?
For stomatitis in a child, antibacterial drugs are prescribed if the ulcerative lesion spreads in the oral cavity and other methods are ineffective. Only a specialist can select the optimal drug. In addition to antibiotics, the doctor will prescribe other auxiliary medications: anesthetics, antipyretics, keratoplasty.
Antibiotics for stomatitis in children really help to quickly cope with the disease if it has a bacterial etiology. In this case, it is important to fully follow the doctor’s recommendations regarding the dosage and regimen of taking the medication. To normalize the state of the intestinal microflora, after completing a course of antibiotic therapy, it is recommended that the child be given drugs from the group of probiotics.
Drug treatment
How to treat stomatitis after antibiotics? Conservative therapy involves the use of antihistamines to remove all allergens from the body. General strengthening medications are also used - gels and ointments, for example, "Cholisal". The use of such drugs alleviates the condition.
The treatment period is 2-3 weeks, and usually the symptoms of the disease disappear within 3-5 days. All drugs within one course of therapy must be prescribed by a doctor. Due to unauthorized use of medications, undesirable consequences arise, including a deterioration in the patient’s general condition and an increase in the intensity of symptoms.