Good day, dear friends of Alexey Shevchenko’s blog “Healthy Lifestyle”. For extensive inflammation, doctors often prescribe various medications in tablet form. Odontogenic periostitis, or more simply put, “flux,” is one of such diseases. With it, the purulent process affects a large area, accompanied by severe pain and symptoms of general intoxication of the body. Often anti-flux tablets become a real salvation.
Briefly about flux
By the word “flux,” dentists mean purulent periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth).
This complicated form of carious lesion is a signal of the patient’s inattention to his health and constantly postponing a trip to the dentist.
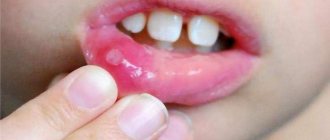
With gumboil, the gums are necessarily swollen, reddened and very painful, with a bright red tumor of a baggy shape.
Flux in the mouth indicates that exudate from a purulent tooth has entered the pulp (connective tissue in the dental cavity, rich in blood vessels and nerve fibers) and the periosteum tissue.
Often with periostitis there is pain radiating to the ear or eye. During flux, pus accumulates under the periosteum, causing irritation of nerve receptors.
Often tissue swelling gives the face an asymmetrical shape (the cheek becomes swollen). And the fact that the flux does not cause any particular pain should not relax or please the patient.
As the disease progresses, the temperature may rise, insomnia may appear, and appetite may disappear. At the same time, nearby jaw lymph nodes begin to disturb.
If the patient does not immediately begin to treat periostitis, pus continues to accumulate in the gums, which is extremely dangerous and without the necessary treatment can lead to irreparable consequences.
Flux that is not cured in time can transform into diseases that are particularly dangerous to the life and health of the patient - a purulent abscess or phlegmon.
Therefore, delaying contacting a doctor or using home remedies for flux treatment is frivolous and dangerous.
Treatment for gumboil is always complex and long-term, with mandatory sanitation of the source of inflammation (opening an abscess, removing a tooth, installing drainage, local administration of drugs into the tooth cavity, etc.), the use of anti-inflammatory drugs and rinses.
A correctly selected antibiotic for flux is a mandatory drug that can most effectively carry out complex treatment and avoid recurrence of this disease.
Why self-medication of flux is dangerous
Periostitis is a rather complex infectious disease that is strictly prohibited from being treated at home without the supervision of a specialist. Only after an examination by a dentist can you determine how to treat the gumboil.
Often, patients resort to self-treatment of periostitis or eliminating its first symptoms by taking painkillers, various rinses, using drops or warm compresses. This is a serious mistake and can lead to serious complications. Thus, it is strictly prohibited:
- self-diagnosis of the disease, prescription of treatment at your own discretion,
- the use of warm compresses, heating pads: this contributes to the accelerated spread of pus throughout the body,
- prescribing antibiotic spectrum drugs to yourself - the wrong dosage can lead to weakened immunity and disruption of the functioning of many organs,
- On the day of your first visit to the doctor, you should not take painkillers (this may complicate the diagnosis).
Cellulitis
Flux can lead to serious consequences if the patient delays a visit to the doctor and self-medicates at home. Let's list them:
- abscess - a significant accumulation of pus in the tissues limited by the periosteum,
- phlegmon is a more extensive purulent inflammation that spreads over the face and neck,
- sepsis is the penetration of infection into the blood and the spread of pus throughout the body.
Reasons for the appearance of flux
Having learned about the appearance of gumboil, many are perplexed: why did it appear if nothing hurt? However, the appearance of periostitis is always preceded by a prolonged presence of an infectious process in the oral cavity. For flux to appear, an infection must somehow penetrate into the gum pocket of the tooth.
The main causes of this pathology are:
- carious lesion of the tooth root;
- infection in the tooth during treatment (usually due to poor asepsis);
- poor-quality filling of dental canals;
- long stay of temporary filling;
- infection in the gum pocket;
- mechanical damage to the teeth (crack in the tooth due to injury);
- infectious focus in the oral cavity (tonsillitis, tonsillitis, furunculosis, etc.)
When is it prescribed?
Antibiotics can be used to treat the underlying disease or to eliminate the consequences of microbes during dental procedures.
There are several cases in which antibiotics are used:
- Gingivitis. The gums become inflamed, but the periodontal junction does not lose its integrity. In the early stages, gentle techniques are used, but when purulent-inflammatory foci appear, urgent antibiotic therapy is needed.
- Periodontitis (damage to the gums). Antibiotics are necessarily included in the therapeutic program.
- Periodontitis. An inflammatory focus of the connective tissue ligaments that fixes the tooth in its standard position, or the apex of the tooth root.
- Periostitis. Inflammatory lesion of the periosteum.
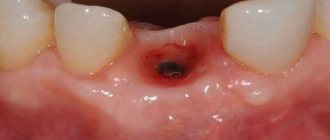
- Complication of healing of the gingival socket after extraction, especially in the case of wisdom teeth removal. It can develop due to the fact that small fragments of dentin remain in the hole, an infection is introduced during removal, or the soft tissues are severely injured.
- Trauma to gingival tissue.
- Long-term lack of treatment for caries.
- Abscess. Purulent inflammation at the base of the tooth root. It threatens the rapid development of complications and further spread through the bloodstream.
- Consequences of installing orthodontic devices or implants.
All these problems are aggravated in people with a weakened immune system: in pregnant women, after serious illnesses, with AIDS, with excessive alcohol consumption, vitamin deficiencies in the diet or poor nutrition. In such patients, treatment without antibiotics may not help, even for relatively simple diseases.
All diseases that require antibiotic therapy are characterized by the following symptoms:
- pain syndrome;
- high sensitivity of enamel;
- swelling of the gums and soft tissues of the oral cavity;
- the presence of erosions, wounds and ulcers in the mouth;
- an unpleasant odor that quickly disappears after brushing your teeth.
Often the condition is complicated by fever and a general deterioration in health.
Why are antibiotics necessary for flux?
The main thing a patient with gumboil needs to do is urgently visit a dentist.
The doctor will have to identify the diseased tooth as quickly as possible and decide on its preservation and proper treatment.
Antibiotics are universal antibacterial drugs and penetrate into all tissues of the body. Your doctor will help you choose the right antibiotic for flux (taking into account the sensitivity of the bacteria). The most common cause of flux is a staphylococcal or streptococcal infection.
An incorrectly selected antibiotic for purulent periostitis will be ineffective and harmful.
Antibiotics are often prescribed both on their own and after tooth extraction. Sometimes the use of antibiotics in the initial stage of the disease helps prevent the appearance of flux. But even after opening the abscess, this group of drugs is irreplaceable, as it helps to heal the infectious lesion as quickly as possible and prevent a recurrence from developing.
The effectiveness of prescribing antibiotics depends on a combination of many factors: how correctly the drug and its dose are selected, what is the age of the patient, whether the factor of intolerance to certain drugs is taken into account, how advanced the disease is, and how strong the immunity of the patient is, etc.
What is flux, its signs
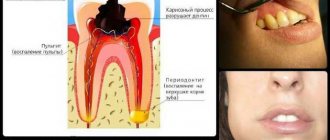
Flux is an inflammatory disease of the periosteum that develops in the area where the root of a tooth is affected by caries or has other signs of crown destruction. In dental practice, the formation of flux is designated by the medical term - periostitis. In most cases, the disease occurs in an acute form, accompanied by severe pain and decay.
Inflammation can spread not only to the soft tissue of the gums, but also to other parts of the mucous membrane that are located in close proximity to the diseased tooth. Flux forms on both the upper and lower jaws.
When tooth flux appears, an antibiotic is used before dental procedures to preserve the incisor and at the same time prevent the spread of infection into the gum tissue, roots of adjacent molars, and the upper and lower jaws.
The causes of flux formation arise under the influence of the following pathological factors:
- the presence of concomitant diseases of the gums and teeth, such as pulpitis and periodontitis, the development of which is accompanied by an extensive inflammatory process;
- fracture of the upper or lower jaw, after which the patient was not promptly provided with quality medical care;
- an open wound on the gum mucosa, into which particularly dangerous types of bacterial infection have penetrated (Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Streptococcus);
- destruction of the tooth crown due to caries, or traumatic amputation, when infectious microorganisms penetrated into the nerve canals and pulp and provoked an inflammatory process;
- mechanical injuries to the soft tissues of the gums or periosteum;
- infection of the dental pulp by pathogenic microorganisms that have penetrated the bloodstream or lymphatic fluid (this cause of tooth flux is possible if the patient’s body has a focus of chronic infection, from which the microbes migrate to healthy tissue);
- the consequences of unsuccessful tooth treatment by a dentist who made a mistake, caused an infection, or damaged blood vessels, which led to an acute inflammatory process.
People who do not maintain oral hygiene and ignore timely visits to the dentist and treatment of diseased teeth are prone to the formation of gumboil. The presence of chronic diseases of internal organs, as well as weakened immunity, increase the risk of developing inflammation of the gums and periosteum.
Signs of periostitis are always acute and are accompanied by a clinical picture that is difficult to confuse with other diseases of the oral cavity. The table below describes in detail the symptoms of flux that forms on the gum under the root of a diseased tooth.
| Symptom name | Clinical picture of manifestation |
| Increased body temperature | After the appearance of the flux, the body temperature rises sharply and can be within 38 degrees Celsius, and during an acute infectious process it can reach higher values. |
| Inflammation | The inflammatory process covers the periosteum and soft tissue of the gums, where the root of the tooth requiring treatment is located. Caused by a bacterial infection that has penetrated the pulp of the incisor. |
| Edema | The site of flux formation, as well as adjacent tissues and mucous membranes, acquire a swollen and hyperemic appearance. If the pathological process is localized from the front teeth, an increase in the size of the cheeks and lips is possible. If flux forms on the upper jaw, then the entire cheek, eye socket and temporal region swell. Damage to the lower jaw is accompanied by swelling spreading to the chin and neck. |
| Pain | The infectious-inflammatory process, which is caused by flux, is accompanied by acute or aching pain. It intensifies in the evening and at night. Has a pulsating character. |
| Purulent abscess | As gum inflammation develops, a small elevation forms on its surface, which in appearance resembles a tubercle. It quickly increases in size, and purulent and ichorous contents accumulate inside it. This liquid is a consequence of the pathogenic activity of bacterial microorganisms. |
| Fistula formation | In the absence of timely dental or surgical care, negative consequences develop. In the purulent sac that has formed on the gum and covers the tissues of the cheeks, eye socket or submandibular area, fistulous tracts are formed from which a yellow liquid with an unpleasant putrefactive odor flows. |
| Prostration | Against the background of general intoxication of the body and a decrease in the protective function of the immune system, physical weakness, headache, and drowsiness occur. |
An antibiotic for tooth flux will help relieve and cure inflammation.
An antibiotic for tooth flux can relieve the above symptoms of dental disease, preventing further development of complications such as osteomyelitis of the upper or lower jaw, as well as the transition of the disease to a chronic form with the formation of multiple abscesses.
What antibiotics are most often prescribed for flux?
To correctly select antibiotics for flux in a tooth, the doctor examines the patient and asks him about the characteristics of the development of the disease and his general condition. A test is often done to accurately select an effective antimicrobial drug.
Antibiotics for gumboils can not only cure the disease, but also prevent the infection from developing again, leading to tooth loss.
Most often, the following antibiotics are used for purulent periostitis:
- Lincomycin;
- Amoxicillin;
- Amoxiclav;
- Ampiox;
- Doxycycline;
- Ciprofloxacin.
Each drug has its own characteristics of purpose and use. The dosage of the chosen antibiotic is selected by the doctor, taking into account:
- patient's weight and age;
- contraindications to the drug;
- existing other diseases.
How to avoid side effects?
It is impossible to completely protect yourself from the consequences of taking medications; a person cannot know exactly how the body will behave. However, you can follow clear rules that will increase the effectiveness of the drug and reduce the risk of adverse reactions:
- do not drink alcohol;
- take only the approved dosage;
- do not exceed the duration of treatment;
- eat right (exclude fatty foods, dairy and fermented milk, sweets and processed foods);
- In parallel with the treatment of flux with antibiotics, take probiotics to normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
I have encountered flux twice in my life. The first time I had to open it up with a surgeon. The second time I immediately went to the doctor and avoided surgery. The disease is painful and requires long treatment and recovery. I took antibiotics both times.
Antibiotics for flux are required! Otherwise, you can wait for complications. The dentist explained to me that purulent inflammations must be treated with antibiotics. I also took them when a ball inflated on my gum, and the surgeon still had to open it.
Read also: Cheek pain causes
Features of the use of individual antibiotics
Let's look at several antibiotics most often used for flux.
Lincomycin
In dentistry it is considered one of the most effective for any purulent-inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. However, this medicine has a lot of side infections. Adults are usually prescribed 500 mg three to four times a day, half an hour before meals or 2 hours after meals, for at least 7 days. If kidney or liver function is impaired, the dose should be reduced. The medicine is not prescribed for children under 6 years of age. It should be used with caution in parallel with other medications - it can cause serious reactions.
Amoxicillin
A broad-spectrum medicine. Often goes well with the bacteria that caused the flux. Used for bacterial infections of soft and bone tissue. Adults usually take 500 mg three times a day (but not more than 6 g per day). The drug can be used in children. However, the medicine is not used for conditions such as allergies, liver failure, and dysbiosis. To prevent salt metabolism disorders, take the medicine with plenty of liquid. An analogue of this drug is Flemoxin.
Amoxiclav
It is a combination of two active ingredients: amoxicillin and clavulanic acid (synonym – Augmentin). Thanks to this, the effect of the drug is enhanced and it has a wider antibacterial spectrum. Amoxiclav is often suitable for infections when cephalosporins or penicillins are ineffective. Contraindicated in case of serious renal pathologies due to provoking seizures. It is also used for children and the elderly.
Adults take the medicine 125-500 mg three times a day. A common complication when taking it is diarrhea.
Ampioks
Contains two active ingredients: ampicillin and oxacillin. It has a minimum of side effects, as it does not accumulate in the stomach and intestines. It has a high bacterial effect in mixed infections and for the prevention of complications of purulent processes. They usually take 0.5 - 1 gram 3-4 times a day (maximum 2-4 grams per day).
Doxycycline
Group of tetracyclines. Has a fairly wide range of uses. It has a detrimental effect on aerobic and anaerobic bacteria. Not compatible with concurrent use of many medications. Take with meals with a sufficient amount of liquid (you can use milk or kefir). On the first day, usually take 100 mg once or twice a day, and on subsequent days, 100 mg per day. The medicine is not prescribed to patients with leukopenia, liver failure and children under 12 years of age.
Tsifran
Synonyms for this medicine are Ciprofloxacin, Ciprolet. Refers to fluoroquinolones. It copes well with purulent tissue inflammation in patients with low immunity. Use 250-500 mg twice a day for 5-7 days. It is better to take the medicine on an empty stomach. However, more often with flux I use injections of the drug 200 mg twice a day. For diseased kidneys, the dose is reduced. Prescribe with caution to patients with pathologies of the nervous system. You should also drink plenty of fluids and avoid sun exposure. The medicine can reduce the patient's attention. The drug is not prescribed to children under 16 years of age.
Which drug should I choose?
After examination, the specialist will determine the extent of the disease and prescribe the necessary medication. Regardless of the form or degree of flux, treatment must begin with antibiotics.
Before starting flux treatment at home with antibiotics, the doctor must conduct a diagnosis to determine the causative agent of the infection.
If the flux was caused by streptococci or staphylococci, the dentist will prescribe doxycycline, tsifran, lincomycin or ampiox.
For flux, the following antibiotics may be prescribed:
- Ampiox is an antibiotic with a wide spectrum of effects on the inflammatory process, especially caused by staphylococcal bacteria.
- Tsifran is a powerful drug that causes virtually no side effects. The antibiotic can be taken by everyone, with the exception of patients with allergies to the components of the drug.
- Doxycycline is a liquid antibiotic that is administered intravenously using a syringe. Fights bacteria that cause suppuration. Contraindicated for persons under 16 years of age; for other patients, the course and frequency of administration is determined by the doctor.
- Lincomycin is an effective drug in the fight against infection, but has many contraindications and side effects.
- Amoxicillin is a strong antibiotic that has a broad effect on harmful bacteria that contribute to the development of gumboil. It is contraindicated for use by pregnant women suffering from liver failure or lymphatic leukemia. Can be used for children over 12 years old.
- Amoxilav is a drug in the form of powder and tablets. Combines amoxicillin and clavulonic acid. Thanks to this tandem, it has an effective local effect on inflammation and ulcers.
- Ciprofloxacin belongs to the fluoroquinol group of drugs. It is a bactericidal antibiotic with broad influence. Prohibited for use by nursing women, patients under 18 years of age, and people suffering from colitis.
It is important to know that antibiotics are drugs that have a strong effect on the body and have quite a few contraindications and side effects.
The most common contraindication is intolerance to the components of the drug.
They are also not recommended to be taken during pregnancy or lactation, only in cases where the benefit to the mother outweighs the harm to the child. The product is prohibited for small children and people with weakened immune systems.
Read also: My cheek is swollen but nothing hurts
Before prescribing a course of antibiotics, the specialist will take into account the characteristics of the patient’s body and his disease. If the prescription rules were not followed or the patient developed a new disease while taking medication, side effects may occur.
- problems in the gastrointestinal tract;
- breakthrough heavy bleeding;
- muscle weakness;
- allergic reaction;
- swelling;
- pressure change.
If any side effects occur, stop taking antibiotics immediately and seek medical attention.
Rules for antibiotic treatment
Antibiotics are drugs that need to be taken strictly according to the rules. If these rules are violated (changing the dose, frequency of administration, skipping medications, or changing the course without permission), these medications may become ineffective or even harmful.
That is why during antibiotic therapy it is necessary to know and follow a number of rules.
Maintaining accuracy and time of reception
It is important to maintain equal intervals between taking antibiotics. This is the only way to maintain the desired and constant concentration of the drug in the blood.
When taking antibiotics three times, the interval should be 8 hours, and when taking antibiotics twice, the interval should be 12 hours. It is also important to use antibiotics at the same time, regardless of the form of administration. For example, when used twice, the antibiotic is drunk (or injected) at 8 and 20 hours daily.
How much antibiotic to take
Most often, antibiotics are taken for 5-7 days, but sometimes the course is increased to 10-14 days. Only a doctor can correctly adjust the timing of taking medications.
You cannot adjust the dose yourself
Patients often find it best to reduce the dose of medications so as not to harm their health. However, this can lead to antibiotic resistance and ineffectiveness.
It is also unacceptable to increase the dosage of the drug without authorization, as this can lead to an overdose and a host of side effects.
Do not interrupt the course of treatment
If the patient has already started taking antibiotics, it is unacceptable to take a break from this process. Often, as soon as the patient feels better, he decides to stop taking the medicine. Doctors usually recommend taking antibiotics for another 2-3 days after you feel better.
It is also necessary to inform your doctor if your health does not improve 72 hours after starting therapy. In this case, this indicates that the antibiotic is not suitable and needs to be replaced.
How to drink and what to take with antibiotics
The instructions must indicate the specifics of taking antibiotics: before, during or after meals. Most often, doctors advise drinking antibiotics with clean, still water. The use of other drinks (unless specifically indicated in the instructions) may lead to a decrease in the effect of the drug. It is not recommended to take medications with juices, tea, coffee, fermented milk and other drinks.
Diet during antibiotic treatment
Antibiotics are a serious burden on the body. Their active ingredients thoroughly inhibit the functioning of the digestive organs. Therefore, it is highly advisable to stick to a diet while doing this.
When treating with antibiotics, it is advisable to exclude fried, fatty, alcohol, canned food, and sour fruits from the diet. It is correct to include sweet fruits, vegetables and plenty of clean, purified water in your diet.
Support your gut
Any course of antibiotics leads to disruption of normal intestinal microflora. This may subsequently result in the following unpleasant symptoms:
- bloating;
- heartburn;
- diarrhea or constipation;
- pain in the stomach or intestines.
To prevent such complications, parallel use of drugs is used to preserve the natural microflora: Linex, Enterozermina, Bifiform, Laktofiltrum, Normoflorin, Simbiter, etc. Fermented milk products are also useful in pauses between taking antibiotics.
What to consider during treatment
When prescribing any antibiotic, it is important to study the instructions and take into account the following nuances:
- use for other diseases;
- contraindications;
- by-effect;
- interaction with other medications;
- use for different age groups.
It is unacceptable to use antibiotics for weakened people, children, pregnant or lactating women without first consulting a doctor.
Ointments and gels
Local use of ointments for periostitis contributes to the rapid extinction of inflammatory processes, faster healing of damaged tissues, and effective elimination of pain.
Vishnevsky ointment
With flux, Vishnevsky ointment can stop the development of the purulent process, quickly eliminate tissue swelling and relieve toothache. The xeroform included in the drug has an antibacterial effect, birch tar increases blood flow at the site of injury, and castor oil promotes deeper penetration of medicinal components.
Read also: Preparations for the treatment of gumboil
Vishnevsky ointment is used in the initial stages of the disease or after opening the abscess. The drug is applied to a sterile small gauze pad and applied to the skin of the cheek in the area of inflammation for several hours.
You cannot use Vishnevsky ointment if you suspect the presence of a purulent focus at the site of periostitis. This can cause worsening of the condition and the development of complications.
Metrogyl denta
The drug is available in the form of a gel, which contains antibacterial components: metronidazole and chlorhexidine. Therapeutic substances penetrate perfectly into the source of inflammation, quickly relieve pain, eliminate tissue swelling and prevent the development of purulent complications. The gel is generously applied directly to the gum mucosa above the site of periostitis. After using it, you should refrain from drinking or eating for at least 30 minutes. The procedure is repeated three times a day until the inflammatory reactions subside.
Levomekol
The ointment contains ingredients that have a wide spectrum of antibacterial activity and promote rapid tissue regeneration. Levomekol does not lose its properties in the presence of pus, therefore it is preferable in cases where it was not possible to avoid the process of suppuration. The ointment is used three times a day. It is applied to a sterile gauze or cotton swab and applied to the flux for 2-3 hours. If a purulent focus has been opened, the drug can be injected directly into the resulting cavity. It is necessary to treat dental flux with Levomekol until complete recovery.
Treatment with medications at home
There are several forms of drug release to relieve the symptoms of the disease, such as:
- pills;
- rinsing solutions;
- ointments and gels.
These forms of the drug are most often prescribed for broad exposure, since the tablets are taken orally. They have anti-inflammatory and anti-allergenic properties.
The most effective tablets are:
- Nimesil (Nimit) is one of the best pain relievers and also effectively fights inflammatory processes. The duration of therapy depends on the form of the disease with the dosage of the drug 1 tablet 2 times a day;
- Diazolin is an antiallergic drug that affects swelling and reduces ulcers. You should take 1 tablet up to 3 times a day, depending on the condition of gum inflammation;
- Diclofenac is one of the best remedies for eliminating severe toothache. You can use 25-50 ml up to 2 times a day.
Rinse solutions
In most cases, solutions and infusions are prescribed as preventive measures or additional measures in the treatment of gumboil. They contain a small proportion of ethyl alcohol, so they are good antiseptics.
Doctors often prefer such remedies as:
- Rotokan is an alcohol-based herbal solution. In the presence of flux, it is used to disinfect and relieve inflammation from the gums and oral mucosa. To use, dissolve a teaspoon of the product in a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth every two hours;
- Malavit is a natural herbal preparation with the addition of silver and copper particles, making it a strong antibacterial agent. It also helps relieve swelling and inhibits infection, preventing its spread. To use, you need 10 drops of the drug and a glass of warm water, after making a solution, you should rinse your mouth up to 7 times a day until the condition improves;
- Chlorhexidine is a strong antiseptic used not only in dentistry. Promotes tissue restoration and has a local anti-inflammatory effect. For rinsing, use a 0.5% solution up to 4 times a day.
Ointments and gels
Preparations of this form better help eliminate inflammatory processes and quickly restore damaged tissue. Some also relieve pain.
For flux, the following drugs are most popular:
– used for flux to influence purulent formations and relieve swelling. It also relieves pain and, thanks to the xeroform included in the composition, effectively fights harmful bacteria. Should be used to prevent infection after surgery on ulcers;
Vishnevsky ointment- Metrogyl denta - gel has a strong local effect - anesthetizes and eliminates severe swelling. It should be applied to the mucous membrane for 30 minutes, during which time you should not eat or drink. Perform actions 3 times a day until inflammation decreases;
- Levomekol - used in cases of severe suppuration, due to its broad antibacterial effects. Apply 3 times a day using a cotton or gauze swab.
Indications for use
Ampiox capsules are prescribed for the following diseases:
- respiratory tract and lung infections (pneumonia, bronchitis);
- angina;
- inflammation of the renal pelvis and kidney tissue (pyelitis, pyelonephritis);
- inflammation of the gallbladder and bile ducts (cholecystitis, cholangitis);
- inflammation of the bladder (cystitis);
- infected wounds and burns, skin infections;
- sepsis (bacterial blood infection);
- postpartum infection;
- prevention and treatment of infections in newborns;
- prevention of purulent postoperative complications.
The use of the drug is also advisable in case of an unknown antibiogram and an unisolated pathogen.
Instructions for use of the drug "Ampiox"
Ampiox is intended for intramuscular, intravenous and oral use:
- For internal use in tablets, a single dose for adults and children over 14 years of age is 0.5-1g, the daily dose should not exceed 4g. Children from 3 to 7 years old are prescribed the drug in a daily dose of 50 mg per 1 kg of body weight, from 7 to 14 years old - 100 mg per 1 kg of body weight. The duration of treatment is usually from 7 to 14 days. The daily dose of Ampiox should be divided into 5-6 doses.
- For intramuscular and intravenous use (drip, stream), adults and children over 14 years of age are prescribed 4 - 6 g of solution, premature and newborn children under 1 year of age are prescribed 100-200 mg per day per 1 kg of body weight, children from 1 to 14 years - 100 mg per 1 kg of weight per day. The daily dose of the injection is administered in 3-4 doses with a break of 6-8 hours. If necessary, the dosage can be increased by 2 times.
- For intramuscular administration, the contents of the bottle with Ampiox solution must be dissolved in water for injection. For intravenous injection (within 2-3 minutes), one single dose must be dissolved in 10-15 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution or water for injection.
- For intravenous drip administration, a single dose for adults should be diluted in 150-200 ml of 5% dextrose solution or 0.9% sodium chloride solution and administered at a rate of 60-80 drops per minute.
- For children, the solution is diluted in 30-100 ml of 5-10% dextrose solution. Ampiox is administered intravenously for 5-7 days, followed by switching to oral administration or intramuscular injections. The solution must be used immediately after preparation.