How dangerous is stomatitis for mother and fetus?
You should not perceive stomatitis during pregnancy simply as ulcers on the roof of your mouth and redness of the mouth. This is an infectious disease that occurs during this period in combination with reduced immunity. This means that the infection will spread freely throughout the entire circulatory system (and the lymphatic system too). It doesn’t matter what the causative agent of the disease is, a fungus, a virus or a bacterium: in any case, they release toxins that poison both the mother and the baby. Find out about the difference between herpes and stomatitis here.
In the early stages of pregnancy, toxins can negatively affect the baby's developing organs.
An infection that has spread throughout the body can also affect the reproductive system, which also negatively affects the child. In some cases, stomatitis is transmitted to the baby himself. And it can cause a lot of problems for the mother herself. This material will tell you about the symptoms and treatment of stomatitis in the throat.
During pregnancy, another oral disease often develops - gingivitis. It affects the gums, but bacteria are also to blame for its development, so gingivitis can also provoke infection of the body and affect the fetus.
How to treat stomatitis?
The choice of drugs for treatment is determined by two factors. First, it is necessary to determine the cause of the disease and select the appropriate medicine. Secondly, the drug must be safe for the fetus.
Bacterial
The cause of the development of this form of the disease is bacteria that multiply on the mucous membrane. Most often, the disease develops as a consequence of injury. Treatment is usually prescribed using the following drugs:
- Antiseptic rinse solutions (with chlorhexidine, miramistin, furatsilin).
- The use of local bactericidal drugs (Ingalipt, Chlorophyllipt).
General antibiotics are rarely prescribed to pregnant women.
General antibiotics are rarely prescribed to pregnant women, only if the infection develops rapidly. Uncontrolled use of antibiotics can harm the heart muscle, digestive organs, and the vascular system of the fetus.
The following groups of antibacterial drugs are especially dangerous:
- Tetracycline - affects the liver, disrupts the mineralization of bones and teeth.
- Ciprofloxacin - damages joints.
- Clarithromycin – leads to intoxication.
- Aminoglycosides cause hearing loss.
- Chloramphenicol - disrupts hematopoietic function.
- Biseptol - provokes heart disease.
Fungal
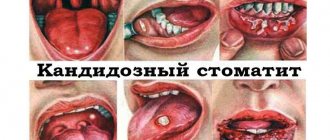
Fungal stomatitis is called candidiasis because its appearance is provoked by fungi of the genus Candida. This is a common occurrence in pregnant women, since the proliferation of the fungus on the mucous membrane begins due to changes in hormonal levels. If the lesion covers a large area, oral medications are prescribed. Most often this is Pimafucin, which does not have a toxic effect on the fetus.
For local lesions, local therapy is prescribed:
- Products based on Levorin: ointment that is applied to the mucous membrane, or powder for preparing a solution.
- Cream Pimafucin.
- Gel Candide, approved for use even by newborn children.
Viral
Viral stomatitis during pregnancy is treated with antiviral drugs. They are prescribed only in the second half, since in the first trimester they can negatively affect the development of the fetus. Of the general medications, Acicovir is most often prescribed. Local medications that may be recommended include:
- Bonafton ointment;
- tebrofen ointment;
- oxolinic ointment.
Viral stomatitis during pregnancy is treated with antiviral drugs.
Symptoms of the disease
First of all, the symptoms depend on the type of disease. The following types of stomatitis occur in pregnant women:
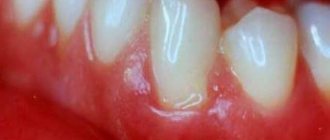
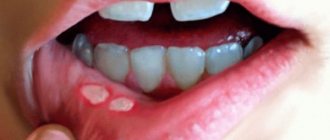
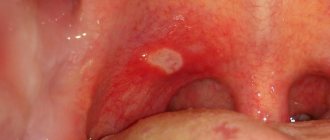
- aphthous. It makes itself felt as ulcers up to 5 mm in diameter. They are usually covered with a light coating.
Often the causes of aphthous stomatitis are ulcers and gastritis.Sometimes they merge and become extensive foci;
- bacterial. It can be triggered by tuberculosis or gonorrhea, but during pregnancy, when the immune system is weak, even the most innocent bacteria can be to blame. It makes itself felt by painful ulcers, swollen lymph nodes and rising temperature;
- viral. With it, spots and bubbles appear on the mucous membrane, which burst and turn into ulcers;
- fungal. With it, the mucous membranes turn red and their temperature rises. A coating appears on the tongue, which makes swallowing a painful process;
- catarrhal With it, the gums bleed, and a yellow coating appears on the mucous membrane and tongue;
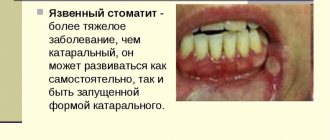
- ulcerative Develops if catarrhal disease is not treated. The mucous membrane becomes inflamed, the head hurts, and the lymph nodes become enlarged.
In general, symptoms in pregnant women are the same as in any other case. With stomatitis the following are observed:
- Redness of the tongue, spots on it;
- Change or absence of taste sensations;
- Inflammation of the mucous membranes of the cheeks, palate, tongue;
- Bleeding gums;
- Itching on all mucous membranes of the mouth and gums;
- Increased salivation;
- Ulcers (usually with a light coating and a red border);
- Erosion;
- Smell from the mouth;
- Swelling and hardening of the tongue (with advanced stomatitis);
- Increase in temperature, vomiting, nausea.
Symptoms of stomatitis in pregnant women
The disease at the initial stage is manifested by the following symptoms:
- burning or itching sensation;
- redness, swelling of the mucous membrane;
- increasing the sensitivity of the tongue;
- pain when talking, while eating;
- the appearance of an unpleasant odor.
It is important to consult a doctor when the first signs occur and begin treatment to prevent the formation of ulcers.
If the disease cannot be cured at the beginning of its development, other symptoms appear. First of all, these are ulcers, the type of which depends on the form of stomatitis:
- The aphthous form is characterized by oval or round aphthae with clear contours, covered with a grayish coating.
- Candidiasis is accompanied by the formation of a white coating, when removed, bleeding wounds are formed.
- Herpetic stomatitis manifests itself as blisters on the mucous membrane and around the mouth, which burst over time.
- For an illness caused by bacteria, ulcers covered with a yellow coating form and the general condition worsens.
When the first signs occur, contact your dentist to prevent the formation of ulcers.
Causes
Both changes in hormonal levels and a decline in immunity are to blame for the development of stomatitis. Normally, many bacteria, fungi and viruses live in our mouth, but lymphocytes in the nasopharynx prevent them from living. During pregnancy, the body is busy with other things. Stomatitis can be provoked by:
- tartar;
In addition to stomatitis, tartar can lead to the development of gingivitis or periodontal disease. - lack of vitamins B or C;
- smoking;
- insufficient hygiene;
- allergies (sometimes to fillings, toothpaste or crowns);
- trauma to the oral mucosa;
- dental or periodontal diseases;
- euberculosis;
- oral candidiasis;
- burn of the mucous membrane (alkali or acid);
- diseases of the stomach and intestines (colitis, gastritis, dysbacteriosis);
- poisoning;
- taking medications (often due to antibiotics or chemotherapy drugs);
- diabetes;
During pregnancy, stomatitis develops with a minimum of erosion and damage to the mucous membranes.
Stomatitis during pregnancy
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the lining of the mouth that can affect specific areas or all of the gums, tongue, palate and cheeks. The disease occurs due to weakened immunity in a pregnant woman, under the influence of infectious agents and after injuries. In the 1st trimester, the risk of the disease is high, and when symptoms appear, a woman should immediately visit a doctor to treat inflammation at an early stage, without waiting for complications.
Reference! A common localization of stomatitis during pregnancy is on the tongue; it can become complicated, spreading to the entire oral mucosa. Manifested by the formation of ulcers, redness, and pain.
There are catarrhal, aphthous, herpes, bacterial, ulcerative and ulcerative-necrotic stomatitis. The last 2 forms are difficult, their treatment is long-term, and requires the use of drugs that are potentially dangerous to the fetus. In the first trimester, pregnant women are more likely to experience catarrh, a mild form of inflammation that goes away within a week.
Gingivitis during pregnancy: causes, consequences and treatment for pregnant women
Diagnostics
There are no specific cultures or tests to diagnose stomatitis. Typically, a doctor determines the presence of a disease by visual examination and by a combination of symptoms. It is also necessary to collect anamnesis and understand what kind of disease could provoke stomatitis. Therefore, it is important to study the medical history. Stomatitis is determined by the appearance of ulcers and spots on the mucous membrane, as well as by its redness. In order to determine the pathogen, a blood test for viruses and mycoses is needed, because at the first stage of stomatitis it can be confused with gingivitis during pregnancy.
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type of stomatitis, on the characteristics of the expectant mother’s body and on the duration of pregnancy. So, until 12-14 weeks, you should not use any means that could harm the baby. During this period, it is only permissible to rinse your mouth with a soda solution as often as possible (take a teaspoon of soda per glass of water). You can also rinse with a decoction of antiseptic herbs, such as chamomile. Also during pregnancy, blackberries, oregano, valerian roots, lingonberry leaves, and string are allowed. This article will tell you how to get rid of bad breath during pregnancy.
After week 14, the range of permitted medications expands. Now you can already use some oral gels. Before using them, it is recommended to rinse with miramistin, or use it as a spray. Some antibiotics may also be prescribed (only by a doctor).
In case of particularly unpleasant sensations, painkillers are also permissible. They are taken only as prescribed by a doctor. Usually this is hexoral or kamistad in minimal dosages. The selection of remedies depends on the type of stomatitis. Let's consider the key features of therapy depending on the form and stage of the disease:
- For the fungal form, fungicidal drugs are used. Pimafucin, natamycin and nystatin are recommended for pregnant women. Ketoconazole and fluconazole, as well as terbinafine and voriconazole, are contraindicated. It is best to use approved products as mouth rinses. The drug dissolves in hot water with soda. Rinse many times a day;
- for candidal stomatitis, use Cholisal gel and a weak soda solution;
- if stomatitis is allergic in nature, you need to start by eliminating the allergen. Antihistamines are prescribed only if the effect of treatment is expected to be greater than the harm and risk of rejection. This could be Erius, Claritin, Vinilin, Allertek, Fexadin, Solcoseryl, Suprastin. It is also acceptable and recommended to rinse your mouth with Miramistin;
- For herpetic stomatitis, Acyclovir is usually prescribed. Course – up to a week;
- Bacterial stomatitis is treated with antibiotics. During pregnancy, amoxicillin, chlorhexidine digluconate, metronizadol, ophtoloxacin, erythromycin are acceptable;
- for viral stomatitis, an antiviral drug such as Viferon and Metrogyl Denta in gel form is most often prescribed . It is applied several times a day to all damaged areas of the mouth. The course lasts up to ten days. You can also use Tantum Verde spray several times a day. Among ointments, interferon, oxolinic and trebofenic are acceptable;
- for purulent stomatitis, antibiotics such as Ofloxacin, Erythromycin, Metronidazole, Amoxicillin are prescribed. Metronidazole can be administered externally in the form of a gel. Zinc paste can also be prescribed externally.
For rinsing, not only soda and herbs will be appropriate, but also furatsilin, one and a half percent hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate (a pinch per glass of boiled and warm water).
Clinical picture
The appearance of painful ulcers in the mouth is the main sign of stomatitis. If a burning sensation occurs, the mucous membrane should be examined. The disease begins with the appearance of a red dot, then a wound with a pale bottom and a bright rim forms. The ulcers are very painful, often covered with a white film or plaque.
Symptoms of stomatitis may vary from person to person. It all depends on the cause of the disease. Rashes with herpetic lesions look a little different. Vesicles—liquid-filled bubbles—appear on the mucous membrane of the mouth, lips, and tongue. The rashes are located in groups, less often - individually. They burst quite quickly and ulcers form.
In parallel with the appearance of vesicles, body temperature rises.
Candida lesions are characterized by the formation of white films that cover the ulcers. Plaque is also found on the tongue and the inner surface of the cheeks. General symptoms of stomatitis:
- the appearance of wounds on the oral mucosa;
- pain when chewing food, talking;
- weakness, loss of appetite, drowsiness;
- bad breath;
- an increase in temperature indicates herpetic stomatitis, a severe course of the pathology.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are also permissible, but only if they are approved by the dentist and they contain components that are safe for pregnant women. Remember that herbs are the same medicines, so do not overuse them. Here are some safe options:
- the oak bark and pour a couple of tablespoons of it with boiling water (one glass). Leave for at least one hour and strain. We rinse our mouth 8 times a day;
- We take two parts of calendula and St. John's wort flowers and one part of celandine. Pour boiling water (1 liter). We rinse our mouth after every meal;
- out of fresh carrots and rinse your mouth, spitting out the juice.
Consequences in the absence of therapy
Untreated stomatitis during pregnancy can become chronic and prevent you from living a full life after the birth of your child. In severe cases, it can provoke gangrene or sepsis. It can be transmitted to a child: he will be born with congenital stomatitis.
There are other problems. So, inflammation easily spreads to other organs. The disease negatively affects the already weak immune system of the expectant mother. Untreated stomatitis can return to a woman after the birth of a child and turn into a chronic disease. Find out about the effect of caries on the fetus during pregnancy here.
High body temperature with untreated stomatitis also has a negative effect: it leads to dehydration and has a negative impact on pregnancy in general.
Prevention
Prevention of stomatitis during pregnancy is quite simple. You need to give up bad habits, don’t forget about oral hygiene, don’t eat too hot food (or spicy), visit the dentist and immediately solve all existing dental problems, be it caries or an unsuitable filling. Oral trauma should also be avoided. Be sure to monitor for the presence of viruses or fungal diseases and fight them promptly. You also need to take vitamin complexes.
Vitamin complexes are recommended to be taken in autumn and spring.
You also need to eat right, wash fruits and vegetables and eat by the hour, and not drink too cold water, so as not to catch a cold in your mucous membranes. Buy products only of high quality and from trusted outlets. You also need to monitor your body temperature and sleep enough time. Don't forget about walks. For oral hygiene, hypoallergenic toothpastes, flosses and rinses should be used. This link will tell you how to relieve toothache during pregnancy.
Symptoms
It began to hurt to chew food, and upon careful examination in the mirror you saw pimples in your mouth? Most likely you have stomatitis. This is how many first “get to know” him. Just yesterday everything was excellent, but in the morning my mouth is on fire.
Some even consider stomatitis as a sign of pregnancy if they have never encountered such a problem before. This is not unreasonable: there are often cases when this is how the body reacts to the appearance of a new person in the womb.
You may suspect you have this disease if:
- An ulcer of unknown etiology appeared in the mouth.
- The palate, cheeks or tongue are red.
- There is an unpleasant feeling.
- Burning and stinging in the mouth, especially while eating.
- Increased body temperature
- There was an unpleasant odor from the mouth.
- Salivation increased.
Based on these symptoms, you or your doctor will determine that you have stomatitis. During pregnancy (around the fifth or sixth week) it appears and goes away over time. Unpleasant symptoms may reappear in the third trimester, when the body does not have enough vitamins, minerals and other substances to fight it.
conclusions
Stomatitis is a disease that affects half of pregnant women. Changed hormonal levels and decreased immunity are to blame for this. It can be transmitted to the child and negatively affect its intrauterine development.
To fight you need:
- eliminate allergens and heal oral injuries;
- fight the disease that provoked it;
- in the early stages of bearing a child, only rinsing with soda and herbs is permissible, antibiotics are prohibited;
- at a later date, you can use ointments and some medications;
- pain relief is acceptable, but only with certain types of drugs.
Prevention consists of oral hygiene and taking multivitamins.
Stomatitis during pregnancy: consequences
If this disease is not treated in time, it can cause a lot of harm. Therefore, consult a doctor as soon as possible to neutralize stomatitis during pregnancy. Treatment will help avoid many troubles. For example, elevated temperature against the background of inflammation will negatively affect the life of the fetus.
In the case when the disease has progressed to an advanced form, and the entire oral cavity is covered with ulcers, this can affect the child at birth. It is believed that the baby will also suffer from stomatitis.
The viral variety, if not treated in time, threatens the fetus with various deformation changes. And this is very dangerous.
For the mother herself, this is fraught with the transition of this disease to a chronic form. Which means that with each decrease in immunity, stomatitis will bother you again.
Pain and discomfort cause the expectant mother severe discomfort. The inability to eat normally sometimes provokes the appearance of vitamin deficiency.