Herpes on the tongue or glossitis: what is it?
Glossitis (or herpes) is an infection of bacterial or viral origin. Accompanied by the appearance of light or yellow bubbles on the tongue. After some time, the blisters burst, forming ulcers, causing severe pain.
According to its mechanism of development, herpes of the tongue can be primary, acting as an independent disease or secondary, as a consequence or sign of another disease.
Forms of herpes
Tongue herpes can be acute or chronic and have several forms:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
Glossitis is characterized by several varieties:
- Surface. Only the mucous membrane of the tongue is affected. Divided into subspecies: Catarrhal. Develops as a complication of oral trauma, stomatitis, and anemia.
- Ulcerative. It is a consequence of insufficiently treated catarrhal herpes.
Other types of illness are also known to medicine:
- desquamative;
- villous;
- allergic;
- Gunter's;
- diamond-shaped;
- candida;
- interstitial;
- atrophic;
- folded
Who is at risk?
Herpes on the tongue affects people whose bodies are sensitive to certain foods, oral hygiene products, or who abuse hot spices, hot foods, alcohol and nicotine.
High-risk groups include:
- Children. When entering kindergarten, the likelihood of infection with a herpes virus increases.
- Pregnancy. In pregnant women, all the forces of the body are aimed at successfully bearing the fetus, so the immune system does not always cope with the infection.
- People with poor health and low immunity. A weakened immune system is unable to suppress infection activity.
It is impossible to completely get rid of the herpes virus in the body. With weakened immunity, the disease is prone to relapse.
Symptoms and forms of the disease
Signs indicating the development of tongue herpes in an adult or child include:
- tingling and burning in the mouth;
- deterioration of sensitivity of the tip of the tongue;
- temperature increase;
- decreased performance, malaise;
- redness and swelling of the affected tissues;
- the appearance of painful, dense pimples on the tongue, which quickly transform into vesicles - bubbles filled with transparent liquid contents;
- opening of the vesicles and the formation of bright red ulcers in their place, increased pain;
- gradual epithelization of ulcers.
Infectious disease doctors distinguish 3 forms of the disease:
- light;
- average;
- heavy.
Mild herpes on the tongue is practically asymptomatic . Single pimples appear on the mucous membrane of the organ, which after 2-3 days transform into small ulcers and heal quickly. In rare cases, the disease is accompanied by a slight increase in temperature and mild pain.
With an average herpetic lesion, a profuse vesicular rash appears on the surface of the tongue, the organ tissues turn red and swell. In a sick person, regional lymph nodes increase in size and begin to ache, the temperature rises, and difficulties appear when eating. With severe herpes, the appearance of rashes is accompanied by profuse salivation, severe fever, loss of strength, drowsiness, headache and aches throughout the body. Due to burning, itching and pain in the mouth, a person can practically neither eat nor drink. In the absence of timely treatment, severe herpes on the tongue can lead to the development of serious complications - herpetic conjunctivitis or encephalitis, diseases of the nervous system.
Reasons for development
The occurrence of glossitis in the tongue is provoked by factors of a different nature:
- viral and bacterial infection;
- burn or mechanical damage to the tongue or oral cavity;
- chronic insomnia;
- weakened immune system;
- helminthic infestation;
- stomatitis;
- overheating or hypothermia of the body;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- avitaminosis;
- bodily contact with a carrier of the herpes virus;
- sedentary lifestyle;
- systematic stress;
- prolonged physical fatigue;
- the presence of systemic pathologies.
Herpes on the tongue in children
Glossitis in children can be congenital (transmitted from mother to child during fetal development) and acquired, the result of contact with a sick person or airborne infection.
The appearance of herpes on a child’s tongue is caused by:
- insufficient sleep;
- stressful situations;
- viral diseases;
- chronic immunodeficiency;
- hormonal imbalance;
- hypothermia;
- unbalanced diet;
- drinking cold drinks;
- insufficient oral hygiene;
- genetic predisposition.
Reasons for relapse
The main cause of herpes on the tongue is exposure to the herpes virus type 1, which lives in the human body. Its awakening and reproduction is provoked by weakening of the immune system. A number of factors can contribute to this:
- frequent ARVI;
- chronic gingivitis, periodontitis, tonsillitis;
- iron deficiency, lack of vitamins B12, B9;
- AIDS, HIV infection, diabetes mellitus, other immunodeficiency diseases;
- gastrointestinal diseases in a permanent form;
- poor nutrition, sedentary lifestyle, lack of sleep;
- frequent stress.
It is worth noting that herpes on the tongue and under the tongue in an adult with inflammation of the oral mucosa appears quite rarely. Basically it all ends with the lips, cheeks, and palate.
It is believed that the appearance of herpes on the tongue in both children and adults is due to insufficient production of lysozyme and immunoglobulin A, which block the proliferation of infectious agents.
Herpes on the tongue during pregnancy
Glossitis in pregnant women occurs due to a weakened immune system. A decrease in the functionality of the immune system during pregnancy is provoked by the body independently in order to avoid rejection of the fetus as a foreign body.
The herpetic virus can negatively affect the intrauterine development of a child. The extent of this effect depends on the type of disease:
- Recurrent herpes. Fetal damage is 3-5%. The low percentage is explained by the presence of antibodies in the pregnant woman’s body, which protect the fetus from viral attack.
- Primary herpes. A negative effect on the fetus is observed in 90% of cases.
Symptoms of herpes on the tongue
The disease has an extensive clinical picture, which is easily confused with signs of stomatitis or tonsillitis.
Common symptoms for all types of herpes on the tongue:
- uncharacteristic color of the tongue;
- severe pain in the mouth;
- feeling of burning and itching;
- blisters on the tongue;
- poorly controlled temperature from +38 °C;
- changing the structure of the language;
- presence of plaque;
- weakness;
- decreased mental work;
- aches in bone and muscle tissues;
- swelling of tongue tissue;
- difficulty chewing and swallowing food.
The severity of symptoms depends on the severity of the disease:
- Easy. Fever, formation of blisters on the tongue, moderate soreness, eating solid food causes discomfort.
- Average. The spread of herpetic blisters throughout the oral mucosa, the temperature remains stable at +39...+40 °C, inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- Heavy. There are signs of intoxication of the body - weakness, excessive drowsiness, migraine, lack of appetite, severe pain in the mouth.
Symptoms
The symptoms of this type of herpes are similar to other diseases of the oral cavity, in particular stomatitis. Based on the severity of the manifestation, mild, moderate and severe varieties of herpetic stomatitis are distinguished.
With a mild form of herpes, a slight (low-grade) increase in temperature is observed, rarely exceeding +38°C. Itching, swelling and soreness in the oral cavity are also noted. Characteristic bubbles appear only after 1-2 days. After the bubbles break and fluid flows out, ulcers with a whitish coating form in these areas. They heal quickly, temperature indicators return to normal. The pain goes away after 2-3 days.
In more severe forms, the signs of herpes appear more clearly. The temperature can rise to +41°C, there is a headache, weakness, muscle and joint pain, and nausea. Upon palpation, enlarged lymph nodes are felt, there are signs of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes, cough and nasal discharge appear.
After 2-3 days, rashes appear on the inner surface of the cheeks, gums, palate, at the entrance to the larynx and on the tongue. Sometimes herpes blisters form under the tongue. There is increased salivation and severe pain during meals. The vesicles burst, forming ulcers, then heal. At the same time, fresh bubbles appear. With severe oral herpes, the disease can be long-lasting.
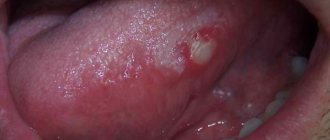
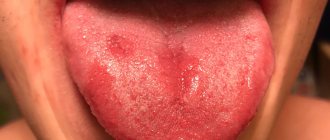
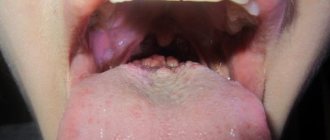
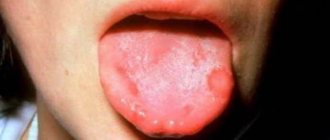
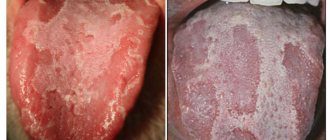
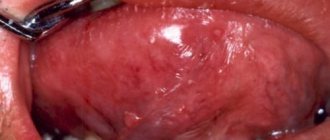
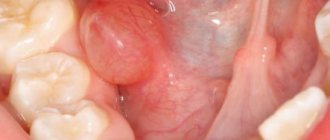
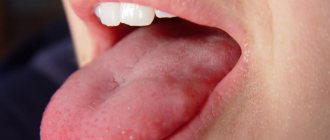
What does herpes look like on the tongue?
Visual manifestations of herpes are blisters filled with a clear white-yellow liquid.
Vesicles in the oral cavity are located in groups of 5-10 pieces. They can be localized on the tip of the tongue, on the sides and below. However, if the pimples are located on the root of the tongue, then it is difficult to notice them, since they are hidden under a layer of epithelium.
In severe cases, the rash covers the entire mucous surface of the mouth. Small formations merge into 1 large wound, which, after the fluid flows out of the bubbles, becomes covered with a scab and heals quickly.
Diagnostics
To diagnose herpes on the tongue, it is necessary to conduct an extensive examination of the body.
Comprehensive testing is prescribed:
- Virological. The presence of the virus in the body is determined.
- Bacteriological. A scraping or smear of a sample of the affected area can determine the type of pathogen.
- Histological. Study of abscess content particles.
- Antibody test. Determines the presence of antibodies to the virus.
- General blood analysis. Allows you to assess the quality of immunity, the severity of the inflammatory process and exclude anemia.
- TANK. The degree of functionality of the kidneys and liver is determined.
- Immunoenzymatic. Allows you to simultaneously identify pathogens of various types of herpes infections.
- PCR. The polymerase chain reaction detects the type of virus in the latent phase of its development.
- Test for syphilis and HIV. Confirms or excludes these pathologies.
Therapeutic measures for tongue herpes
Many patients think that it is not necessary to treat herpes on the tongue. In their opinion, this disease goes away on its own and there is no need to take any medications.
This opinion is wrong. The uncontrolled course of an infectious disease is fraught with the development of hazardous health consequences. The herpes virus causes irreversible changes that are difficult to correct.
Drug therapy for herpes virus infection should be complete and comprehensive. Otherwise, when favorable conditions arise for the development of the pathogen, the infection will again give symptoms.
Treatment of the disease
At the first symptoms of glossitis in children and pregnant women, you should consult a dentist, virologist or infectious disease specialist.
The use of therapeutic methods for tongue herpes in expectant mothers and children depends on the complexity of the disease and general health:
- Easy. Antiviral drugs.
- Average. Antiviral, analgesics, immunomodulators, antipyretic medications.
- Heavy. In the event of the formation of purulent areas, severe hyperkeratosis and other complications, surgical opening of the vesicles is performed, followed by the use of antibiotic therapy.
For any severity and type of herpes on the tongue, antiviral drugs are paramount in complex therapy, otherwise further treatment will not bring a positive result.
In complex therapy, drugs from different drug groups are used - tablets, ointments, gels and solutions for external use and injection:
- Antiviral. Effectively suppress the activity of herpes infection (Acyclovir, Cycloferon, Zovirax, Valacyclovir).
- Anti-inflammatory. They have a complex effect and effectively relieve inflammation (Prednisolone, Hydrocortisone).
- Immunostimulants. They have a complex effect - immunomodulatory, antitumor and antiviral, increase the synthesis of immunoglobulin A, strengthen the immunity of the mucous membranes in the oral cavity and tongue (Interferon, Imudon).
- Antipyretic. Relieve inflammation, normalize temperature, relieve pain (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol).
- Antibiotics. Recommended in case of bacterial infection (Amoxiclav, Ceftriaxone or Clarithromycin).
- Analgesics. Eliminate pain (Lidocaine, Panadol, Nurofen, Kamistad).
- Healing. Accelerate the regeneration of damaged tissues (Vinizol, Cholisal).
- Antiseptics. Used for disinfection of the oral cavity (Furacilin, Chlorhexidine, Biopin, Hexoral, Lizobakt, potassium permanganate).
- Antihistamines. Relieves itching and burning in the tongue area (Fenistil).
The dosage of all prescribed medications is selected by the doctor, taking into account the person’s age and the severity of the disease.
Drug therapy for glossitis in pregnant women has some features, which is associated with the inability to take many medications due to their harmful effects on the fetus:
- Valaciclovir is prescribed for the treatment of primary glossitis.
- To prevent the addition of another infection against the background of herpes, it is recommended to rinse the mouth with disinfectant solutions.
- If the temperature rises, reaching +39 °C, Paracetamol is used to eliminate hyperthermia.
- Acute phases of the disease are treated with Acyclovir in combination with Viferon.
The doctor will tell you about the treatment of herpes in the mouth in the following video:
Therapeutic tactics for glossitis
If there is a cold on the tongue, then comprehensive treatment is required. Therapy should be etiotropic and symptomatic. The main goals of treatment are:
- increased immune status;
- HSV suppression;
- elimination of the main symptoms;
- prevention of complications.
When herpesvirus is isolated from the mucous membrane of the tongue, systemic and local medications are prescribed. The first are taken orally in tablet form. Every experienced doctor should know how to treat herpes. For this infection, antiviral drugs are prescribed (Acyclovir Forte, Zovirax, Valtrex, Valvir, Famvir).
For signs of inflammation of the tongue mucosa, the following local remedies can be used:
- antiseptics;
- chamomile tincture;
- sage;
- decoction of oak bark;
- tincture of calendula;
- rosehip and tea tree oil.
Pain in the tongue with herpes can intensify while eating, so a gentle diet is prescribed for the duration of treatment - purees, stews, pureed soups. Food should not be very hot.
Rotokan and Stomatofit will be useful. These are combined herbal tinctures. To restore damaged epithelium of the mucous membrane, it is recommended to treat the tongue with rosehip, eucalyptus, sea buckthorn or tea tree oil. Treatment of herpes on the tongue requires the use of local antiseptics. These include Stopangin, Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, methylene blue, Furacilin, Cameton, Hexasprey, Hexoral and Stomatidin.
Patients should not eat spicy or rough foods. Dishes must be warm. If necessary, patients are given gamma globulin. Immunotherapy drugs are widely used. These include alpha interferons and immunomodulators. You need to know not only whether the tongue can be affected by herpes, but also how treatment is carried out.
For glossitis, H1-histamine receptor blockers are often prescribed. These include Zyrtec, Zodac and Flemoxin. Sometimes patients are given a vaccine. Additionally, complex vitamins are prescribed. Not everyone knows where herpes can be and how to treat it. In the event of a secondary infection and the development of complications (abscess, phlegmon), antibiotics are prescribed. Thus, herpetic glossitis is very common. If a rash, pain or burning sensation appears in the tongue area, you should visit an otolaryngologist.
Tweet
Pin It
- Causes of frequent herpes rash on the lips
- How to treat herpes on the lip during pregnancy: 2nd trimester
- The lip is very swollen from herpes: causes and treatment
- Are antibiotics used for herpes on the lips?
Traditional methods of treatment
Glossitis requires a comprehensive treatment approach, therefore, simultaneously with medications, it is advisable to use alternative medicine methods. This treatment regimen allows you to achieve recovery in a short time.
Benefits come from natural herbal remedies with the following properties:
- antiseptic;
- antibiotic;
- immunomodulatory.
The products are used to lubricate herpetic ulcers on the tongue and treat the oral cavity. A good healing effect is shown by:
- Licorice root tincture. It is an antiviral agent. The drink is prepared from 2 tbsp. l. chopped rhizome and 250 ml of water. Pour the raw material with water, bring to a boil, leave for 20 minutes. Use 1-2 tsp. 2 times a day for 7 days.
- Alcohol tincture of propolis. Has antibacterial properties. To prepare the product, take 1 part propolis and 10 parts vodka. Combine the components and keep in a dark place for 20 days. Take 30 drops 2 times a day. The treatment course is 10 days.
- Tea tree oil. Shows antibacterial effect. Take 1 tbsp. l. oils, dissolve in 250 ml of warm water. Rinse your mouth with the resulting product 1-2 times a day. The duration of therapy is until recovery.
- A decoction of chamomile, calendula or sage. Suppresses bacterial activity, accelerates the healing of erosions, relieves inflammation and pain. To prepare the decoction, take 1 tbsp. l. any of these plants. Pour a glass of boiling water, let it brew for 30 minutes, strain, moisten a cotton swab, and apply to the sore spot.
Dietary recommendations
During the treatment period it is necessary to follow a diet. Food should be soft (ground), nutritious and warm (about +36…+40 °C). It is required to adhere to the drinking regime - at least 2 liters of liquid per day.
The best nutrition options for glossitis are:
- soups and broths;
- yoghurts;
- meat and vegetable purees;
- milk;
- cottage cheese;
- milk porridge;
- herbal decoctions;
- butter.
It is required to refrain from using:
- cold, hot and sour foods;
- candies and caramel;
- fish with bones and chicken;
- spices and hot spices;
- strong coffee;
- marinades and pickles;
- smoked meats and alcohol;
- drinks with chemical components.
Possible complications and consequences
Delayed treatment in children and pregnant women leads to worsening of the disease, which can provoke dangerous complications:
- spread of rashes to the lips, face and mucous membranes of the esophagus;
- blurred vision, blindness;
- development of leukoplakia of the tongue (precancerous condition) with further formation of a malignant tumor;
- addition of a secondary infection;
- the appearance of streptococcal tonsillitis;
- the occurrence of toxic hepatitis;
- digestive system disorder (vomiting, diarrhea);
- sepsis of the whole body;
- DIC syndrome;
- encephalitis;
- herpetic pneumonia;
- respiratory arrest;
- damage to hearing and vision;
- infectious-toxic shock;
- dysfunction of metabolic processes;
- nervous system disorder.
In pregnant women, the risk increases:
- First trimester. Risk of spontaneous abortion.
- Third trimester. With primary glossitis, there is a risk of developing deformities, brain damage in the fetus, and stillbirth.
Possible complications
If left untreated, herpetic stomatitis is complicated by infection, in which pustular lesions appear on the oral mucosa, including the tongue. In this case, you must urgently seek medical help. Improper treatment of herpetic stomatitis can lead to infection:
- spread to the mucous membrane of the throat (make breathing and swallowing difficult);
- will cause inflammation of the trigeminal nerve of the head (this leads to facial paralysis);
- affects the mucous membrane of the eyes (threatens with decreased vision, blindness);
- will cause swelling of the brain tissue.
Herpetic stomatitis can also cause a precancerous condition in the form of leukoplakia. The pathology is compaction and keratinization of the epithelial layer of the mucous membrane of the tongue. Treatment requires the participation of a surgeon.
Prevention
The disease is easier to prevent than to treat. To prevent glossitis you need to:
- after eating, perform oral and dental hygiene using dental floss;
- brush your teeth several times a day;
- promptly treat infectious diseases;
- minimize the consumption of hot spices and irritating foods;
- wash your hands after going to public places;
- visit the dentist regularly;
- actively harden the body;
- do not abuse alcohol and smoking;
- To prevent relapse of chronic herpes, drink tincture of eleutherococcus, lemongrass, ginseng, and take multivitamins.
A preventive measure is vaccination against herpes. Vaccination is carried out with the drug Vitagerpavak and other medications.
Herpes on the tongue appears for many reasons and requires mandatory comprehensive treatment. The lack of proper therapy causes a number of serious complications. Glossitis is extremely dangerous for young children and women expecting to give birth.
Causes of herpes?
Finding out the cause of an exacerbation of an infectious disease is quite difficult. Experts identify a number of predisposing factors:
- hormonal changes in the body;
- stressful situations;
- physical fatigue;
- injury to the mucous membrane.
You should not guess on your own what exactly caused the appearance of herpes blisters on the tongue. You should definitely contact a specialist. The doctor will prescribe a diagnosis and take measures to eliminate the cause and symptoms of the disease.