Symptoms
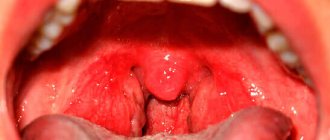
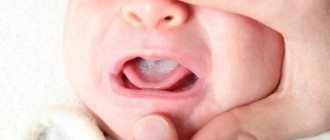
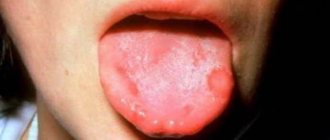
In a child’s mouth, ulcers usually appear on moving parts: near the gums, on the tongue, inside the cheeks and lips. At first, the ulcerative formations are oval or round in shape and resemble red tumors.
During the day, these rashes can appear one by one or several at a time. Over time, mouth sores may rupture, become covered with a membrane, and have red circles around the edges.
Eating causes severe discomfort and pain to the child, and appetite is noticeably reduced. Medical practice shows that usually ulcerative rashes disappear within two weeks, leaving no scars. In some cases, simultaneously with the appearance of rashes in the oral cavity, the body temperature rises slightly.
If the sores did not appear due to mechanical damage, the following symptoms of inflammation of the connective membrane may bother you:
- feeling of dryness and burning in the mouth;
- swelling of the gums and neck;
- nausea and chills;
- headache;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- pain when swallowing food.
In a situation where the formation of pustules is provoked by traumatic factors, hematomas, abscesses, redness and erosions may appear.
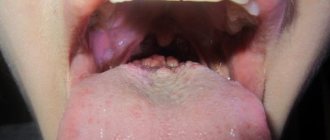
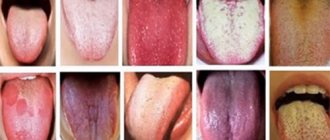
Symptoms of wounds and ulcers on the tongue
Ulcers are erosive formations that often cause pain and inflammation. For each individual pathology, wounds and ulcers have their own characteristic features. They may differ:
Read also: Drugs for stomatitis in children
- By color. They can be white, red, bruised, or have a different color.
- By localization. Distributed throughout the tongue or just on the tip, sides or base.
- By appearance. They can be flat or, conversely, convex, resembling pimples and blisters.
Symptoms also vary depending on the disease:
- with thrush, white ulcers and plaque form on the tongue;
- with scarlet fever – bright red spots;
- in case of stomatitis, one ulcer appears, the middle of which is covered with a thin whitish film;
- reddish pimples often indicate glossitis;
- blisters with unclear boundaries that appear on the palate or on the lower part of the tongue - about herpes;
- white dots are a sign of a cold or gastrointestinal disease;
- with syphilis, smooth red lumps with raised edges form on the tongue.
For comparison, you can always find photos on the Internet with similar formations on the tongue. However, relying on other people’s photos, you should not draw conclusions and make a diagnosis yourself. It is better to seek help from specialists.
Causes
The following reasons can provoke the appearance of ulcers in the mouth of a child:
- Aphthous stomatitis is an inflammatory pathology, which is characterized by the appearance of gray-white ulcers. The reason for the development of such a disease can be a decrease in the body’s defenses, disruptions in the endocrine system, vitamin deficiency, infections and wearing braces.
- Ulcerative stomatitis most often develops as a result of untreated or neglected stomatitis, which does not cause the appearance of pronounced symptoms and therefore often goes unattended. Ulcerative stomatitis, on the contrary, causes severe discomfort to the patient and is accompanied by bleeding gums, a rise in body temperature and enlarged lymph nodes.
- Dental defects and malocclusion provoke the appearance of ulcers in the child’s mouth. With such pathologies, the mucous membrane is severely injured and becomes too vulnerable to penetration by pathogenic microorganisms.
Reasons for appearance
According to statistics, every second person, including children, may develop mouth ulcers. They can be triggered by various reasons.
For example, oral injuries may be caused by biting the lip or cheek. These injuries have red or bloody sores that bleed or hurt.
Possible causes of mouth sores may include:
- thrush;
- herpes;
- stress;
- dental defects;
- lack of vitamin C;
- chickenpox virus, diphtheria, allergies, etc.;
- damage to the oral cavity;
- some medications.
Typically, these forms of the disease are caused by a weakened immune system, vitamin deficiency, the presence of autoimmune diseases, or the presence of infection.
It is not known exactly what causes stomatitis. Multiple factors are believed to be involved in the disease. Diet may play a role, incl. low in folic acid, vitamin B12 and iron can trigger stomatitis in children with food allergies.
Oral trauma, such as biting the inside of the lip or cheek, can damage the delicate tissues in the mouth and cause stomatitis. Sodium lauryl sulfate, an ingredient in many toothpastes and mouthwashes, has also been statistically linked to this disease.
In some cases, even emotional stress can be a trigger for this disease.
Most often, stomatitis affects young people in their teens and early twenties. Women suffer from this disease twice as often as men.
Although stomatitis is not contagious, outbreaks of aphthous stomatitis tend to recur as a familial disease.
It is known that a sore in the corner of the mouth can be a sign of certain types of diseases, for example, angulitis, zeda or the common cold.
Read about ways to strengthen teeth enamel here.
For a home method of teeth whitening using activated charcoal, see here.
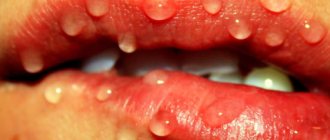
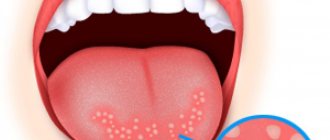
Stomatitis is the most common type of sores in the mouth, located inside the cheeks and lips, at the base of the gums, or on the tongue.
The disease usually manifests itself as round, painful, open sores that have a white or yellowish coating and a red “halo” around them.
Most often, stomatitis manifests itself as single rashes, but it can also appear in the form of small clusters. Sometimes the area of the upcoming rash may tingle or "burn" before stomatitis develops in that area.
Most wounds are small (about 6 mm in diameter), but smaller ulcers or larger and deeper ones may appear. A child may have one or more painful sores.
Stomatitis usually lasts 7-10 days and heals without scarring. Large ulcers can last for weeks to months and may leave scars.
Stomatitis is different from herpes, which is caused by an intracellular parasite virus. Cold sores often protrude outside the mouth around the lips, onto the cheeks, chin, or inside the nostrils. Herpes is a contagious disease, stomatitis is not.
Symptoms of stomatitis may include:
- pain;
- swelling;
- soreness;
- redness;
- salivation;
- fever or headache;
- irritability.
Diagnosis of ulcers in the oral cavity is carried out by their appearance. To get more information, your doctor may ask a series of questions about your canker sore symptoms and medical history. The doctor will also determine whether any tests and treatment are needed for this disease.
Read also: How to cure stomatitis in a child
If a child's pain extends beyond the oral cavity, then most likely the cause is herpes.
What is the best way to treat white and red ulcers in a child’s mouth?
You can alleviate a child’s condition with white and red rashes in the mouth using the following means:
- Baking soda and lemon. You need to mix ¼ teaspoon of baking soda with the juice of half a lemon. Pour a teaspoon of water and ½ spoon of honey into the resulting mixture. All components should be mixed until a homogeneous mass is formed and applied to mouth ulcers several times a day.
- Salt rinses. To prepare the solution, dissolve 1-2 tablespoons of table salt in 200 ml of warm water. It is necessary to rinse your mouth with this solution after each meal and always before going to bed.
- Hydrogen peroxide. You should take 3% peroxide and combine it with water in a 1:1 ratio. You need to moisten a cotton swab in the solution and lubricate the sores in the mouth with it. After this, you need to wipe off the remaining product with a dry cotton swab so that the child does not swallow it.
If ulcers appear simultaneously on the lips and the root of the tongue, you should enrich the child’s menu with foods that contain sufficient amounts of vitamins B2 and B6.
Find out how to treat a child's mouth ulcer. What are the types of local anesthesia in dentistry? The answer is here.
Medication
If the cause of mouth ulcers is a virus, then antiviral drugs are prescribed:
- Virolex;
- Atsik;
- Viferon;
- Acyclovir;
- Gerpevir.
When wounds appear due to candidal stomatitis, the use of antifungal ointments is indicated. Drugs such as Candizol, Clotrimazole and Candide have a good effect in combating mouth ulcers in children.
In rare cases, when the pathology is caused by a bacterial infection, antibacterial drugs may be prescribed. For traumatic ulcerative formations, treatment is carried out using antiseptics and folk recipes.
An important place in the treatment of mouth ulcers in a child belongs to increasing the immunity of the child’s body.
A course of the following immunostimulants may be prescribed:
- Immunal;
- Anaferon;
- Arbidol.
It is necessary to coordinate their use with your doctor, since the duration of therapy and dosage depend on the age of the child and the severity of his condition.
At home
When treating ulcers in the mouth, you can use folk remedies, taking into account the age of the child. Many plants have analgesic, sedative and antiseptic effects.
At home, you can use the following alternative medicine recipes:
- To prepare a decoction of chamomile or sage, pour a glass of boiling water over a tablespoon of the plant. The resulting mixture should be left to infuse for several hours, then strain and treat the oral cavity with the solution.
- A soda-salt solution has an antiseptic effect. To prepare it, you need to mix a tablespoon of salt and soda, and pour a glass of warm water. The prepared solution should be used to rinse the mouth of children over 3 years of age.
- Aloe juice, which is recommended to be used in its pure form, is an effective remedy for treating oral ulcers. It is necessary to cut a leaf of the plant, cool it slightly and lubricate the wounds in the mouth with the juice. In case of severe disease, it is recommended to chop the leaf and squeeze the juice from it. After this, dissolve the resulting juice in a glass of water and use it as a rinse.
- Potato compress has a wound-healing effect. To prepare it, you need to grate the root vegetable on a coarse grater and lubricate the inflamed areas of the mucous membrane with the resulting mass. After 15 minutes, the mouth should be rinsed with warm water.
To strengthen your child’s immunity, you can use folk remedies such as propolis, honey, garlic, onions and carrots.
Treatment of oral diseases
Having noticed an abscess in a child’s mouth, parents should quickly show it to a pediatrician or dentist. The doctor will determine the cause and tell you how to treat the abscess at home (usually only infants are hospitalized).
Having established the cause of ulcers in the baby’s mouth, doctors prescribe complex therapy. It usually includes treatment with dental gels, immunomodulators and other medications, as well as vitamin complexes. For severe lesions, local painkillers are prescribed.
Treatment of ulcers
Any procedures for treating ulcers are carried out after meals, at least 2 hours before the next meal or drink. The choice of remedy depends on the nature and cause of the disease:
- for viral (herpes) stomatitis, the wound is treated with a weak solution of potassium permanganate, Acyclovir, Zovirax and other drugs are used;
- for fungal or herpetic stomatitis, pharmaceutical blue (methylene blue dye) is effective, which is used to treat the affected areas, including the palate;
- white ulcers caused by mechanical trauma can be treated with sea buckthorn or rosehip oil, Metrogil Denta gel (allowed from 6 years of age);
- A solution of vitamin B12 and hydrogen peroxide helps well in treating ulcers;
- Traditional medicine suggests treating the abscess with a mixture of honey and chopped almonds (be careful, allergies are possible!).
Read also: How to treat stomatitis in a 2-year-old child
Painkillers
To eliminate pain, doctors recommend anesthetic medications, lozenges, gels, sprays, and solutions for the affected area.
- In ENT practice, the drug Hexoral Tabs, which has antiseptic and local anesthetic properties, is widely used. It is indicated for stomatitis and ulcerative gingivitis, but is allowed only from 4 years of age.
- Younger children (from one year old) are prescribed "Cholisal Gel". It has proven itself as a local anesthetic and anti-inflammatory drug.
- The Kamistad gel is no less effective when used. The manufacturer has changed its formula, and now for use by children under 12 years of age, be sure to consult a doctor.
- Additionally, in case of severe pain, Nurofen syrup should be taken orally.
Mouth rinses
For rinsing with numerous wounds, the doctor prescribes “Chlorhexidine” (0.05%), “Miramistin” (0.01% solution), and a ready-made solution of furatsilin. The most effective is “Chlorhexidine”, the components of which are active against herpes viruses, tubercle bacilli, and other pathogenic bacteria. Chlorphyllipt, Tantum Verde, and Stomatofit are used as anti-inflammatory drugs.
Rinsing with traditional medicine at home is an additional way to improve the child’s condition. It is important to show him how to do the procedure correctly and choose the most pleasant remedy. The following recipes are most effective:
- mix half a glass of cabbage or carrot juice and half a glass of water;
- dissolve 1 tsp in a glass of warm water. tinctures of calendula or soda;
- use decoctions of calendula, sage, chamomile for the procedure 4-5 times a day;
- chicken protein dissolved in 100 ml. water is used every 2 hours.
What not to do
If ulcers appear in the child’s mouth, they should not be treated with blue and brilliant green. The fact is that such treatment can provoke additional irritation of the mucous membranes and increase pain.
It is imperative to seek medical help if the discomfort does not disappear within two weeks, or if the child has problems swallowing. Indications for emergency hospitalization are a rise in body temperature above 40 degrees, the appearance of signs of dehydration and fever for several days.
Treatment
If a child has ulcers on his tongue, what should he do?
Usually, ulcers due to mechanical damage do not require any specific treatment and go away on their own in the shortest possible time.
The mucous membrane is unique in that it can quickly regenerate, especially in a young organism.
If ulcers are detected in older children who are no longer fed breast milk or formula, the menu should be reviewed.
Exclude from it traumatic foods, hot, sour, salty dishes. You need to monitor how the child brushes his teeth, cut his nails very short so that he does not injure his tongue again (this applies to children from one to 2 years old).
If the cause of the ulcers was damage from improperly growing teeth, the help of a dentist is required, because there will definitely be relapses.
If injury occurs due to improper oral hygiene, you should change the baby’s toothbrush, explain to him how to properly brush his teeth and control this process.
In any case, if ulcers are found on a child’s tongue, they must be disinfected.
A solution of hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexidine, Miramistin, is suitable for treating the tongue.
Infants and small children need to gently blot the ulcers with a cotton swab soaked in peroxide or chlorhexidine.
In this case, the preparations must be pre-diluted with boiled water in a 1:1 ratio. Older children who no longer accidentally swallow liquid can rinse their mouths with the same solutions, in the same proportions.
Pharmacy herbs have proven themselves well: chamomile, St. John's wort, sage, oak bark.
They can also be used to moisten wounds on the tongue or rinse your mouth.
If the ulcers bring severe discomfort or the temperature rises against their background, then it is necessary to give the child an anesthetic and antipyretic in a dose appropriate for his age. This could be Panadol, Nurofen or any other proven children's remedy.
After disinfecting the sores, you can lubricate them with local anesthetics. For children, special products are produced that relieve pain during teething, for example, Kalgel. This will help relieve itching, burning and pain in the tongue area.
In cases where the ulcers are caused by a fungus of the genus Candida and there is a cheesy coating, it is necessary to treat the baby’s oral cavity with a weak soda solution.
To do this, wrap a sterile bandage around your finger, moisten it lightly in a soda solution (1 teaspoon per glass of boiled water) and thoroughly wipe the child’s mouth. Baking soda is an alkali that effectively combats acidic environments, so the results will be noticeable.
Of the medications, children are most often prescribed Nystatin or Candide. You cannot use them on your own; you should definitely consult a doctor who will prescribe the correct dosage.
In addition, the child needs to take immunostimulating drugs and strengthen the body to avoid the recurrence of thrush and ulcers.
Acyclovir ointment
If the ulcers are caused by the herpes simplex virus, the pediatrician may prescribe antiviral drugs such as Acyclovir or Zovirax and immunomodulatory drugs such as Viferon, Anaferon, Interferon.
There are particularly severe cases of diseases that cause ulcers. Then the doctor can prescribe antibiotics and other necessary medications.
For an ailment such as an ulcer on a child’s tongue, treatment should in no case include treatment with iodine, brilliant green, potassium permanganate or alcohol-containing drugs. Firstly, this will only worsen the situation, the ulcers will be irritated even more, and this will bring severe pain to the child. Secondly, it is dangerous, since a child can swallow such substances.
Diagnostics
If white ulcers form in a child’s mouth, it is necessary to show it to a dentist or pediatrician. Diagnosis involves an external examination of the patient, but in rare cases a blood test and saliva smear are necessary.
Based on the results obtained, the doctor can diagnose the disease and select effective treatment.
Parents are not recommended to self-medicate, except in cases where the child is simply burned or bit his cheek. The fact is that the cause of the appearance of ulcerative formations in the oral cavity can be not only ordinary stomatitis, but also more dangerous pathologies that require serious treatment.
Symptoms and signs
The formation of ulcers on the gums of a child can be accompanied not only by characteristic symptoms of inflammation, but also by accompanying signs reminiscent of diseases not related to the dental group .
For example, increased body temperature, lack of appetite, increased salivation, sore throat and disturbances in psycho-emotional state. An abscess can be identified at any stage of development by visual examination of the oral cavity.
Read also: A child has stomatitis, what to do?
Symptoms of an abscess on the gum are the following factors:
- swelling of the gums in a certain area with clear localization;
- the formation of a red swelling with a characteristic white dot in the center;
- the development of swelling is accompanied by pain of varying intensity;
- at the last stage of development, the abscess turns into a ball with gray or yellowish contents.
Editorial advice
There are a number of conclusions about the dangers of washing cosmetics. Unfortunately, not all new mothers listen to them. 97% of children's shampoos use the dangerous substance Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (SLS) or its analogues. Many articles have been written about the effects of this chemistry on the health of both children and adults. At the request of our readers, we tested the most popular brands. The results were disappointing - the most advertised companies showed the presence of those very dangerous components in their composition. In order not to violate the legal rights of manufacturers, we cannot name specific brands. Mulsan Cosmetic, the only company that passed all the tests, successfully received 10 points out of 10. Each product is made from natural ingredients, completely safe and hypoallergenic. We confidently recommend the official online store mulsan.ru. If you doubt the naturalness of your cosmetics, check the expiration date; it should not exceed 10 months. Be careful when choosing cosmetics, this is important for you and your child.
Prevention
In order to prevent the appearance of ulcers in a child, it is necessary to monitor the hygienic condition of the oral cavity. It is necessary to teach him to use a toothbrush and toothpaste from birth.
It is recommended to fill the child’s diet with a sufficient amount of vegetables and fruits, and periodically take vitamin complexes.
You should avoid severe hypothermia and try to ensure that the child does not get sick even with common colds.
Parents should try to wean their child from bad habits, among which the most common is the desire to taste everything. This hobby leads to the fact that a large number of bacteria enter the body. In addition, the mucous membrane of the mouth is severely injured, which can also cause the appearance of ulcers.
Rules for processing and treatment in children
Ulcerative defects on the mucous membrane in children appear when personal hygiene rules are not followed. Children can injure the inner surface of the oral cavity with foreign objects. Before starting treatment, it is better to consult a pediatrician. Pharmaceutical drugs, when used incorrectly, cause allergic reactions in children's bodies. You can treat a wound in the mouth using special ointments, gels, and powders.
Children are prescribed Solcoseryl, Chlorophyllipt, Stopangin, Furacilin.
Pain syndrome in children older than six months is relieved with Ibuprofen and Paracetamol.
When treating the oral mucosa, you must adhere to the following rules:
- You cannot independently increase children’s doses of medications or the frequency of administration.
- If the child does not know how to rinse his mouth, then it is necessary to lubricate the wounds with antiseptics. Do not allow your baby to swallow the medicinal solution.
- If allergic rashes appear, stop treatment and consult a doctor.
- When treating a wound, it is necessary to follow the rules of using aseptic techniques. Before treatment, wash your hands and lubricate the inflammatory areas with a clean cotton swab with the applied medication.