Causes of inflammatory processes of the tongue
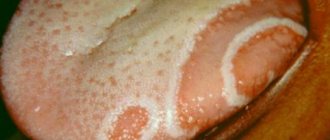
Inflammation of the papillae of the tongue is papillitis, the cause of which can be injury to the tongue, which occurred as a result of chemical damage (acid, alkali), improperly made dentures, sharp dental edges, or a fish bone became the cause.
In other cases, papillitis occurs with various infections of the oral cavity, for example, complicated caries, or diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Sometimes this can be a manifestation of allergic reactions to toothpastes, mouth rinses, and medications. Such damage to the tongue is accompanied by pain, thickening and redness of the surface of the tongue, while there is no plaque and coherent speech is impaired.
During such an inflammatory process, a burning sensation may be observed in the area where the tongue is affected. Red papillae on the tongue, depending on their location, may indicate various diseases of the internal organs. For example, redness of the papillae located at the tip of the tongue may appear with diseases of the pelvic organs, and reddened edges and the middle of the tongue indicate a possible lung disease.
Symptoms
When the papillae on the tongue become inflamed, tissue sensitivity increases significantly and taste changes. Patients complain of unpleasant discomfort in the mouth. The taste spectrum is distorted and becomes unnatural. In addition, a number of other symptoms appear.
- Noticeable tissue swelling.
- Marked increase in size of the papillae.
- Tingling and itching.
- Burning, mild soreness.
If you do not consult a dentist in time, complications may develop: lingual eruptive papillitis. This disease occurs over a long period of time with an increase in body temperature. Most often the disease affects children. An alarming symptom is the appearance on the surface of the vocal organ of bubbles (pustules) filled with a transparent liquid.
{amp}gt; Dentistry Blog {amp}gt; Inflammation of the papillae on the tongue
Navigation:
- Causes
- Symptoms
- Localization
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Inflammation in a child
In medicine, inflammatory disease of the papillae is called papillitis or glossitis. The gustatory sensory organ is an indicator of taste.
It allows you to perceive relish in all its shades and ranges. The organ tissue is completely renewed every 10-15 days. If damage occurs, the taste changes and the oral cavity hurts. To restore health, you need to undergo treatment. Inflammation of the papillae on the tongue will be eliminated by the dentist.
The patient must go to the clinic and tell the doctor about his complaints.
From the reference book! The receptors are located in the posterior zone of the tongue. They help to perceive different taste spectrums: tart, sweet, bitter, spicy, sour, salty. Sensory cells transmit the signal to the brain for processing. Then the person has a certain feeling.
With systemic diseases, burns of a muscle organ and other factors, impulse transmission is disrupted. At the same time, perception changes, atypical, uncharacteristic sensations are added.
Usually, the patient feels pathological changes - the appearance of plaque, swelling, and increase in size. The longer this clinical picture persists, the more the taste becomes distorted. Papillitis can be temporary or chronic.
To speed up recovery, you need to strictly follow the dentist’s recommendations.
If the child’s body is weakened and he complains of discomfort in the mouth and pain in the muscle organ, parents should immediately show him to the pediatrician and pediatric dentist. The doctor will determine whether his papillae are red and whether there is an inflammatory process in the mouth. Once the diagnosis is made, therapy is prescribed.
As a preventive measure, parents should ensure that the baby regularly brushes his teeth and rinses his mouth thoroughly. Children's immunity is not strong enough, so the body cannot cope with the disease on its own. The situation is complicated by the fact that children are curious; they put most objects in their mouths.
To avoid serious complications, take your child to the dentist regularly.
Make an appointment at the ARTES clinic!
The papillae appear elongated, have a rough surface, and they may also be irritated and/or inflamed. In the article we will present information about inflamed taste buds separately.
Depending on the reasons that actually caused the changes, other changes may occur simultaneously with the enlargement of the papillae.
Most often appear:
- redness (hyperemia) of the papillae;
- changes in the color of the surface of the tongue (in large areas or in the form of white or red dots);
- ulcers of various sizes and sensitivity;
- sore throat, pharyngitis (inflammation of the tonsils and throat mucosa);
- loss of ability to distinguish tastes;
- tongue soreness.
To understand that you really have glossitis, look closely at your tongue in the mirror. Provide yourself with the best lighting possible and inspect it. The first thing that will catch your eye is a change in color: your tongue will turn from light pink to bright red or even purple. Also
a burning sensation may appear, it will be difficult for you to eat food, especially sour food, it will seem incredibly painful.
With some variants of glossitis, the tongue may enlarge, become softer, and swell. White plaque on the papillae occurs when there is not enough iron in the body. We noted earlier that a sore tongue is not just a problem. It prevents a person from living fully, communicating, even eating becomes difficult, and in the case of edema, the swallowing function is also impaired.
What is the sucking reflex?
It is formed in a child in the first minutes of life, and its inclinations appear in the womb; on an ultrasound, it is often visible how the fetus holds its finger in its mouth. If the baby was born healthy and full-term, he is immediately applied to the mother's breast, and he calms down, receiving a few drops of colostrum. This is how maternity hospitals support the innate instinct and promote the correct establishment of the sucking reflex.
Any kind of touching the baby’s lips causes responses in the form of sucking movements. Doctors know until what age the sucking reflex is normal, performing a protective function - this is the first 12 months of life.
The sucking reflex is realized with the participation of the nuclei of certain nerves located in the stem part of the medulla oblongata. These are the trigeminal nerve, facial, vestibular, glossopharyngeal, vagus and hypoglossal.
The interconnection of these pairs of nerves ensures strict coordination of the sucking process. After finishing feeding, the reflex first weakens, and after an hour or an hour and a half it comes to life again. If the central nervous system or any of the above nerves is damaged, it decreases or disappears completely.
Babies weaned early from mother's milk and fed with formula have the problem of an incompletely realized sucking reflex, which can lead to the development of neurosis of obsessive movements of varying degrees. This is expressed in particular in the following:
- the habit of sucking various objects (finger, pen, pencil, blanket, dolls, etc.);
- habit of biting your nails;
- Adults have a desire to smoke, hold a cigarette in their mouth for a long time, and try to light up quickly under any stress.
Thus, the child must correctly go through the oral stage of development so that there is no formation of neurotic reactions in the future. People deprived of mother's milk at an early stage of development must be brought up with the use of a pacifier as an object of sucking, otherwise an adult during his life may show oral aggression in an active form (biting, snapping verbally, being sarcastic) and passive (poor appetite, all sorts of painful state).
A baby is given a pacifier between feedings; it must be weaned off gradually, during play, with talking and affection, without punishment or screaming. When the sucking reflex fades, nature has determined that a child older than one or one and a half years old does not need it, although the baby will continue to have sucking movements for a long time in his sleep and in subsequent years, until about 3 or 4 years old.
Treatment of papillitis
For successful treatment, it is necessary to eliminate the factor that caused the inflammation. To do this, you need to contact a specialist who can draw the right conclusions, on the basis of which further treatment will be carried out.
In case of fungal infection, antibiotics are prescribed; in case of allergies to medications, these drugs are canceled or replaced with appropriate ones.
You cannot do without vitamin preparations, which are prescribed additionally.
For topical use, agents are used that relieve pain and relieve inflammation - baths, rinses, ointments. You should not neglect therapeutic and preventive measures to improve the health of the whole body, because, as a result of the addition of additional infections, the inflammatory process can occur in a more complicated form. Therefore, it is in the patient’s best interest to consult a dentist to remove plaque, tartar, and also to treat caries.
Taste receptors are located in taste buds, which are part of tiny structures called lingual papillae, located on the “tongue, soft palate, upper esophagus, cheeks and epiglottis” [Wikipedia]. They are responsible for distinguishing between five main tastes: bitter, salty, sour, sweet and umami (in the Eastern culinary tradition, an accepted long-lasting enveloping “meat” or “broth” taste, caused by the presence of certain amino acids in food), the combination of which helps us feel the diversity of taste food.
We suggest you read: Treatment of gums with hydrogen peroxide for inflammation and periodontal disease: is it possible to rinse?
Taste buds are present in only three of the four types of papillae: grooved, fungiform and foliate, while they are absent in filiform papillae.
Treatment of enlarged papillae on the tongue
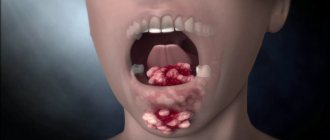
To give you a visual impression, we present several photographs. We hope that the images of swollen enlarged taste buds will help you clarify what they look like.
Enlarged papillae at the base of the tongue
Often the place in the language where the problem appeared can help to more accurately determine why it happened.
On the tip of the tongue
Since there is a high concentration of fungiform papillae at the tip of the tongue, damage to this region may be the basis for a problem with this particular type of papilla.
The main reason is trauma, in particular:
- tongue biting;
- friction of the tongue on the teeth;
- damage with the formation of flaps on the tongue during hard brushing.
If swelling of the taste buds appears on the tip of the tongue during pregnancy, you should consult a doctor for medical help, as this may or may not be related to pregnancy.
On the sides of the tongue
From time to time, you may experience an increase in the size of the taste buds on one or both sides of your tongue. Its lateral surface has mainly mushroom-shaped and also leaf-shaped papillae. Likewise, treatment will depend on what is causing the problem.
If the swelling of the papillae has reached the back of the tongue, then you may have trouble recognizing the bitter taste. Changed papillae can be small or large, or raised above the mucosal surface, depending on what is causing the problem. If you have large taste buds on the sides of the back of your tongue, you may experience changes to the foliate papillae, as these are where they are located.
Sometimes swelling of the taste buds, especially on the back of the tongue, and inflammatory processes in the throat (sore throat and/or pharyngitis) are combined.
The likely cause is an upper respiratory tract infection if the following symptoms are present at the same time:
- problem of sinus drainage (congestion or increased discharge from the paranasal sinuses);
- cough;
- fever;
- headache.
Other infections, such as gonorrhea, can also cause a sore throat, difficulty breathing, and changes on the back of your tongue. Finally, a severely dry throat can be caused by large taste buds.
Hypertrophy of the taste buds of the tongue often occurs in children and unbalanced people. The first ones to put dirty toys and hands into their mouths cause infection. The latter may bite their nails or stationery, from the surface of which pathogenic bacteria enter the mouth.
Inflammation of the white fungiform papillae of the tongue is provoked by viruses, bacteria, fungal infections, and systemic diseases. In this case, quite unpleasant symptoms are felt: burning and loss of taste, sensation of a foreign body on the tongue, pain when eating, talking, brushing teeth.
The cause of red spots is often irritation of the circumvallate papillae. They can become inflamed due to chemical and thermal burns of the oral cavity, gastroesophageal reflux disease. People with dentures and lovers of hard sweets and lollipops also complain about this problem. Inflammation cannot be avoided in the presence of chipped teeth that injure the mucous membrane of the tongue.
If the papilla on your tongue is inflamed, visit the dentist. Only he will be able to correctly determine the causes of the disease, find out what caused the damage to the mucous membrane of the mouth and the body of the tongue. The area where the disease is localized plays an important role in making the correct diagnosis. Pathology can cover the entire organ, part of it, or the sides. Based on this factor and the clinical picture, we can assume what exactly caused the inflammation.
In all languages
When the mucous layer of an organ is affected over its entire surface, the most common cause is a thermal or chemical burn. One can assume the infectious nature of the pathology. If the damage is severe, there may be no taste at all. Patients complain of severe burning.
On the root
Most often, the papillae on the tongue at the base become inflamed due to the action of allergens. The affected root of the muscular organ causes difficulties such as the perception of bitterness, because the inflammatory process has affected the circumvallate papillae. They are the ones responsible for this function. The patient's salivation increases, and the tissues in the oral cavity swell.
On the tip
The disease can affect the tip. This often occurs due to mechanical injuries or damage. The edge of the tongue is the first to come into contact with excessively hot food or aggressive drinks, which burns this area. Soft tissues often rub against sharp chips of crowns and are subject to accidental biting.
The delicate surface on the sides often suffers from various anomalies. Leaf-shaped, conical, filamentous, mushroom-shaped structures are exposed by the teeth. This leads to an increase in the papillae, their hyperemia due to mechanical damage from fangs and molars. Also provoking factors are painful microorganisms and burns of chemical origin.
Causes: what causes tongue cancer?
Like any malignant tumor, tongue cancer occurs when genetic mutations occur in one of the cells. Because of these mutations, the cell does not respond to molecular signals and begins to multiply uncontrollably. Over time, there are so many of these “wrong” cells that they form a malignant tumor. The exact causes of tongue cancer are unknown. It is impossible to say unambiguously why genetic changes occurred in a particular cell, and it began to behave so aggressively. There are some risk factors:
- Smoking cigarettes, pipes and cigars. The risk of tongue and oral cancer in smokers is several times higher than in non-smokers, and it directly depends on the smoking experience and the daily number of cigarettes smoked. Tobacco smoke contains thousands of different substances, many of which are carcinogenic.
- Alcohol consumption. 70% of people diagnosed with malignant tumors of the tongue regularly drank alcohol. If a person smokes and often drinks alcohol, his risks increase even more: according to some data, 100 times compared to non-drinkers and non-smokers.
- Floor. According to statistics, men suffer from tongue cancer more often than women. This is probably due to the fact that they are more likely to have bad habits.
- The human papillomavirus (HPV) is transmitted through sexual contact, including oral sex. More than 150 types of pathogen are known. 13 of them can cause cancer.
- HPV type 16 is associated with malignant tumors of the mouth. Recently, the prevalence of oral and throat cancer in non-drinkers and non-smokers has been increasing, and human papillomavirus infection is often detected in them.
- Age. Most often, people over 55–60 years old get tongue cancer. But HPV-related tumors are usually found in younger people.
- Nutritional features. Some studies have shown that people whose diets are low in vegetables and fruits get sick more often.
- Weakened immunity. At increased risk are people suffering from AIDS and immunodeficiency conditions caused by other reasons.
None of these factors leads to malignant tumors of the tongue with one hundred percent probability. Their presence only means that a person has increased risks.
The role of such factors as rinsing the mouth with liquids with a high content of certain substances, irritation of the mucous membrane with dentures, and chronic inflammation in the oral cavity has not been proven. More research is needed to assess whether there are any risks in these cases.
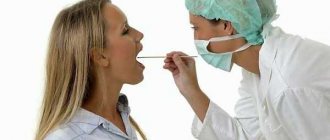
Diagnostics
Basic diagnostic methods in dentistry allow a thorough examination to be made in order to make the correct diagnosis. During the initial examination, the dentist determines the size of the pathological zones, appearance, color, and shape of the organ. The doctor finds out whether there is swelling of the tongue, ascertains plaque and its localization, abrasions, punctures, eczema, ulcers. The health of gum tissue and teeth is important.
In order to determine the type of pathogen and the form of the disease, a number of tests are prescribed:
- Histological smear;
- Sensitivity is determined using a special test;
- A general blood test is informative;
Systemic pathologists are also excluded: HIV, syphilis, hepatitis, AIDS. If necessary, the patient is referred for consultation to a gastroenterologist, dermatologist, endocrinologist, otolaryngologist, or immunologist.
Treatment
The diagnostic result allows you to prescribe treatment. Therapeutic dentistry has new methods and technologies that will return the patient to health.
- The patient is advised to adjust his diet and reduce spicy and sour foods in his diet. Dishes should not be hot.
- Fillings and dentures that injure the mucous membranes need to be replaced.
- You should have your oral cavity professionally sanitized.
- Remove soft and hard deposits on crowns.
- Cure caries, gum inflammation.
The therapeutic course may include taking antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, and a course of treatment for diseases of internal organs. Regular visits to the dentist are a way to prevent oral problems and complications of existing diseases.
An injured, inflamed muscle organ requires tissue regeneration. For this purpose, drugs containing carotene are prescribed: Aekol, Retinol, Chlorophyllipt, Lugol. Ointment applications are made from Solcoseryl and Cholisal. For pain, anesthetics are used: Trimecaine solution, Anastezin emulsion. Patients are recommended medications to stimulate the body's defenses and vitamins.
If the disease is infectious, a scraping is first done. A pathogenic microorganism is identified in the laboratory. Then therapy is carried out according to the obtained strains. Candidiasis is eliminated with fluconazole. Acyclovir is prescribed against herpes. Metrogil-denta treats protozoal infections.
We suggest you read: Gum disease types description symptoms and treatment
Inflammation of the papillae on a child's tongue
If the child’s body is weakened and he complains of discomfort in the mouth and pain in the muscle organ, parents should immediately show him to the pediatrician and pediatric dentist. The doctor will determine whether his papillae are red and whether there is an inflammatory process in the mouth. Once the diagnosis is made, therapy is prescribed. As a preventive measure, parents should ensure that the baby regularly brushes his teeth and rinses his mouth thoroughly. Children's immunity is not strong enough, so the body cannot cope with the disease on its own. The situation is complicated by the fact that children are curious; they put most objects in their mouths. To avoid serious complications, take your child to the dentist regularly.
Treatment of papillitis should be comprehensive: a gentle diet, drugs for local treatment of the oral cavity and tongue, healing agents, antibiotics if the disease is bacterial in nature or antimycotics if yeast is detected.
Medicines are selected individually depending on the diagnosis.
Diagnosis of tongue diseases
Basic diagnostic methods in dentistry allow a thorough examination to be made in order to make the correct diagnosis. During the initial examination, the dentist determines the size of the pathological zones, appearance, color, and shape of the organ. The doctor finds out whether there is swelling of the tongue, ascertains plaque and its localization, abrasions, punctures, eczema, ulcers. The health of gum tissue and teeth is important.
In order to determine the type of pathogen and the form of the disease, a number of tests are prescribed:
- Histological smear;
- Sensitivity is determined using a special test;
- A general blood test is informative;
Systemic pathologists are also excluded: HIV, syphilis, hepatitis, AIDS. If necessary, the patient is referred for consultation to a gastroenterologist, dermatologist, endocrinologist, otolaryngologist, or immunologist.
A dentist will help you. The very first thing the doctor needs to do is examine the patient’s tongue and oral cavity. Next comes the survey. During the interview, the doctor can determine what other lesions exist in the human body and what is worth paying attention to. In cases where there is reason to suspect a systemic disease, the dentist refers the patient to a qualified specialist in a certain area.
The first thing to start with is to eliminate the original source of infection, both in the oral cavity and outside it. The patient will have to be more attentive to oral hygiene, brush his teeth more often, using a special paste, as well as medications prescribed by the doctor.
To relieve other symptoms, such as swelling, anti-inflammatory drugs are used, which reduce swelling and have a certain analgesic effect, which helps reduce the sensitivity of the affected surface of the tongue and its papillae.
If you find glossitis, a coated tongue, rush to the doctor. Timely treatment will save you from complications and relapses, and the process itself will be easy and quick, since the disease has not had time to develop very strongly.
Since the symptoms of pneumonia can indicate other diseases of the upper respiratory tract, it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination to make sure that the cause of the illness is indeed pneumonia. To do this, you need to take a general blood test, do a chest x-ray and sputum examination.
A chest x-ray helps not only diagnose pneumonia, but also determine the number of foci of infection in the lungs. The study is carried out repeatedly and helps to monitor the dynamics of the process during treatment.
For successful treatment of pneumonia, it is important to identify the causative agent of the disease and select effective drugs to combat it. For viral pneumonia, antiviral agents are indicated, for fungal pneumonia, antifungal agents, and for bacterial pneumonia, antibiotics. In addition, immunomodulators, expectorants and sputum thinners are used, as well as antipyretics, vitamins and other medications that help improve well-being and eliminate signs of intoxication.
Inhalations, physical therapy, oxygen therapy and chest and back massage are also indicated for the treatment of pneumonia. In severe cases, when fluid accumulates in the pleural cavity, bronchi and lungs, pleural puncture and bronchoscopy are performed under local anesthesia.
A healthy diet is of great importance. It should contain all the necessary vitamins and microelements to make it easier for the body to recover after treatment. You should also pay attention to strengthening the immune system, otherwise there is a high risk of recurrence of the disease.
The dentist diagnoses tongue diseases by its appearance, size, thickness, and state of the receptors. Almost always there is an abnormal shade of its surface, uncontrolled copious secretion of saliva, and immobility of the organ. It increases in size, making it difficult to swallow, and an unpleasant odor appears from the mouth. When examining the oral cavity, the specialist pays attention to the condition of the teeth and gums, the presence of pustules, pimples and rashes.
In addition to visual inspection, the following tests are carried out:
- smear to determine the causative agent of the inflammatory process;
- biochemical and general blood tests to assess the condition of the body;
- blood tests for viral and bacterial infections, AIDS;
- tissue histology (in the presence of an abscess);
- if necessary, a referral is given to an immunologist, infectious disease specialist, rheumatologist, gastroenterologist, otolaryngologist and other specialists.
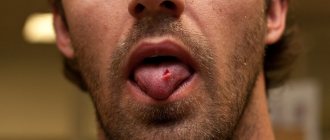
Glossitis
Glossitis is caused by bacteria and viruses (most often herpes and Candida fungus). The spread of infection occurs through injuries and microcracks of the mucous membrane, consumption of hot foods, alcoholic beverages, and smoking. Sometimes it is a symptom of iron deficiency anemia, HIV, lichen planus, and oncology.
A characteristic sign of glossitis is red dots on the tip and in the area of the root of the tongue (vallate papillae enlarge), its inflammation and swelling. The surface of the organ becomes smooth, it hurts when swallowing and talking. Additionally, the patient complains of a constant burning sensation in the mouth and that the tongue is greatly enlarged.
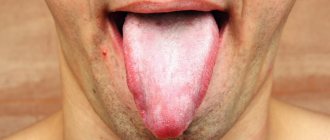
Papillitis
Inflammation resulting from injury, burns, or poor hygiene is called papillitis. The circumvallate papillae can become inflamed in those who have dentures or are allergic to the components of rinses and medications. Characteristic symptoms of the disease are impaired taste, itching and soreness, hardening and redness of the surface of the tongue. Usually papillitis goes away in 7-10 days without complications. Often it reflects hidden inflammatory processes in the body.
The diagnosis is made by the dentist based on the results of a clinical examination. To exclude syphilitic infection and determine the causative agent of the disease, laboratory diagnostics are performed.
Shown:
- scraping of tongue tissue;
- blood test for Treponema pallidum;
- PCR diagnostics using ELISA to determine other pathogens of the inflammatory process.
Scraping of tongue tissue is carried out to obtain material for laboratory research.
Reasons why a child puts his fingers in his mouth
Children's doctors are categorically against children sucking their thumbs. They give many recommendations on how to wean your child off this, advise purchasing special finger pads, and even schedule a visit to a psychologist. So why do children suck their fingers?
- studying your body. The baby, with the help of the sucking reflex, tries to understand the world through his own sensations;
- fear. The child’s desire to hide from events that frighten him;
- abrupt cessation of breastfeeding. The lack of maternal warmth is replaced by finger sucking;
- teething. An attempt to stop the unpleasant aching pain in the gums.
Harmless, as many parents think, an innate reflex contributes to disorders that in adult life will lead to mental and physical problems, and an inability to adapt in society.
What does it mean if an adult sucks his thumb?
Unlike an unintelligent child, mature, experienced men and women may feel the need for a child’s way of solving problems. An attempt to hide from the whole world and be alone with yourself, to feel protected is one of the reasons for sucking fingers in adulthood. Why else do adults have the habit of putting their fingers in their mouths?
- emotional disturbances. Low self-esteem, unresolved problems, life difficulties. A natural way to calm yourself since childhood;
- diseases of teeth and gums. Pain reliever;
- sexual arousal. A guy or man who puts his finger in his partner's mouth, in most cases, experiences great attraction.
The sources of active thumb sucking in men and women are serious psychological problems. The norms of behavior in society, which explain why thumb sucking should not be done in adulthood, contribute to isolation and self-doubt. The personality is gradually destroyed. Neuroses, depression and even suicide attempts may occur.
Thumb sucking is harmful
Existing standards of life do not allow you to show your weaknesses and shortcomings to others. Especially if they harm human health. What consequences may occur after constant thumb sucking:
- malocclusion. The structure of the teeth and jaw is damaged;
- acute otitis media Inflammatory process in the middle ear;
- speech problems. Difficulty pronouncing the letters “z”, “r”, “d”, stretching out the tongue when speaking, burring;
- bone calluses. Constant friction and pressure provoke thickening of the skin and the appearance of keratinized areas on the fingers;
- worms and bacteria, viruses and infections. They enter the body through dirty or poorly washed hands.
These are the main and most important negative complications that explain why thumb sucking is prohibited for either a child or an adult. You need to deal with this problem yourself or with the help of a specialist. It is necessary to constantly monitor yourself, control your actions and learn to cope with difficulties, develop willpower and character.
Tongue sucking is considered a less complex bad habit in orthodontics, mainly because psychological factors play a lesser role.
Etiology of the development of the bad habit of tongue sucking: 1. Genetic factor. 2. Copying behavioral reactions from adults. 3. Mechanical factor, for example, with temporary loss of teeth. 4. Psychological factor. Significantly less than with the bad habit of thumb sucking. Psychological factors are the cause in approximately 40% of patients. 5. Neurological nature.
Classification BACKLUND 1963 ▪ Anterior tongue thrust Pushing out the tongue in the anterior area. ▪ Forceful anterior thrust Forceful pushing from the front. ▪ Posterior tongue thrust Thrusts in the posterior position of the tongue. ▪ Lateral thrusting in case of missing teeth. Lateral thrusts in the absence of lateral teeth.
Classification Fletcher A. Simple: associated with thumb sucking, open bite. Simple form associated with thumb sucking, open bite. B. Complex: associated with tonsils, URTI. Complex, associated with the tonsils.
Clinical manifestations of the bad habit of tongue sucking: 1. Open bite in the anterior or lateral area. 2. The inclination of the front teeth. 3. Protrusion. The orthodontist should control tongue sucking starting from the age of 3; the psychological factor does not have such a strong effect on the child, so early treatment can be started. It is important to conduct a differential diagnosis and identify tongue sucking as a bad habit or an adaptation during the period of tooth loss during a physiological change.
Treatment of inflammation of the taste buds without drugs
On the sides of the tongue
If you have swollen white taste buds, which may occur on the tip of your tongue, on the back of your tongue, or on the top surface, you may have a condition called transient lingual papillitis. This condition is characterized by the appearance of red or white small pimples on the tongue.
Enlarged white taste buds can appear on the tongue for many reasons.
We suggest you read: Inflammation of the salivary gland under the tongue: causes, symptoms and treatment of a tumor under the tongue
Most common:
- "stress;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- menstruation;
- sour (for example, with vinegar) or sour (sour tomatoes, cucumbers, watermelons) food;
- smoking;
- local trauma of the tongue" [Wikipedia].
Given the variety of conditions of occurrence, treatment depends entirely on the cause.
Brush your teeth, paying special attention to the gums and spaces between the teeth;
Rinse your mouth thoroughly to remove any leftover food and toothpaste;
Avoid eating certain foods.
Spicy, fatty foods, spices, and salt provoke an increase in the inflammatory process. By eating incorrectly, you can be sure that the symptoms of glossitis will only get worse over time. If the tongue receptors are inflamed, it is necessary to eat exclusively liquid food cooled to room temperature.
Elimination of the manifestations of the disease at home is facilitated by regular rinsing of the mouth with an infusion of calendula, sage, and chamomile. These herbs have an anti-inflammatory and wound-healing effect on the oral mucosa.
If treating glossitis at home does not give a positive result, you should consult a specialist. Perhaps the problem of the disease lies within the body. This could be an infection or a malfunction of internal organs.
Sources:
- Inflammation of the papillae of the tongue
- Glossitis
- Glossitis: treatment for different types of disease
Glossitis is inflammation of the tongue due to viral and bacterial infections. Inflammation occurs due to the presence of infection or may be the first sign of a more serious disease. Glossitis comes in acute and chronic forms. With this disease, the shade of the tongue changes, its structure changes, and inflammatory processes begin. If the disease is neglected, papillomas may form on the tongue.
You will need
- – chamomile infusion;
- – raw potato juice;
- - bedstraw.
Instructions
Treatment for glossitis begins with ridding the patient of the infectious agent. Depending on what caused the disease, the doctor prescribes appropriate treatment.
Maintain oral hygiene. Teeth are brushed several times a day with special pastes.
In acute cases, the doctor prescribes antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. These can be antimicrobial solutions for rinsing the mouth, for example, ordinary furatsilin. The tablet is diluted in a glass of warm water, and the mouth is rinsed.
From traditional medicine, we can recommend rinsing the mouth with chamomile infusion 6 times a day. Rinsing is carried out after meals and in the intervals between main meals. Pour a tablespoon of chamomile into a glass of boiling water and let it brew for 40 minutes, strain and rinse. Raw potato juice will help with glossitis. Also rinse.
Take 2 tbsp. bedstraw, pour 2 cups of boiling water over it, let it brew for 1 hour, strain. Rinsing is carried out according to the same scheme, and the decoction is taken orally 3 times during the day, a quarter of a glass.
Glossitis must be treated! The most effective way to treat and prevent glossitis is to increase your body's resistance, that is, immunity. You will be able to get rid of the disease and reduce the risk of complications.
Video on the topic
note
How to treat glossitis? If you have glossitis, do not eat aggressive foods or hot spices. To disinfect, treat your tongue with solutions of furatsilin or potassium permanganate. For 2-3 weeks, treat your mouth 3 times a day with raw potato juice and 5-6 times a day with chamomile infusion.
Helpful advice
Patients also use medications - local immunocorrectors, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Treatment of glossitis with folk remedies. How to cure glossitis yourself? In addition, it is necessary to eat well, take a vitamin complex and promptly treat diseases that provoke glossitis.
Glossitis is inflammation of the tissues of the tongue. It can be both superficial and deep. It can be an independent disease, but often it is a symptom of some general disease of the body. There are more than a dozen forms of this disease, both requiring surgical intervention (phlegmonous, deep), and being a congenital pathology that does not require treatment. Glossitis is characterized by changes in the color and size of the tongue, a burning sensation, and difficulty chewing food, speaking, and swallowing.
You will need
- – antibiotics;
- – anti-inflammatory drugs;
- - antiseptics;
- – rosehip seed oil, vitamin A oil solution, “Vinisol”;
- - medicinal herbs.
Instructions
If the above symptoms appear, immediately contact your dentist, who will examine the condition of your tongue and prescribe the necessary tests to identify a systemic disease.
For disinfection, use antiseptic solutions of furatsilin, potassium permanganate, chlorhexidine - in the form of applications, rinses, baths. Anesthetics are also used, possibly in combination with antiseptics - lidocaine, etc.
Without canceling treatment with medications, also use traditional medicine recipes. This will help to quickly cope with the disease, especially with the catarrhal form of glossitis. Rinse with decoctions and infusions of herbs that have anti-inflammatory and wound-healing properties. These are chamomile, sage, bedstraw, celandine. Potato juice, horseradish juice, cabbage juice, and carrot juice help well.
Video on the topic
note
The causes of glossitis may be iron deficiency anemia, syphilis, erythema, lichen, vitamin B deficiency. A complication of the disease may be swelling and purulent melting of the soft tissues of the entire oral cavity and neck.
Helpful advice
Avoid injuring your tongue, either from hot food or mechanical damage from dentures or the sharp edge of a broken tooth. Places of injury are an ideal environment for the development of infection, and, accordingly, glossitis.
Sources:
- how to treat inflammation of the tongue with folk remedies
Pneumonia, or pneumonia, is a group of diseases in which the alveoli and lung tissue are damaged. If not diagnosed promptly, the disease can lead to serious complications and even death. That is why it is important to know the symptoms of pneumonia in order to distinguish it from other bronchopulmonary diseases and consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Why might he be missing?
If this action is weak, the baby sucks very sluggishly at the breast or bottle, quickly falling asleep during feeding, or even refusing to eat altogether. This happens in weakened, injured during childbirth or premature babies. They are discharged from the inpatient department when the baby gets used to sucking milk well. A decrease in the sucking reflex can be observed for the following reasons:
- hypoxic-traumatic damage to the central nervous system of the child in the womb or during childbirth;
- severe somatic diseases (due to general weakness and malaise);
- paresis and paralysis of the cranial nerves, in particular the facial one;
- mentally retarded children;
- severe stomatitis, respiratory viral infections, rhinitis;
- flat-shaped mother's nipples.
With a reduced sucking reflex, the child is constantly malnourished, so he must be fed with a spoon or expressed milk from a bottle every 2 or 2.5 hours.
Any deviation in the baby’s condition is a reason to consult a doctor, because this may be a signal of the development of a serious pathology that requires immediate treatment. A decrease in the sucking reflex requires dynamic monitoring with the involvement of a neurologist.
The absence of a sucking reflex is the first symptom of damage to the central nervous system, or rather the stem part of the medulla oblongata, and an unfavorable prognostic sign. Such babies have very little chance of survival; they have to be fed only through a tube.
Reasons for the complete absence of sucking in children:
- trauma to the medulla oblongata during childbirth;
- weakness of the masticatory muscles, orbicularis oris muscle, tongue;
- deep prematurity.
Inflammation of the papillae on a child's tongue
If the child’s body is weakened and he complains of discomfort in the mouth and pain in the muscle organ, parents should immediately show him to the pediatrician and pediatric dentist. The doctor will determine whether his papillae are red and whether there is an inflammatory process in the mouth. Once the diagnosis is made, therapy is prescribed.
As a preventive measure, parents should ensure that the baby regularly brushes his teeth and rinses his mouth thoroughly. Children's immunity is not strong enough, so the body cannot cope with the disease on its own. The situation is complicated by the fact that children are curious; they put most objects in their mouths. To avoid serious complications, take your child to the dentist regularly.
Causes
The main reason for thumb sucking is the child's desire to satisfy the sucking instinct. It has been noted that children who have a higher frequency of feedings suck their fingers less often. Also, those babies who suck milk faster are more likely to resort to thumb sucking than babies who suck milk for a long time.
A child may suck his thumb because:
- He is hungry or still wants to nurse.
- He is teething and wants to scratch his gums.
- The baby lacks the attention and love of his parents.
- This is how the child calms himself down.
- He's just bored.
- He was weaned too early or too abruptly.
Most often, a child who sucks his fingers was weaned quite early.