Causes in adults and children
Every young mother needs to make a daily morning examination of her child’s mouth a mandatory procedure.
It should be borne in mind that a small whitish layer, which is easily removed by hygiene procedures or disappears on its own after eating, is the norm. But the appearance of a thick layer or a change in color should cause serious concern. It is especially necessary to react quickly to a child’s blue tongue. Why should the blue tint of the tongue attract such increased attention? This shade serves as one of the main signals that can reflect the occurrence of a number of pathological problems that begin to progress in the important organs of the child.
In such a situation, parents are advised to immediately consult a doctor. Young children are not always able to fully describe the sensations that arise, and young parents are not always able to correctly identify what the child is describing. That is why such an important signal should encourage parents to visit a medical facility.
A change in tongue color may indicate problems:
- of cardio-vascular system;
- scurvy disease;
- poisoning with salts of heavy metals (mercury);
- oxygen deficiency;
- renal pathology;
- problems with the adrenal glands (blue-black plaque);
- tendency to bleed;
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- development of ischemic processes in the heart muscle;
- glossitis (in men who smoke).
The tongue may become bluish from food and drinks, for example, wine, blueberries. In this case, the symptom quickly disappears on its own or after treatment of the tongue.
Localization of the cyanosis of the tongue can indicate the source of the problem. The cause of a blue tongue can be determined by the location of the plaque:
- tip of the tongue – cardiopulmonary failure;
- root – kidney problems;
- upper surface – development of problems with the cardiovascular system in the initial period.
Contacting medical centers for examination will prevent the development of an acute or exacerbation of a chronic disease.
A blue tongue in a child under one year old serves as a signal of the progression of diseases in the internal organs. Pathologies include:
- anemia (with vitamin deficiency of folic acid, cyanocobalamin, iron);
- diseases of the abdominal cavity are accompanied by corresponding symptoms;
- cyanosis of the skin and mucous membranes (lack of oxygen).
The child, depending on his age, cannot adequately describe the problems and what worries him. The need for medical consultation and additional diagnostic procedures is beyond doubt.
Tongue is a map of the body
In Tibet, China and India, the “Five Elements” theory has long existed, according to which doctors in these countries always begin examining a patient with the tongue. Using a mirror, you can do this yourself, paying attention to its color, shape and size, plaque, the presence of stars and wrinkles, whether it is wet or dry, dense or soft. Changes in the mucous membrane are very often not at all associated with diseases of the oral cavity.
Read also: Increased salivation
Human language and projection of organ function
The zones on the surface of the tongue exactly repeat our body: the tip is the upper part of the body, and the root is the lower part. Depending on where changes appear on the mucosa, it is necessary to judge the nature of the disease.
You should also adhere to the following correspondence map:
- the tip of the tongue - the work of the lungs and heart system;
- middle (horizontal part) - pancreas and stomach, spleen, liver;
- root - responsible for the intestines;
- lateral areas - show kidney function;
- the middle (vertical part) is the spine.
A boy's blue tongue is the result of kidney disease
In a healthy person, the surface of the tongue is smooth and has a pale pink tone. Depending on the season, it may vary slightly. At the tip of a healthy organ you can see small papillae, in its central part there are larger ones, and at the root there is a huge accumulation of more massive papillae. They represent a variety of taste thermal and biochemical analyzers. It is these papillae that are connected to various organs of the human body.
Associated symptoms
The blue coating on the tongue has characteristic features that are taken into account during examination. Visual inspection allows you to determine the dryness and heterogeneity of plaque on the surface. The looseness of the plaque and its density, pain when removed, indicates a pathological process. Oily plaque is determined by an unpleasant aftertaste and increased moisture on the tongue. There may not be any noticeable symptoms during plaque. Pathology is determined by the following signs:
- plaque remains after rinsing;
- when you try to remove it, it appears again;
- pain when scraping.
Associated symptoms during visual examination of an adult and a child:
- pale skin;
- shortness of breath when walking;
- pain and heaviness in the epigastrium.
There are many symptoms of pathologies that a purple tongue may indicate, but they are delayed in time and manifest themselves already at the stage of development and the onset of the acute period.
Diagnostics by language - photos and descriptions of human diseases and diagnoses
Currently, the popularity of diagnosing diseases based on the condition of the tongue is growing. It is believed that it represents the state of almost all internal organs, a kind of “mirror” of their health.
Due to the fact that signs of pathology appear on the tongue earlier than a person notices the usual symptoms, with a well-organized diagnosis, the development of the disease can be recognized at the earliest stages, which means that treatment will be quick, simple and successful.
To determine the state of health by the tongue, it should be taken into account that the tongue is conventionally divided into separate zones responsible for certain internal organs. When identifying pathologies, the doctor will first of all pay attention to the dislocation of changes in the tongue. An interesting fact is that from the point of view of ancient eastern practices, language is also divided into areas according to five “primary elements”:
- back - Water;
- central region - Earth;
- sides – Wood;
- between the tip and the central part - Metal;
- tip – Fire.
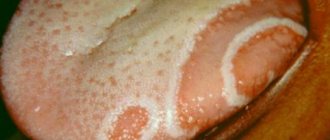
Blue Plaque
The tongue is a very sensitive organ and any malfunction in the body is immediately manifested by any changes on its surface, for example, it may turn blue. This shade has several particularly common reasons:
- Malfunctions of the heart. If the entire surface of the tongue is blue, then there are problems associated with blood circulation, and they are often accompanied by complications, for example, cardiovascular failure. There will be no other visible symptoms in the early stages of the disease, and this will make it possible to begin treatment of the pathology in its infancy;
- Lack of vitamin C. A blue surface on the tongue can be caused by an acute lack of ascorbic acid and this disease is called scurvy. In this case, the surface of the organ becomes loose, and the gums bleed heavily.
- Poor blood circulation. This problem manifests itself as a blue tint on the tongue and its causes can only be found out after an examination;
- Poisoning. It may occur due to ingestion of mercury or other heavy metals;
- Kidney problems. If the whole reason lies in them, then the blue coating is on the tongue near the pharynx;
- Malfunctions of the adrenal glands. In this case, the tongue becomes covered with blue-black spots, which will disappear when hormones begin to be produced normally.
Read also: Tongue hurts like it’s burned
Spots on the tongue: photos, possible diseases, treatment options
If your tongue turns blue, both the root cause and the symptom are treated.
Medicines
A cyanotic tongue is a signal of intoxication of the body and to treat it, regardless of the pathology, it is advisable to use antibacterial therapy. For an infectious disease, treatment tactics are based on the use of antibiotics and other drugs. Consultation with specialists will help you decide on treatment tactics.
| Group of drugs | Name | Mechanism of action |
| Antiseptics | Furacilin, Chlorophyllipt solution (oil, water), Chlorhexidine, Methylene blue, borax solution. | Antiseptics selectively act on flora and are recommended for use in infectious diseases as a means for sanitation of the mouth for stomatitis, to reduce the activity of fungal microflora and other flora. Not used for fungal infections. Chlorhexidine. Chlorophyllipt oil solution is used externally. Furacilin has antibacterial activity. |
| Anesthetics | Lidocaine, Analgin, Trimecaine. | Used externally in the form of special gels and applications. |
| Antibiotics | Macrolides, cephalosporins, penicillins with clavulanic acid. | The action of antibiotics is aimed at reducing the activity and destroying the bacterial cell membrane. Cephalosporin antibiotics have a broad spectrum of action. |
| Antifungal drugs | Fluconazole, Ketoconazole, Nystatin, Diflucan, Flucostat. | Antifungal drugs are used externally, orally, and parenterally (by injection). They are used to reduce the activity of fungal cells, destroy enzymes and the products of their activity. Their use is long lasting. |
The use of drugs in the treatment of glossitis for problems of a systemic nature is aimed at reducing and preventing acute forms of the disease. Treatment of diseases requires the use of a wide range of medications, their prescription is adjusted by specialists.
Traditional methods
Medicinal plants are used in the form of decoctions and infusions for rinsing. Ready-made solutions, such as hydrogen peroxide 3%, can reduce the activity of microflora in the oral cavity when rinsing.
The following folk remedies are widely used:
- chamomile decoction;
- decoction of oak bark;
- horsetail (like chewing gum);
- potato juice;
- basil leaf decoction.
A wide range of medicinal plants used for glossitis as rinses are taken orally when determining the exact diagnosis of what caused the blue coating on the tongue.
Rinse aids
The use of ready-made pharmaceutical solutions with antiseptic properties has a positive effect in complex treatment.
| Medicinal plant | Application |
| Sage extract | In 1 l. pour boiling water and 2 tbsp sage. After 30 min. strain. Rinse the oropharynx 3 times a day. |
| A collection of chamomile, bay leaf, sage, wormwood (50 grams each). | Add 2 tbsp to 0.5 liters of boiled hot water. collect and leave for 3 hours. Strain and rinse the oropharynx 3 times a day. |
| Olive, sea buckthorn, tea oil. | Mix the oils and add tea before use. Roll 1 tbsp of liquid in the mouth for 4 minutes. Spit it out. |
The use of medicinal plants has a gentle effect on the body.
Nutrition plays an important role in human health. Following proper nutrition and diet for the underlying disease reduces the risk of any plaque forming on the tongue. Preventive and routine medical examinations, control of the underlying disease reduces the development of the acute period of the disease. A healthy lifestyle remains the top priority in disease prevention.
People often ignore spots that appear on the tongue. And they take a lot of risks. After all, unusual pigmentation in the oral cavity poses a hidden threat. Of course, it may simply be a reaction to an external stimulus, but sometimes in this way the body gives a sign that something is wrong.
Reasons for appearance
The main factors that provoke the appearance of pigmentation:
- allergies to oral hygiene products;
- irritating foods;
- smoking;
- alcohol;
- bite;
- wearing braces;
- dehydration.
Such spots on the tongue appear and disappear in the absence of negative effects on the mucous membrane. The situation with pigmentation that has arisen as a consequence of a developing pathological process is much more complicated. The color, shape and location of the rash helps in making a diagnosis.
The most common pathologies are:
- Glossitis. Inflammation of the tongue caused by a bacterial or viral infection. It manifests itself in the form of swelling of the organ, the appearance of plaque and irregularly shaped spots on it. Salivation is impaired, a repulsive odor and ulcers appear. There are several types of glossitis, each of which has specific symptoms. To eliminate the disease, antiseptic rinses and applications are used. To heal ulcers, gels are applied to accelerate tissue regeneration. Depending on the pathogen, antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal agents are prescribed.
- Scarlet fever. An infectious disease caused by streptococcus. It begins with the appearance of fever, malaise, and headaches. A small rash appears on the mucous membranes of the mouth. It spreads to the groin, bends of the limbs, and sides of the torso. After a couple of days, granular growths appear on the tongue, and the organ acquires a crimson color. A constant companion of scarlet fever is tonsillitis. Treatment is usually carried out on an outpatient basis with antibiotics, infusion therapy, and vitamins. Patients are prescribed special nutrition and bed rest.
- Measles. An infectious viral disease that affects the respiratory system, mouth, and eyes. A highly contagious disease that often leads to death. Characterized by a sharp increase in temperature and other signs of a cold. Then conjunctivitis occurs, red and white spots appear on the tongue, palate, and inner surface of the cheeks. The rash then spreads to the entire body. A cure for measles has not yet been invented. Symptomatic treatment is used. Vitamin A supplementation is recommended to reduce the risk of death.
- STD. Sexually transmitted diseases can also affect the oral mucosa if infection occurs during oral sex. A rash and sores appear on the membranes, which can spread significantly. A purulent plaque forms there. Often such symptoms are combined with rashes on the genitals. Patients are prescribed antibiotics and antiseptics for local use.
- Lichen planus. Skin fungal disease. Sometimes it affects the oral mucosa. It is characterized by the appearance of numerous grayish nodules that merge together and resemble a cobweb in outline. Depending on the characteristics of the clinical picture and the type of disease, antifungal and anti-inflammatory drugs, immunity boosters, and corticosteroids are prescribed.
- Tongue cancer. Malignant neoplasm in epithelial and mucosal tissues. The main cause is smoking. Oncology can also be caused by injuries, herpes and the human papillomavirus. The tumor first appears as whitish plaques, lumps and red spots on the sides of the tongue. Then pain appears, salivation increases, and the submandibular lymph nodes enlarge. Part of the organ becomes numb, its surface bleeds. Ulcers, growths and cracks may appear. Combination cancer therapy. It includes chemotherapy, radiation and surgery up to complete removal of the organ.
- Leukoplakia. Thickening and keratinization of the epithelium. It occurs due to mechanical damage, chemical poisoning, and poor functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. White or gray areas appear in the oral cavity, the consistency of which resembles tissue paper. The formation of cracks, erosions, and warts is possible. For mild cases of the disease, epithelializing agents, anesthetics, and antiseptics are prescribed. In severe cases, surgery is indicated.
- Aphthous stomatitis. Inflammation of the oral cavity, characterized by the appearance of yellow or white spots surrounded by a red rim. Patients feel unwell, their body temperature rises and nearby lymph nodes become enlarged. For treatment, antiseptic treatment of the oral cavity is performed and symptomatic treatment is prescribed. During the recovery process, it is important to eat right and strengthen your immune system.