Damage to the tongue
Damage to the tongue can be superficial - this is biting, trauma with the edge of a carious tooth, a denture, a fish bone, sharp objects (for example, a fork, etc.), as well as deeper ones, as a result of which an abscess or phlegmon can develop in the submucosal layer and muscles of the tongue .
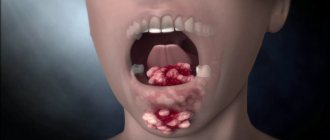
With an abscess in the thickness of the tongue, limited painful swelling occurs, swallowing and speech are difficult; with phlegmon, the inflammation intensifies - the tongue is sharply increased in size, movements and swallowing are sometimes impossible, breathing is difficult, the general condition is severe. The patient must be hospitalized. Treatment: for abscess and phlegmon of the tongue root, incisions are made through the skin along the midline of the submental region, the tissues are bluntly pushed apart towards the root of the tongue; Prescribe antibiotics, restorative treatment, rinsing the mouth with a solution of potassium permanganate (1: 3000), inhalation with a solution of sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) 1 teaspoon per glass of water.
Gunshot wounds are usually combined with injuries to the soft tissues of the face and jaws. The main primary complications in this case are bleeding and asphyxia. Treatment of superficial wounds involves rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions. For deep cut and gunshot wounds, primary surgical treatment of the wound is performed with suturing. If a significant part of the tongue is torn off, sutures are placed on the stump (later a Filatov skin stalk is used). When the tongue is retracted, it is stitched with a thick silk thread, brought forward and fixed to the teeth or clothing. Bleeding from wounds of the tongue is stopped by tight tamponade of the wound or by applying a hemostatic clamp in the wound, or by pressing the common carotid artery (on the side of the injury) to the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae. The final stop of bleeding is carried out in the hospital.
Tongue biting is more often observed during chewing of food in middle-aged and elderly people, in whom the edges of the teeth become sharp due to abrasion (grinding) of the chewing surfaces.
Epileptics often bite their tongue with their teeth during a seizure. In children suffering from whooping cough, bruises, abrasions, and sometimes more serious damage due to the tongue protruding beyond the front teeth during coughing attacks occur on the frenulum of the tongue. The tongue is also subject to injury from the teeth when the lower jaw is bruised (for example, during boxing).
There are accidental injuries to the tongue with sharp and blunt objects (pencil, pen, fish and other bones, fork, etc.).
There are known cases of cut wounds in children caused by leaves of hard grasses. Damage to the mucous membrane of the tip of the tongue in children has been noted in cases where they apply the tongue to cooled metal objects.
Toxic damage includes damage to the tongue by insects when it is protruded during sleep, as well as the introduction of the sting of a dead bee into the tongue when eating comb honey. In all of these cases, the tongue swells, sometimes the swelling reaches such a size that the tongue can hardly fit in the oral cavity, resulting in a risk of breathing problems.
Burns of the tongue, both thermal and chemical, in some cases can be superficial and limited, easily curable, in others they are accompanied by the formation of blisters and ulcerations with subsequent cicatricial disfigurement, which sharply impairs the function of the tongue.
Gunshot wounds of the tongue in most cases are combined with damage to the face and jaws. Isolated tongue injuries are rare. Injuries are caused by bullets or shell fragments, fragments of crushed jaws and teeth, and fragments of accidentally nearby objects. Getting stuck in the thickness of the tongue, these fragments often cause purulent inflammation, as well as the formation of non-healing fistulas. Complications after injury include loss of taste and superficial sensitivity, paralysis, and speech impairment. When the floor of the mouth is simultaneously wounded, the tongue, as a result of scarring of the wound, becomes more or less fused with the tissues of the sublingual space and gum. Healing of tongue wounds proceeds slowly (up to 2-3 weeks).
Treatment. For superficial wounds of the tongue, it is enough to keep the oral cavity hygienic and treat the wound with iodine tincture, 1% solution of brilliant green, rinsing with disinfectants (solutions of potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide, boric acid, furatsilin), chamomile decoction. Foreign bodies must be removed. Fresh lacerated wounds of the tongue are subject to primary surgical treatment, followed by sutures to bring the edges of the wound closer together. Sutures are applied to an uninfected incised wound of the tongue without prior surgical treatment. In cases where part of the tongue is torn off, sutures are placed on the stump. When the tongue is retracted with asphyxia (in cases of separation of the genioglossus and other muscles of this group), it is stitched with a silk ligature and secured to the teeth, dental splints, etc., and, in extreme cases, to clothing. If the tongue is injured, if there is a threat of asphyxia, a tracheotomy should be performed. Deforming scars after injury to the tongue are subject to excision with mobilization of tongue tissue. Defects on the lower surface of the tongue are closed with a free skin flap. When a significant part of the tongue is torn off, the Filatov skin stalk is successfully used to lengthen it.
How to treat tongue wounds and how long they take to heal
Wounds on the tongue significantly complicate the performance of usual functions. They interfere with speaking and eating. Although such wounds are often superficial and do not pose a great threat, in cases of deep damage and improper treatment there is a risk of complications : speech impairment, loss of taste.
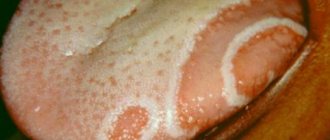
Photo 1. Minor injuries to the tongue do not pose a big threat. Source: Flickr (Drew Leavy) Read also: Black tongue reasons
Causes of tongue injury
We all know what a healthy tongue looks like: an even pink color, without scratches, peeling or excess plaque. If his appearance has changed, signs of pathology have appeared, then you should think about what exactly was the reason.
The causes of wounds on the tongue can be divided into groups:
- Mechanical : sharp cutlery, rough dry food, tongue getting between teeth.
- Physical . Namely, the temperature is too high or low. Burns from boiling water or hot food are more common, but frostbite is also possible (when trying to lick a pipe in cold weather).
- Chemical : aggressive reagents (acids, alkalis), excess hot seasonings and salt in food.
- Biological . Wounds on the tongue may turn out to be ulcers, the appearance of which is provoked by pathogenic microflora due to stomatitis, oral candidiasis, foot and mouth disease and other diseases.
External factors of damage
The causes of wounds and cuts on the tongue can be not only diseases, but also mechanical, chemical, and thermal effects.
Main causes of injuries:
- Cut, puncture, scratch with dentist's instruments - disc, bur, probe;
- Damage from sharp objects - cutlery, bone fragments;
- Biting the surface while eating, epilepsy attack;
- An injury to the tongue can occur from a strong blow to the face.
Injury from the outside can occur under the influence of hot steam, water, fire, or electric current. Almost all physical injuries to the tongue lead to the development of acute catarrhal glossitis; consultation with a doctor is required. Next, you will learn what and how to treat wounds on the tongue.
Classification of tongue injuries and their symptoms
Wounds of different origins also have external differences. It is important to distinguish between the characteristics of mechanical and burn wounds in order to apply the correct first aid methods.
Mechanical impact
Mechanical injuries include cut, puncture, and lacerations of the tongue. The most common types are cutting (a cut, for example, from glass shards) and biting (when hastily chewing or trying to speak with a mouth full).
Their features :
- the wound gapes, its edges diverge due to contraction of muscle fibers;
- the wound lumen is bleeding;
- the person feels pain, which intensifies when trying to move the tongue;
- speech changes (a lisp appears) - this is due to an unconscious attempt not to use the injured area of the tongue.
Puncture wounds include a defect formed as a result of piercing the tongue . In this case, symptoms appear until scar tissue forms around the piercing site (a couple of days).
A laceration can form if the earring in the tongue gets caught on another object (a fork, a partner’s piercing during a kiss). A careless jerk in this case will result in a complete or incomplete rupture of the tongue.
Note! Damage to the tongue can occur during dental procedures (drill, probe, etc.). Therefore, it is important, while sitting in the dentist’s chair, to listen to his requests and not to move your tongue unnecessarily when you have instruments in your mouth.
Physical damage
Injuries of physical origin - burns . Thermal burns can be mild - when drinking tea that has not cooled down, and severe - when denser hot substances (oil, metal, etc.) come into contact with the tongue.
Symptoms of thermal burn of the tongue:
- sharp redness at the site of the lesion;
- swelling;
- pain, burning;
- loss of taste sensitivity;
- with severe burns, blisters and erosions of the mucous membrane appear;
- 3rd-4th degree burns are characterized by the presence of a zone of gray tissue death;
- the patient experiences difficulty when trying to speak and eat.
Chemical exposure
When the mucous membrane of the tongue is exposed to chemicals that excessively irritate it, a chemical burn clinic , which completely coincides with the symptoms of a thermal burn. The mucous membrane can also peel off, exposing blood vessels and muscle tissue.
Antibacterial treatment
Taking antibacterial medications is not necessary in all cases of glossitis treatment. The need for such therapy is determined by the doctor, and indications for prescribing antibiotics are purulent and phlegmonous processes, when the inflammatory process spreads not only to the deep tissues of the tongue, but also to neighboring areas (oral cavity, chin, neck). Antibacterial agents are also prescribed to patients with high fever, enlarged peripheral lymph nodes and signs of intoxication.
What drugs are used according to indications for the treatment of glossitis:
- Doxycycline is a drug from the tetracycline group, which is taken 100-200 mg per day, divided into 2 doses. Contraindications: pregnancy, children under 8 years of age and allergic reactions to the drug.
- Suprax is an antibacterial drug related to cephalosporins; it should be taken orally at a dose of 800 mg per day, in one or two doses, for 7-10 days in a row.
- Rocephin is an analogue of Ceftriaxone, also belongs to the group of cephalosporins, 2-4 g are administered intramuscularly or intravenously throughout the day until the general condition is normalized and the inflammatory process subsides.
- Tetracycline is a broad-spectrum antibiotic that is not prescribed for fungal and viral etiologies of the disease; it is taken 250–500 mg three times a day, the dosage and duration of treatment depends on the severity of the clinical picture.
First aid for a tongue injury
It is recommended to provide first aid for tongue wounds in accordance with the following algorithm:
- Stop the effect of the traumatic factor . Remove large shards of glass and pieces of food - clean the oral cavity as much as possible.
- If the injury is mechanical, stop the bleeding by packing the wound with cotton wool soaked in a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide.
- In case of burns, rinse your mouth with plenty of cold water. Place ice on your tongue until the burning sensation stops.
- Rinse your mouth with chamomile decoction at room temperature or a weak solution of furatsilin (1:5000).
- Contact your doctor.
Note! Medical help may not be needed if the injury is a shallow cut or a minor burn. However, if the bleeding does not stop for a long time, the pain does not go away, or suppuration appears in the wound area, you should immediately seek the advice of a specialist.
See a doctor urgently
It is necessary to urgently contact a specialist if:
- A large number of ulcers, wounds and neoplasms appear in the oral cavity.
- Open wounds appear, accompanied by severe pain.
- The sores appeared due to wearing dentures or artificial structures in the oral cavity.
- Sores have appeared on the tongue and are bleeding.
- The general condition worsens, the temperature rises, weakness.
- Sores and sores quickly increase in size.
- I have a headache and a feeling of fullness in the mouth.
Treatment of tongue wounds
When the patient sees a doctor, the first dangerous manifestations (severe bleeding) are usually eliminated. Further, his actions will be aimed at restoring the integrity of tissues and accelerating their regeneration.
All wounds are treated with an antiseptic (usually iodine). If the wound is not deep, then it is given the opportunity to heal on its own.
If the cut or laceration wound is deep, then it is sutured . More often this is done under local anesthesia with Novocaine or Lidocaine, a self-absorbing material.
If there are bubbles, they should be opened. This should only be done by a doctor under sterile conditions. After opening the blisters, they are also treated with an antiseptic.
Consequences and complications
Tangible consequences are observed only with serious injuries to the tongue (complete ruptures, amputations).
In this case, even with proper treatment, there is a high chance that the person will have a lisp for the rest of his life.
Possible consequences of improper treatment or its complete absence:
- suppuration of the wound, spread of the infectious process;
- massive death of muscle tissue leads to dysfunction of the tongue;
- deformation of the tongue due to its “tightening” by scar tissue.
Rehabilitation period
Oral tissues regenerate quite quickly. Light burns go away within a few hours, and cuts heal within a day.
Photo 2. Soups and purees are the only food available to a patient with a tongue wound. Source: Flickr (baron valium).
The recovery period after treatment of deep injuries may take a couple of weeks. For the first time after surgery, the patient should not chew ; food is given in liquid form (mashed soups and cereals through a straw). Rinse with an antiseptic solution is prescribed several times a day (morning, evening and after each meal).
Read also: Why are there red spots on the tongue?
When the doctor allows you to eat normally, it is better to refrain from traumatic foods (crackers, chips, hot spices) until complete healing.
Treatment of wounds on the tongue
If a wound on the tongue occurs after biting your teeth, you can rinse with a solution of soda or hydrogen peroxide. To eliminate pain, you can dissolve tablets with Lidocaine.
In the case where the provocateur of ulcers and wounds on the tongue is an infection, the therapy may be as follows:
- For stomatitis of a fungal nature, the wounds can be treated with ointments with an antifungal effect. For adults, Nystatin is suitable.
- You cannot do without antiviral ointments if you have wounds due to a viral disease.
- The resulting sores with purulent contents must be treated with antibacterial agents, for example, Tetracycline or Achromycin.
- The fight against the inflammatory process in the oral cavity is carried out using Fluocinonide or Triamcinolone.
- In case of severe pain, wounds can be treated with a gel with analgesic properties “Oragel”. You need to apply the product to the sores several times a day.
- To prevent the formation of scars at the site of wounds after healing, it is recommended to use gels or ointments with regenerating properties.
- It is recommended to rinse your mouth daily with pharmaceutical rinses; you can prepare such products yourself using sage or chamomile.
Considering that white formations on the tongue often occur due to disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, the fight against them should also combine the use of probiotics to normalize the intestinal microflora.
Tip 1: How quickly wounds on the tongue heal
- How quickly do wounds on the tongue heal?
- Lunar calendar: recommendations for the 20th lunar day
- 5 most common myths about cats
In case of minor injuries (minor abrasions, cuts, bites, etc.), well-known antiseptics, such as boric acid, potassium permanganate, hydrogen peroxide, chlorhexidine, are of great help. We should not forget that the above products are best diluted, especially when it comes to children. You should rinse your mouth with them after eating, thus washing away any remaining food that can cause an infection.
Medicinal plants such as chamomile, calendula, string grass, etc. have also proven themselves well. Decoctions from these plants should be quite concentrated. For one or two teaspoons of herbarium there is half a glass of boiled, warm water, but not boiling water. Doctors recommend rinsing your mouth with such decoctions at least three times a day, preferably also after meals. Solutions of this kind do not help in all cases, so they can be alternated with rinsing with antiseptics.
In a situation where decoctions and light solutions of antiseptics do not help, you can use an alcohol tincture of iodine or a 1% solution of brilliant green. These products are best applied directly to wounds. The surface around the wound itself should be carefully treated, using a cotton swab. However, you need to apply very little to avoid burning your tongue.
Less common in medical practice are more serious injuries to the tongue. Usually these are puncture, deep cuts, lacerations and even gunshot wounds. In such cases, it is necessary to first seek help from surgeons. Otherwise, complications such as abscesses or cellulitis may develop. The most dangerous outcome of events is difficulty breathing (asphyxia) and bleeding.
As for cut, lacerated and puncture wounds of the tongue, the first step is to stop the bleeding and apply stitches. If the bleeding cannot be stopped, special clamps or tampons are used. If there are no complications, processes of suppuration, etc., wounds of this type heal within a month. Unfortunately, wounds that get wet all the time, such as tongue injuries, heal slowly.
Shallow wounds of the tongue can heal quite quickly. With proper treatment and constant care, in the absence of any complications, the healing period of such damage takes from several days to a week. During this period, doctors do not recommend abusing salty, spicy and sour foods. If the wounds do not go away within a week, you should immediately seek help from specialists.
How do dental medications work?
In most cases, diseases of the oral mucosa manifest themselves in the form of unpleasant, disturbing signs:
This course of the disease complicates the patient’s life, causes discomfort and distracts from everyday activities. But with proper treatment, it is possible to get rid of such symptoms quite quickly. To be completely cured, you will need to undergo a full therapeutic course. Only in this case will the painful symptoms not recur.
Complex therapy includes drugs with local action: ointments, gels, creams. Most of them have a fairly fast effect, they eliminate pain, swelling and itching after just a few minutes.
Some of the remedies have 1-2 effects, while others, most often multi-component, can affect most symptoms. They act as an antiseptic, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, healing medicine:
- quickly relieve itching;
- heal damaged mucous membranes, including ulcers;
- reduce and eliminate bleeding;
- stop the inflammatory process, eliminating pathogens;
- form a protective layer in the form of a film on mucous tissues;
- strengthen gums.
Which is better: ointments or gels
In dental practice, doctors often choose to treat patients with medications in the form of water-based gels. Ointments have a greasy consistency that does not adhere well to moist mucous membranes, and their active ingredients penetrate the tissue more slowly.
In this case, gels turn out to be more effective: their structure allows the product to better connect to the surface of the oral cavity, and their active components quickly penetrate through the layers of the skin to the inflammation that has arisen even in the depths.
Regardless of the advantages and disadvantages, only a specialist can fully assess the effectiveness of drugs and prescribe the most suitable one.
In any case, topical medications have certain advantages:
- the active ingredients of the drug penetrate directly into the site of inflammation, bypassing circulation throughout the body;
- components of ointments and gels, including active ones, are able to penetrate into the blood, but in small quantities;
- there are side effects, they are indicated in the instructions for the medicine, but, based on practice, they occur extremely rarely;
- Dental ointments and gels can be purchased at almost any pharmacy, and a prescription is not required when purchasing;
- Such products are very easy to use and no special skill is required to apply them to the damaged area of the mouth.
What diseases cause damage to the oral mucosa
Before using a healing ointment, it is important to identify what is causing the mouth ulcers and other damage. Often these are dental problems, but sometimes the mucous membrane suffers for other reasons. The most common ailments include the following:
| Herpetiform stomatitis. | The mucous membrane is covered with a large number of small ulcers that do not have clear boundaries. They are located on the bottom of the cavity. The ointment for this disease should not only heal tissue, but also fight herpes. |
| Aphthous stomatitis. | The inside of the mouth becomes covered with white ulcers; in case of relapse, ulcerations may appear in other areas of the mucous membrane. The disease is accompanied by severe pain, so it is worth choosing an ointment with a pronounced healing and analgesic effect. |
| Tuberculosis. | Bacteria provoke the formation of numerous ulcers of various shapes; when large, they become painful. Bleeding often occurs. Local ointment is part of complex therapy; its main effect is antibacterial. |
| Candidiasis. | The fungus grows on the surface, covering everything with a white, cheesy coating, under which redness and ulcers are found. Ointments and gels with an antifungal effect are prescribed. |
Considering the variety of diseases, it is easy to imagine that an incorrectly selected healing ointment will not bring relief. Some people claim that they used the most popular, expensive drug, smeared the mucous membrane as indicated in the instructions, but did not notice any improvement, and often the disease began to develop more intensively. That is why it is important to know the disease and use a remedy that is suitable to combat it.