What is candidiasis
Thrush is a fungal disease that is caused by a microscopic yeast fungus of the genus Candida, namely Candida albicans. The scientific name for the group of diseases caused by the genus Candida is candidiasis or candidiasis.
These fungi are one of many components of the natural microflora of the oral cavity, respiratory tract, large intestine and vagina of absolutely healthy people. These are opportunistic microorganisms, i.e. under normal, normal conditions they do not cause disease. But if their number increases, candida can become a source of many troubles.
Diagnosis of fungus in the mouth
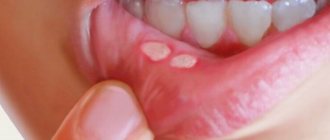
Already on the basis of an examination, a doctor can diagnose a fungus in the oral cavity if he sees a white coating on the mucous membrane of the gums, palate, and tongue. In severe cases, the plaque may acquire a dark tint, similar to a chromogenic fungus.
When you try to remove the plaque, you find reddened mucous underneath, which can bleed. A smear examination under a microscope will help confirm the doctor’s prognosis. If esophageal candidiasis and a complicated infection are suspected, the attending physician will prescribe endoscopy and x-ray of the esophagus with a contrast agent.
Fungal infection of the oral mucosa develops against the background of an imbalance in the chemical balance of microflora, a decrease in local or general immunity. In particular, fungal candidiasis in the oral cavity develops due to the following factors:
- pregnancy, accompanied by changes in metabolism, hormonal levels, and a decrease in the body’s defenses;
- tuberculosis, diabetes mellitus, diseases of the adrenal glands and gastrointestinal tract, HIV;
- taking cytostatics and hormonal drugs, oral contraceptives;
- long-term use of antibiotics, which provokes a change in the composition of microorganisms in the microflora;
- deficiency of vitamins B, C, PP;
- alcohol and drug abuse;
- injuries to the mucous membrane due to damaged teeth, malocclusion, etc.;
- having dentures that don’t fit well or are made from material that causes allergies;
- contact with an infected person – through kissing, sexual intercourse, childbirth, as well as when using other people’s objects (dishes, toothbrush, etc.).
Introduction to fungi
For the first time, a fungus of the genus Candida was identified in the placenta, umbilical cord membranes and amniotic fluid of the fetus of an infected woman in labor.
Bacterial candidiasis
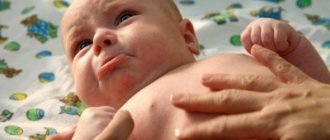
Quite often, the first acquaintance with fungi of the genus Candida occurs in utero. If this does not happen, then the newborn’s first contact with the fungus may occur during the passage of the birth canal, and later through contact with the skin of the hands. Candida can enter the oral mucosa from the surface of the nipple of an infected mother during breastfeeding or from contaminated food. Infection with yeast fungi in the first year of life is confirmed by the appearance of characteristic rashes on the mucous membranes of the cheeks and gums.
The first thing we associate with when we hear the diagnosis “thrush” is a problem that many women have localized in the genital area. We also mention thrush in women as the most common side effect when taking broad-spectrum antibiotics. To some extent, this is true, but in fact, candidiasis can affect absolutely any part of the body, cause pathologies of internal organs, and equally in both women and men.
Types and symptoms of candidiasis
Manifestations of the disease are very diverse and depend on the specific location of development of the inflammatory process.
Oral candidiasis
Oral candidiasis is most common in childhood. It manifests itself as redness of the mucous membranes of the throat, gums and tongue. Swelling develops. As the disease develops, areas of white plaque with a cheesy consistency form on the oral mucosa. If treatment measures are not taken, their number increases, and erosions occur under the plaque.
When oral candidiasis becomes chronic, damage to the mucous membranes of the nose, pharynx and esophagus is possible.
Candidiasis of the skin
Fungal pathology can spread in the folds of the skin: in the armpits, under the mammary glands. The folds between the fingers and toes are affected. In some cases, skin lesions outside the folds are noted.
The disease manifests itself in the form of small blisters. Individual areas merge to form affected areas. Between the toes of the limbs there is peeling of the skin, cracks, and itching. Externally, the palms look like they are burned.
Candidiasis of the genital organs
This type of disease affects the external organs of the reproductive system: in women – the vaginal mucosa, in the stronger sex – the glans penis and foreskin. A clear sign of the disease is copious white curdled discharge accompanied by itching. There is discomfort during intimate contact and when urinating.
Candidiasis localized in the intestines
Most often it occurs as a result of previous intestinal infections and the use of antibacterial drugs. In children, this condition can be caused by poor nutrition.
Intestinal candidiasis is manifested by pain in the abdomen, flatulence, diarrhea, and the presence of white cheesy flakes in the stool.
Read also: Ulcer on the oral mucosa treatment
Favorable living conditions
What conditions are favorable for increasing the fungal population:
- disruption of the body's resistance systems and decreased immunity;
- hormonal changes due to various physiological conditions or taking hormonal medications;
- dysbiosis;
- metabolic disorders and endocrine diseases;
- violation of the integrity of the mucous membranes;
- taking antibiotics or cytostatics;
- taking contraceptives;
- venereal diseases;
- acute and chronic diseases of the genitourinary system;
- tuberculosis;
- HIV AIDS;
- a large number and frequent change of sexual partners;
- hot and humid climate;
- work in damp or damp areas;
- contact with concentrated chemicals or work in chemical production.
Treatment of candidiasis
The process of getting rid of unpleasant manifestations begins with diagnosis. After examining the patient, a bacterial culture is prescribed - a method that allows one to determine the causative agent of the disease.
During the study, a scraping is taken from the mucous membrane at the site of the lesion. The material is placed in a special environment for several days, where the fungus grows, forming colonies. Based on the data obtained, a final diagnosis is made and a treatment regimen is prescribed.
Drug therapy for candidiasis
For any type of localization of the lesion, complex treatment is required:
Normalization of the immune system: restoration of intestinal microflora, use of immunomodulators.
Elimination of local manifestations of the disease: ointments, suppositories, creams, vaginal tablets (Clotrimazole, Pimafucin, Miconazole).
Systemic treatment: tablets or capsules taken orally (Diflucan).
The process of getting rid of thrush during pregnancy differs from the treatment of this disease in patients of other categories. First of all, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of adverse effects of drugs on the fetus. Therefore, topical agents with low toxicity and absorption, with a minimum number of side effects, are prescribed.
Candidiasis and diet
Human immunity largely depends on the state of the intestinal microflora. With an existing fungal disease, it is almost always impaired. Therefore, to speed up recovery, it is important to follow a diet, which is an element of general treatment.
It is necessary to exclude from the menu foods that contain large quantities of simple carbohydrates: confectionery, sweets, honey, sweet fruits and packaged juices, alcohol.
- The consumption of pasta and starchy vegetables: potatoes, carrots, pumpkin should be limited.
- It is recommended to give preference to lean varieties of meat and fish, stewed, boiled and baked vegetables.
- To normalize the intestinal microflora, you need to include fermented milk products in your menu.
Traditional methods in the treatment of candidiasis
There are many popular ways to get rid of unpleasant symptoms, but it should be remembered that they are auxiliary and often minimize pathological symptoms without eliminating the cause of the disease.
- Pour 2 tablespoons of dry calendula (flowers) into 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 40 minutes to infuse. It is recommended to wash the genitals with the strained product. In addition to calendula, you can use celandine, chamomile, oak bark, and yarrow for these purposes.
- Baking soda is a common way to treat candidiasis at home. This substance has a detrimental effect on the fungal habitat. Dissolve 2 tablespoons of baking soda in a liter of boiled water. You can wash the genital area daily with this solution (it is better to do the procedure in the evening). It is important not to leave excess moisture on the genitals after it.
In women, soda procedures should be carried out with caution: this can provoke disturbances in the vaginal microflora.
How is thrush transmitted?
We have already found out that thrush can be transmitted from mother to child in utero and during the first bodily contacts. The most common route of transmission of candidiasis is sexual. Although thrush is a sexually transmitted disease, it is not a sexually transmitted disease.
You can also become infected with candidiasis through contact and household contact, for example through bed linen, when visiting public baths, etc. In addition to people, young domestic animals and poultry can be carriers of the infection.
Candida is widespread in the environment and is often contaminated in vegetables, fruits, dairy products and raw meats.
Diagnosis of candidiasis
To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor must know the clinical picture and learn about the symptoms that bother the patient.
The results of laboratory examinations and clinical blood tests are of great importance; a blood glucose test is mandatory.
Since the causative agents of candidiasis (yeast-like fungi) are capable of multiplying in parallel in several areas, the skin and nail plates are examined. Treatment aimed at destroying parasitic microorganisms is in most cases prescribed by the dentist.
But in order to identify and treat concomitant diseases, you need to contact specialized doctors. Making an accurate diagnosis is possible only after taking scrapings from the patient’s oral mucosa. It is worth noting that the scraping is given as follows:
- on an empty stomach, while brushing your teeth is prohibited;
- after five hours after eating or rinsing the mouth.
If candidiasis occurs in a chronic form, the scraping will contain a large number of so-called chains of long round-shaped cells that bud, and filaments of pseudomycelium will be present. In acute candidiasis, scraping results show that cellular rounded forms are predominantly distributed, occasionally budding.
Forms of the disease
Regardless of location, thrush has three forms: acute, chronic and carrier.
- Carriage (or candidiasis) is the mildest form. It occurs latently in the body, without any clinical manifestations. For a healthy person, such candidiasis does not pose a danger, since strong immunity does not allow the disease to develop. Candidiasis can only be determined through tests. If fungi of the genus Candida are detected in large quantities in a pregnant woman, she must undergo a course of treatment to protect the child from infection.
- The acute form is the most common form of candidiasis. It is divided into simple (uncomplicated) and complicated.
- The simple form is accompanied by itching, cheesy discharge or plaque and other characteristic signs.
- Complicated form - develops against the background of significantly reduced immunity, the presence of a complete infection in the body and inflammatory processes.
- Chronic candidiasis is candidiasis that cannot be treated for a long time (more than three months). Characterized by periodic relapses of the disease, provoked by hypothermia, colds, menstruation, climate change, etc. People with very low immunity, those with AIDS or cancer pathology, mainly suffer.
Causes of candidiasis
Fungus of the genus Candida belongs to the normal microflora of the human body, therefore there is no such thing as primary candidiasis. This disease is always a complication or consequence of some pathological process in the body. Major risk factors for candidiasis
:
- congenital immunodeficiencies, for example, DiGeorge syndrome;
- acquired immunological pathologies (HIV, chronic infectious diseases in the stage of decompensation);
- general exhaustion of the body;
- long-term use of antibacterial drugs;
- treatment with hormonal drugs or cytostatics.
If a doctor is consulted for candidiasis for the first time, it means the patient missed the effect of the provoking factor or ignored its importance.
Signs of thrush in women and men
In men, thrush occurs almost unnoticed, while women notice the presence of symptoms, but do not always attach importance to it. In the acute form of urogenital disease, both cases are characterized by the presence of:
- redness and swelling of the foreskin or vaginal mucosa;
- feelings of burning, itching and discomfort;
- the appearance of a white coating or discharge similar to cottage cheese, with a faint smell of sour milk.
When these symptoms appear, women should contact a gynecologist, and men should contact a urologist, for examination and taking smears to confirm the diagnosis.
How does candidiasis manifest in men?
The most common manifestation of candidal urogenital infection in men is balanoposthitis.
Symptoms of cadidal balanoposthitis:
- redness, swelling of the glans and foreskin
- sensations of discomfort, burning and itching
- rashes (red spots, papules, erosions) on the head with a white curdled coating
- cracks in the head area
- unpleasant “sour” smell
- painful sexual intercourse (dyspareunia)
- urinary disorders (dysuria, manifested by pain, burning, itching when urinating)
If 4 or more episodes of urogenital candidiasis were observed during the year, then this condition is called recurrent.
The recurrent form in men occurs in no more than 2%.
As a rule, such a problem is associated with the patient having diabetes mellitus and/or HIV infection.
Signs of oral candidiasis include focal changes in the oral mucosa, the appearance of a characteristic plaque that can be easily removed with a spatula.
Intestinal candidiasis is accompanied by manifestations of colitis, enteritis: abdominal pain, bloating, watery stools, sometimes with blood.
Different diseases - different doctors
In addition to the urogenital form, other types of candidiasis are quite common in both women and men. Which doctor will treat candidiasis depends on the type of fungal infection in the body.
- Cutaneous candidiasis - swelling, itching, redness of the skin and a characteristic rash appear in the armpits, inguinal folds and in the anus. The treatment of the cutaneous form of thrush is carried out by a dermatovenerologist. You should also contact a dermatologist or dermatovenrerologist for another, quite common form of fungal infection - nail candidiasis. It is characterized by thinning of the nail plates, which easily peel and even crumble, as well as redness of the nail folds. A timely visit to a doctor and adequate therapy will help you quickly get rid of these problems.
- Intestinal candidiasis. The outermost parts of the colon are most often affected. In this case, the patient suffers from flatulence, periodic diarrhea, and the appearance of white plaque or white spots in the stool. A gastroenterologist deals with the treatment of intestinal candidiasis.
- Thrush of the mucous membranes of the mouth most often affects children due to disturbances in the microflora of the oral cavity. The disease is characterized by the presence of white plaque, swelling and redness of the mucous membranes. The problem of treating oral thrush (fungal stomatitis) is the prerogative of the dentist or general practitioner.
- As mentioned earlier, the most difficult to treat is the chronic form with systemic damage to the body against the background of significant suppression of the immune system. In this case, the treatment is complex, it is carried out by an infectious disease specialist and an immunologist.
Thrush, like any disease, should be taken seriously and not self-medicated. A timely visit to a doctor will allow you to stop the disease at its very beginning and avoid unpleasant complications and relapses.
Which doctor treats candidiasis?
Candidiasis of the male genital organs – which doctor treats it?
For candidiasis on the penis or genital skin in men, the most popular attending physician is a dermatovenerologist. Fortunately, the symptoms, as they say, are in plain sight:
- Redness of the head.
- White loose coating with a sour odor.
- Swelling of the foreskin.
- Pain and burning in the affected areas of the genitals.
A common cause of the disease is untreated candidiasis in a sexual partner. Sometimes such patients seek to see a urologist, but this is a surgical doctor. Yes, the doctor will be able to give practical recommendations, but it is better to consult a dermatovenerologist.
Which doctor treats skin and nail lesions with candidiasis?
For fungi of the genus Candida, such localization is not very typical, but it does occur. And most often - against the backdrop of a weakening of the body’s immune forces.
The characteristic symptoms of candidiasis of the skin or nails are not expressed. Therefore, what kind of fungus caused the lesion should be determined by a dermatologist.
Typical signs are:
- White loose coating on individual surfaces of the limbs or torso.
- Severe itching, burning in these places.
- After removing the plaque, a hyperemic surface with areas of erosion remains.
- Deformation, fragility, change of color of one or more nails.
To clarify the diagnosis, specific studies are required - scraping and microscopy of the affected area, cultural seeding. They are carried out in laboratories of the first and second levels upon the direction of a doctor.
Which doctor treats candidiasis in the mouth?
In this section of the digestive tract, very favorable conditions have formed for the life and reproduction of candida.
And here there is a significant load on the humoral part of the immune system, which often “sags.” As for the question of which doctor to contact for oral candidiasis The obvious solution is to go to the dentist.
However, with candidiasis of the oral cavity, the ENT organs are often affected: the larynx, pharynx. Therefore, if you suspect candidal stomatitis (burning, redness, pain and white plaque), it would not hurt to first see a therapist. From him you can get a referral to a specialized specialist: an otolaryngologist, a dentist, or even a gastroenterologist.
Candidiasis of the esophagus and intestines - which doctor should I contact?
In a healthy person, these parts of the digestive system are covered with candida only in the presence of foci of chronic candidal infection. Most often these are self-treated cases of thrush.
Symptoms of gastrointestinal candidiasis do not allow one to suspect fungi, and therefore in such situations, patients, when deciding which doctor to go to, choose a gastroenterologist.
Complaints do indicate digestive problems:
- Pain when swallowing.
- Burning sensation in the esophagus (as with heartburn).
- Bloating.
- Cutting in the epigastrium and around the navel.
- Loose stools.
- Blood in the stool.
When examining the stool, many yeasts are found. And instead of gastroenterological drugs, antifungal drugs are prescribed.
The task of treating such patients most often falls on therapists.
Generalized forms of candidiasis and their treatment
Generalization means the simultaneous defeat of several anatomically heterogeneous sections by candida. For example, the genitals and skin of the extremities or the oral cavity, genitals and intestines.
In the vast majority of such cases, the cause of generalization is a pronounced weakening of the immune system due to AIDS. These patients are treated by doctors of various specialties, the main one being an infectious disease specialist.
Candidiasis is diverse, and the health of men, women and even children depends on the choice of which doctor to contact when problems arise. If in any doubt, contact an available general practitioner. And this doctor will already refer you to specialized specialists.
The main thing is that you cannot sit at home and buy medications yourself: without establishing an accurate diagnosis and monitoring the effectiveness of the treatment process.
Self-medication will only lead to deterioration of health and the spread of candida.
Symptoms of candidiasis
Among gastroenterological diseases, esophageal candidiasis is the most difficult to diagnose. After all, the degree of damage to the walls of the esophagus and what the patient feels do not correspond to each other.
A third of the sick are not bothered by any symptoms; when the pathology develops, people are not aware of their illness. There are signs by which the disease can be identified. The following symptoms indicate esophageal candidiasis:
- Heartburn.
- Lack of appetite.
- Dysphagia is an abnormal process of swallowing food.
- Odynophagia is pain when swallowing.
- Frequent manifestations of nausea and vomiting.
- Pain in the stomach and chest.
- Loose stools.
- Unreasonable increase in temperature.
I would like to draw attention to the symptoms of vomiting and pain when swallowing, which may appear slightly, or may be so pronounced that it will become impossible to eat and drink water. And with nausea and vomiting, specific whitish films are present in the vomit.
There are bloody spots in loose stools. With loss of appetite, body weight decreases. With esophageal candidiasis, a characteristic concomitant disease is oral thrush.
This disease begins with penetration into the mucous cavity, then goes deep into the tissue. The resulting films can close the lumen of the esophagus, and ulcers and necrotic areas appear in the esophagus itself and on its walls. This means adding a bacterial infection. Esophageal candidiasis has complications, but they manifest themselves to a lesser extent compared to intestinal candidiasis, such as the development of ulcers, bleeding and tissue necrosis.
The disease manifests itself as yellow or white foci on the affected walls of the esophagus. These zones are raised and after some time are able to merge. Fungal colonies get inside the joints, penetrating into blood vessels and muscle tissue.
Composition of plaque ⏤ epithelial cells mixed with fungi, bacteria and inflamed cells. When analyzing microscopy, characteristic threads with fungal mycelia are found. The yeast-like structure and uniform color of the research object are characteristic. According to the severity of esophageal candidiasis, they are divided into three groups:
First. There are whitish plaques with pseudomycelium of the fungus between the epithelial cells.
Second. The plaques form a film and vast fields, merging together. In this case, the pseudomycelium of the fungus penetrates deeper into the layer of submucosal tissue.
Third. Pseudomembrane type of deposits, and the fungus penetrates into the muscle tissue.
Oral candidiasis: treatment
Treating candidiasis in the mouth is not an easy process. Getting rid of the disease will have to be done not only by taking drug therapy. Doctors recommend that patients be sure to follow many measures, thanks to which:
- the immune system will be strengthened,
- It will be possible to identify and treat concomitant diseases.
Also of great importance in therapy are measures to treat the oral cavity and improve the patient’s lifestyle. By the way, in some cases, quitting smoking or drinking alcohol, an established and balanced diet, and proper oral hygiene help get rid of an unpleasant illness.
Since people who wear dentures are more likely to get candidiasis, they should keep their dental implants clean.
If the development of fungal flora is caused by long-term use of antibiotic drugs, cytostatics or corticosteroids, you will need to resort to antimycotic drugs.
Causes of blood candidiasis
The direct cause of candidiasis is the penetration of the fungus into the human body. However, the root cause in the manifestation of symptoms plays a lesser role than the factors that provoke the development of the disease.
These include:
- Long-term use of antibacterial drugs, which suppresses the development of microflora that inhibits the proliferation of candida albicans;
- The presence of chronic diseases such as tuberculosis, diabetes, immunodeficiencies;
- Dysbacteriosis of the vagina or gastrointestinal tract;
- Taking cytotoxic drugs and corticosteroids;
- Lack of vitamins and microelements in the body;
- Deficiency of protein foods;
- Autoimmune disorders;
- Working in an enterprise with high air humidity;
- Organ transplantation;
- For newborns, frequent regurgitation and weight loss are of great importance.
All these factors can give rise to the active reproduction of candida albicans, as a result of which the fungus enters the blood from the “depot”. Further development of the situation depends on the state of the body's defenses.
Complications of candidiasis
Candidiasis can spread to other tissues and internal organs. The following complications arise:
- vulvovaginitis;
- balanitis;
- mastitis;
- esophagitis;
- endocarditis;
- pericarditis;
- meningitis;
- empyema;
- pneumonia;
- changes in the shape of the lips, cancerous tumors.
In advanced cases, against the background of immunodeficiency, the fungus can even spread to the brain.
Candidiasis is not life-threatening, but it must be treated promptly. Chronic forms reduce the patient’s quality of life and can cause serious complications.
Factors for the development of candidiasis
The main factor in the development of candidiasis remains weak immunity; children and people with immunodeficiency diseases are often susceptible to infection with candidiasis. There are frequent cases when candidiasis in the digestive system affects several organs.
Conditions are needed for the development of the disease, and in the esophagus, esophageal candidiasis develops under the following favorable factors:
- poisoning, alcoholism and smoking;
- malnutrition;
- the presence of chronic diseases in the body;
- reduced acidity of gastric juice;
- diabetes;
- allergies;
- enteral and parenteral nutrition;
- antacid therapy;
- use of corticosteroids (injections or inhalers);
- obstruction of the esophagus;
- improper motility of the esophagus;
- organ or bone marrow transplantation;
- with a lack of protein;
- for cancer (radiation therapy and chemotherapy).
Spasmophilia, which occurs as a result of phosphorus metabolism disorders due to hypofunction of the parathyroid glands, leads to a weakening of the protective functions of the esophagus.
Protein deficiency caused by long-term consumption of low-calorie foods and diets leads to nutritional status that gives an advantage to fungi for the development of candidiasis.
Cultures for candidiasis
Culture is one of the most informative tests for candidiasis. It has high sensitivity and specificity. Any clinical material can be cultured.
For urogenital candidiasis, this is usually a smear from the urethra or vagina. Although feces, blood, and sputum can also be sown.
You get the following results:
- the presence or absence of colony growth on the nutrient medium (if growth is present, the fact of candidal infection is confirmed);
- quantitative indicators;
- pathogen species;
- sensitivity to drugs with antifungal effect.
Quantitative indicators are assessed in CFU. A fungal concentration of 104 CFU or higher is considered excessive. In this case, it is believed that candida can cause an inflammatory process. If the concentration is lower, other microorganisms may be the cause of inflammation.
The most valuable information a doctor receives is sensitivity to antimycotics. It allows you to immediately prescribe an effective drug and not waste time on unsuccessful treatment.
Despite the high information content, seeding is rarely used.
There are several reasons for this:
- In general, candidiasis responds well to empirical treatment;
- cultural examination takes from 7 to 10 days;
- There are simpler and cheaper diagnostic methods (for example, smear microscopy).
Therefore, culture is used only in difficult cases. For example, with recurrent candidiasis and ineffective treatment with antifungals.
Intestinal candidiasis
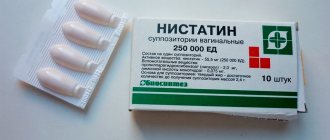
If you have symptoms of intestinal thrush, you should make an appointment with a gastroenterologist. Intestinal candidiasis is a consequence of an imbalance in the gastrointestinal tract as a result of the active proliferation of fungi. After the endoscopy, the doctor will prescribe treatment. It is important to eliminate the inflammatory process in the intestines. The gastroenterologist prescribes antifungal drugs such as Nystatin and Levorin.
Candidal stomatitis most often affects young children, women who smoke, as well as people who wear dentures and the elderly. If symptoms of the disease appear, you will need the help of a dentist. If a child gets sick, it is better to contact a pediatric dentist. You should not treat the disease yourself.
Diagnostics
With typical forms of genital candidiasis, the diagnosis can be made based on examination. At home, candidiasis can be identified by a specific cheesy discharge.
In such cases, smears from the urethra and vagina are taken for examination for concomitant sexually transmitted infections.
For laboratory diagnostics the following can be used:
- microscopic examination of samples with the addition of 10% KOH solution, Gram staining with methylene blue;
- cultural studies with species identification of the pathogen;
- molecular biological techniques aimed at identifying DNA fragments of fungi of the genus Candida.
For reference. If necessary, the sensitivity of the pathogen to antifungal drugs is also assessed. Most often, this study is used for recurrent or severe forms of candidiasis that are difficult to treat.
Diagnosis of thrush in the mouth
In most cases, your doctor or dentist will diagnose thrush simply by examining your mouth. However, some additional tests may be performed to confirm the diagnosis. Your doctor may recommend that you have blood tests to check for certain conditions associated with oral thrush, such as diabetes and nutritional deficiencies.
A biopsy may also be performed. It involves taking a sample of the oral mucosa in the affected area and examining it under a microscope for the presence of Candida alba fungus. The dentist may also take a swab of the affected area to monitor how the fungus grows over a few days.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the causes of tooth damage that have nothing to do with caries
Causes and symptoms of oral thrush
Candida is found in most people's bodies and does not harm them. But deterioration of immunity or changes in microflora lead to the development of oral fungus disease. The following reasons contribute to the infection of the oral mucosa by fungus:
- Immunodeficiency, weakening of the immune system.
- Changes in hormonal levels in pregnant women.
- Chronic gastrointestinal diseases, consumption, AIDS, adrenal diseases.
- Antibiotics, cytostatics, hormonal drugs, the use of oral contraceptives, which can disrupt the natural balance of microflora.
- Excessive use of alcohol and drugs.
- The use of poorly fitting dentures or those made from allergenic material.
- Thermal burns of the oral cavity or injuries resulting from malocclusion.
- Lack of vitamins B, C and PP.
- Allergy to any food or medicine.
- Contact with sick people: kissing, sexual intercourse, childbirth, using things of an infected person, as well as contact with animals.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Cracks in teeth - types, symptoms, causes, treatment - Doctor Zub
There are four types of fungus, each of which has its own causes.