Herpangina
red vesicles of herpes sore throat
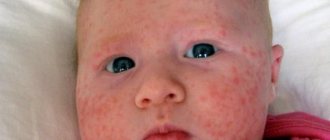
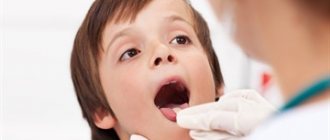
This is the most common cause of the formation of red blisters on the tonsils and palate in children.
The disease is caused by Coxsackie enteroviruses types A and B, which usually infect the body at an age when the immune system is just developing: preschoolers and children of primary school age are affected.
The most characteristic symptom of infection is the red vesicles covering the throat (shown in the photo).
If in all other diseases that lead to the development of a rash on the throat, this sign may or may not be present, then in the case of herpes sore throat, red dots are always present. An atypical course of the disease without a rash is very rare.
The disease begins acutely. Characterized by an extremely high rise in temperature (up to 41 degrees) and severe sore throat.
Treatment is symptomatic. In most cases, the disease goes away in 7-10 days.
In this article you can read in more detail about what the symptoms of herpetic sore throat are and what measures should be taken to ensure a speedy recovery of the child.
Viral diseases in children and adults
Red rashes can appear due to any respiratory diseases. In this case, in addition to damage to the mucous membrane of the larynx, inflammation of the mucous membranes of the nose and rhinitis are observed.
Causes
Causes of a red rash in the throat in adults:
| Cause | Clinic | Photo |
| Flu | Accompanied by high fever, chills, headaches, dry mouth, muscle weakness. Rhinitis gradually appears, and nasal breathing becomes difficult. Erythematous rashes appear on the mucous membrane of the throat | |
| Herpangina (also called herpangina or enteroviral vesicular pharyngitis) | It is caused by Coxsackie viruses. The disease is accompanied by high temperature, up to 41 degrees. A rash appears in the oropharynx, and it becomes painful to swallow. Sometimes there is abdominal pain | |
| Herpetic stomatitis | It develops in acute and chronic forms. The latter often occurs without fever. In the acute form, on the contrary, fever is noted. Small pinpoint rashes appear on the mucous membrane. There is a feeling of soreness in the throat, and the lymph nodes become enlarged. It becomes painful for a person to swallow | |
| Infectious mononucleosis | Accompanied by fever, inflammation of the pharynx, enlarged lymph nodes, pain when swallowing. Red spots appear in the mouth and throat. Characteristic signs are fever, headaches, weakness | |
| Viral pharyngitis | Symptoms such as sore throat, slight fever, and difficulty breathing are common. A red rash appears on the roof of the mouth and throat |
Treatment
Treatment for these diseases is prescribed by a doctor after a full examination. Not each of them has specific therapy. Basic tactics:
- For herpetic type sore throat, symptomatic treatment is recommended. At high temperatures, take antipyretics, and if there is a threat of bacterial infection, take antibiotics. Multivitamin complexes and gargling with antiseptic solutions are also prescribed. Drinking plenty of fluids and eating a balanced diet play an important role. This also applies to viral pharyngitis. You need to drink more warm water, weak tea, rosehip decoction. It is recommended to avoid rough foods, salty, spicy, sour dishes, which lead to irritation of the mucous membranes and aggravate the situation.
- For herpetic stomatitis, systemic antiviral drugs are prescribed. Local treatment is indicated - interferon is used in the form of an ointment or solution. It is possible to use bonaftone, florenal or tebrofen ointment. They are applied to spots covering the mucous membrane, after which they are treated with an antiseptic solution or herbal decoction - 1 tbsp. l. raw materials per glass of boiling water (sage and chamomile have these properties).
- No specific therapy has been developed for infectious mononucleosis Symptomatic treatment is prescribed, strengthening agents are prescribed. Bed rest is not necessary in principle, but there should be a restriction of physical activity, which is maintained for at least one month. If there is a risk of secondary bacterial infection, then broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed.
- If you have the flu, you should take antiviral drugs (Novirin), antipyretics (Milistan, other similar paracetamol-based tablets). Children are given Nurofen to reduce fever.
Infectious mononucleosis
The disease is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. Adolescent males are more often affected.
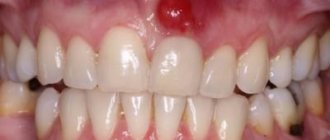
red spots on the roof of the mouth due to infectious mononucleosis
The red rash on the throat is localized in the palate and consists of palatal petechiae - pinpoint hemorrhages. What petechiae look like during mononucleosis is shown in the photo.
Other symptoms of the disease include:
- fever and signs of general intoxication;
- sweating;
- a sore throat;
- enlarged lymph nodes, liver and spleen;
- swelling of the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx, sometimes making breathing difficult;
- rash on the body.
The diagnosis is made based on a blood test and a characteristic clinical picture.
There is no specific treatment. Therapy is aimed at relieving symptoms. In most patients, the disease goes away without leaving a trace, without causing serious complications. However, the period of complete recovery after an infection is long – up to six months.
Rash with sore throat
A rash with a sore throat is not a characteristic sign of the disease, but is considered a secondary pathology that arose before or during the course of the disease.
Skin rash due to sore throat - causes
Sore throat is a bacterial disease caused by streptococci, streptococci and other bacteria. The first symptoms of the disease are sore throat, headache and fever.
All clinical signs of the disease may be accompanied by a rash with sore throat, which requires additional diagnostics to determine the cause. The rash can appear in both adults and children.
The appearance of a rash against the background of tonsillitis indicates the addition of a secondary disease or complications. Among the reasons that can affect the appearance of rashes are:
- allergic reaction;
- diphtheria;
- measles;
- scarlet fever;
- Infectious mononucleosis;
- measles;
- chicken pox.
The appearance of any rash against the background of the development of tonsillitis requires a mandatory visit to a doctor and additional diagnostics. The cause of the rash can also be determined by the nature of the rash and immediately take the necessary methods of combating and preventing a possible disease.
Scarlet fever
A rash with a sore throat can occur in a child due to scarlet fever.
This is an acute infectious disease that occurs with fever, symptoms of intoxication, sore throat, and pinpoint rash against the background of general skin hyperemia.
The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets, household contact, nutrition and through a third individual. There are typical and atypical forms of scarlet fever.
In the clinic, the prodromal period is either absent or does not last long. It begins acutely, the temperature rises to high levels, and there are severe symptoms of intoxication. If scarlet fever occurs against the background of a sore throat, then the child complains that his throat hurts and hurts, but worse. The tonsils are hyperemic, swollen, with or without pronounced purulent plaques.
Usually, on the first or second day of the disease, a simultaneous, pinpoint rash of a bright pink or red color appears in the child against the background of hyperemic skin, more often on the flexural and lateral surfaces.
On the face, only the nasolabial triangle, Filatov’s triangle, remains free from rashes; the rash causes itching, and the submandibular lymph nodes become enlarged. On the second or third day, symptoms appear that will definitely tell you whether it’s just a sore throat or scarlet fever.
The patient's tongue becomes a pronounced crimson color and a flaming pharynx appears, with pronounced white demography.
Sore throat and rash can occur for various reasons, but scarlet fever, in addition to severe clinical symptoms, can leave behind a number of complications:
- toxic myocarditis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- pneumonia;
- otitis;
- peritonsellar abscesses;
- sinusitis;
- pyoderma;
- chorea;
- arthritis;
- conjunctivitis.
After a thorough diagnosis, when treating scarlet fever, penicillin or erythromycin is prescribed orally for mild forms, and intravenously for severe forms. Antihistamines, antipyretics, sedatives and antiseptics are also used. There is no specific prophylaxis against scarlet fever.
Herpes sore throat and rash
One of the most common types of rash with tonsillitis is herpes sore throat. It is caused not only by bacteria, but also by viruses. A common virus that causes herpetic rash with sore throat is Coxsackie.
Based on the initial symptoms, it is not always possible to immediately determine whether it is herpes sore throat or scarlet fever, although the former has its own number of features. With scarlet fever, rashes appear on the first day of the disease, and with herpes sore throat, the rash appears much later.
This rash has its own special appearance, which is typical for all herpes infections - the rashes appear in the form of small blisters with serous fluid inside, which are usually localized in groups on the body.
They are mainly found on the skin of the hands and feet.
With herpes sore throat, rashes always appear on the mucous membrane of the tonsils, arches, mouth and cheeks. They merge into groups, can burst and cause severe pain in babies and children. The rash appears and disappears all the time and lasts from 3 to 5 days.
In addition to the rash, there are other symptoms:
- high temperature rises to 40 degrees;
- chills;
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- a sore throat;
- headache;
- children are restless, capricious, cry, refuse to eat.
After suffering herpetic sore throat in childhood, the child develops immunity, and this pathology reoccurs in rare cases. A rash after a sore throat is also rare and may be a symptom of another disease.
For this form of the disease, complex treatment is prescribed, including not only antibiotics, but also antiviral drugs.
Sore throat or the same scarlet fever are treated a little easier, but herpes sore throat, in addition to medications that act on the general condition of the patient and destroy the main causes of the disease, also requires local treatment.
To combat rashes, antiviral ointments are used, for example, “Atsyk” or “Gerpevir”, which are applied directly to the rashes; they remove burning and itching. Lotions will still be effective methods of treatment.
Infectious mononucleosis
Sore throat and a rash that appears on the body also occur with infectious mononucleosis, or another name for this disease is “Kissing Disease.” Sore throat or scarlet fever can cause this disease if the Ebstein Barr virus enters the body. Transmitted by airborne droplets.
The first period of the disease is intoxication. Fever, lymphadenopathy, acute tonsillitis, enlargement of the liver and spleen appear. The incubation period lasts 6-40 days, there may be a prodromal period - fever, loss of appetite, lethargy, but usually the disease begins acutely.
The temperature rises to 38-39 degrees, severe headache, nasal congestion without a runny nose, sore throat during swallowing, increased sweating, enlarged lymph nodes, liver, spleen. The fever lasts from 4-5 days to two weeks or even a month, and can be either constant or change.
Many people develop a rash on their body, pain, and fever. The rash is macular, maculopapular or hemorrhagic. They last from one to three days, and then disappear, leaving no traces on the skin.
Mainly the cervical lymph nodes become enlarged, rarely the inguinal and axillary ones. Nasal breathing is difficult, but there is no discharge. The tonsils become enlarged and there may be plaque, which often extends to the braces.
This disease can become chronic, affecting the nervous system or kidneys.
Hand-foot-mouth syndrome
This pathology is often added to complications after a sore throat, but this is a misconception. Doctors make the wrong diagnosis, starting from the child’s complaints, which are very similar to those inherent in a sore throat or a common ARVI.
The incubation period lasts from 5 to 7 days, but an infected child becomes dangerous to others already at the first symptoms of the disease, so he should be immediately isolated. As a rule, this disease is characteristic of children, since they are the ones who come into closest contact with each other, and the peculiarity of children's immunity also affects it.
The first symptoms are indeed somewhat similar to a common cold, and parents may not immediately suspect something is wrong and consult a doctor; instead, they begin to treat their child on their own. First, the general state of health worsens, the temperature rises, weakness, loss of appetite, headache, sore throat and hyperemia appear.
The next day, stomatitis develops in the oral cavity, which causes pain in the throat, which resembles a symptom of a sore throat, and rashes appear. The rash on a child’s body has a special character, appearing only on the limbs and sometimes on the skin of the lips.
It resembles red spots or there are bubbles with a bright, pronounced red border. On the oral mucosa, bubbles with serous fluid inside are found, which burst after a few hours and form ulcers.
The rash on the skin leaves behind peeling, and ulcers on the mucous membranes disappear without a trace.
Because of the clinic, the general condition of children worsens, salivation increases, pain begins during meals, therefore appetite decreases, there may be nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, weakness, children sleep poorly and become restless.
As a rule, the disease proceeds normally and without complications. With timely treatment, symptoms disappear within a week. But sometimes complications are possible that manifest themselves in a progressive clinical picture. The fever lasts a long time, the vomiting does not stop, the headache and drowsiness intensify, the child rubs his eyes in pain and cries all the time.
Associated symptoms
In addition to the symptoms characteristic of angina, there are also those that are completely not inherent in this pathology. In addition to a sore throat, cough, and high temperature, other body systems can be affected. For example, the gastrointestinal tract. Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or stool occurs, and the child may experience periodic colic or abdominal pain.
If the genitourinary system is affected, children may often go to the toilet, and urination will be painful or insignificant.
A common complication after a sore throat is acute glomerulonephritis, which is manifested by the presence of red blood cells in the urine.
The child’s urine turns pink or bright red, the temperature rises, pain appears in the lower back and lower abdomen, the child is capricious, sleeps and eats poorly.
The heart and blood vessels may also be affected, which will manifest itself in periodic aching pain in the heart area, increased or decreased pressure, tachycardia or bradycardia, which can soon lead to serious diseases such as hypertension, angina pectoris or myocardial infarction.
The nervous system suffers, as many organs are affected. There is sleep disturbance, tearfulness, tremors of the arms, legs, and head. Severe forms with improper or untimely treatment can become paralysis, paresis, meningitis or encephalitis.
How to treat a rash with a sore throat
For a sore throat, of course, you first need to prescribe medications that will remove the main cause of the disease. As a rule, these are antibiotics and antiviral drugs.
To improve the general condition and symptomatic therapy, antipyretics, antispasmodics or narcotic analgesics, antihistamines, sedatives, vitamins, and sleeping pills are used.
It is also useful to prescribe a special diet for children, which will increase immunity and stimulate it to fight the disease.
Local treatment is prescribed to remove the rash. Since the rash can be caused by different reasons, a different treatment method is selected for each type. For example, these will often be ointments that contain vitamins, an antiviral drug and antihistamines.
They may prescribe lotions with various medications, and proper skin care and hygiene also play an important role.
It is recommended not to use soap and other cosmetics during the treatment period; it is better to wipe the skin with an antiseptic solution, for example, furatsilin or chlorhexidine.
Prevention and treatment tips
When following prevention, you need to understand that you should not come into contact with children and adults who are coughing, sneezing, have a rash or any other symptoms. If the child himself begins to get sick, it is better to leave him at home and show him to the doctor.
Treatment of sore throat requires care and caution.
It is necessary to strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations and prescriptions, take medications correctly and on time, limit physical and emotional stress and set the body up for recovery.
If a child gets sick, you need to create the most comfortable conditions for him to recover and treat him according to the recommendations of a specialist, as well as follow prevention methods at home.
(1 5,00 of 5) Loading...
Source: https://nasmork.net/syp-pri-angine/
Erythema multiforme exudative
Pruritic dermatosis, or erythema of Gerba. More often affects young people. The exact causes of the pathology have not yet been established. But it is known that in the body of most patients there is a focus of chronic inflammation, for example, sinusitis or
rash in the throat with erythema multiforme exudative
chronic tonsillitis, against which sensitization develops. A common ARVI can provoke the onset of the disease.
The disease begins acutely:
- a sore throat;
- general malaise;
- temperature increase;
- headaches, muscle and joint pain.
Then a rash appears, the main location of which is the extensor surfaces of the limbs, the backs of the feet and hands. The mucous membranes of the mouth and lips are often affected.
Red spots can also form in the throat (shown in the photo).
The disease is often relapsing. There is no universal treatment. For severe forms, betamethasone is indicated. Desensitizing therapy is always carried out. For relapses, antibiotics are used.
Causes of rashes in the throat
As most likely, many have already guessed, the reason why pimples appear in the throat, especially those with a characteristic whitish or yellowish color, is most often infectious diseases. They can be either viral, bacterial or even fungal, but the causes are unchanged; rashes occur as a result of infection entering our body.
All possible infections penetrate and settle in the throat due to the fact that our immune system fails, and the tonsils, located in the throat and acting as a human shield on the path of all diseases, become the first frontier on which all possible consequences of the disease are reflected. Of the most likely ailments that cause a characteristic white rash in the throat, the following are found:
- Follicular tonsillitis;
- Chronic tonsillitis.
It is these two diseases that can and are usually accompanied by purulent formations that look either like pimples in the throat (follicles, ulcers, blisters, etc.) or like small white dots representing pus clogged in the tonsils. In any case, these symptoms are most often accompanied by unpleasant sensations, have a number of aggravating consequences and need to be gotten rid of. But how to get rid of such troubles should be considered in more detail, touching on the very specifics of the ailments listed above.
Measles
The disease usually occurs in children and is the most dangerous childhood infection that can be fatal.
red throat due to measles
The causative agent is paramyxovirus.
Signs of the disease:
- high temperature accompanied by psychomotor agitation;
- sore throat, runny nose, cough;
- conjunctivitis and photophobia;
- skin rash and peeling.
Velsky-Filatov-Koplik spots often form on the mucous membranes of the cheeks and throat. Usually these are white dots, similar to semolina. But sometimes they can be red, as shown in the picture.
There is no specific treatment. Previously, people were hospitalized with measles. Today the child remains at home, but under the watchful supervision of a local doctor. If there are no complications associated with measles, the disease goes away in 7-10 days. But it leaves behind reduced immunity for several months.
Rash with a sore throat on a child’s body
Sore throat is an unpleasant, but familiar disease to almost everyone. It is usually first experienced in childhood. However, sometimes, in addition to sore throat and fever, patients notice the appearance of a rash on the body. With what it can be connected?
Angina
The diagnosis of “angina” is often made by doctors, but it is not always true. Most often, this disease refers to inflammation of the tonsils with fever.
But these two symptoms usually correspond to acute tonsillitis, which is a companion to many bacterial and viral infections.
Domestic experts define sore throat as a highly contagious infectious disease. It is characterized by the following features:
- Fever.
- Intoxication.
- Damage to the lymphadenoid apparatus of the pharynx.
- Involvement of regional lymph nodes in the pathological process with the development of lymphadenitis.
Based on this definition, there are tonsillitis of the pharyngeal, lingual, palatine tonsils, larynx and epiglottis.
However, in medical practice, this disease is much more often understood as acute tonsillitis with severe fever and severe intoxication.
Sometimes this pathology is accompanied by a rash. Located on the skin, it is called exanthema, on the mucous membranes - enanthema. The reasons for this phenomenon are various.
A rash with a sore throat may be a symptom of complications, a side effect of medications, or indicate that the causative agent of the disease is an atypical bacterium.
The most common cause of tonsil damage is streptococcus. It leads to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms - sore throat, intoxication, fever, but never manifests itself as a rash.
A typical sore throat, as a rule, is quickly relieved with penicillin antibiotics or cephalosporins and, with adequate treatment, ends without complications.
The following diseases and reactions may be the cause of the rash:
- Allergic dermatitis.
- Infectious mononucleosis.
- Scarlet fever.
- Hand-foot-mouth syndrome.
Allergic dermatitis
Allergic, or toxic-allergic dermatitis is usually a reaction to the medications used. The second name for this complication is toxicoderma.
It is often observed while taking antibiotics. Sometimes toxic-allergic dermatitis is caused directly by the pathogen and its waste products.
There are also situations when it is impossible to accurately determine the cause of the rash.
With toxicoderma, these can be red spots (macules), compactions (papules) and even blisters. Sometimes the rash resembles hives or prickly heat.
In severe cases, its elements merge and rise above the skin level, covering large areas of the body.
One of the variants of toxic-allergic dermatitis is Lyell's syndrome. This is acute epidermolysis bullosa, a condition in which the skin practically peels off in large blisters.
Lyell's syndrome can develop from any, even the most harmless medicine. Its treatment is not easy, and this complication can be fatal. Fortunately, epidermolysis bullosa is extremely rare.
Most often, an allergic rash after a sore throat or during a maculopapular disease is accompanied by itching. It is not characterized by a certain staged pattern of rashes. It can be located either in a small area or cover most of the body, especially the stomach and back.
The main diagnostic criterion for allergic dermatitis is the disappearance of the rash after antihistamines or steroid hormones.
Hand-foot-mouth syndrome
Hand-foot-mouth syndrome is a disease caused by Coxsackie viruses (enteroviruses). It is extremely rare in adults; it usually affects young children.
A characteristic clinical symptom is the appearance of rashes in the area of the hands and feet. In this case, painful ulcers are found in the oral cavity - stomatitis.
This syndrome is characterized by the following manifestations:
Sore throat, like tonsillitis, is absent from the clinical picture of this pathology. However, discomfort in the mouth due to stomatitis can often be interpreted as a sore throat.
Previously, when identifying blisters in the throat area, pediatricians diagnosed herpangina. However, today the name “hand-foot-mouth” syndrome more accurately explains the essence and symptoms of the disease.
A sore throat with a rash on the body is a reason to see a doctor again. Perhaps the preliminary diagnosis was erroneous or therapy adjustment is required.
Causes and treatment of rash with sore throat
Among all infectious diseases in children, sore throat is considered the most common. The infection is unpredictable and can cause a lot of serious complications, even leading to death. Parents often complain of a rash with a sore throat. It can arise for many reasons of an exogenous and endogenous nature. But should you be afraid of such rashes?
For uncomplicated acute catarrhal tonsillitis, skin rashes are not at all typical. Typically, patients complain of a sore throat, general malaise, aching bones, and fever. However, there are many varieties of this disease, which can manifest as a specific rash.
Source: https://dou99.ru/syp/syp-pri-angine-u-rebenka-na-tele
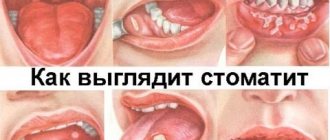
Herpetic stomatitis
Caused by the herpes simplex virus. At risk are children from one to five years old.
blisters of herpes stomatitis
The appearance of red blisters on the tonsils and palate is typical. In this case, similar rashes always appear on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, often on the lips. The disease is precisely stomatitis, so it does not occur without a rash in the mouth. And this distinguishes it from other pathologies that may have a similar picture of throat damage.
The only thing that can easily be confused with the appearance of dots during stomatitis is erythema multiforme. But erythema most often affects adults, and stomatitis most often affects children.
The disease can be severe, with a temperature rise of up to 40 degrees and signs of general intoxication. Or it may have a gradual course without a significant change in the patient’s well-being. Sometimes it becomes chronic.
Symptomatic therapy methods are usually used. In severe cases, antiviral agents are used.
Diseases that occur more often in children
In children, a red rash can occur for the same reasons as in adults, however, there are a number of specific pathologies that occur more often in children.
Causes
In children, red dots on the throat can be the result of the following diseases:
| Disease | Peculiarities | |
| Measles | The temperature rises sharply (sometimes up to 40 degrees), weakness occurs, the mucous membrane of the eyes becomes inflamed, sneezing, hoarseness, and photophobia appear. White rashes appear on the inside of the cheeks, which grow and spread to the mucous membrane of the throat, becoming red. Gradually they merge into a large spot | |
| Rubella | The rash most often appears on the skin, but the mucous membrane of the throat cannot be ruled out. The disease is accompanied by headaches. The tonsils increase in size and become loose. Small red dots appear on the back of the throat and palatine arches | |
| Chickenpox | Mostly a childhood disease, although sometimes it occurs in adults (in which case it occurs in a much more severe form). Almost every person under the age of 14 manages to get chickenpox. Although most people associate it with spots on the body, the same rashes also appear on the mucous membrane of the mouth. As a rule, the rash there is smaller in size. The blisters burst over time, in their place small ulcers of a yellowish or grayish tint form, the areas of the mucous membrane around them turn red |
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for measles. Patients are given expectorants and mucolytics - Bromhexine, Ambroxol, various syrups based on ivy extract.
If you have a headache and a high temperature, you should give Ibuprofen or Paracetamol.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for measles. Patients are given expectorants and mucolytics - Bromhexine, Ambroxol, various syrups based on ivy extract.
If you have a headache and a high temperature, you should give Ibuprofen or Paracetamol.
To gargle, you can use a solution of chlorhexidine (if the child already knows how to rinse the mouth), chamomile infusion - 1 tbsp. l. dried inflorescences per glass of boiling water. If the child is at risk of developing complications, including pneumonia, antibiotics and corticosteroids are indicated. There are WHO recommendations that you should give your baby vitamin A during treatment.
There is also no specific treatment for rubella. Only lowering the temperature with paracetamol and rinsing the mouth with antiseptic solutions are provided.
If you have chickenpox, you also need to gargle with an antiseptic composition. Some doctors advise taking blue or a 1% solution of brilliant green for this. The latter only if the child already knows how to rinse and spit out. Antibiotics are rarely prescribed, mainly when there is a threat of secondary infection.
Sometimes white dots appear on the throat, surrounded by reddened areas of the mucous membrane. This disease is caused by fungi of the genus Candida. In the absence of timely treatment, they can enter the lower parts of the respiratory system. To avoid this, antifungal agents (Nystatin) are used.
Allergic rashes
If isolated red spots appear in the throat of a child or an adult, and the general health remains virtually unchanged, then most likely it is an allergy.
allergic spots on the palate
Similar reactions can develop to food and toothpaste. They are often used for dental structures, for example, briquettes.
Red spots in the throat due to allergies can itch and cause soreness. Or they may not cause any concern.
In case of allergic diseases, the temperature in children and adults will not rise.
Treatment is elimination of the allergen and taking antihistamines: Suprastin, Tavegil, etc.
Common diseases
Viruses and bacteria, once in the body, actively multiply, releasing waste products that destroy tissue. Once in the pharynx, pathogenic microorganisms attach to the tissue of the ciliated epithelium, literally melting it. As a result, multiple hemorrhages form on its surface, resembling red dots in appearance.
There are common diseases that often affect not only children, but also adults. They are the ones who in most cases become the culprits for the appearance of rashes in the throat. These diseases include:
- herpetic sore throat;
- viral pemphigus;
- allergy;
- herpetic pharyngitis.
You can determine which disease caused the rash by looking at the characteristic symptoms. However, only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis after examination and additional examination.
Signs of herpetic sore throat
Herpetic sore throat is an acute infectious disease caused by Coxsackie viruses group A, B or echoviruses. This disease is characterized by an acute course, accompanied by a violation of the act of swallowing caused by inflammation of the pharyngeal formations. A distinctive feature of herpetic sore throat is the appearance of vesicles in the throat, which later turn into ulcers.
The main signs of herpetic sore throat are the following:
- red rash localized on the back of the throat and soft palate;
- increase in body temperature up to 410C;
- sore throat, sore throat;
- violation of the act of swallowing;
- runny nose;
- muscle aches, weakness.
The progression of the disease contributes to an increase in the size of the rash in diameter.
During the treatment process, special attention is paid to the patient’s diet. The food you eat should contain the maximum amount of vitamins. To prevent mechanical damage to the mucous membrane, hard, spicy, and too hot foods are excluded from the diet.
Signs of viral pemphigus
Viral pemphigus is an infectious disease. It develops under the influence of Coxsackie viruses and enteroviruses. When infected, the skin of the feet, hands, buttocks, mouth and throat becomes covered with blisters filled with clear liquid.
The disease develops gradually. First, the patient feels a slight malaise, then the body temperature rises. The first signs of the disease, manifested in the form of a characteristic rash, appear after a few days.
Viral pemphigus has a severe course. However, it does not pose a threat to the child's life. With proper treatment, after a week the signs of the disease completely disappear.
Signs of allergies
An allergic reaction is the most common cause of red spots in the throat. Children under 8 years of age are most susceptible to allergic diseases. The reason for this is insufficiently developed immunity.
A feature of an allergic reaction is the absence of pain, soreness, and itching in the throat. Patients do not experience any discomfort. Rashes are the only sign indicating a malfunction in the body.
The following factors can provoke the appearance of red dots in the throat area:
- toothpaste, rinses and other oral care products;
- all types of citrus fruits;
- cocoa products;
- volatile chemicals.
Allergies rarely cause discomfort. However, when it appears, the child should be prevented from coming into contact with the allergen. Otherwise, angioedema may develop, causing difficulty breathing and subsequent hypoxia.
To relieve allergy symptoms, antihistamines are used (Suprastin, Claritin, Zyrtec and others).
Signs of herpetic pharyngitis
Herpetic pharyngitis is an inflammatory process that occurs on the mucous membranes of the throat. Its causative agent is herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. Among all types of pharyngitis, this type of disease accounts for 5%.
Herpetic pharyngitis is characterized by the formation of painful vesicles in the throat, localized on the back wall of the pharynx and palatine arches. Lack of treatment can provoke the development of serious complications.
The occurrence of herpetic pharyngitis is facilitated by frequent colds that weaken the immune system. The main features are:
- inflammation of the mucous membranes, accompanied by itching and burning;
- red rash in throat;
- significant increase in body temperature;
- signs of intoxication;
- increased salivation;
- pain when swallowing.
The disease most often affects young children, which is due to an imperfect immune system, lack of vitamins and pharyngeal injuries. If treatment is not started in time, the vesicles merge with each other, forming large blisters and causing severe pain.
The disease is treated with antiviral drugs. Local remedies (ointments, gels, solutions, aerosols) that have a wound-healing effect help to reduce the manifestations of the disease and relieve pain.
Other causes of the problem
Sometimes, when independently examining the throat, people may notice red blood vessels on the tonsils and palate due to the influenza virus and ARVI. These pathologies are not characterized by specific throat rashes. But petechiae - pinpoint hemorrhages - can form. They often occur against the background of a strong dry cough, which injures the inflamed mucous membrane.
Sometimes the appearance of various red formations in the throat may indicate severe rare diseases:
- typhus;
- Kaposi's sarcoma;
- pyogenic granuloma;
- Kawasaki syndrome, etc.
Pharyngitis ↑
Another pathology in which bubbles appear on the walls of the pharynx. Often, with pharyngitis, even after recovery from the disease, bubbles on the back wall remain for several days or even a month. There are two types of pharyngitis: acute and chronic. Acute pharyngitis without proper treatment quickly becomes chronic. The main symptoms include:
- dry throat;
- soreness;
- pain when swallowing;
- the appearance of pimples and red spots in the throat;
- elevated temperature;
Pharyngitis - weakness and malaise.
Treatment of the disease consists of the use of anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antiseptic agents. Gargling with infusions of chamomile, sage, and calendula has a beneficial effect. Spraying the pharynx with antiseptic solutions, for example, stopangin, orasept, propolis, etc. Local antiseptics in the form of lozenges, strepsils, septolete, and faringosept are also widely used. Lozenges have low activity; they are used as an addition to the main therapy and for mild forms of pathology.
Scarlet fever
A rash with a sore throat can occur in a child due to scarlet fever. This is an acute infectious disease that occurs with fever, symptoms of intoxication, sore throat, and pinpoint rash against the background of general skin hyperemia. The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets, household contact, nutrition and through a third individual. There are typical and atypical forms of scarlet fever.
In the clinic, the prodromal period is either absent or does not last long. It begins acutely, the temperature rises to high levels, and there are severe symptoms of intoxication. If scarlet fever occurs against the background of a sore throat, then the child complains that his throat hurts and hurts, but worse. The tonsils are hyperemic, swollen, with or without pronounced purulent plaques.
Usually, on the first or second day of the disease, a simultaneous, pinpoint rash of a bright pink or red color appears in the child against the background of hyperemic skin, more often on the flexural and lateral surfaces. On the face, only the nasolabial triangle, Filatov’s triangle, remains free from rashes; the rash causes itching, and the submandibular lymph nodes become enlarged. On the second or third day, symptoms appear that will definitely tell you whether it’s just a sore throat or scarlet fever. The patient's tongue becomes a pronounced crimson color and a flaming pharynx appears, with pronounced white demography.
Sore throat and rash can occur for various reasons, but scarlet fever, in addition to severe clinical symptoms, can leave behind a number of complications:
- toxic myocarditis;
- glomerulonephritis;
- pneumonia;
- otitis;
- peritonsellar abscesses;
- sinusitis;
- pyoderma;
- chorea;
- arthritis;
- conjunctivitis.
After a thorough diagnosis, when treating scarlet fever, penicillin or erythromycin is prescribed orally for mild forms, and intravenously for severe forms. Antihistamines, antipyretics, sedatives and antiseptics are also used. There is no specific prophylaxis against scarlet fever.