A fistula on the gum is a pathological cavity in the soft tissues, formed as a result of a long-term, sluggish purulent inflammatory process in the area of the roots of the teeth. In medical practice, the problem occurs quite often, usually due to non-compliance with preventive measures and advanced dental diseases of an infectious nature. The capabilities of modern medicine make it possible to effectively eliminate the disease in various ways. Let us consider in detail the causes, features, symptoms, diagnosis, as well as methods of treatment of this pathology.
What is a dental fistula and what does it look like?
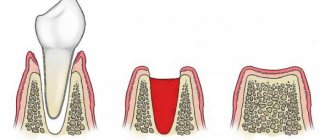
A dental fistula is a canal formed in the gum as a result of processes of decay and necrosis. Through this channel, pus comes out from the source of inflammation. Such a perforation channel is called a fistula - from the Latin “fistula”, which means tube. As a rule, the lesion is located in the deep layers of soft tissue (periodontium) and is adjacent to the root of the tooth.
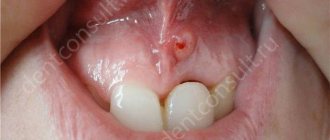
Externally, the fistula looks like a small formation with a rounded hole, the diameter of which is from 3 to 8-9 mm, depending on the severity of the disease and the duration of the inflammatory process directly at the site. The tissues surrounding the canal can also be inflamed, and in especially severe cases they are susceptible to necrosis (death).
What is a fistula on the gum?
Externally, the pathology looks like a convex edematous formation up to 1 cm in diameter with a white spot or hole in the middle. Its presence indicates an active process with a large amount of pus. There are 2 possible forms of dental fistula:
- External – the classic location of the fistula with access to the gum surface.
- Internal - the exiting end of the fistula tube does not reach the surface of the gum, forming a hidden process that cannot be detected by visual inspection. This option requires an x-ray examination.
The fistula itself is not dangerous - on the contrary, it releases purulent contents from the source of infection, thereby relieving internal pressure on the tissue and, accordingly, reducing the affected area. However, the presence of a fistula indicates a serious purulent process in the maxillofacial region, which is fraught with various complications. The most dangerous of them:
- loss of teeth in the area of inflammation;
- destruction of bone tissue and associated fragility of the jaw bones;
- infection of adjacent structures of the body - sinuses, ears, brain, lymph nodes;
- penetration of infection into the general bloodstream with the development of sepsis.
Symptoms of the disease
Fistula does not develop in a short time - it is a disease that occurs as a result of long-term exposure to pathogenic microorganisms on soft tissue. As a result, periodontal damage and necrosis gradually occurs, a perforating channel is formed, through which pus from the abscess comes out.
Symptoms of the inflammatory process can be noticeable much earlier than the formation of a fistula, however, if no measures are taken, a fistula tract gradually forms.
A number of signs indicate this disease:
- The most obvious manifestation is the periodic discharge of pus and blood from the opening of the fistula on the gum.
- In the area of the tooth located close to the canal, severe pain appears. The pain can become acute or aching in nature, and be of varying degrees of intensity.
- A characteristic unpleasant odor emanates from the oral cavity, which does not disappear after brushing the teeth, rinsing or using special products to freshen breath.
- The presence of a purulent abscess often provokes an increase in body temperature, above subfebrile. A sluggish inflammatory process is accompanied by a slight increase in body temperature - up to 37-38 degrees.
- The roots of the affected tooth become mobile, the surrounding tissues become red and swollen.
The formation of fistulas on the gums cannot be ignored , as it is accompanied by constant discomfort, pain and other unpleasant symptoms. Timely diagnosis, accurate identification and elimination of the causes of the disease, as well as highly effective therapy can restore the affected tissues and restore health to the patient.
Symptoms
All symptoms are classified by type:
Outer
Symptoms:
- Bad breath, even after proper oral care.
- Unpleasant constant taste and yellowish salivation, even after some time after eating.
- Changes in the structure of the gums - with the tongue you can feel the resulting hole or the thinnest partition behind which a void is felt if the suppuration moves into the periodontium or a hole in the tooth enamel if the suppuration moves towards it.
- Release of liquid with an unpleasant odor and taste when pressing on a sore spot.
Interior
Symptoms of an internal fistula are similar to those of other dental diseases, such as periodontal disease.
The symptoms of an internal fistula are quite varied: swelling of the gums; high temperature - in the evenings more than 38, and in the mornings not lower than 37.2 degrees, despite taking antipyretic drugs; headache; enlargement of the tooth and or gums, possibly the tongue; enlarged lymph nodes.
Depending on the type, a dental fistula is accompanied by redness on the gum, pain in the tooth if you press on it, and sometimes mobility of the tooth.
Causes of the disease
Fistulas on the gums do not develop on their own; they are formed as a result of complications of other dental problems and diseases of the oral cavity. Dentists identify several main reasons that provoke the development of a perforation channel or fistula:
- Chronic periodontitis can, under unfavorable conditions, lead to complications in the form of the formation of pathological fistulas. Patients suffering from granulomatous periodontitis are especially prone to the appearance of fistulas on the gums.
- Chronic periodontitis and periodontal disease increase the risk of developing fistulas as a result of the formation of purulent cysts and abscesses in the tissues adjacent to the tooth root.
- Advanced forms of caries in the third and fourth stages often provoke the development of pulpitis and the formation of purulent cysts in the periodontium. Lack of treatment for an abscess leads to gradual tissue decomposition, resulting in the formation of fistulas on the gums.
- Medical errors in the treatment of caries and the consequences of surgical intervention can also lead to the formation of fistula tracts.
- A fistula on the gum is formed as a result of chronic or acute osteomyelitis - purulent inflammation of bone tissue.
Additional factors contributing to the development of fistulas are: decreased immunity, hypothermia, systematic violation of the rules of hygienic care of teeth and oral cavity.
Causes of a fistula on the gum
The main reason for the formation of a fistula is the presence of an infectious process in the root of the tooth or in the periodontal space. Among the factors contributing to this, several provoking reasons can be identified. Basic:
- Deep caries with pulpitis , its untimely or improper treatment. Without proper therapy, this pathology quickly develops into periodontitis and periostitis with the formation of a purulent infiltrate.
- Chronic form of periodontitis - inflammation from the pulp chamber through the root canals penetrates beyond the apex with the formation of a periapical abscess. The pus affects the bone tissue, grows and, under pressure, forms a sinus tract (fistula) in the direction of least resistance.
- Periostitis (inflammation of the periosteum) – typical for severe periodontitis, complicated eruption of “eights”, injury.
- Chronic periodontitis - in this case, the infection enters the periodontal area not through a carious cavity, but through periodontal pockets. Pathogenic microorganisms destroy the dentogingival ligaments, and accumulations of pus form a periodontal abscess, in the projection of which a fistulous tract is formed.
- Perforations of the root wall - various abnormal holes in the tooth wall can appear as a result of poor-quality endodontic treatment, deep caries, destruction of hard tooth tissues, trauma, etc.
- Inflammation of a granuloma or dental cyst - the pathology can “sleep” for a long time without manifesting itself. All major troubles begin with a weakened immune system.
- Poor quality filling - especially if the filling is not installed hermetically, in violation of the technology, with the presence of pathological cavities in the root apex, etc. The probability of such an error in some clinics reaches 65%.
- Inflammation of tissues during severe eruption of wisdom teeth - develops when injured gum walls become infected with the formation of a purulent abscess.
- Poor fit of the crown or bridge prosthesis - the gap between the tissues and the prosthesis becomes a reservoir for bacterial infection.
- Tooth injuries (cracks and fractures) allow bacteria access to the pulp chamber.
- Oncological diseases in the jaw area, as well as treatment with radio irradiation and chemotherapy - in this case, fistulas can be multiple.
- Violation of the rules of asepsis and antisepsis during dental operations.
A number of additional factors enhance the influence of the main causes. Among them:
- pathologies of the immune system;
- poor oral hygiene;
- severe and constant stress;
- physical and mental overload;
- lack of nutrition, unbalanced diet with a deficiency of vitamins and minerals;
- abuse of sweet and high-carbon foods;
- smoking;
- some malocclusions.
On a note! In rare cases, a fistula may result from an error during implant installation. Poor design, unaccounted for allergies, untreated infections, and poor sanitation can cause pathology.
Diagnostic methods
If symptoms characterizing the development of fistulas on the gums appear, you must immediately contact your dentist for further diagnosis and treatment. Modern methods make it possible to accurately identify the disease in one go, identify its causes and develop a plan of therapeutic measures.
Diagnosis of the problem occurs in several stages:
- The first stage of diagnosis to identify a fistula on the gum is a visual examination by a doctor of the oral cavity .
- Dental tomography is an examination of the dentition using special equipment based on X-rays. This is a modern scientific achievement that opens up the possibility of more accurate diagnosis of fistulas on the gums, their localization, features of cysts and abscesses. Not in all cases, doctors resort to tomography in diagnosis, but in complicated forms of the disease and polycystic disease, this method is the most informative.
- In some cases, a biopsy is indicated . The purulent cyst is punctured, and the doctor takes a small amount of cystic fluid to analyze, exclude or confirm the malignant nature of the formation.
To diagnose other diseases that are indirectly related to the development of fistula tracts, additional examination may be necessary.
Types of disease
It goes without saying that such a complex disease has a number of varieties caused by various factors, from the growth of wisdom teeth to operations performed in a dental clinic.
The following types are worth highlighting:
- Fistula after tooth extraction - the process of resection (removal) of a problematic tooth can cause a fistula due to the processes of suppuration in the sinuses, gum tissue or jaw. It’s worth noting right away that it doesn’t occur too often. A fistula may be a consequence of infection during the operation itself. Also, the place where the tooth was removed has little resistance to the formation of a fistula from foci of inflammation located under other teeth located nearby.
- A serious complication after the removal of teeth in the upper jaw can be the appearance of a fistula from the diseased area in the mouth to the maxillary sinuses, resulting in inflammation of the latter.
- A cyst formed at the root of a tooth, which is suppuration in the form of a capsule, and it also needs to find a way out through a fistula, although this does not always happen. Then, surgical intervention and opening of the inflamed area is necessary. As a rule, the disease manifests itself in the form of gum outflow of impressive size. The same applies to such a disease as granuloma. Interestingly, the latter is treated by creating an “artificial” fistula, that is, piercing it, allowing the fluid to come out.
- A fistula under the crown is quite common. After complex and frequent procedures for installing crowns, the formation of a fistula is quite likely; it occurs as a result of non-healing of the dental canals, which leads to their subsequent inflammation. The situation is very complicated by the fact that the person already has crowns installed, and they have to be removed to completely treat the problem area. In addition, it is necessary to take an x-ray, because otherwise it is extremely difficult to diagnose this type of fistula in the mouth.
- Fistula after dental implantation - as in the case of a crown, a fistula after implantation occurs as a result of improper cleaning of the place where the implant is installed or its incorrect installation. In this case, the affected area requires an x-ray and a course of treatment, which is complicated by the presence of an already installed implant.
Read also: Curettage of periodontal pockets
Photo and X-ray
In fact, all fistulas are purulent in nature and look like in this photo.
Therapeutic methods
To determine how to treat a gum fistula, the dentist determines the patient’s condition at the diagnostic stage and selects appropriate therapeutic methods on an individual basis. Treatment can be endodontic, surgical and conservative . However, in dental practice, as a rule, these three types of therapeutic measures are combined.
In most cases, without opening the purulent sac, it is not possible to solve the problem of gum fistula, and without medication support and rehabilitation procedures, it will not be possible to eliminate the causative agent of the infection and restore the affected area. Let's look at the features of these types of treatment.
Endodontic measures
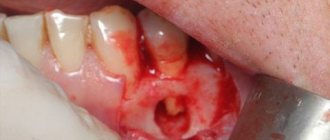
After diagnosis and administration of an anesthetic drug, the dentist eliminates the cause of the perforation channel - an abscess. To do this, complete cleansing of dental tissues affected by caries, removal of necrotic pulp and the contents of a purulent cyst.
In some cases, to cure a fistula on the gum, tooth extraction is indicated . After all the manipulations, the doctor treats the root canals with antiseptic solutions and leaves them for further treatment.
Conservative methods
After cleaning the root canals, the patient is advised to take antibiotics to eliminate the infection, as well as the use of local antiseptic and anti-inflammatory agents, and rinsing the mouth. Having eliminated the inflammation and saved the tooth, the dentist installs a filling and prescribes rehabilitation procedures - laser and ultrasound treatment of fistula tracts, ozone therapy, vitamins for recovery, ointments and gels for healing.
Surgical intervention
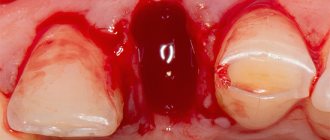
In case of serious periodontal damage, inflammatory process affecting bone tissue or polycystic disease, surgical intervention is indicated. After diagnostic procedures and preliminary preparatory measures, tissue resection, cyst cleaning, removal of formed granulation, treatment with antiseptic agents and suturing are performed.
During the rehabilitation period, treatment in a hospital department of maxillofacial surgery, antibiotics and local treatment of the postoperative wound are indicated. After the stitches are removed and the course of antibiotics is completed, the doctor decides on further conservative treatment of the patient .
How to cure a tooth fistula
Therapy is aimed at relieving inflammation and preventing its recurrence.
The ways in which this will be achieved depends on the stage of the pathology and the factors that provoked it. Treatment always begins with an examination. The doctor examines the purulent lesion and determines what caused it. X-ray diagnostics can be used for this.
If it turns out that the fistula has formed recently and the necrotic masses have not yet spread greatly, it is opened. The root canals are washed and cleaned. When the pain subsides, the swelling subsides, and pus stops secreting, a temporary filling is installed. Then wait for one to two weeks to see if an exacerbation occurs. If everything is in order, the regeneration processes proceed at a rapid pace and permanent filling is carried out.
If the disease is very advanced, the tooth has become loose and it is not possible to save it, its emergency removal is carried out. Doctors today resort to this method in extreme cases - they usually manage to reverse the inflammatory reactions and strengthen the movable unit.
After acute symptoms are relieved, the client is always prescribed therapeutic rinses with wound-healing and antiseptic agents, and undergoes physiotherapy. In parallel with liquid solutions, antibacterial gels and ointments are often used. At the dentist's discretion, the patient may also be prescribed oral antibiotics and antivirals.
Folk remedies
In dental practice, when treating any disease, folk remedies can only be used in addition to drug therapy. Moreover, traditional medicine is not effective in eliminating dental fistula. Traditional medicine can enhance the effectiveness of medications and procedures, help eliminate symptoms and speed up recovery during the rehabilitation period.
In folk medicine, the antiseptic properties of chamomile flower infusions are often used. Prepare an antibacterial infusion for mouth rinsing. Calendula and oak bark have similar properties. For rapid healing and regeneration of affected tissues, aloe vera juice is used.
use additional folk remedies to improve your condition and eliminate symptoms only in consultation with your doctor . In folk medicine, there are often recommendations that contradict science and can only aggravate the situation. Traditional methods cannot replace effective endodontic therapy and surgery.
Under no circumstances should you try to open an abscess yourself - if you do it incorrectly, healthy tissues will become infected. Pathogenic microorganisms, having penetrated the blood, can provoke sepsis, which puts a person’s life in danger.
How to treat?
Before choosing one or another method of treating a dental fistula, like any other disease, the dentist conducts a diagnosis. To detect externally, a visual inspection is sufficient.
For internal diagnostics, a dental x-ray is needed. An X-ray is performed in any case, since a fistula may be a consequence of a concomitant disease.
In this case, the main attention is paid to treating the disease, then the main source of infection is removed, and treatment of the pus exit channel is either carried out in parallel with the main treatment, or is treated after eliminating another disease, or only the fistula as the main ailment is eliminated.
Methods
The method (method) depends on the type of effect on the fistula:
- Medication - carried out at the early stage of suppuration, or when, due to the large depth of the formation, it is not possible to use other methods. The medicinal method is the main one. It is used as the only method of treatment or in combination with other methods, because only antiseptic drugs can completely destroy harmful microorganisms in the source of suppuration. The choice of drug is made by the attending physician depending on the effectiveness against microorganisms of a given class, the patient’s individual tolerance, and other factors.
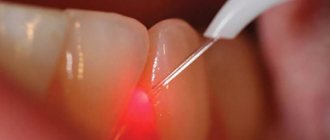
- Laser and ultrasound therapy. This method is used for external fistula after undergoing drug therapy. The main task is to cauterize the dentin before filling.
- Surgical intervention - at an advanced stage, when a cyst (benign solid formation) or granuloma (purulent bladder) has formed at the site of the main suppuration, the breakthrough of which can develop into a gingival fistula.
- Tooth extraction – if it is impossible to carry out the operation without complications or in order to save money for the patient at his request.
If a fistula is found in a child, it is better to remove this tooth. Firstly, baby teeth fly out sooner or later; secondly, there is a risk of pus getting into the stomach or soft tissues, and these are additional complications, and pain negatively affects the child’s psyche.
Prognosis for recovery
A fistula on the gum is not a fatal disease. Provided timely diagnosis and selection of an effective complex of drug and endodontic therapy, the prognosis is favorable - recovery and complete recovery occurs quickly , its duration depends on the individual characteristics of the body and the patient’s health status.
In advanced cases, rehabilitation may take longer. The possibility of losing the affected tooth cannot be ruled out. Despite this, timely and properly selected therapy ensures complete recovery in almost all cases.
The only situation when doctors cannot guarantee a favorable outcome is the degeneration of a purulent cyst into a malignant tumor. But even in this situation, timely measures taken - surgical intervention and conservative treatment - provide a high chance of recovery.
The mortality rate from malignant tumors of this type today is no more than 10%.
How to get rid of a fistula surgically
Surgical removal of a fistula on the gum is carried out if the pathology is not amenable to therapeutic intervention or has become threatening. The operation is indicated in the following situations:
- the presence of a crown, a pin, the impossibility of opening or removing them under normal conditions,
- degeneration of the periosteum and bone tissue of the jaw,
- involvement of a large volume of soft tissue in the inflammatory process.
The surgical method of treatment consists of opening the abscess through an incision in the gum. After cleaning and antiseptic treatment of the affected area, the edges of the wound are connected with sutures. If necessary, a drainage is placed to allow the remaining pus to drain. Antibacterial drugs and symptomatic therapy (painkillers, anti-inflammatory, antihistamines and other drugs) must be prescribed.
Prevention
Dental fistula is a disease that can be easily prevented by following preventive rules and providing proper oral care. To do this you need:
- Regularly take care of maintaining proper oral hygiene. Brush your teeth twice a day with a properly selected toothpaste and brush, periodically remove tartar deposits, and use dental floss.
- Get preventative dental checkups every 6 months. This will allow pathologies to be identified at an early stage.
- Treat caries and other oral problems in a timely manner.
- Take care of a nutritious, balanced diet and exclude harmful foods and drinks.
- Lead a healthy lifestyle, stop smoking.
The condition of the teeth and oral cavity affects the functioning of other organs and systems. If there is a focus of infection in the mouth and pathogenic microorganisms spread, other dangerous diseases may develop. Therefore, you should not postpone the treatment of dental diseases - this is important for the health of the whole body, especially the digestive system. Treatment started in the initial stages of the development of any dental disease almost always gives positive results and takes less time.
Treatment options
It is worth immediately noting that the treatment of a fistula on the gums is a rather complex process and requires an integrated approach, consultation with a dentist and his intervention.
The dentist can open the problem area, place a drain there to drain pus, etc. If installed crowns, fillings, implants, etc. interfere with treatment, the doctor can remove them.
Antibiotics
As already noted, treatment of a fistula with antibiotics is an auxiliary measure; dental operations are considered the main ones.
However, a properly selected course of antibiotics can effectively contribute to the treatment process. In this case, antibiotics can be taken either in tablet form or by injection.
Traditional methods
This method can be used to limit the spread of infection and relieve pain in the affected area, however, traditional methods should be used only after consultation with a doctor and in parallel with the measures prescribed by him.
Since there are many herbs in nature whose effects are comparable to those of antibiotics, it is appropriate to use them in this case.
- In this case, decoctions of eucalyptus, millennial, and calendula are excellent. They need to rinse your mouth in the affected area several times a day for 4-5 minutes;
- To disinfect the area with a fistula on the gum, you can rinse your mouth with propolis tincture in alcohol. To do this, pour 25-30 drops of tincture into 150 grams of boiled water.
Fistula during pregnancy
While expecting a baby, women are susceptible to various infections and diseases, as hormonal changes and changes occur in their bodies. A decrease in immune defense can lead to exacerbation of chronic diseases. In addition to such reasons, a fistula on the gums during pregnancy can occur after incorrect dental treatment, in the presence of a cyst, or dental diseases.
In order not to expose a pregnant woman to additional stress, the dentist chooses a special treatment tactic. A full course must include drug therapy, including the use of antibiotics, so doctors often postpone treatment until after the baby is born.
In an acute situation in the oral cavity, when a purulent fistula appears on the gum, doctors provide the necessary first aid: open the diseased tooth, clean the root canals, carry out massive antiseptic treatment, and allow the pus to drain out. And then they prescribe treatment at home: rinses, mouth baths to eliminate the infection.