What is a fistula?
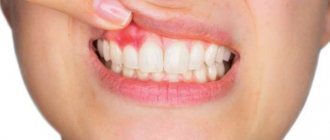
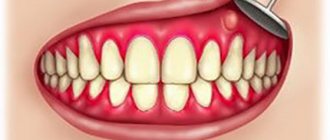
A fistula is a small purulent lump with a hole. Most often this is a symptom of some disease, therefore it is often accompanied by an increase in body temperature, acute pain and the appearance of an unpleasant odor from the mouth. If such conditions develop, it is better to seek help from a specialist as soon as possible. To understand what a fistula looks like, just look at the photo below.
The photo shows a fistula on the gum of a child
In some cases, to determine the cause of this phenomenon, it is necessary to take into account the age of the child:
- up to 2 years: the formation of a fistula at this age may indicate the presence of congenital pathologies of the dentition,
- from 2 to 3 years: a purulent tubercle on the gum often becomes a symptom of osteomyelitis,
- from 3 to 4-5 years: the cause may be inflammation of the maxillary sinuses,
- from 5 to 6 years: at this age, a fistula often results from injury to the gums. In addition, at 6-7 years of age, this phenomenon can be triggered by inflammatory processes occurring in the body1.
Forecast
The prognosis for parotid fistula is generally favorable. Its infection is stopped without difficulty, and after surgery there is a complete recovery.
The prognosis may worsen if complications occur and are advanced.
Kovtonyuk Oksana Vladimirovna, medical observer, surgeon, consultant doctor
3, total, today
( 51 votes, average: 4.92 out of 5)
How to treat colds during pregnancy: rules of treatment in each trimester
Sensorineural hearing loss
Related Posts
Possible causes of the problem
The cause of a fistula is usually a pathological process. To understand why a child has a tubercle above a tooth, you should pay attention to the accompanying symptoms, which may indicate the following conditions:
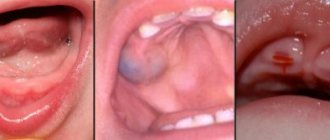
- granulating periodontitis: one of the most common causes of fistula in childhood. This disease often becomes a complication of advanced caries. Inflammatory processes in the periodontium - the tissues surrounding the tooth root - are accompanied by the proliferation of granulation connective tissue. Most often, this form occurs in children. The catalyst becomes one of the external factors: hypothermia, severe fatigue and viral diseases,
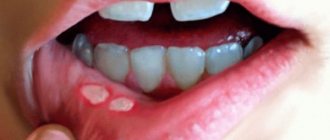
The photo shows periodontitis in a child - osteomyelitis: inflammatory processes in the jaw bone are infectious in nature and usually occur against the background of certain dental diseases. A child's fragile immune system allows the disease to spread quite quickly. The child develops a fever, and in some cases it is necessary to resort to hospital treatment,
- cyst: a kind of capsule with liquid that occurs as a result of certain disturbances in the development of teeth or due to untimely treatment of dental diseases. If appropriate measures are not taken in time, the cyst will develop into a fistula,
- sinusitis: inflammation of the maxillary sinuses is accompanied not only by the formation of fistulas, but also by nasal congestion, headaches and general weakness of the body,
- tooth retention: difficulties in teething can also provoke the appearance of a purulent tubercle on the gum. A phenomenon such as retention may be associated with abnormalities in the structure of the gums or too early loss of baby teeth. In such situations, a cyst with an infected membrane is formed, which gradually develops into a fistula,
Formation of a tubercle on the gum during teething - trauma to the tissues of the oral cavity: damage to the mucous membrane and teeth from sharp objects and too hard foods, injury due to a blow or fall,
- medical errors: incompletely sealed canals leave room for the rapid proliferation of bacteria. In addition, a fistula can appear due to an incorrectly installed filling or careless injury to soft tissues during a dental procedure.
Features of symptoms
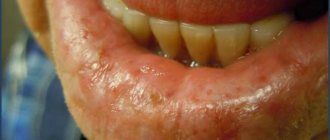
A fistula on the gum is always visible to the naked eye. In this case, a tubercle can appear both on the outer and inner side of the gum. Sometimes a white head is visible at the top, which stands out noticeably against the background of the surrounding tissues. According to reviews from parents and doctors, other symptoms include the following:
- painful sensations in the tooth, which only intensify when pressing on it or while eating,
- swelling and redness of soft tissues,
- bad breath,
- loose tooth,
- discharge of purulent masses when pressed,
- increase in temperature in advanced stages.
Loose teeth are a possible sign of disease
Effective treatments
According to experts in the field of pediatric dentistry, during diagnosis, the doctor must take into account that the fistula has similar external signs with other phenomena that differ in the reasons for their appearance and course. We are talking about cysts and wen - seals that consist of adipose tissue. It is also important to determine the localization of inflammatory processes, so treatment, as a rule, begins with an X-ray examination. Having complete information about the clinical picture in hand, the doctor decides how to treat the fistula and chooses the appropriate method:
- therapeutic treatment: eliminating the source of the problem, that is, treating the causative disease, or correcting mistakes made by the doctor. So, for example, if a tubercle on the gum appears as a result of an incorrectly installed filling, the specialist will remove it, open the canals, remove necrotic tissue and remove pus, after which he will disinfect and place a new filling,
“My son and I had a similar problem. A fistula appeared, and the filling was the cause! As it turned out, the doctor did not completely seal the canals, but we already found this out when the child began to cry in pain and had to run to the duty room. They removed the filling, removed the pus, and cleaned everything out. I couldn’t imagine that a mistake in such a routine procedure could lead to such consequences.”
Galina, Moscow, fragment of message from correspondence on the forum
- surgical method: involves the removal of the causative tooth - this is a mandatory procedure when it comes to baby teeth. If this is not done, the granulation tissue will continue to grow and the pus may spread to the permanent tooth bud. The result is caries and other, more serious consequences that can affect the condition of the gum tissue and jawbone. For extensive lesions, removal of the overgrown tissue may be necessary. Today, this procedure is carried out using modern laser equipment, which allows you to quickly and painlessly remove damaged areas,
- drug therapy: prescribing antibiotics and antihistamines. The doctor may also prescribe gels and ointments with anti-inflammatory effects, and rinses with special antiseptic solutions.
Removal of the causative tooth in the treatment of a fistula on the gums of a child
Diagnostics
To determine a fistula in a newborn and clarify the type of pathology, examination and palpation are not enough. Hardware research is required:
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
- Ultrasonography of the anterior peritoneal wall to examine the umbilical cord.
- Channel sounding. If the rod goes deeper than 2 cm, the diagnosis is definitely confirmed.
- X-ray using a contrast agent, or fistulography. The picture helps to clarify the type of fistula (complete, incomplete).
- Injection into the umbilical hole of a contrast agent - indigo carmine solution. If the drug is detected in the urine and bladder, a diagnosis of vesico-umbilical fistula is made.
Modern methods for studying developmental anomalies in newborns make it possible to obtain results in a few hours.
What can you do at home?
Many parents are concerned about whether it is possible to cure a fistula on their own and what to do if a suspicious lump appears on the child’s gum. It should be understood that any traditional medicine methods can only be used with the permission of a professional specialist. They usually act as additional measures to reduce inflammation, but the main treatment should be carried out under the supervision of a physician.
Important! If a child develops any neoplasm on the soft tissues of the oral cavity, you should immediately consult a dentist. Only a doctor can advise what to rinse your mouth with and what medicinal decoctions and infusions can be used in this case.
Chamomile decoction for treatment
Among the most popular remedies that can be prepared at home are decoctions of St. John's wort, calendula flowers and strawberry leaves. Infusions of chamomile, oak bark and sage have proven themselves to be quite good. You can also prepare an ointment from crushed medicinal herbs and sea buckthorn oil. All this really helps relieve inflammation, but the use of such drugs must be agreed upon with a doctor.
Traditional medicine
It is impossible to treat fistulas on a child’s gums only with folk remedies. But such recipes can be a good addition to traditional methods. Traditional medicine should not be used in infants and children under 2 years of age.
- A good mouth rinse is chamomile infusion. Its flowers (about a tablespoon) are poured with boiling water and infused for at least two hours. After filtering through several layers of gauze, you can rinse your mouth with the infusion after each meal. To enhance the effect, you can add calendula to chamomile flowers.
- Grind 3 small leaves of Kalanchoe and aloe in a meat grinder, add a clove of garlic. Wrap the resulting pulp in several layers of sterile gauze and apply to the sore spot for 7-10 minutes.
- Dissolve a level teaspoon of baking soda in a glass of heated boiled water and rinse your mouth with this product 3-4 times a day. You can enhance the effect of the solution with iodine - just add a few drops.
Potential Complications
If the problem is not detected in time and appropriate measures are not taken to resolve it, a fistula can lead to serious complications:
- penetration of pus into the digestive tract, which can provoke inflammatory processes in the internal organs,
- gradual destruction of soft tissues and, as a consequence, the development of purulent sinusitis, if we are talking about a fistula in the area of the maxillary sinuses,
- periostitis (flux) – appears when inflammation spreads to the periosteum of the tooth.
To avoid such an unpleasant phenomenon as a fistula, parents need to be extremely attentive to the health of the child’s teeth and teach him or her oral hygiene from early childhood. It is also necessary to regularly visit the dentist for preventive examinations and take care of a properly balanced diet.
- Maksimovsky Yu.M. Endodontics and preservation of tooth function, 2001.