Your gums are swollen, it hurts to chew, your temperature has risen, but you still hope that it will go away on its own? You are most likely experiencing symptoms of a periodontal abscess, which is a medical emergency. The Renaissance Dent network of clinics provides services for therapeutic and surgical treatment of patients with periodontal diseases.
A periodontal abscess is a limited focus of purulent inflammation localized in the tissues surrounding the tooth.
Causes
The main cause of periodontal abscess is infection in the gum pockets, resulting in the development of purulent inflammation of the soft tissues around the tooth.
The following factors contribute to the appearance of periodontal abscess:
- Gum diseases: gingivitis, periodontitis, periodontal disease.
- Injury to the soft tissue around the tooth by hard food or a crown.
- A foreign body gets into the gum pocket (the space between the tooth and gum): a piece of food, bristles from a toothbrush.
- Tooth diseases: caries, pulpitis.
Prevention and prognosis
To avoid the appearance of periodontal abscess, it is necessary to adhere to simple general rules of prevention:
- giving up addictions;
- balanced diet;
- avoiding gum injuries;
- timely identification and treatment of any anomalies that may lead to the formation of an abscess;
- compliance with the clinician’s recommendations after tooth extraction;
- adequate selection of dentures;
- regular visits to the dentist.
In cases of timely seeking qualified help and implementing complex therapy, the prognosis will be favorable: the pathological process can be completely stopped or long-term remission can be achieved.
However, an abscess has serious consequences - irreversible destruction of bone tissue and a high probability of relapse or exacerbation.
Types and symptoms of periodontal abscess
According to the flow, two types of periodontal abscesses are distinguished:
- Acute, which is characterized by vivid clinical manifestations in the form of severe pain, swelling of soft tissues, and the appearance of a formation filled with pus on the gum. The development of an abscess is combined with general malaise and fever.
- With chronic (cold) abscesses, the symptoms are erased: only bleeding and soreness of the gums are observed. Gradually, the roots of the teeth are exposed, the gum pockets are filled with pus and granulations. Chronic periodontal abscesses periodically worsen, especially against the background of decreased immunity after illness.
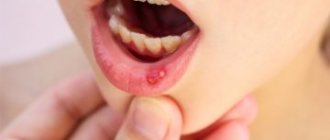
A gum abscess begins with the appearance of a swelling that is painful when pressed. The tumor gradually increases, chewing movements cause severe pain. Often pus seeps out from the gap between the tooth and gum. Pathological mobility of teeth appears. The patient’s general well-being worsens: loss of appetite, sleep disturbance, headaches, fever.
The main causes of gum abscess
The main reason is the presence of an infection that affects the soft tissue of the gums and the periodontal pocket (the area between the root of the tooth and the gum itself). If no action is taken, the infection spreads throughout the body, affecting organs and systems.
The following pathologies of teeth and gums can provoke the development of infection:
- gingivitis;
- periodontal disease;
- periodontitis;
- deep caries.
Also reasons may be:
- incorrect installation of prosthetic systems or implants;
- mechanical injuries;
- chemical or thermal burns;
- unprofessional installation of braces;
- imperfect filling.
With an abscess on the gum, the inflammatory process develops in the periodontal pocket against the background of the active proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. At the site of inflammation, dead tissue accumulates in the form of pus, forming a serious abscess, which is accompanied by acute symptoms.
First aid
- Before visiting the dentist, you can take painkillers to reduce pain: Paracetamol, Nurofen.
- It is recommended to rinse the mouth with antiseptic solutions: furatsilin, potassium permanganate.
- It is forbidden to squeeze out the abscess, as well as use any thermal procedures in the area of the abscess: compresses, heating pads, as this can lead to the spread of the purulent process.
- In case of intoxication (fever, headache), it is necessary to increase the drinking regime to 2.5–3 liters per day.
Symptoms of gum abscess
- a painful tubercle on the gum, which upon palpation causes pain and discomfort;
- increased pain during chewing;
- loosening of one or a number of teeth;
- discharge of pus;
- unpleasant taste in the mouth;
- smell from the mouth;
- weakness;
- elevated temperature;
- swelling of the cheek;
- sleep disturbance;
- lack of appetite;
- headaches and dizziness.
In the acute period, all signs of intoxication of the body are observed. When a purulent sac spontaneously ruptures near the gingival margin, a fistula is formed, through which purulent exudate is evacuated. Pus flows into the oral cavity, the pain becomes less. The wound can heal without medication, but in this case there is a high risk of infection of the tissues surrounding the lesion.
Treatment
The diagnosis of periodontal abscess is made based on the patient’s complaints, characteristic clinical picture and examination data. The abscess is not visible on an x-ray, but x-rays are performed to assess the condition of the bone tissue at the site of inflammation and the quality of root canal filling.
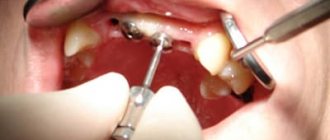
Surgical treatment consists of opening the periodontal abscess to ensure good drainage of purulent exudate.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
An incision is made in the gum mucosa at the site of the lesion, the cavity is cleared of pus, washed with antiseptics, and drainage is installed if necessary.
Antibacterial agents are prescribed for the entire postoperative period.
A periodontal abscess, the treatment of which must continue after the acute period, sometimes leaves behind deep gum pockets that require periodic rinsing with antiseptics in the dental office.
Classification. Photo. ICD-10 code
Periodontal and periodontal abscesses are divided into acute and chronic forms according to their course.
| Abscess shape | Characteristic |
| Spicy | The symptoms are clearly expressed. There is an active release of blood and purulent exudate through the hyperemic gums. Pathological mobility is noted. My health deteriorates sharply. |
| Chronic | The periodontal tissue is swollen. Bleeding gums are noted. Purulent blisters either grow or disappear. Purulent discharge accumulates inside deep gum pockets. With colds, the chronic form of the abscess becomes acute. |
Periodontal and periodontal abscess can be either single or multiple. By localization: on the papillary-marginal region of the periodontium, alveolar process, on the floor of the oral cavity.
According to the international classification of dental diseases, purulent lesions of periodontal and periodontal tissue are coded under the following indices:
- K05.2 “Acute periodontitis” (periodontal abscess);
- K04.4 “Acute apical periodontitis”;
- K04.5 “Chronic apical periodontitis” (periodontal abscess).
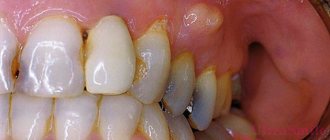
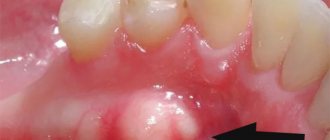
The photo below shows a hyperemic abscess, which is a typical sign of a periodontal abscess.
Prevention
- Thorough dental hygiene: brushing your teeth in the morning and evening, rinsing your mouth after every meal, using various devices: dental floss, brushes. If there are dentures in the mouth, it is recommended to clean them of food debris using an irrigator - a special device that supplies water under pressure.
- Timely treatment of diseases of teeth and gums.
- Preventative dental examinations are necessary at least 2 times a year to assess the condition of the teeth and oral cavity. If there is hard dental plaque, use hardware teeth cleaning.
Diagnostics
A periodontal abscess can be diagnosed by a general dentist or periodontist. In addition to prescribing laboratory tests and instrumental examinations, the clinician must independently perform several manipulations.
Thus, primary diagnosis includes:
- studying the medical history - to look for an acute or chronic pathological process that could lead to the formation of an abscess on the gums of a child or adult;
- collection and analysis of life history;
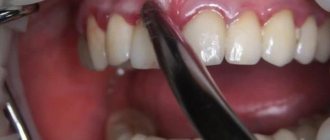
- palpation of the problem area of the gum;
- assessment of the condition of teeth and their mobility;
- detailed survey - to establish the first appearance and severity of clinical signs.
Laboratory tests for diagnosis are represented by the following analyses:
- general clinical blood test;
- blood biochemistry;
- PCR tests;
- cytological study of purulent fluid;
- examination of saliva using chemiluminescence.
Among the instrumental procedures are:
- dental radiography;
- orthopantomography;
- CT.
Orthopantomography
Periodontal abscess must be differentiated from the following pathologies:
- acute course or exacerbation of chronic periodontitis;
- suppuration of the jaw cyst;
- periostitis;
- osteomyelitis.
In addition, consultation with a dental surgeon may be required.
Cost of treating periodontal abscess
Prices for the treatment of periodontal abscess in branches of the Renaissance Dent clinic depend on the volume of pathology and the severity of the disease and the chosen technique. The sooner the patient addresses his problem, the cheaper the treatment will cost him. In any case, the patient will receive highly professional care, which will protect him from dangerous complications.
More detailed information about the prices and list of services for surgical periodontology at Renaissance Dent can be found in the price list on the official website of the clinic or by calling 242-10-20, daily from 9.00-21.00.
Gum treatment
The abscess on the gum must be removed by a dentist. Periodontal abscess, deeper dental abscess and any form of purulent inflammation lead to the need to open the gums. By getting down to business at the very beginning of gum suppuration, you can fight it conservatively.
Removing a periodontal abscess at home is impossible. Surgical removal of periodontal abscess is performed under local anesthesia.
An acute case of dental abscess requires immediate attention to the dentist. However, before visiting a doctor, the patient should be given first aid. Cold will help relieve pain. You should rinse your mouth with a warm solution of Furacilin, Chlorhexedine or herbal decoctions. Food should be liquid and warm. After cleaning a periodontal abscess, it is important to take good care of your mouth to prevent infection.
At the dentist
Gum abscess is treated surgically. The abscess on the gum is opened, clearing the cavity of pus. Only a doctor will determine whether it is time to open an abscess on the gum, whether it is ripe. Premature opening of a periodontal abscess can easily cause harm and will lead to relapse. If purulent inflammation that has arisen in the pulp does not allow saving the tooth, it is removed.
Therapeutic treatment consisting of taking antibiotics and rinsing the mouth with antiseptics in the form of warm solutions is also used to combat periodontal inflammation. Afterwards, restorative treatment is prescribed. It is possible to use electrophoresis with enzymes or antibiotics, darsonval.
Traditional ways to draw out pus
It is not recommended to treat a purulent abscess on your own. However, if it is not possible to visit a doctor, you can draw out the pus using one of the folk remedies:
- Clove oil – a few drops of oil are dripped onto a cotton ball and applied to the area that has festered for half an hour. Then rinse your mouth with warm water. Repeat the procedure 3 – 5 times a day.
- Salt is an effective remedy, found in every home. A teaspoon of salt is diluted in a glass of warm water, the solution is taken into the mouth and held for 30-40 seconds, then spat out. Repeat the procedure 2–3 times, up to 3–5 times a day. The same remedy will help protect it from infection after tooth extraction or opening of the gum (we recommend reading: hole in the gum after tooth extraction: photos and ways to speed up healing).
- For gum abscess, rinse your mouth with a warm herbal decoction. Take chamomile, sage, thyme, calendula and arnica in equal parts, pour 1 teaspoon into a glass of cold water, bring to a boil, leave for 20 minutes. The broth is filtered and used for rinsing. It is also suitable for making compresses.
Possible complications of an abscess on the gum
They are often associated with the lack of any therapeutic effect. In principle, all abscesses that occur in the maxillofacial area can be successfully treated. But prolonged ignoring reduces the chances of this.
Complication of an abscess in the form of phlegmon
Table. The most common complications of an abscess on the gums:
| No. P/P | Type of complication | Main symptoms | Medical prognosis |
| 1. | Fistula tract | Against the background of hyperemic and swollen gums, a red or white spot is found, sharply different from the surrounding tissues. With early appearance, the release of serous or purulent exudate is observed. | In 50% of cases, when a fistula appears, the tooth must be removed. |
| 2. | Tooth loss | Tooth mobility is 2-3 degrees, more than 1/3 of the roots are exposed. | Only orthopedic restoration of the dentition. |
| 3. | Brain abscess | Persistent high body temperature, severe headaches, nasal congestion, tinnitus, diplopia, confusion, loss of coordination. | Formation of a coma, death, disability. |
| 4. | Sinusitis | It is possible to develop sinusitis if the tips of the roots are located directly in the air sinus. It manifests itself as severe nasal congestion, suppuration from the nose, and pain mainly in the frontal area of the face. | The causative tooth has to be removed. The cure rate for sinusitis is on average 70%; in other cases, a chronic form of the disease develops. |
| 5. | Ludwig's tonsillitis | Spread of the infectious focus to the upper respiratory tract, signs of suffocation, cyanosis of the skin of the face. It occurs more often in middle-aged people. | If left untreated, blockage of the upper respiratory tract will result in death. |
| 6. | Osteomyelitis | Severe deformation of the jaw bone, high body temperature, general weakness, malaise, headache, difficulty eating, severe pain in the maxillofacial area. |
Periodontal and periodontal abscesses: treatment in dentistry and at home
Periodontal and periodontal abscesses are serious dental diseases that represent the accumulation and release of purulent contents onto the mucous tissues of the oral cavity.
The inflammatory process in the mouth causes discomfort, pain, and suppuration leads to an unpleasant taste in the mouth and halitosis.
What are the causes of exudative diseases of mucous tissues and how to eliminate periodontal inflammation in the oral cavity.
What is a periodontal abscess
Periodontal abscess is an inflammatory disease of periodontal tissues, accompanied by the formation of lesions with purulent contents. As a rule, the localization of periodontal lesions is in the papillary-marginal region of the gums.
Most often, periodontal growth with pus occurs against the background of infectious and inflammatory periodontal lesions. Through deep periodontal pockets, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate into the subgingival area, after which they release toxic products of their vital activity. Thus, unremoved food debris and oral bacteria provoke the release of pus from the gums.
Periodontal abscess
Periodontal abscess is an inflammatory disease of the periodontium, which is the formation of a purulent ball in the area of the alveolar process.
Many experts equate periodontal abscess with periodontal abscess. This is explained by the fact that both periodontal and periodontal tissues are involved in the secretion of purulent exudate.
In this case, the periodontal infection accumulates under the layer of gum tissue and then breaks into the oral cavity through the fistula.
The gum mucosa becomes inflamed, causing discomfort.
Causes of gum abscess formation
The main cause of periodontal and periodontal abscess is the presence of pathogens in the oral cavity.
Failure to comply with hygiene rules and excessive consumption of high-carbohydrate foods provoke the active proliferation of coccal bacteria, lactobacilli and actinomycetes. The vital activity of pathogens causes inflammatory diseases of the periodontium and periodontal ligament.
Other causes of periodontal and periodontal abscess include:
- inflammatory gum diseases (gingivitis, periodontitis);
- periodontal disease;
- caries and its complications (pulpitis, periodontitis);
- mineralized deposits in the cervical area;
- errors in orthopedic prosthetics;
- mechanical, thermal and chemical damage to the periodontal mucosa;
- errors in filling the dental canals (leaving an overhanging filling, insufficient filling of the canals with filling material, deformation of the dental root);
- infection in periodontal pockets or tooth canals during therapeutic treatment;
- decreased immune system;
- metabolic disorders in the body;
- disorders of the endocrine system.
Often, purulent gum disease can begin after surgical tooth extraction. Failure to comply with the rules of asepsis and antisepsis, severe damage to the soft tissues of the oral cavity are a common cause of periodontal and periodontal abscess.
Classification. Photo. ICD-10 code
Periodontal and periodontal abscesses are divided into acute and chronic forms according to their course.
| Abscess shape | Characteristic |
| Spicy | The symptoms are clearly expressed. There is an active release of blood and purulent exudate through the hyperemic gums. Pathological mobility is noted. My health deteriorates sharply. |
| Chronic | The periodontal tissue is swollen. Bleeding gums are noted. Purulent blisters either grow or disappear. Purulent discharge accumulates inside deep gum pockets. With colds, the chronic form of the abscess becomes acute. |
Periodontal and periodontal abscess can be either single or multiple. By localization: on the papillary-marginal region of the periodontium, alveolar process, on the floor of the oral cavity.
According to the international classification of dental diseases, purulent lesions of periodontal and periodontal tissue are coded under the following indices:
- K05.2 “Acute periodontitis” (periodontal abscess);
- K04.4 “Acute apical periodontitis”;
- K04.5 “Chronic apical periodontitis” (periodontal abscess).
The photo below shows a hyperemic abscess, which is a typical sign of a periodontal abscess.
Symptoms of periodontal and periodontal abscess
Symptoms of periodontal and periodontal abscess on the gums depend on the form of the clinical case.
The clinical picture of dental disease consists of hyperemic areas of the gums, painful on palpation. Patients complain of difficulty chewing, bleeding and bad breath.
Other equally important signs of an abscess in the mouth include:
- pain when chewing and brushing teeth;
- discharge of pus from periodontal pockets and growths;
- the presence of tartar and pigmented bacterial plaque;
- exposure of the necks and roots of the teeth;
- discoloration of teeth (with periodontal abscess);
- pathological mobility grades 2 and 3;
- hyperesthesia from all types of stimuli.
In addition to local signs of intraoral abscess, the general condition of the body worsens, namely:
- increase in body temperature up to 38 degrees;
- constant headache;
- weakness;
- drowsiness;
- disturbance of night sleep;
- loss of appetite.
Diagnostics
The attending physician, a dentist, will be able to make an accurate diagnosis based on the results of a medical examination. Diagnostic measures for periodontal and periodontal abscess include several stages:
- Collecting anamnesis of life and the disease itself.
- Analysis of hereditary somatic diseases.
- Examination of the configuration of the face and skin.
- External examination of the oral cavity.
- Palpation of the affected areas of the gums.
- Carrying out periodontal hygienic indices (PMA, CPI).
- Analysis of the condition of teeth and periosteum.
- Laboratory examination of saliva and bacterial composition of the oral cavity.
- Radiography.
- Computed tomography (for severe tooth mobility).
- General blood and urine analysis.
Almost always, a dental therapist refers a periodontal patient to a periodontist and a surgeon.
Treatment of periodontal abscess
Treatment of periodontal abscess begins with professional cleaning of the oral cavity. Dental removal of bacterial plaque and stones includes several stages:
- Removal of mineralized deposits from the surface of teeth and gums using the Woodpecker ultrasonic device.
- Cleaning food debris from interdental spaces with dental floss.
- Removing pigmented plaque using abrasive pastes and brushes.
- Enamel polishing.
- Treatment of gums with antiseptic agents (aqueous solution of chlorhexidine, miramistin).
After cleansing the oral cavity, treatment tactics are selected. The method of therapy depends on the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient (allergic reactions to drugs, endocrine disorders).
Drug therapy
To treat periodontal and periodontal abscesses, as well as eliminate oral discomfort, it is necessary to resort to drug therapy. Medication treatment of periodontal and periodontal abscess includes:
- taking antibiotics to which pathogens are sensitive;
- oral baths with a 0.05% solution of chlorhexidine or miramistin every 2–3 hours;
- rinsing the mouth with infusions of chamomile and calendula;
- carrying out local applications of anti-inflammatory and antiseptic gels (Metrogil denta, Cholisal).
- treating the affected areas with lidocaine spray (to eliminate pain).
Surgical assistance
In case of severe damage to periodontal and periodontal tissues, surgical intervention is resorted to.
After local anesthesia, the dental surgeon opens the periodontal abscess, after which the contents of the exudate are drawn out. The open wound surface is treated with antiseptic agents to prevent additional infection. After surgery, a course of antibiotics is prescribed.
Treatment of periodontal abscess at home
Treatment at home for purulent processes is extremely undesirable. An exception may be home treatment prescribed by the doctor himself.
Self-therapy can only be effective if the aids are used in conjunction with drug therapy prescribed by the dentist.
At home, you can alleviate the problem in the following ways:
- plant substances (infusion of chamomile, calendula, oak bark, sage);
- applying dry cold to the sore spot;
- careful removal of food debris using dental floss and irrigator;
- use of painkillers.
Treatment of periodontal abscess
Treatment of periodontal abscess directly depends on the cause of the disease. In addition to drug and surgical therapy, inflammation occurring in the tooth itself is eliminated. This eliminates carious lesions and its complications (pulpitis, periodontitis). Tartar and decayed teeth are removed and, if necessary, prosthetics are used.
Treatment in dentistry
Dental treatment of periodontal and periodontal abscess includes: preventive, surgical, therapeutic, orthopedic and orthodontic therapy. Since the first 2 treatment methods are described above, attention should be paid to therapeutic treatment.
In most cases, the accumulation of pus in periodontal tissue is a complication of pulpitis. Periodontitis, in which a purulent fistula develops, occurs against the background of deep carious cavities, where a large amount of pathogenic microflora accumulates. Therefore, the therapeutic treatment of periodontal abscess consists of the following steps:
- Conducting local anesthesia.
- Preparation of the affected tooth.
- Removal of softened dentin and food lumps.
- Treatment of the prepared cavity with chlorhexidine.
- Using an adhesive for better adhesion of dentin to the filling.
- Tooth filling.
- Polishing the filling.
If the causes of periodontal and periodontal abscesses are crowding of teeth and their irreversible destruction, then they resort to prosthetics and the installation of orthodontic structures. Missing teeth are filled with orthopedic crowns, and the pathological position of the dentition is corrected with braces.
Prevention and prognosis
With timely treatment of periodontal and periodontal abscess, as well as compliance with all recommendations of the treating dentist, the prognosis is considered favorable. At the same time, the development of complications and a long rehabilitation process are excluded.
To protect yourself from periodontal dental problems, you need to follow the rules of prevention:
- Brush your teeth 2 times a day (morning and night) according to the standard method.
- An annual visit to a dentist for early detection and treatment of dental diseases.
- Carrying out professional oral hygiene every 6 months.
- Introducing a healthy lifestyle and quitting smoking.
- The use of vitamin and mineral complexes.
If there are concomitant diseases, such as diabetes or gastritis, the pathological process inside the body should be treated together with specialized specialists.
In addition, you need to eat hot food carefully, and eat sour and spicy foods in minimal quantities.
Bad habits such as “chewing” pencils, pens, sweets and other hard objects must be unlearned.
- Banchenko G.V. — Combination of diseases of the oral mucosa and internal organs, M.: Medicine, 1979.
- Maksimovsky Yu.M. – Therapeutic dentistry, Textbook, M.: Medicine, 2002.
- Loginova N.K., Volozhin A.I. — Pathophysiology of periodontal disease (methodological manual), M., Medicine, 1993.
- Borovsky E.V., Leus P.A. — Dental caries, M., Medicine, 1979.
- Borovsky E.V. - Clinical endodontics, M.: JSC Dentistry, 2003.
- Kenneth M. Hargreaves, Louis H. Berman - Cohen's Pathways of the Pulp - 2020.
- Leontyev V.K., Pakhomov G.N. — Prevention of dental diseases, M., 2006.
- L. V. Kharkov, L. N. Yakovenko - Directory of a dental surgeon: diagnosis, clinic, principles of surgical and drug treatment (in children and adults), M.: Book Plus, 2008.
- Grudyanov A.I. — Antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory therapy in periodontology, M., 2004.
Source: https://DesnaZub.ru/zabolevaniya/periodontalnyj-i-parodontalnyj-abstsess
Diagnosis and treatment
An abscess on the gum is diagnosed by examining the oral cavity, where a painful lump is detected. X-rays are taken to make sure that the inflammation has not reached the bone tissue.
A general blood test and PCR are done. In the general analysis, an increase in leukocytes and ESR is noted, the leukocyte formula is shifted to the left. Using PCR, the composition of the microflora in the gum pocket is determined.
Along with other methods, a cytological study is carried out, with the help of which it is possible to identify a huge number of destroyed neutrophil granulocytes.
These examinations help differentiate a periodontal abscess from acute periodontitis, or an exacerbation of its chronic form, with suppuration of a jaw cyst, osteomyelitis and other diseases.
Pre-medical intervention
You cannot treat a periodontal abscess yourself at home, because... this can lead to serious complications. But you can carry out a number of procedures that will help relieve pain and alleviate the general condition.
You can do the following:
- Rinsing the mouth with an antiseptic. This may be potassium permanganate, Chlorhexidine or Furacilin. The temperature of the rinse solution should be between 20 and 25.
- Rinsing the mouth with decoctions of medicinal herbs. These include chamomile, St. John's wort, and sage.
- Applying cold to the swollen side of the cheek. You can take ice by first wrapping it in a waffle towel.
- Only analgesics (Analgin, Paracetamol, Tempalgin) can be taken as painkillers.
- Carefully clean the mouth and aching teeth, in particular from food residues.
The following actions are prohibited:
- Self-administration of antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs. These groups of drugs are taken only as prescribed by the dentist. Self-initiative may lead to worsening of the condition. In addition, by using the drug before seeing a doctor, you can relieve some symptoms and the dentist will not be able to objectively assess the nature of the disease.
- Pressing, piercing or heating the swelling is strictly prohibited. This can intensify the inflammatory process, and it can spread to nearby tissues.
Surgery
Periodontal abscess is treated exclusively by surgery. The operation is carried out as follows:
- The dentist resolves the gums using a pinpoint method.
- The abscess is drained. Sometimes cleansing is carried out through the periodontal pocket.
- All pus, dead tissue, and blood are eliminated.
- The wound surface and oral cavity are treated with antiseptic solutions.
- Analgesics are prescribed to relieve pain. Depending on the severity of the condition, antibacterial therapy may be prescribed. Immunostimulating therapy is also prescribed to increase the body's defenses.
To quickly heal the wound, laser procedures or physical therapy are prescribed. To ensure complete recovery, it is necessary to repeat the visit to the dentist some time after treatment (1-1.5 weeks). He will not only examine the oral cavity, but will also give further recommendations on how to care for the damaged area.
Features of symptoms
At the initial stage of the disease, discomfort will be felt. When palpating or chewing food, pain occurs.
Over time, the pain will intensify and chewing will become impossible. After a couple of days, a dense swelling will appear in the area of the inflamed gum. It increases quite quickly, and accordingly constant pain appears, which can radiate to the area of the cheek, jaw, and ear.
In the photo there is a bloody abscess on the gum - a typical picture of a periodontal abscess
The abscess can open on its own, then local inflammation and pain will subside. In this case, the pus flows into the oral cavity, and the wound will heal on its own. But without treating the oral cavity with an antiseptic, there is a risk of infection of neighboring tissues.
As the inflammatory process develops, general intoxication of the body will be observed. Its severity depends on the stage of the disease. The patient may experience dizziness, fever, headaches, insomnia, decreased or lack of appetite, decreased ability to work, and deterioration in health.
Squeezing an abscess is strictly prohibited. External pressure on the site of inflammation can lead to loosening of adjacent teeth.
With further progression of the disease, the tumor will grow. A swelling of the cheek will appear on the side of the affected gum.
Periodontal abscess - causes of the formation of a purulent focus in the gum and methods for its elimination
A periodontal abscess is an inflammatory process in the gum, against the background of which a formation with sizes from a small pea to a walnut is formed, and purulent fluid is formed inside the lesion. Men and women suffer from the pathology equally.
Online consultation on the disease “Periodontal abscess”. Ask a question to the experts for free: Dentist.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Prevention and prognosis
The main causes of an abscess are the exacerbation of the inflammatory-destructive process in the periodontium, the presence of deep gum pockets and hard deposits accumulating under the gum.
Symptoms of the disease are specific (pathological mobility of teeth) and general (fever and deterioration of general condition).
Diagnosis is based on laboratory and instrumental examinations, which are necessarily supplemented by manipulations performed directly by the dentist, in particular a physical examination of the oral cavity.
It is customary to treat gum abscess only with surgical techniques that are aimed at preventing the development of irreparable complications and achieving stable remission.
In the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, abscess does not have a separate code, but belongs to the category “Other periodontal damage.” It follows from this that the ICD-10 code will be K05.2.
A periodontal abscess is understood as inflammation in the gums, the formation of which is caused by the accumulation of purulent exudate in the thickness of the soft tissues and its gradual release to the outside in the form of a painful purulent lump.
The pathology does not go away on its own and requires urgent dental treatment. If you delay going to a specialist for too long, the inflammatory processes will reach the bone tissue, which will lead to the development of even more serious and dangerous complications.
Read more about the history of the disease and methods of its treatment further in the article.
What kind of diagnosis is this?
A periodontal or periodontal abscess is a purulent neoplasm that occurs against the background of the development of destructive processes in the gum tissue.
According to the international classification of the 10th revision (ICD-10), the disease is coded K05.2, which is included in the group “Acute periodontitis”.
The disease varies in form, severity and location.
This is what it looks like in the photo:
To determine the development of an abscess in the oral cavity, you need to know its symptoms, have an idea of what caused the problem and how it is treated.
The effectiveness of treatment directly depends on the stage of development of purulent inflammation. The sooner you react to its appearance, the easier and faster you will get rid of the problem.
What is the essence of pathology
As the pathology develops, a cavity is formed in the thickness of the periodontal tissue, inside which purulent exudate begins to accumulate.
The source of inflammation is usually localized in the immediate vicinity of the causative tooth.
In fact, this is a small formation inside the gingival tissue, which gradually appears in the form of a lump on the surface of the mucosa, often with a fistula. The patient experiences obvious discomfort and acute pain.
Periodontal abscess, how does it manifest?
Typically, the cause of the problem is voluminous periodontal pockets and hard subgingival deposits. Most often, the acute form of the disease is diagnosed, while only 30% of patients who seek help suffer from chronic periodontal abscess1.
This kind of trouble can occur in both adults and children; neither men nor women are equally immune from it. However, it is worth noting that the peak incidence occurs in the autumn-spring period, when most people have weakened immunity.
Useful tips
Here are some more ways to treat an abscess on your gums.
- Take two tablespoons each of sage and regular green tea (without additives). Brew the ingredients in a liter of boiling water. Add two teaspoons of table salt there. After the medicine has cooled, filter it and use it for rinsing. Brew sage like tea and rinse your mouth with the infusion as often as possible.
- At the pharmacy you can buy a ready-made disinfectant called “Chlorophyllipt”. To prepare the solution, you just need to dissolve a spoonful of the product in a glass of boiled water.
- When we urgently need to numb the affected area, fresh onion juice will help us. We soak a small swab in it and apply it to the sore spot.
- Regular table salt will help draw out the pus. You just need to dissolve a teaspoon of crystals in a glass of water. The solution must be taken into the mouth and kept on the side where the abscess occurred. Then spit and repeat with a new portion of the product. Such manipulations are good at drawing out pus from the deep layers of soft tissue.
- After the inflammation has broken through, you can rinse your mouth with a solution containing manganese (potassium permanganate).
Causes of abscess formation
First, you should figure out why you might encounter such a problem. In fact, this is a purulent abscess, the main cause of which is the penetration of infection into the gum pockets with the subsequent development of inflammation. Let's look at the most common provoking factors in a little more detail.
Source: https://PlastikaPlus.ru/desny/parodontalnyj-abscess.html
Consequences and complications
Lack of treatment leads to serious consequences. The easiest of all possible complications of an abscess is the appearance of a chronic focus of infection. The rest have a more dangerous prognosis and serious treatment.
The infection can spread to nearby tissues - bone, periosteum, and internal organs, including the brain.
Periodontal tissues can become necrotic, teeth become loose and then fall out. There is also a risk of osteomyelitis of the jaw. The jaw will become deformed, which will lead to a distortion of the face.